1 hr. ago
#Pinterest makes money mainly through #advertising , where #brands pay to show promoted Pins to users who are actively searching for ideas, products, and purchase inspiration. The platform also earns from shopping integrations, affiliate-style product links, and merchant tools that help sellers drive conversions.
Now let’s go deeper.
If you’ve ever wondered “Pinterest ka #business model kya hai? How does it earn so much by just showing Pins?” this #article breaks it down in the simplest way.
https://pratsdigital.in/pi...
Now let’s go deeper.
If you’ve ever wondered “Pinterest ka #business model kya hai? How does it earn so much by just showing Pins?” this #article breaks it down in the simplest way.
https://pratsdigital.in/pi...
1 hr. ago
#Netflix remains one of the world’s most influential #entertainment brands, even in a hyper-competitive #streaming market. Platforms like Disney+, Prime Video, Apple TV+, YouTube, and regional OTT players are constantly fighting for viewer attention, yet Netflix continues to hold a dominant global presence.
The reason?
A sharp, evolving, and highly data-driven #marketing #strategy .
In this #article , I’ll break down Netflix’s current marketing strategy (2025) with a approach covering everything from #content strategy to #technology , partnerships, social media, and #growth tactics.
https://pratsdigital.in/ne...
The reason?
A sharp, evolving, and highly data-driven #marketing #strategy .
In this #article , I’ll break down Netflix’s current marketing strategy (2025) with a approach covering everything from #content strategy to #technology , partnerships, social media, and #growth tactics.
https://pratsdigital.in/ne...
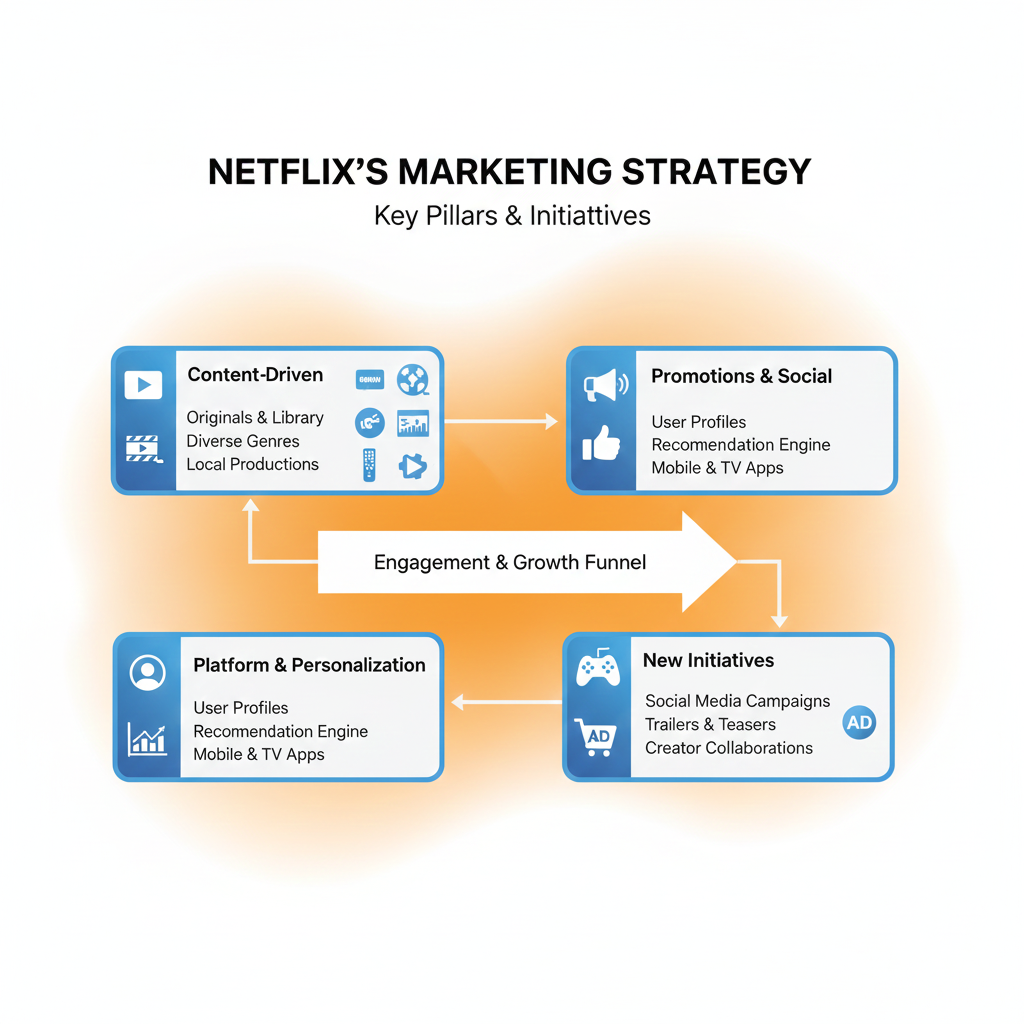
Netflix’s Current Marketing Strategy (2025): A Complete Breakdown - PratsDigital
Netflix’s current marketing strategy explained: data-driven personalization, global content, ad-tier expansion, partnerships, and social media innovations.
https://pratsdigital.in/netflix-current-marketing-strategy/
2 hours ago
If you’ve ever watched a #Netflix show and wondered, “How does this company stay so dominant despite so many competitors?” a #SWOT #analysis is the best way to understand it.
I’ve been #writing about #business models and #marketing strategies of top #tech platforms for a long time, and Netflix is one of the most fascinating #brands . Their story is all about reinvention — DVDs → streaming → originals → gaming → AI-driven entertainment.
So in this #article , I’m breaking down Netflix’s full SWOT analysis so you can understand how the company survives, grows, and competes in an industry that changes every month.
https://pratsdigital.in/ne...
I’ve been #writing about #business models and #marketing strategies of top #tech platforms for a long time, and Netflix is one of the most fascinating #brands . Their story is all about reinvention — DVDs → streaming → originals → gaming → AI-driven entertainment.
So in this #article , I’m breaking down Netflix’s full SWOT analysis so you can understand how the company survives, grows, and competes in an industry that changes every month.
https://pratsdigital.in/ne...
14 days ago
In today’s digital marketplace, your #website isn’t just a storefront it’s the heart of your business. As a leading #EcommerceWebsiteDevelopment Company, at #KrishnaPadamITSolution , we design and develop next-generation #ecommerce platforms powered by modern #technology and innovation. Our Expertise Includes:
#AI -Driven Commerce Intelligence
#AR / #VR Shopping Experiences
#AIVoice & Conversational Commerce
Cloud & #EdgeComputing
#Blockchain -Powered Payments
Predictive #DataAnalytics
#Automation & Workflow Integration
Our mission is simple to help brands sell smarter, scale faster, and deliver seamless digital shopping experiences. We combine modern technology stacks (#React, NodeJS, Next.js, Python) with deep ecommerce expertise to build robust, scalable, and future-ready solutions.
Let our #webdevelopers turn your vision into a powerful online store built for the future.
-------------
: https://www.kpis.in/ecomme...
: infokpis.in
+91-6350359218
-------------
#EcommerceWebDevelopment #EcommerceDevelopment #DigitalTransformation #AIChatbots #WebDevelopment #EcommerceWebsiteDevelopment #WebsiteDevelopment #digitalmarketing #HireeCommerceWebsiteDevelopers #gojekclone #AppDevelopment #ITCompany #KPISPvtLtd #Jaipur
#AI -Driven Commerce Intelligence
#AR / #VR Shopping Experiences
#AIVoice & Conversational Commerce
Cloud & #EdgeComputing
#Blockchain -Powered Payments
Predictive #DataAnalytics
#Automation & Workflow Integration
Our mission is simple to help brands sell smarter, scale faster, and deliver seamless digital shopping experiences. We combine modern technology stacks (#React, NodeJS, Next.js, Python) with deep ecommerce expertise to build robust, scalable, and future-ready solutions.
Let our #webdevelopers turn your vision into a powerful online store built for the future.
-------------
: https://www.kpis.in/ecomme...
: infokpis.in
+91-6350359218
-------------
#EcommerceWebDevelopment #EcommerceDevelopment #DigitalTransformation #AIChatbots #WebDevelopment #EcommerceWebsiteDevelopment #WebsiteDevelopment #digitalmarketing #HireeCommerceWebsiteDevelopers #gojekclone #AppDevelopment #ITCompany #KPISPvtLtd #Jaipur
15 days ago
You’ve built a beautiful #portfolio now it’s time to make sure the right people see it.
With #seo for #interiordesign , your website becomes a lead-generating tool that attracts dream clients searching for your design #services online.
I help interior designers, studios, and #homedecor brands increase visibility, attract high-quality leads, and build online authority through SEO strategies crafted specifically for the design world.
https://pratsify.com/seo-f...
With #seo for #interiordesign , your website becomes a lead-generating tool that attracts dream clients searching for your design #services online.
I help interior designers, studios, and #homedecor brands increase visibility, attract high-quality leads, and build online authority through SEO strategies crafted specifically for the design world.
https://pratsify.com/seo-f...
6 months ago
China and France have agreed to resolve their trade disputes through dialogue, China's foreign ministry said on Friday, though there was no indication that agreement had been reached in talks on lifting Chinese levies on European brandy.
Talks to resolve the cognac dispute accelerated this week with China's commerce minister Wang Wentao meeting his French counterpart in Paris on the sidelines of an OECD conference, and technical talks on the matter taking place in Beijing.
The latest round of negotiations have raised hopes of a settlement, two industry sources with knowledge of the discussions said.
"The two sides have reached consensus on resolving economic and trade issues through dialogue and consultation", the Chinese foreign ministry said after a call between the Chinese and French foreign ministers.
Chinese anti-dumping measures that applied duties of up to 39% on imports of European brandy - with French cognac bearing the brunt - have strained relations between Paris and Beijing.
The brandy duties were enforced days after the European Union took action against Chinese-made electric vehicle imports to shield its local industry, prompting France's President Emmanuel Macron to accuse Beijing of "pure retaliation".
The Chinese duties have dented sales of brands including LVMH's Hennessy, Pernod Ricard's Martell and Remy Cointreau.
Beijing was initially meant to make a final decision on the duties by January, but extended the deadline to April and then again to July 5.
China is seeking to strengthen trade ties with the 27-member bloc as relations with the United States have soured in the escalating trade war.
"France will not compromise on ... the protection of its industries, such as cognac," French trade minister Laurent Saint-Martin said after talks with Wang on Wednesday.
Chinese officials, meanwhile, signalled to industry officials during three rounds of technical meetings in Beijing this week they wanted to settle the matter, one of the sources said, but added some sticking points remained.
With annual imports of around $1.7 billion last year, China is the French brandy industry's most important measured by value and the second-largest by volume after the United States.
Talks to resolve the cognac dispute accelerated this week with China's commerce minister Wang Wentao meeting his French counterpart in Paris on the sidelines of an OECD conference, and technical talks on the matter taking place in Beijing.
The latest round of negotiations have raised hopes of a settlement, two industry sources with knowledge of the discussions said.
"The two sides have reached consensus on resolving economic and trade issues through dialogue and consultation", the Chinese foreign ministry said after a call between the Chinese and French foreign ministers.
Chinese anti-dumping measures that applied duties of up to 39% on imports of European brandy - with French cognac bearing the brunt - have strained relations between Paris and Beijing.
The brandy duties were enforced days after the European Union took action against Chinese-made electric vehicle imports to shield its local industry, prompting France's President Emmanuel Macron to accuse Beijing of "pure retaliation".
The Chinese duties have dented sales of brands including LVMH's Hennessy, Pernod Ricard's Martell and Remy Cointreau.
Beijing was initially meant to make a final decision on the duties by January, but extended the deadline to April and then again to July 5.
China is seeking to strengthen trade ties with the 27-member bloc as relations with the United States have soured in the escalating trade war.
"France will not compromise on ... the protection of its industries, such as cognac," French trade minister Laurent Saint-Martin said after talks with Wang on Wednesday.
Chinese officials, meanwhile, signalled to industry officials during three rounds of technical meetings in Beijing this week they wanted to settle the matter, one of the sources said, but added some sticking points remained.
With annual imports of around $1.7 billion last year, China is the French brandy industry's most important measured by value and the second-largest by volume after the United States.
6 months ago
Strikes, roadblocks bring Panama to near standstill
Panama is facing one of its most intense social crises since the return to democracy in 1989, with nearly 40 days of nationwide protests, strikes and roadblocks sparked by a controversial pension reform law approved by President José Raúl Mulino's administration.
The protests escalated April 23, when the national teachers' union launched an indefinite strike. Construction workers and banana industry laborers soon joined, expanding the demonstrations nationwide.
Mulino has taken a hard stance, referring to some unions as "mafias" and insisting he will not repeal the pension law, which he says is necessary to preserve the system's financial viability.
On Monday, Mulino sent a delegation of seven cabinet ministers to Bocas del Toro province, the center of the protests, and offered to draft a bill restoring labor benefits for banana workers, provided the roadblocks are lifted.
"The minute they permanently lift the strikes, that law goes to the Assembly," he said.
The proposal had little effect. Banana workers and other protest groups responded by intensifying demonstrations.
Protesters are demanding the repeal of the law, which raises the retirement age, increases worker contributions and separates new individual accounts from the collective pension fund.
They also oppose a security cooperation agreement with the United States that allows the use of former military bases in Panama and the possible reopening of the Cobre Panamá copper mine -- shut in 2023 after being declared unconstitutional. Such a potential reopening has reignited environmental and social protests.
U.S.-based Chiquita Brands has emerged at the center of the crisis. The company announced it would shut its banana operations in Changuinola, a key production hub in the Caribbean province of Bocas del Toro near the Costa Rica border.
A few days ago, after a full work stoppage by employees protesting the new pension law, Chiquita Panama and Ilara Holding fired 4,900 workers for job abandonment and said the company had lost more than $75 million, with irreversible damage to banana production.
Panama's Labor Minister Jackeline Muñoz said the company plans to lay off its remaining workers this week.
"They are filing a request to terminate more than 1,600 workers. There won't be a single employee left on the company's payroll," she said.
In 2024, Panama's Social Security Fund, which operates under a model of pooled resources, reported a deficit of nearly $900 million, placing a significant burden on the system.
The situation has worsened due to a decline in active contributors, as new workers are entering a mixed system with individual retirement accounts.
Panama is facing one of its most intense social crises since the return to democracy in 1989, with nearly 40 days of nationwide protests, strikes and roadblocks sparked by a controversial pension reform law approved by President José Raúl Mulino's administration.
The protests escalated April 23, when the national teachers' union launched an indefinite strike. Construction workers and banana industry laborers soon joined, expanding the demonstrations nationwide.
Mulino has taken a hard stance, referring to some unions as "mafias" and insisting he will not repeal the pension law, which he says is necessary to preserve the system's financial viability.
On Monday, Mulino sent a delegation of seven cabinet ministers to Bocas del Toro province, the center of the protests, and offered to draft a bill restoring labor benefits for banana workers, provided the roadblocks are lifted.
"The minute they permanently lift the strikes, that law goes to the Assembly," he said.
The proposal had little effect. Banana workers and other protest groups responded by intensifying demonstrations.
Protesters are demanding the repeal of the law, which raises the retirement age, increases worker contributions and separates new individual accounts from the collective pension fund.
They also oppose a security cooperation agreement with the United States that allows the use of former military bases in Panama and the possible reopening of the Cobre Panamá copper mine -- shut in 2023 after being declared unconstitutional. Such a potential reopening has reignited environmental and social protests.
U.S.-based Chiquita Brands has emerged at the center of the crisis. The company announced it would shut its banana operations in Changuinola, a key production hub in the Caribbean province of Bocas del Toro near the Costa Rica border.
A few days ago, after a full work stoppage by employees protesting the new pension law, Chiquita Panama and Ilara Holding fired 4,900 workers for job abandonment and said the company had lost more than $75 million, with irreversible damage to banana production.
Panama's Labor Minister Jackeline Muñoz said the company plans to lay off its remaining workers this week.
"They are filing a request to terminate more than 1,600 workers. There won't be a single employee left on the company's payroll," she said.
In 2024, Panama's Social Security Fund, which operates under a model of pooled resources, reported a deficit of nearly $900 million, placing a significant burden on the system.
The situation has worsened due to a decline in active contributors, as new workers are entering a mixed system with individual retirement accounts.
7 months ago
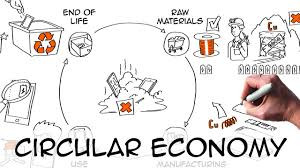
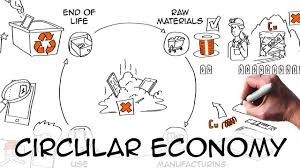
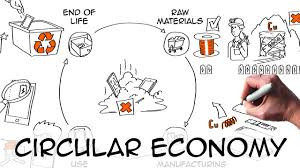
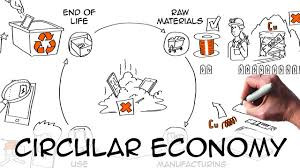
Make in Africa, Buy in Africa
Visual: Supermarket shelves with “Made in Africa” tags.
Why import what we can make? Support local brands. Trade regionally. Export finished goods, not dreams.
By Jo Ikeji-Uju
https://afriprime.net/page...
Visual: Supermarket shelves with “Made in Africa” tags.
Why import what we can make? Support local brands. Trade regionally. Export finished goods, not dreams.
By Jo Ikeji-Uju
https://afriprime.net/page...

Anything Goes
Share your memories, connect with others, make new friends
https://afriprime.net/pages/Anything
7 months ago
Africa-Our Motherland calling-...
“Africa’s Wealth Must Work for Africa”
Build Local Processing & Manufacturing Industries
Actions:
Invest in processing plants: Governments and private sectors should invest in cocoa grinders, aluminum smelters, textile mills, etc.
Create industrial zones: Establish agro-processing and mineral refining hubs near resource sites.
Public-private partnerships: Encourage foreign and local investors to co-develop factories with skills and technology transfer.
Example:
Ghana and Côte d’Ivoire can move from just exporting cocoa beans to making premium chocolate brands for African and global markets.
Raw to Riches – Choose Key Products
Visual: Map of Africa with raw materials icons (e.g., cocoa pod, cotton, bauxite).
Caption:
👉 We grow it, mine it, and harvest it — but sell it raw.
Why not transform it here?
By Jo Ikeji-Uju
https://afriprime.net/page...
“Africa’s Wealth Must Work for Africa”
Build Local Processing & Manufacturing Industries
Actions:
Invest in processing plants: Governments and private sectors should invest in cocoa grinders, aluminum smelters, textile mills, etc.
Create industrial zones: Establish agro-processing and mineral refining hubs near resource sites.
Public-private partnerships: Encourage foreign and local investors to co-develop factories with skills and technology transfer.
Example:
Ghana and Côte d’Ivoire can move from just exporting cocoa beans to making premium chocolate brands for African and global markets.
Raw to Riches – Choose Key Products
Visual: Map of Africa with raw materials icons (e.g., cocoa pod, cotton, bauxite).
Caption:
👉 We grow it, mine it, and harvest it — but sell it raw.
Why not transform it here?
By Jo Ikeji-Uju
https://afriprime.net/page...

Anything Goes
Share your memories, connect with others, make new friends
https://afriprime.net/pages/Anything
7 months ago
Chinese-owned carmaker MG is accelerating plans to build its first factory in Europe as Beijing seeks to forge closer ties with Brussels to combat Donald Trump’s trade war.
The historic British sports car brand, which was sold to Chinese owners two decades ago, is poised to reveal proposals for the new plant as soon as this summer, with a second site on the continent also understood to be under consideration.
China is seeking to build stronger ties with the EU after accusing Mr Trump of “acts of bullying” over his 145pc tariffs on Chinese imports. China has imposed retaliatory tariffs of 125pc in response.
While MG does not sell cars in the US, the Chinese carmaker’s push to build two European plants in quick succession is likely to fuel concerns in the White House about Beijing’s push to court Brussels.
Mr Trump has cited buoyant US sales of brands like BMW and VW and the aversion of European consumers to buy US cars as one of the main drivers of his car tariffs policy.
The historic British sports car brand, which was sold to Chinese owners two decades ago, is poised to reveal proposals for the new plant as soon as this summer, with a second site on the continent also understood to be under consideration.
China is seeking to build stronger ties with the EU after accusing Mr Trump of “acts of bullying” over his 145pc tariffs on Chinese imports. China has imposed retaliatory tariffs of 125pc in response.
While MG does not sell cars in the US, the Chinese carmaker’s push to build two European plants in quick succession is likely to fuel concerns in the White House about Beijing’s push to court Brussels.
Mr Trump has cited buoyant US sales of brands like BMW and VW and the aversion of European consumers to buy US cars as one of the main drivers of his car tariffs policy.
11 months ago
Chinese electric cars have surged to account for almost 10% of new car sales in Norway in only five years, data from the country's road federation (OFV) showed on Thursday.
Wealthy Norway is far ahead of most countries in the switch to electric vehicles and unlike the European Union and the United States has not imposed import tariffs on Chinese EVs.
Brussels and Washington say Chinese EVs benefit from unfair subsidies, which Beijing denies, and Western automakers have warned they could be hit hard by cheap Chinese imports, although there have been doubts if buyers would adopt unfamiliar brands.
In Norway, the combined market share of Chinese manufacturers such as MG, part of SAIC Motor, BYD and XPeng increased to 8.8% last year, up from 5.1% in 2023 and 4.1% in 2021, according to Reuters calculations based on OFV data on the top 20 car brands sold.
The first Chinese EV to arrive in Norway, from MG, was shipped only five years ago.
Wealthy Norway is far ahead of most countries in the switch to electric vehicles and unlike the European Union and the United States has not imposed import tariffs on Chinese EVs.
Brussels and Washington say Chinese EVs benefit from unfair subsidies, which Beijing denies, and Western automakers have warned they could be hit hard by cheap Chinese imports, although there have been doubts if buyers would adopt unfamiliar brands.
In Norway, the combined market share of Chinese manufacturers such as MG, part of SAIC Motor, BYD and XPeng increased to 8.8% last year, up from 5.1% in 2023 and 4.1% in 2021, according to Reuters calculations based on OFV data on the top 20 car brands sold.
The first Chinese EV to arrive in Norway, from MG, was shipped only five years ago.
11 months ago
China's commerce ministry said on Wednesday it would extend its anti-dumping investigation into brandy originating from the European Union by three months, less than the full extension allowed under its previous guidance.
The probe, which was launched on Jan. 5 and due to be completed in a year, will be extended to April 5 due to the "complexity" of the investigation, the ministry said in a brief statement, without elaborating.
The ministry previously said the probe could be extended by six months under special circumstances.
Preliminary findings from the probe have shown dumping of EU brandy threatens to damage China's sector, the ministry said in October as it imposed temporary measures on EU brandy imports, hitting French brands including Hennessy and Remy Martin.
The probe was widely seen as the outcome of France's support of EU tariffs on China-made electric vehicles.
The probe, which was launched on Jan. 5 and due to be completed in a year, will be extended to April 5 due to the "complexity" of the investigation, the ministry said in a brief statement, without elaborating.
The ministry previously said the probe could be extended by six months under special circumstances.
Preliminary findings from the probe have shown dumping of EU brandy threatens to damage China's sector, the ministry said in October as it imposed temporary measures on EU brandy imports, hitting French brands including Hennessy and Remy Martin.
The probe was widely seen as the outcome of France's support of EU tariffs on China-made electric vehicles.
1 yr. ago
China’s richest man has hit out at online shopping platforms, accusing them of starting price wars that have damaged a wide range of companies and industries as the country tackles an economic slump.
Rare remarks censored by state media, Zhong Shanshan, founder of drinks company Nongfu Springs, also took aim at the Chinese government, saying it was “negligent” in failing to prevent the trend of cut-throat pricing.
It is very unusual for Chinese businesspeople to take public aim at the government and those who have done so have often faced repercussions.
Zhong was widely quoted as taking direct aim at Pinduoduo, criticizing the popular e-commerce site owned by PDD Holdings for hurting businesses.
“Internet platforms have brought down (our) pricing system. In particular, Pinduoduo’s pricing system has done great harm to China’s brands and its industries,” . “It is not just that bad money is driving out good money. It is an industry orientation, and pricing the industry orientat
Rare remarks censored by state media, Zhong Shanshan, founder of drinks company Nongfu Springs, also took aim at the Chinese government, saying it was “negligent” in failing to prevent the trend of cut-throat pricing.
It is very unusual for Chinese businesspeople to take public aim at the government and those who have done so have often faced repercussions.
Zhong was widely quoted as taking direct aim at Pinduoduo, criticizing the popular e-commerce site owned by PDD Holdings for hurting businesses.
“Internet platforms have brought down (our) pricing system. In particular, Pinduoduo’s pricing system has done great harm to China’s brands and its industries,” . “It is not just that bad money is driving out good money. It is an industry orientation, and pricing the industry orientat
1 yr. ago
China's second-richest man has lobbed a rare public attack on Pinduoduo, a bargain e-commerce site, alleging that the platform's pricing system is hurting the industry.
Zhong Shanshan - the 69-year-old founder and chairman of China's largest packaged drinks company, Nongfu Spring, and the country's second-richest person, according to Hurun Research's latest rankings -
"The internet platforms have brought down the prices, in particular the pricing system of Pinduoduo - they are a huge harm for Chinese brands and Chinese industries," Zhong said. His speech was widely reported by Chinese media, including the Chinese internet portal Sina.com.
Pinduoduo was founded by billionaire Colin Huang Zheng in 2015. It is known for its cut-to-the-bone deals in China, serving as the blueprint for Temu, with which it shares owner PDD Holdings. Its aggressive pricing strategy has helped it quickly gain market share over the past few years.
Zhong Shanshan - the 69-year-old founder and chairman of China's largest packaged drinks company, Nongfu Spring, and the country's second-richest person, according to Hurun Research's latest rankings -
"The internet platforms have brought down the prices, in particular the pricing system of Pinduoduo - they are a huge harm for Chinese brands and Chinese industries," Zhong said. His speech was widely reported by Chinese media, including the Chinese internet portal Sina.com.
Pinduoduo was founded by billionaire Colin Huang Zheng in 2015. It is known for its cut-to-the-bone deals in China, serving as the blueprint for Temu, with which it shares owner PDD Holdings. Its aggressive pricing strategy has helped it quickly gain market share over the past few years.
1 yr. ago
Chinese cars are selling at record levels in Russia.
Competition from European, Korean, and Japanese carmakers has vanished since Western sanctions were imposed on Russia.
Chinese automakers face increasing tariffs in other regions.
Chinese cars are selling at record levels in Russia, according to data from Russian analytics agency Autostat, reported by The Financial Times.
The country has turned to Chinese autos from brands such as Chery, Geely, and Great Wall Motor after sanctions forced Western brands to stop doing business with Moscow.
European, Korean, and Japanese carmakers had dominated the Russian market with a 69% share, per Autostat. However, since Western sanctions were imposed against Russia following its invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, Autostat's data showed a steep decline in sales.
The three regions now hold just 8.5% of the market, while Chinese carmakers such as have jumped from 9% to 57% over the same period.
Competition from European, Korean, and Japanese carmakers has vanished since Western sanctions were imposed on Russia.
Chinese automakers face increasing tariffs in other regions.
Chinese cars are selling at record levels in Russia, according to data from Russian analytics agency Autostat, reported by The Financial Times.
The country has turned to Chinese autos from brands such as Chery, Geely, and Great Wall Motor after sanctions forced Western brands to stop doing business with Moscow.
European, Korean, and Japanese carmakers had dominated the Russian market with a 69% share, per Autostat. However, since Western sanctions were imposed against Russia following its invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, Autostat's data showed a steep decline in sales.
The three regions now hold just 8.5% of the market, while Chinese carmakers such as have jumped from 9% to 57% over the same period.
1 yr. ago
Chinese battery giant CATL launched its first battery product focused on extended-range hybrids at a time when this category of electrified cars is seeing the fastest growth in sales among all segments.
The battery, known as Freevoy, is the world's first hybrid battery with a range of over 400 km (249 miles), according to CATL's Gao Huan, chief technology officer of its electric vehicle business in China.
Freevoy was being used by various Chinese EV brands, including Li Auto, and would be installed in models made by industry giants, such as Geely and Chery.
Nearly 30 extended-range hybrid models will be equipped with the CATL Freevoy battery, Gao said.
An extended-range hybrid, or EREV, has a larger battery pack than other hybrid cars and runs on electricity only, with its gasoline engine serving as a power bank to recharge the batteries when they run low.
More Chinese consumers favour EREVs as they offer longer driving range than EVs and can cost less than gasoline cars.
The battery, known as Freevoy, is the world's first hybrid battery with a range of over 400 km (249 miles), according to CATL's Gao Huan, chief technology officer of its electric vehicle business in China.
Freevoy was being used by various Chinese EV brands, including Li Auto, and would be installed in models made by industry giants, such as Geely and Chery.
Nearly 30 extended-range hybrid models will be equipped with the CATL Freevoy battery, Gao said.
An extended-range hybrid, or EREV, has a larger battery pack than other hybrid cars and runs on electricity only, with its gasoline engine serving as a power bank to recharge the batteries when they run low.
More Chinese consumers favour EREVs as they offer longer driving range than EVs and can cost less than gasoline cars.
1 yr. ago
Japan has had a tough few decades, economically speaking, but China may soon follow in its footsteps.
“We are now at a tipping point [in China],” Suntory Holdings CEO Takeshi Niinami told Yahoo Finance Executive Editor Brian Sozzi on Yahoo Finance's Opening Bid podcast (video above; listen below). Suntory is the maker of globally renowned Japanese whiskey brands such as Yamazaki and Hibiki and has owned Jim Beam since 2014 as part of a $16 billion acquisition.
“The deflation in China is very similar to the one we experienced,” Niinami said from inside Suntory's New York City headquarters. “The key issue is people have money but people don’t want to spend money, and overproduction.”
It's a struggle “an invisible monster”
Consumers are avoiding spending money and buying items on credit over an extended period of time.
“We are now at a tipping point [in China],” Suntory Holdings CEO Takeshi Niinami told Yahoo Finance Executive Editor Brian Sozzi on Yahoo Finance's Opening Bid podcast (video above; listen below). Suntory is the maker of globally renowned Japanese whiskey brands such as Yamazaki and Hibiki and has owned Jim Beam since 2014 as part of a $16 billion acquisition.
“The deflation in China is very similar to the one we experienced,” Niinami said from inside Suntory's New York City headquarters. “The key issue is people have money but people don’t want to spend money, and overproduction.”
It's a struggle “an invisible monster”
Consumers are avoiding spending money and buying items on credit over an extended period of time.
1 yr. ago
China's anti-dumping measures against brandies imported from the European Union are "legitimate trade remedy measures", the commerce ministry said on Wednesday, a day after imposing the temporary curb.
French brands such as Hennessy and Remy Martin will face the strictures, adopted just days after the 27-nation bloc voted for tariffs on Chinese-made electric vehicles (EVs), sparking its biggest trade row with Beijing in a decade.
China's commerce ministry said preliminary findings of an investigation showed that dumping of brandy from the European Union threatened "substantial damage" to domestic industry.
On Wednesday the ministry said the EU's actions against Chinese EVs "seriously lack a factual and legal basis" and "clearly violate" World Trade Organization (WTO) rules.
Trade tensions have surged since the European Commission said last week it would press ahead with tariffs on China-made EVs, even after Germany, the bloc's largest economy, rejected them.
French brands such as Hennessy and Remy Martin will face the strictures, adopted just days after the 27-nation bloc voted for tariffs on Chinese-made electric vehicles (EVs), sparking its biggest trade row with Beijing in a decade.
China's commerce ministry said preliminary findings of an investigation showed that dumping of brandy from the European Union threatened "substantial damage" to domestic industry.
On Wednesday the ministry said the EU's actions against Chinese EVs "seriously lack a factual and legal basis" and "clearly violate" World Trade Organization (WTO) rules.
Trade tensions have surged since the European Commission said last week it would press ahead with tariffs on China-made EVs, even after Germany, the bloc's largest economy, rejected them.
1 yr. ago
China’s Commerce Ministry said Thursday that it will investigate the fashion company PVH, which owns brands like Tommy Hilfiger and Calvin Klein, for suspected violations of trade rules.
The ministry said Thursday in statements posted online that it would investigate the company’s suspected boycott of products from the far western Xinjiang region, where China’s ruling Communist Party is accused of holding members of mostly Muslim ethnic groups in detention camps.
Washington has blocked some imports from Xinjiang, while Beijing has protested against such moves. China denies any abuses and says steps it has taken are necessary to combat terrorism and a separatist movement.
Companies that buy clothing, cotton, tomatoes and other goods from Xinjiang face pressure from western consumers over alleged human rights violations in the region, while Beijing has whipped up Chinese anger at brands that express concern about possible forced labor.
The ministry said Thursday in statements posted online that it would investigate the company’s suspected boycott of products from the far western Xinjiang region, where China’s ruling Communist Party is accused of holding members of mostly Muslim ethnic groups in detention camps.
Washington has blocked some imports from Xinjiang, while Beijing has protested against such moves. China denies any abuses and says steps it has taken are necessary to combat terrorism and a separatist movement.
Companies that buy clothing, cotton, tomatoes and other goods from Xinjiang face pressure from western consumers over alleged human rights violations in the region, while Beijing has whipped up Chinese anger at brands that express concern about possible forced labor.
1 yr. ago
What are the social implications of a heavy reliance on imported goods?
By Hugo Keji
Heavy reliance on imported goods can have several social implications, including:
1. Economic Inequality
Income Disparities: Increased reliance on imported goods can exacerbate income inequality, as wealthier individuals and businesses may have better access to these goods, while poorer segments of society may struggle to afford them.
Job Displacement: Local industries and small businesses might suffer due to competition with cheaper or better-quality imported goods, leading to job losses and reduced economic opportunities for workers in those sectors.
2. Cultural Erosion
Loss of Cultural Identity: The dominance of imported goods can overshadow local products and traditions, leading to a loss of cultural identity and heritage.
Homogenization: Exposure to and adoption of foreign goods can lead to cultural homogenization, where unique cultural practices and products are replaced by a more uniform global culture.
3. Social Cohesion
Community Disruption: The decline of local industries can disrupt communities that are economically dependent on those industries, leading to social dislocation and a loss of community cohesion.
Consumer Preferences and Lifestyles: Changing consumer preferences towards imported goods can alter lifestyles and social norms, potentially creating a divide between those who embrace foreign influences and those who prefer traditional ways.
4. Dependence and Vulnerability
Economic Vulnerability: Heavy reliance on imported goods makes a country vulnerable to global market fluctuations, trade policies, and geopolitical tensions. Supply chain disruptions can lead to shortages and price volatility, affecting social stability.
Food Security: Dependence on imported food products can threaten food security, especially during global crises that disrupt supply chains.
5. Health and Safety
Quality and Safety Standards: Imported goods may not always meet local quality and safety standards, leading to potential health risks for consumers.
Nutritional Changes: The availability of imported processed foods can contribute to dietary changes, often leading to an increase in diet-related health issues such as obesity and diabetes.
6. Environmental and Ethical Concerns
Environmental Impact: Importing goods over long distances has a significant environmental footprint due to transportation emissions. Additionally, reliance on imported goods may discourage local sustainable practices.
Ethical Issues: Imported goods may be produced under conditions that do not align with local labor laws and ethical standards, raising concerns about workers' rights and fair trade practices.
7. Social Attitudes and Behavior
Perceptions and Values: Over time, heavy reliance on imported goods can influence social attitudes and values, fostering a preference for foreign products and a perception that they are superior to local alternatives.
Consumer Behavior: A shift towards imported goods can change consumer behavior, with increased consumption patterns and a focus on global brands.
8. Policy and Governance
Policy Challenges: Governments may face challenges in creating policies that balance the benefits of imports with the need to protect local industries and cultural heritage.
Regulatory Issues: Ensuring that imported goods comply with local regulations and standards requires robust regulatory frameworks and enforcement mechanisms.
Overall, while imported goods can provide benefits such as variety, affordability, and access to advanced technology, a heavy reliance on them can have wide-ranging social implications that need to be carefully managed through informed policies and community engagement.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Be part of Health Data 101.... Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan. With servers in Asia, Europe and America. Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365 For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Heavy reliance on imported goods can have several social implications, including:
1. Economic Inequality
Income Disparities: Increased reliance on imported goods can exacerbate income inequality, as wealthier individuals and businesses may have better access to these goods, while poorer segments of society may struggle to afford them.
Job Displacement: Local industries and small businesses might suffer due to competition with cheaper or better-quality imported goods, leading to job losses and reduced economic opportunities for workers in those sectors.
2. Cultural Erosion
Loss of Cultural Identity: The dominance of imported goods can overshadow local products and traditions, leading to a loss of cultural identity and heritage.
Homogenization: Exposure to and adoption of foreign goods can lead to cultural homogenization, where unique cultural practices and products are replaced by a more uniform global culture.
3. Social Cohesion
Community Disruption: The decline of local industries can disrupt communities that are economically dependent on those industries, leading to social dislocation and a loss of community cohesion.
Consumer Preferences and Lifestyles: Changing consumer preferences towards imported goods can alter lifestyles and social norms, potentially creating a divide between those who embrace foreign influences and those who prefer traditional ways.
4. Dependence and Vulnerability
Economic Vulnerability: Heavy reliance on imported goods makes a country vulnerable to global market fluctuations, trade policies, and geopolitical tensions. Supply chain disruptions can lead to shortages and price volatility, affecting social stability.
Food Security: Dependence on imported food products can threaten food security, especially during global crises that disrupt supply chains.
5. Health and Safety
Quality and Safety Standards: Imported goods may not always meet local quality and safety standards, leading to potential health risks for consumers.
Nutritional Changes: The availability of imported processed foods can contribute to dietary changes, often leading to an increase in diet-related health issues such as obesity and diabetes.
6. Environmental and Ethical Concerns
Environmental Impact: Importing goods over long distances has a significant environmental footprint due to transportation emissions. Additionally, reliance on imported goods may discourage local sustainable practices.
Ethical Issues: Imported goods may be produced under conditions that do not align with local labor laws and ethical standards, raising concerns about workers' rights and fair trade practices.
7. Social Attitudes and Behavior
Perceptions and Values: Over time, heavy reliance on imported goods can influence social attitudes and values, fostering a preference for foreign products and a perception that they are superior to local alternatives.
Consumer Behavior: A shift towards imported goods can change consumer behavior, with increased consumption patterns and a focus on global brands.
8. Policy and Governance
Policy Challenges: Governments may face challenges in creating policies that balance the benefits of imports with the need to protect local industries and cultural heritage.
Regulatory Issues: Ensuring that imported goods comply with local regulations and standards requires robust regulatory frameworks and enforcement mechanisms.
Overall, while imported goods can provide benefits such as variety, affordability, and access to advanced technology, a heavy reliance on them can have wide-ranging social implications that need to be carefully managed through informed policies and community engagement.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Be part of Health Data 101.... Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan. With servers in Asia, Europe and America. Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365 For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
1 yr. ago
How does mass importation influence local cultures and consumer behavior?
By Hugo Keji
Mass importation significantly influences local cultures and consumer behavior in several ways:
1. Cultural Impact
Cultural Homogenization: Mass importation can lead to the homogenization of cultures, where local traditions and customs might be overshadowed by foreign influences.
This is often seen in the spread of Western culture through media, fashion, food, and lifestyle products.
Cultural Exchange and Fusion: On a positive note, mass importation can also lead to cultural exchange and fusion. Local cultures may adopt and adapt foreign elements, creating new, hybrid cultural practices and products.
Erosion of Traditional Practices: The influx of imported goods can sometimes undermine traditional industries and crafts, leading to the erosion of local cultural practices and skills.
Increased Cultural Awareness: Exposure to foreign goods can also increase cultural awareness and appreciation among local populations, fostering a more global perspective.
2. Consumer Behavior
Variety and Choice: Consumers benefit from a wider variety of goods and services, which can lead to increased satisfaction and the ability to choose products that better meet their needs and preferences.
Changes in Preferences and Tastes: The availability of imported goods can shift consumer preferences and tastes towards foreign products, sometimes at the expense of local products.
Price Competition: Imported goods often lead to increased competition, which can drive down prices and make goods more affordable for consumers. However, this can also put pressure on local producers to lower their prices, potentially impacting their profitability.
Quality and Innovation: Exposure to international standards can lead local producers to improve the quality of their products and adopt innovative practices to remain competitive.
Dependency on Imports: Over-reliance on imported goods can make local markets vulnerable to global market fluctuations, supply chain disruptions, and changes in international trade policies.
Brand Loyalty and Perception: Consumers may develop brand loyalty towards foreign brands, which are often perceived as higher quality or more prestigious. This can influence buying behavior and loyalty patterns in the long term.
3. Economic and Social Implications
Economic Growth: Importation can stimulate economic growth by providing access to goods that are not produced locally and by encouraging trade relationships.
Job Creation and Loss: While mass importation can create jobs in sectors such as retail and logistics, it can also lead to job losses in local industries that cannot compete with cheaper or better-quality imports.
Income Disparity: The benefits of mass importation may not be evenly distributed, potentially exacerbating income disparities. Wealthier consumers may have greater access to imported goods, while lower-income consumers may benefit less from these goods.
Overall, the influence of mass importation on local cultures and consumer behavior is multifaceted, with both positive and negative outcomes depending on the context and how societies manage these changes.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Be part of Health Data 101.... Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan. With servers in Asia, Europe and America. Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365 For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Mass importation significantly influences local cultures and consumer behavior in several ways:
1. Cultural Impact
Cultural Homogenization: Mass importation can lead to the homogenization of cultures, where local traditions and customs might be overshadowed by foreign influences.
This is often seen in the spread of Western culture through media, fashion, food, and lifestyle products.
Cultural Exchange and Fusion: On a positive note, mass importation can also lead to cultural exchange and fusion. Local cultures may adopt and adapt foreign elements, creating new, hybrid cultural practices and products.
Erosion of Traditional Practices: The influx of imported goods can sometimes undermine traditional industries and crafts, leading to the erosion of local cultural practices and skills.
Increased Cultural Awareness: Exposure to foreign goods can also increase cultural awareness and appreciation among local populations, fostering a more global perspective.
2. Consumer Behavior
Variety and Choice: Consumers benefit from a wider variety of goods and services, which can lead to increased satisfaction and the ability to choose products that better meet their needs and preferences.
Changes in Preferences and Tastes: The availability of imported goods can shift consumer preferences and tastes towards foreign products, sometimes at the expense of local products.
Price Competition: Imported goods often lead to increased competition, which can drive down prices and make goods more affordable for consumers. However, this can also put pressure on local producers to lower their prices, potentially impacting their profitability.
Quality and Innovation: Exposure to international standards can lead local producers to improve the quality of their products and adopt innovative practices to remain competitive.
Dependency on Imports: Over-reliance on imported goods can make local markets vulnerable to global market fluctuations, supply chain disruptions, and changes in international trade policies.
Brand Loyalty and Perception: Consumers may develop brand loyalty towards foreign brands, which are often perceived as higher quality or more prestigious. This can influence buying behavior and loyalty patterns in the long term.
3. Economic and Social Implications
Economic Growth: Importation can stimulate economic growth by providing access to goods that are not produced locally and by encouraging trade relationships.
Job Creation and Loss: While mass importation can create jobs in sectors such as retail and logistics, it can also lead to job losses in local industries that cannot compete with cheaper or better-quality imports.
Income Disparity: The benefits of mass importation may not be evenly distributed, potentially exacerbating income disparities. Wealthier consumers may have greater access to imported goods, while lower-income consumers may benefit less from these goods.
Overall, the influence of mass importation on local cultures and consumer behavior is multifaceted, with both positive and negative outcomes depending on the context and how societies manage these changes.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Be part of Health Data 101.... Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan. With servers in Asia, Europe and America. Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365 For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
1 yr. ago
What role do consumer perceptions and trust play in the preference for imported versus local goods? (Part 2)
By Hugo Keji
Section 1: Introduction
Consumer perceptions and trust play a crucial role in influencing purchasing decisions between imported and locally produced goods.
Understanding these factors is essential for local industries to effectively compete with high-quality imports and for imported goods to maintain their market presence.
This article delves into the various aspects of consumer perceptions and trust and their impact on the preference for imported versus local goods.
Section 2: Factors Influencing Consumer Perceptions
Quality Perception
Consumers often perceive imported goods as higher quality due to the reputation of certain countries for specific products. For instance:
Electronics from Japan: Known for precision, innovation, and reliability, Japanese electronics are often preferred for their perceived superior quality.
Luxury Goods from Europe: European brands like Louis Vuitton and Gucci have built a global reputation for craftsmanship and exclusivity, leading to a perception of high quality.
Marketing and branding significantly shape these perceptions. Effective campaigns that highlight the quality and heritage of imported products can enhance their appeal to consumers.
Price Perception-
Price perception is a critical factor in consumer preference. Imported goods can be seen as offering better value for money, especially when produced in countries with lower production costs. For example:
Textiles from Southeast Asia: These are often more affordable due to lower labor and production costs in the region.
On the other hand, local goods may be perceived as more expensive, but they often justify this with arguments around superior quality, freshness, or ethical production practices.
Cultural Influence-
Cultural factors also play a significant role. The desire for exotic or foreign products can drive consumer preference for imports. Conversely, national pride and a desire to support the local economy can lead to a preference for local goods. For instance:
French Wines vs. Local Wines: While French wines are often revered for their heritage and quality, local wines can appeal to consumers who value supporting regional producers.
Availability and Accessibility-
The ease of accessing products influences consumer preferences. Imported goods might be more readily available through global retail chains and e-commerce platforms.
In contrast, locally produced goods might benefit from shorter supply chains, leading to fresher products, particularly in the food sector.
Section 3: The Role of Trust
Product Safety and Reliability-
Trust in product safety and reliability is paramount. Products from countries with stringent safety standards, such as Germany for machinery, often enjoy high trust levels.
Local products may also be trusted more due to familiarity and the ability to directly address any issues with the producer.
Brand Reputation-
Strong brand reputation is crucial for building consumer trust. Established foreign brands leverage their global reputation, while local brands can capitalize on their deep understanding of local market needs and community connections. For example:
Apple (USA): Known for its innovation and quality, Apple enjoys a strong global reputation.
Patagonia (USA): This local brand is trusted for its commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Transparency and Traceability-
Consumers increasingly value transparency in production processes. Imported goods with clear traceability can build trust, as can local producers who provide detailed information about their supply chain. Blockchain technology is one tool being used to enhance traceability and transparency.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations-
Ethical production practices and sustainability are key to building trust. Consumers are often wary of imported goods from countries with poor labor practices or environmental records.
Local goods, on the other hand, benefit from perceptions of being more sustainable and ethically produced, which aligns with the values of environmentally conscious consumers.
Section 4: Case Studies:
Imported Goods-
Electronics from Japan: Renowned for innovation and reliability, Japanese electronics are trusted and preferred by many consumers globally.
Luxury Goods from Europe: European luxury brands like Louis Vuitton and Gucci are perceived as high-quality and exclusive, attracting consumers looking for premium products.
Local Goods-
Organic Foods: Locally sourced organic foods are trusted for their freshness and traceability, appealing to health-conscious consumers.
Handicrafts and Artisanal Products: Local craftspeople often garner trust and preference for their unique, handmade items that reflect cultural heritage and craftsmanship.
Section 5: Strategies for Local Industries to Build Perceptions and Trust:
Quality Assurance and Certification-
Obtaining and prominently displaying certifications that attest to the quality and safety of local products is crucial. Local industries should:
Ensure continuous improvement and quality control to maintain high standards.
Highlight these certifications in marketing materials to build consumer trust.
Effective Branding and Marketing-
Developing strong local brands that emphasize quality, reliability, and cultural value is essential. This includes:
Investing in marketing campaigns that tell the story of the local product and its benefits.
Using storytelling to connect with consumers emotionally, emphasizing unique aspects such as local heritage or sustainability.
Engagement and Transparency-
Direct engagement with consumers through social media, community events, and transparent business practices fosters trust. Local industries can:
Provide detailed information about sourcing, production processes, and sustainability efforts.
Engage in open dialogues with consumers to address concerns and gather feedback.
Leveraging Local Advantages-
Highlighting the advantages of local production, such as freshness, support for the local economy, and reduced environmental impact, can attract consumers. Strategies include:
Collaborating with local influencers and advocates to promote the benefits of buying local.
Emphasizing the unique qualities of local products in marketing efforts.
Section 6: Conclusion
Consumer perceptions and trust significantly impact the preference for imported versus local goods.
By understanding and strategically addressing these factors, local industries can enhance their competitiveness and build strong relationships with consumers.
Improving product quality, effective branding, transparency, and leveraging local advantages are key strategies for local industries to succeed in a global market.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Be part of Health Data 101.... Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan. With servers in Asia, Europe and America. Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365 For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/... https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Section 1: Introduction
Consumer perceptions and trust play a crucial role in influencing purchasing decisions between imported and locally produced goods.
Understanding these factors is essential for local industries to effectively compete with high-quality imports and for imported goods to maintain their market presence.
This article delves into the various aspects of consumer perceptions and trust and their impact on the preference for imported versus local goods.
Section 2: Factors Influencing Consumer Perceptions
Quality Perception
Consumers often perceive imported goods as higher quality due to the reputation of certain countries for specific products. For instance:
Electronics from Japan: Known for precision, innovation, and reliability, Japanese electronics are often preferred for their perceived superior quality.
Luxury Goods from Europe: European brands like Louis Vuitton and Gucci have built a global reputation for craftsmanship and exclusivity, leading to a perception of high quality.
Marketing and branding significantly shape these perceptions. Effective campaigns that highlight the quality and heritage of imported products can enhance their appeal to consumers.
Price Perception-
Price perception is a critical factor in consumer preference. Imported goods can be seen as offering better value for money, especially when produced in countries with lower production costs. For example:
Textiles from Southeast Asia: These are often more affordable due to lower labor and production costs in the region.
On the other hand, local goods may be perceived as more expensive, but they often justify this with arguments around superior quality, freshness, or ethical production practices.
Cultural Influence-
Cultural factors also play a significant role. The desire for exotic or foreign products can drive consumer preference for imports. Conversely, national pride and a desire to support the local economy can lead to a preference for local goods. For instance:
French Wines vs. Local Wines: While French wines are often revered for their heritage and quality, local wines can appeal to consumers who value supporting regional producers.
Availability and Accessibility-
The ease of accessing products influences consumer preferences. Imported goods might be more readily available through global retail chains and e-commerce platforms.
In contrast, locally produced goods might benefit from shorter supply chains, leading to fresher products, particularly in the food sector.
Section 3: The Role of Trust
Product Safety and Reliability-
Trust in product safety and reliability is paramount. Products from countries with stringent safety standards, such as Germany for machinery, often enjoy high trust levels.
Local products may also be trusted more due to familiarity and the ability to directly address any issues with the producer.
Brand Reputation-
Strong brand reputation is crucial for building consumer trust. Established foreign brands leverage their global reputation, while local brands can capitalize on their deep understanding of local market needs and community connections. For example:
Apple (USA): Known for its innovation and quality, Apple enjoys a strong global reputation.
Patagonia (USA): This local brand is trusted for its commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Transparency and Traceability-
Consumers increasingly value transparency in production processes. Imported goods with clear traceability can build trust, as can local producers who provide detailed information about their supply chain. Blockchain technology is one tool being used to enhance traceability and transparency.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations-
Ethical production practices and sustainability are key to building trust. Consumers are often wary of imported goods from countries with poor labor practices or environmental records.
Local goods, on the other hand, benefit from perceptions of being more sustainable and ethically produced, which aligns with the values of environmentally conscious consumers.
Section 4: Case Studies:
Imported Goods-
Electronics from Japan: Renowned for innovation and reliability, Japanese electronics are trusted and preferred by many consumers globally.
Luxury Goods from Europe: European luxury brands like Louis Vuitton and Gucci are perceived as high-quality and exclusive, attracting consumers looking for premium products.
Local Goods-
Organic Foods: Locally sourced organic foods are trusted for their freshness and traceability, appealing to health-conscious consumers.
Handicrafts and Artisanal Products: Local craftspeople often garner trust and preference for their unique, handmade items that reflect cultural heritage and craftsmanship.
Section 5: Strategies for Local Industries to Build Perceptions and Trust:
Quality Assurance and Certification-
Obtaining and prominently displaying certifications that attest to the quality and safety of local products is crucial. Local industries should:
Ensure continuous improvement and quality control to maintain high standards.
Highlight these certifications in marketing materials to build consumer trust.
Effective Branding and Marketing-
Developing strong local brands that emphasize quality, reliability, and cultural value is essential. This includes:
Investing in marketing campaigns that tell the story of the local product and its benefits.
Using storytelling to connect with consumers emotionally, emphasizing unique aspects such as local heritage or sustainability.
Engagement and Transparency-
Direct engagement with consumers through social media, community events, and transparent business practices fosters trust. Local industries can:
Provide detailed information about sourcing, production processes, and sustainability efforts.
Engage in open dialogues with consumers to address concerns and gather feedback.
Leveraging Local Advantages-
Highlighting the advantages of local production, such as freshness, support for the local economy, and reduced environmental impact, can attract consumers. Strategies include:
Collaborating with local influencers and advocates to promote the benefits of buying local.
Emphasizing the unique qualities of local products in marketing efforts.
Section 6: Conclusion
Consumer perceptions and trust significantly impact the preference for imported versus local goods.
By understanding and strategically addressing these factors, local industries can enhance their competitiveness and build strong relationships with consumers.
Improving product quality, effective branding, transparency, and leveraging local advantages are key strategies for local industries to succeed in a global market.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Be part of Health Data 101.... Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan. With servers in Asia, Europe and America. Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365 For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/... https://healthdata101.com
1 yr. ago
What role do consumer perceptions and trust play in the preference for imported versus local goods? (Part 1)
By Hugo Keji
The Role of Consumer Perceptions and Trust in the Preference for Imported Versus Local Goods.
Overview of the influence of consumer perceptions and trust on purchasing decisions.
Importance of understanding these factors in the competition between imported and local goods.
Factors Influencing Consumer Perceptions:-
Quality Perception-
Consumers often perceive imported goods as higher quality due to the reputation of certain countries for specific products (e.g., electronics from Japan, luxury goods from Europe).
Marketing and branding play significant roles in shaping these perceptions.
Price Perception-
Imported goods can be perceived as more affordable or offering better value for money, particularly when produced in countries with lower production costs.
Conversely, local goods may be seen as more expensive due to smaller economies of scale.
Cultural Influence-
Cultural factors influence consumer preferences, such as the desire for exotic or foreign products.
National pride and the desire to support the local economy can drive preference for locally produced goods.
Availability and Accessibility-
The ease of accessing imported versus local goods affects consumer preference. Imports might be more readily available through global retail chains.
Locally produced goods might benefit from shorter supply chains, leading to fresher products, especially in the case of food items.
The Role of Trust:
Product Safety and Reliability-
Trust in product safety and reliability significantly impacts consumer preference. Products from countries with stringent safety standards are often trusted more.
Local products might be trusted more due to familiarity and easier recourse in case of issues.
Brand Reputation-
Strong brands, whether local or international, build consumer trust through consistent quality and effective marketing.
Established foreign brands can leverage their global reputation to gain trust, while local brands can capitalize on local market knowledge and community ties.
Transparency and Traceability-
Consumers are increasingly valuing transparency in production processes and supply chains. Imported goods with clear traceability can build trust.
Local producers often have an advantage in transparency, being closer to the market and more accountable to local consumers.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations-
Ethical production practices and sustainability influence consumer trust. Imported goods may suffer from perceptions of unethical labor practices or environmental harm.
Local goods often benefit from a perception of being more sustainable and ethically produced, aligning with consumers' values.
Case Studies:-
Imported Goods-
Electronics from Japan: Known for innovation and reliability, Japanese electronics are trusted and preferred by many consumers globally.
Luxury Goods from Europe: European luxury brands like Louis Vuitton and Gucci are perceived as high-quality and exclusive.
Local Goods-
Organic Foods: Locally sourced organic foods are trusted for their freshness and traceability.
Handicrafts and Artisanal Products: Local craftspeople often garner trust and preference for their unique, handmade items that reflect cultural heritage.
Strategies for Local Industries to Build Perceptions and Trust:
Quality Assurance and Certification-
Obtain and prominently display certifications that attest to the quality and safety of local products.
Engage in continuous improvement and quality control to ensure consistent product quality.
Effective Branding and Marketing-
Develop strong local brands that emphasize quality, reliability, and cultural value.
Use storytelling to connect with consumers on an emotional level, highlighting the benefits and uniqueness of local products.
Engagement and Transparency-
Foster direct engagement with consumers through social media, community events, and transparency in business practices.
Provide detailed information about sourcing, production processes, and sustainability efforts.
Leveraging Local Advantages-
Highlight the advantages of local production, such as freshness, support for the local economy, and reduced environmental impact.
Collaborate with local influencers and advocates to promote the benefits of buying local.
Summary of the significant role of consumer perceptions and trust in shaping preferences for imported versus local goods.
Emphasis on the need for local industries to strategically build and maintain trust and positive perceptions to compete effectively.
By Hugo Keji
The Role of Consumer Perceptions and Trust in the Preference for Imported Versus Local Goods.
Overview of the influence of consumer perceptions and trust on purchasing decisions.
Importance of understanding these factors in the competition between imported and local goods.
Factors Influencing Consumer Perceptions:-
Quality Perception-
Consumers often perceive imported goods as higher quality due to the reputation of certain countries for specific products (e.g., electronics from Japan, luxury goods from Europe).
Marketing and branding play significant roles in shaping these perceptions.
Price Perception-
Imported goods can be perceived as more affordable or offering better value for money, particularly when produced in countries with lower production costs.
Conversely, local goods may be seen as more expensive due to smaller economies of scale.
Cultural Influence-
Cultural factors influence consumer preferences, such as the desire for exotic or foreign products.
National pride and the desire to support the local economy can drive preference for locally produced goods.
Availability and Accessibility-
The ease of accessing imported versus local goods affects consumer preference. Imports might be more readily available through global retail chains.
Locally produced goods might benefit from shorter supply chains, leading to fresher products, especially in the case of food items.
The Role of Trust:
Product Safety and Reliability-
Trust in product safety and reliability significantly impacts consumer preference. Products from countries with stringent safety standards are often trusted more.
Local products might be trusted more due to familiarity and easier recourse in case of issues.
Brand Reputation-
Strong brands, whether local or international, build consumer trust through consistent quality and effective marketing.
Established foreign brands can leverage their global reputation to gain trust, while local brands can capitalize on local market knowledge and community ties.
Transparency and Traceability-
Consumers are increasingly valuing transparency in production processes and supply chains. Imported goods with clear traceability can build trust.
Local producers often have an advantage in transparency, being closer to the market and more accountable to local consumers.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations-
Ethical production practices and sustainability influence consumer trust. Imported goods may suffer from perceptions of unethical labor practices or environmental harm.
Local goods often benefit from a perception of being more sustainable and ethically produced, aligning with consumers' values.
Case Studies:-
Imported Goods-
Electronics from Japan: Known for innovation and reliability, Japanese electronics are trusted and preferred by many consumers globally.
Luxury Goods from Europe: European luxury brands like Louis Vuitton and Gucci are perceived as high-quality and exclusive.
Local Goods-
Organic Foods: Locally sourced organic foods are trusted for their freshness and traceability.
Handicrafts and Artisanal Products: Local craftspeople often garner trust and preference for their unique, handmade items that reflect cultural heritage.
Strategies for Local Industries to Build Perceptions and Trust:
Quality Assurance and Certification-
Obtain and prominently display certifications that attest to the quality and safety of local products.
Engage in continuous improvement and quality control to ensure consistent product quality.
Effective Branding and Marketing-
Develop strong local brands that emphasize quality, reliability, and cultural value.
Use storytelling to connect with consumers on an emotional level, highlighting the benefits and uniqueness of local products.
Engagement and Transparency-
Foster direct engagement with consumers through social media, community events, and transparency in business practices.
Provide detailed information about sourcing, production processes, and sustainability efforts.
Leveraging Local Advantages-
Highlight the advantages of local production, such as freshness, support for the local economy, and reduced environmental impact.
Collaborate with local influencers and advocates to promote the benefits of buying local.
Summary of the significant role of consumer perceptions and trust in shaping preferences for imported versus local goods.
Emphasis on the need for local industries to strategically build and maintain trust and positive perceptions to compete effectively.

Health Data 101 - App on Amazon Appstore
Healthdata101-Manage Hospital and Health data.
https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B0D514TH5S
1 yr. ago
Does Vietnam have educated and skilled workers to do the job?
By Hugo Keji
Vietnam has made significant progress in developing an educated and skilled workforce, but there are still challenges and opportunities for improvement to meet the demands of modern manufacturing industries.
Current Situation:-
Education System-
Basic Education: Vietnam has a strong basic education system with high literacy rates and a high enrollment rate in primary and secondary education.
Higher Education: The number of universities and colleges has increased, producing a growing number of graduates in various fields.
STEM Focus: There is an increasing emphasis on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education.
Vocational Training-
Vocational Schools: Vietnam has a network of vocational schools that offer training in various trades and technical skills.
Government Programs: Initiatives like the National Target Program on Education and Training aim to improve vocational training and skill development.
Language Skills-
English Proficiency: English language skills are improving, particularly among younger generations, which is important for integrating into global supply chains and working with multinational companies.
Challenges:-
Skill Mismatch-
Industry Needs: There is often a gap between the skills taught in educational institutions and the specific needs of industries, especially in high-tech and advanced manufacturing sectors.
Quality of Training-
Training Standards: The quality of vocational training can vary, and there is a need for standardized curricula and better training facilities.
Continuous Learning
Lifelong Learning: There is a need to promote lifelong learning and continuous skill development to keep up with technological advancements.
Government and Industry Initiatives:-
Skill Development Programs-
National Programs: Programs like the "National Target Program on Education and Training" aim to enhance the skill levels of the workforce.
Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborations between the government and private sector to develop training programs tailored to industry needs.
Education Reforms-
Curriculum Updates: Updating curricula to include more practical and industry-relevant skills, especially in STEM fields.
International Collaboration: Partnerships with foreign educational institutions to improve the quality of education and training.
Vocational Training Enhancement-
Infrastructure Investment: Investing in modern training facilities and equipment to provide hands-on experience.
Industry Involvement: Encouraging industries to participate in designing and delivering vocational training programs.
Promotion of STEM Education-
Incentives and Scholarships: Providing incentives and scholarships to students pursuing STEM fields.
Competitions and Workshops: Organizing competitions, workshops, and other activities to promote interest in STEM subjects.
Language Training-
English Language Programs: Expanding English language training programs to improve proficiency among the workforce.
Multilingual Education: Encouraging multilingual education to better prepare workers for global engagement.
While Vietnam has a solid foundation in terms of basic education and vocational training, there is a continuous need for improvements to fully meet the demands of modern manufacturing industries.
By addressing skill mismatches, enhancing training quality, and fostering industry-education collaboration, Vietnam can further develop its workforce to support the influx of factories and drive economic growth.
Vietnam’s food, culture, and service sectors play significant roles in the country's economy and its appeal as a destination for tourism and business.
Here’s an overview of each:
Vietnamese Food:-
Diverse and Flavorful Cuisine-
Traditional Dishes: Pho, Banh Mi, Bun Cha, and spring rolls are internationally renowned. Vietnamese cuisine emphasizes fresh ingredients, herbs, and balanced flavors.
Regional Variations: Each region has its specialties. Northern cuisine is known for its simplicity and harmony, central cuisine for its complexity and spiciness, and southern cuisine for its sweetness and abundance of fresh vegetables and fruits.
Street Food Culture-
Street Vendors: Street food is a significant part of Vietnamese culture. Markets and street vendors offer a variety of affordable and delicious options, making Vietnamese food widely accessible.
Culinary Tourism: Vietnam is a popular destination for food enthusiasts. Culinary tours and cooking classes attract tourists keen to learn about and taste Vietnamese cuisine.
Food Industry Growth
Export Market: Vietnam exports a variety of food products, including coffee, seafood, rice, and spices, contributing significantly to the economy.
Restaurant Industry: The growth of both local and international restaurants reflects the increasing urbanization and changing lifestyles.
Vietnamese Culture:-
Rich Heritage-
Historical Influences: Vietnamese culture is shaped by its history, including influences from China, France, and other Southeast Asian nations.
Festivals: Traditional festivals such as Tet (Lunar New Year), Mid-Autumn Festival, and various regional festivals celebrate cultural heritage and attract tourists.
Art and Literature-
Traditional Arts: Water puppetry, traditional music (Ca Tru, Quan Ho), and dance are integral parts of Vietnamese culture.
Modern Arts: There is a growing contemporary art scene with galleries, exhibitions, and performance arts gaining popularity.
Cultural Practices-
Confucian Values: Confucianism influences social values, emphasizing respect for elders, family ties, and education.
Buddhism: Buddhism is a major religion, influencing various aspects of life, including festivals, rituals, and everyday practices.
Service Sectors:-
Tourism-
Tourist Attractions: Vietnam offers diverse attractions, from natural landscapes like Ha Long Bay and the Mekong Delta to cultural sites like Hoi An and Hue.
Eco-tourism: Increasing focus on eco-tourism and sustainable travel practices to preserve natural and cultural heritage.
Hospitality Industry: Rapid growth in hotels, resorts, and travel services to accommodate the increasing number of tourists.
Retail and E-commerce-
Retail Sector: Modern shopping malls, traditional markets, and a growing number of international brands reflect the dynamic retail landscape.
E-commerce Growth: With increasing internet penetration and smartphone usage, e-commerce is booming, providing new opportunities for businesses and consumers.
Financial Services-
Banking and Finance: Expansion of banking services, including digital banking, to cater to a growing economy and an increasingly tech-savvy population.
Investment Services: Development of financial markets and investment services to attract both domestic and foreign investors.
Education and Healthcare-
Education Sector: Expansion of international schools, universities, and vocational training centers to meet the demands of a growing middle class and foreign expatriates.
Healthcare Services: Improvement in healthcare infrastructure and services, with an increasing number of private hospitals and clinics providing high-quality care.
Technology and IT Services-
IT Outsourcing: Vietnam is becoming a hub for IT outsourcing, with a growing number of companies providing software development and IT services.
Tech Startups: A vibrant startup ecosystem supported by government initiatives, venture capital, and innovation hubs.
Vietnam’s food, culture, and service sectors are integral to its economy and attractiveness as a destination for tourists and businesses.
Continued investment and development in these areas will not only enhance the country's global standing but also contribute to sustainable economic growth.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Vietnam has made significant progress in developing an educated and skilled workforce, but there are still challenges and opportunities for improvement to meet the demands of modern manufacturing industries.
Current Situation:-
Education System-
Basic Education: Vietnam has a strong basic education system with high literacy rates and a high enrollment rate in primary and secondary education.
Higher Education: The number of universities and colleges has increased, producing a growing number of graduates in various fields.
STEM Focus: There is an increasing emphasis on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education.
Vocational Training-
Vocational Schools: Vietnam has a network of vocational schools that offer training in various trades and technical skills.
Government Programs: Initiatives like the National Target Program on Education and Training aim to improve vocational training and skill development.
Language Skills-
English Proficiency: English language skills are improving, particularly among younger generations, which is important for integrating into global supply chains and working with multinational companies.
Challenges:-
Skill Mismatch-
Industry Needs: There is often a gap between the skills taught in educational institutions and the specific needs of industries, especially in high-tech and advanced manufacturing sectors.
Quality of Training-
Training Standards: The quality of vocational training can vary, and there is a need for standardized curricula and better training facilities.
Continuous Learning
Lifelong Learning: There is a need to promote lifelong learning and continuous skill development to keep up with technological advancements.
Government and Industry Initiatives:-
Skill Development Programs-
National Programs: Programs like the "National Target Program on Education and Training" aim to enhance the skill levels of the workforce.
Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborations between the government and private sector to develop training programs tailored to industry needs.
Education Reforms-
Curriculum Updates: Updating curricula to include more practical and industry-relevant skills, especially in STEM fields.
International Collaboration: Partnerships with foreign educational institutions to improve the quality of education and training.
Vocational Training Enhancement-
Infrastructure Investment: Investing in modern training facilities and equipment to provide hands-on experience.
Industry Involvement: Encouraging industries to participate in designing and delivering vocational training programs.
Promotion of STEM Education-
Incentives and Scholarships: Providing incentives and scholarships to students pursuing STEM fields.
Competitions and Workshops: Organizing competitions, workshops, and other activities to promote interest in STEM subjects.
Language Training-
English Language Programs: Expanding English language training programs to improve proficiency among the workforce.
Multilingual Education: Encouraging multilingual education to better prepare workers for global engagement.
While Vietnam has a solid foundation in terms of basic education and vocational training, there is a continuous need for improvements to fully meet the demands of modern manufacturing industries.
By addressing skill mismatches, enhancing training quality, and fostering industry-education collaboration, Vietnam can further develop its workforce to support the influx of factories and drive economic growth.
Vietnam’s food, culture, and service sectors play significant roles in the country's economy and its appeal as a destination for tourism and business.
Here’s an overview of each:
Vietnamese Food:-
Diverse and Flavorful Cuisine-
Traditional Dishes: Pho, Banh Mi, Bun Cha, and spring rolls are internationally renowned. Vietnamese cuisine emphasizes fresh ingredients, herbs, and balanced flavors.
Regional Variations: Each region has its specialties. Northern cuisine is known for its simplicity and harmony, central cuisine for its complexity and spiciness, and southern cuisine for its sweetness and abundance of fresh vegetables and fruits.
Street Food Culture-
Street Vendors: Street food is a significant part of Vietnamese culture. Markets and street vendors offer a variety of affordable and delicious options, making Vietnamese food widely accessible.
Culinary Tourism: Vietnam is a popular destination for food enthusiasts. Culinary tours and cooking classes attract tourists keen to learn about and taste Vietnamese cuisine.
Food Industry Growth
Export Market: Vietnam exports a variety of food products, including coffee, seafood, rice, and spices, contributing significantly to the economy.
Restaurant Industry: The growth of both local and international restaurants reflects the increasing urbanization and changing lifestyles.
Vietnamese Culture:-
Rich Heritage-
Historical Influences: Vietnamese culture is shaped by its history, including influences from China, France, and other Southeast Asian nations.
Festivals: Traditional festivals such as Tet (Lunar New Year), Mid-Autumn Festival, and various regional festivals celebrate cultural heritage and attract tourists.
Art and Literature-
Traditional Arts: Water puppetry, traditional music (Ca Tru, Quan Ho), and dance are integral parts of Vietnamese culture.
Modern Arts: There is a growing contemporary art scene with galleries, exhibitions, and performance arts gaining popularity.
Cultural Practices-
Confucian Values: Confucianism influences social values, emphasizing respect for elders, family ties, and education.
Buddhism: Buddhism is a major religion, influencing various aspects of life, including festivals, rituals, and everyday practices.
Service Sectors:-
Tourism-
Tourist Attractions: Vietnam offers diverse attractions, from natural landscapes like Ha Long Bay and the Mekong Delta to cultural sites like Hoi An and Hue.
Eco-tourism: Increasing focus on eco-tourism and sustainable travel practices to preserve natural and cultural heritage.
Hospitality Industry: Rapid growth in hotels, resorts, and travel services to accommodate the increasing number of tourists.
Retail and E-commerce-
Retail Sector: Modern shopping malls, traditional markets, and a growing number of international brands reflect the dynamic retail landscape.
E-commerce Growth: With increasing internet penetration and smartphone usage, e-commerce is booming, providing new opportunities for businesses and consumers.
Financial Services-
Banking and Finance: Expansion of banking services, including digital banking, to cater to a growing economy and an increasingly tech-savvy population.
Investment Services: Development of financial markets and investment services to attract both domestic and foreign investors.
Education and Healthcare-
Education Sector: Expansion of international schools, universities, and vocational training centers to meet the demands of a growing middle class and foreign expatriates.
Healthcare Services: Improvement in healthcare infrastructure and services, with an increasing number of private hospitals and clinics providing high-quality care.
Technology and IT Services-
IT Outsourcing: Vietnam is becoming a hub for IT outsourcing, with a growing number of companies providing software development and IT services.
Tech Startups: A vibrant startup ecosystem supported by government initiatives, venture capital, and innovation hubs.
Vietnam’s food, culture, and service sectors are integral to its economy and attractiveness as a destination for tourists and businesses.
Continued investment and development in these areas will not only enhance the country's global standing but also contribute to sustainable economic growth.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
1 yr. ago
How can local industries improve their product quality to compete with high-quality imports? (Part-2)
By Hugo Keji
Detailed Section:-
Section 1: Introduction
In the face of increasing globalization, local industries must focus on enhancing product quality to remain competitive against high-quality imports.
Improving product quality not only boosts competitiveness but also fosters customer loyalty and drives sustainable growth.
This article explores strategies that local industries can employ to elevate their product quality and compete effectively in the global market.
Section 2: Investment in Research and Development (R&D)
Innovation and Product Improvement-
Investing in R&D is crucial for local industries to innovate and enhance their product offerings. This includes:
Allocating resources to develop new technologies and improve existing processes.
Fostering a culture of innovation within the organization to continuously generate new ideas.
Collaboration with Research Institutions-
Partnering with universities and research centers provides access to expertise and advanced research facilities. Local industries should:
Engage in joint research projects and leverage government-funded programs.
Stay updated on the latest industry trends and technological advancements through these collaborations.
Section 3: Quality Management Systems
Adoption of International Standards-
Implementing quality management systems like ISO 9001 helps local industries align with international best practices. This involves:
Regularly updating and maintaining certifications to ensure compliance with global standards.
Conducting internal audits to identify and address areas for improvement.
Continuous Improvement Processes-
Employing methodologies such as Six Sigma and Total Quality Management (TQM) helps streamline processes and eliminate defects. Key steps include:
Training employees in these methodologies to build internal capabilities.
Establishing a continuous improvement culture that encourages proactive problem-solving.
Section 4: Skilled Workforce Development
Training and Education
Investing in employee training programs enhances skills and knowledge. This can be achieved by:
Offering regular workshops and courses on the latest industry practices and technologies.
Encouraging employees to pursue higher education and professional certifications.
Attracting and Retaining Talent-
Creating an attractive work environment and competitive compensation packages helps attract and retain skilled workers. This includes:
Implementing career development plans and offering growth opportunities within the organization.
Fostering a positive workplace culture that values employee contributions.
Section 5: Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Automation and Robotics
Investing in automation and robotics increases precision and consistency in manufacturing processes. This involves:
Utilizing advanced machinery to reduce human error and improve efficiency.
Integrating robotics into production lines to enhance product quality.
Industry 4.0-
Adopting Industry 4.0 technologies such as IoT, AI, and data analytics optimizes production processes. Steps to implement these technologies include:
Utilizing IoT devices to monitor and control manufacturing processes in real-time.
Applying AI and data analytics to identify and address production inefficiencies.
Section 6: Supply Chain Optimization
Supplier Quality Management
Establishing strict quality standards for suppliers ensures that raw materials and components meet high standards. This includes:
Conducting regular audits of suppliers to verify compliance with quality standards.
Developing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers to ensure consistent quality.
Lean Manufacturing-
Implementing lean manufacturing principles reduces waste and improves efficiency. Key practices include:
Focusing on value-added activities that enhance product quality.
Continuously identifying and eliminating non-value-added processes.
Section 7: Customer Feedback and Engagement
Listening to Customers
Actively seeking and analyzing customer feedback helps identify areas for improvement. This involves:
Conducting surveys, focus groups, and monitoring social media to gather customer insights.
Using feedback to drive product and service enhancements.
Responsive Customer Service
Providing excellent customer service addresses issues promptly and effectively. Key actions include:
Establishing a responsive customer service team to handle inquiries and complaints.
Using customer feedback to inform continuous improvement efforts.
Section 8: Branding and Marketing Strategies
Building a Strong Brand
Developing a strong brand identity that emphasizes quality and reliability enhances market competitiveness. This involves:
Investing in marketing campaigns that highlight the unique qualities of local products.
Creating a brand story that resonates with consumers and builds trust.
Market Differentiation-
Differentiating products by focusing on unique selling points such as sustainability, local craftsmanship, and superior customer service. Strategies include:
Tailoring marketing efforts to target specific consumer segments.
Highlighting the benefits and unique attributes of local products in marketing materials.
Section 9: Government and Industry Support
Policy and Incentives
Advocating for government policies that support local industries, such as tax incentives and subsidies. This includes:
Participating in industry associations to influence policy decisions and share best practices.
Collaborating with government bodies to develop supportive regulations.
Export Promotion
Utilizing government and industry programs to promote local products in international markets. Key actions include:
Participating in trade shows and international exhibitions to showcase local products.
Leveraging export promotion initiatives to expand market reach.
Section 10:
Improving product quality is essential for local industries to compete with high-quality imports. By investing in R&D, implementing quality management systems, developing a skilled workforce, adopting advanced manufacturing technologies, optimizing supply chains, engaging with customers, building strong brands, and leveraging government and industry support, local industries can enhance their competitiveness and achieve sustainable growth.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Detailed Section:-
Section 1: Introduction
In the face of increasing globalization, local industries must focus on enhancing product quality to remain competitive against high-quality imports.
Improving product quality not only boosts competitiveness but also fosters customer loyalty and drives sustainable growth.
This article explores strategies that local industries can employ to elevate their product quality and compete effectively in the global market.
Section 2: Investment in Research and Development (R&D)
Innovation and Product Improvement-
Investing in R&D is crucial for local industries to innovate and enhance their product offerings. This includes:
Allocating resources to develop new technologies and improve existing processes.
Fostering a culture of innovation within the organization to continuously generate new ideas.
Collaboration with Research Institutions-
Partnering with universities and research centers provides access to expertise and advanced research facilities. Local industries should:
Engage in joint research projects and leverage government-funded programs.
Stay updated on the latest industry trends and technological advancements through these collaborations.
Section 3: Quality Management Systems
Adoption of International Standards-
Implementing quality management systems like ISO 9001 helps local industries align with international best practices. This involves:
Regularly updating and maintaining certifications to ensure compliance with global standards.
Conducting internal audits to identify and address areas for improvement.
Continuous Improvement Processes-
Employing methodologies such as Six Sigma and Total Quality Management (TQM) helps streamline processes and eliminate defects. Key steps include:
Training employees in these methodologies to build internal capabilities.
Establishing a continuous improvement culture that encourages proactive problem-solving.
Section 4: Skilled Workforce Development
Training and Education
Investing in employee training programs enhances skills and knowledge. This can be achieved by:
Offering regular workshops and courses on the latest industry practices and technologies.
Encouraging employees to pursue higher education and professional certifications.
Attracting and Retaining Talent-
Creating an attractive work environment and competitive compensation packages helps attract and retain skilled workers. This includes:
Implementing career development plans and offering growth opportunities within the organization.
Fostering a positive workplace culture that values employee contributions.
Section 5: Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Automation and Robotics
Investing in automation and robotics increases precision and consistency in manufacturing processes. This involves:
Utilizing advanced machinery to reduce human error and improve efficiency.
Integrating robotics into production lines to enhance product quality.
Industry 4.0-
Adopting Industry 4.0 technologies such as IoT, AI, and data analytics optimizes production processes. Steps to implement these technologies include:
Utilizing IoT devices to monitor and control manufacturing processes in real-time.
Applying AI and data analytics to identify and address production inefficiencies.
Section 6: Supply Chain Optimization
Supplier Quality Management
Establishing strict quality standards for suppliers ensures that raw materials and components meet high standards. This includes:
Conducting regular audits of suppliers to verify compliance with quality standards.
Developing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers to ensure consistent quality.
Lean Manufacturing-
Implementing lean manufacturing principles reduces waste and improves efficiency. Key practices include:
Focusing on value-added activities that enhance product quality.
Continuously identifying and eliminating non-value-added processes.
Section 7: Customer Feedback and Engagement
Listening to Customers
Actively seeking and analyzing customer feedback helps identify areas for improvement. This involves:
Conducting surveys, focus groups, and monitoring social media to gather customer insights.
Using feedback to drive product and service enhancements.
Responsive Customer Service
Providing excellent customer service addresses issues promptly and effectively. Key actions include:
Establishing a responsive customer service team to handle inquiries and complaints.
Using customer feedback to inform continuous improvement efforts.
Section 8: Branding and Marketing Strategies
Building a Strong Brand
Developing a strong brand identity that emphasizes quality and reliability enhances market competitiveness. This involves:
Investing in marketing campaigns that highlight the unique qualities of local products.
Creating a brand story that resonates with consumers and builds trust.
Market Differentiation-
Differentiating products by focusing on unique selling points such as sustainability, local craftsmanship, and superior customer service. Strategies include:
Tailoring marketing efforts to target specific consumer segments.
Highlighting the benefits and unique attributes of local products in marketing materials.
Section 9: Government and Industry Support
Policy and Incentives
Advocating for government policies that support local industries, such as tax incentives and subsidies. This includes:
Participating in industry associations to influence policy decisions and share best practices.
Collaborating with government bodies to develop supportive regulations.
Export Promotion
Utilizing government and industry programs to promote local products in international markets. Key actions include:
Participating in trade shows and international exhibitions to showcase local products.
Leveraging export promotion initiatives to expand market reach.
Section 10:
Improving product quality is essential for local industries to compete with high-quality imports. By investing in R&D, implementing quality management systems, developing a skilled workforce, adopting advanced manufacturing technologies, optimizing supply chains, engaging with customers, building strong brands, and leveraging government and industry support, local industries can enhance their competitiveness and achieve sustainable growth.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
1 yr. ago
Quality and Standards- How do the quality and safety standards of imported goods compare to locally produced items?
By Hugo Keji
Quality and Standards: Comparing Imported and Locally Produced Goods:-
Introduction-
Brief overview of the importance of quality and safety standards in goods.
Mention the growing concern over the standards of imported vs. locally produced goods.
Regulatory Framework-
Imported Goods:
Discuss the international regulations and agreements governing quality and safety standards (e.g., WTO, ISO)
Explain the role of customs and border protection agencies in inspecting and enforcing standards
Locally Produced Goods:
Detail the national regulatory bodies and standards (e.g., FDA, USDA in the USA, EFSA in the EU)
Highlight how these agencies monitor and enforce standards within the country.
Quality Standards-
Imported Goods:
Potential variability in quality due to differences in manufacturing standards across countries.
Instances of high-quality imports meeting stringent international standards.
Examples of common quality issues with certain imported goods (e.g., counterfeit products, substandard materials).
Locally Produced Goods:
Typically higher consistency in quality due to uniform national standards.
Benefits of traceability and accountability in local production
Examples of high-quality locally produced goods (e.g., organic foods, artisanal products).
Safety Standards-
Imported Goods:
Risks associated with imports from countries with less stringent safety regulations.
The role of third-party testing and certification in ensuring safety.
Case studies of safety breaches in imported goods (e.g., lead in toys, contaminated food products)
Locally Produced Goods:
Generally stricter safety oversight and faster response to safety issues.
Advantages of shorter supply chains in maintaining safety standards.
Examples of safety recalls and how they are managed locally.
Consumer Perception and Trust-
Imported Goods:
Consumer concerns over the authenticity and safety of imported products.
Instances where imported goods are preferred due to perceived higher quality or lower cost.
Locally Produced Goods:
Higher consumer trust due to transparency and familiarity with local brands.
The trend towards supporting local economies and sustainable practices.
Economic and Environmental Impact-
Imported Goods:
Economic benefits of access to a broader range of goods and competitive pricing.
Environmental concerns related to long-distance transportation and carbon footprint.
Locally Produced Goods:
Positive impact on the local economy and job creation.
Environmental benefits of reduced transportation and support for local agriculture.
Summary of the key points comparing the quality and safety standards of imported and locally produced goods.
Final thoughts on the importance of informed consumer choices and ongoing efforts to enhance standards globally and locally.
References:-
List of sources and further reading on quality and safety standards in imported and locally produced goods.
Section 1: Introduction
Quality and safety standards play a crucial role in ensuring that goods meet certain benchmarks for consumer use. With the globalization of trade, consumers have access to a wide range of imported goods, which raises questions about how these products compare to those produced locally.
This article explores the regulatory frameworks, quality and safety standards, consumer perceptions, and economic impacts of imported versus locally produced goods.
Section 2: Regulatory Framework
Imported Goods-
Imported goods are subject to international regulations and agreements designed to maintain quality and safety standards. Organizations such as the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) establish guidelines that member countries are expected to follow.
Customs and border protection agencies play a critical role in inspecting imported goods and enforcing these standards to prevent substandard or unsafe products from entering the market.
Locally Produced Goods-
Locally produced goods are regulated by national bodies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) in the USA, or the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) in the EU.
These agencies ensure that goods produced within the country adhere to specific quality and safety standards, providing a consistent and reliable benchmark for consumers.
Section 3: Quality Standards-
Imported Goods:
The quality of imported goods can vary significantly depending on the country of origin and its manufacturing standards.
While many imported products meet or exceed international standards, there are instances where imports fall short, resulting in issues such as counterfeit products or the use of substandard materials.
Despite these challenges, there are also many examples of high-quality imports that are recognized for their excellence.
Locally Produced Goods-
Locally produced goods generally benefit from more consistent quality due to uniform national standards.
The ability to trace the origin and production process of local goods enhances accountability and trust.
For instance, locally produced organic foods and artisanal products often enjoy a reputation for higher quality due to stringent local standards and consumer trust in the local production process.
Section 4: Safety Standards-
Imported Goods:
The safety of imported goods can be compromised when they come from countries with less rigorous safety regulations.
Third-party testing and certification are crucial in ensuring that these products meet safety standards before reaching consumers.
However, there have been notable safety breaches in imported goods, such as the presence of lead in toys or contaminated food products, highlighting the risks involved.
Locally Produced Goods-
Local products typically undergo stricter safety oversight, with faster response times to address any safety issues that arise. Shorter supply chains also contribute to maintaining higher safety standards.
Local authorities can quickly implement recalls and corrective actions, as seen in various instances where local products were swiftly removed from shelves to protect consumers.
Section 5: Consumer Perception and Trust-
Imported Goods:
Consumers often harbor concerns about the authenticity and safety of imported products, particularly from regions known for lower standards. However, imported goods can also be favored for their perceived higher quality or lower cost, depending on the product category and origin.
Locally Produced Goods:
Locally produced goods generally enjoy higher consumer trust due to greater transparency and familiarity with local brands. There is a growing trend towards supporting local economies and sustainable practices, which boosts the reputation and appeal of locally produced goods.
Section 6: Economic and Environmental Impact:-
Imported Goods-
The importation of goods provides economic benefits by offering a wider range of products and fostering competitive pricing. However, the environmental impact of long-distance transportation and the associated carbon footprint are significant concerns that need to be addressed.
Locally Produced Goods-
Producing goods locally supports the local economy and creates jobs, contributing to economic stability. Environmentally, local production reduces transportation emissions and supports sustainable practices, making it a favorable option for eco-conscious consumers.
In conclusion, both imported and locally produced goods have their advantages and challenges in terms of quality and safety standards.
While imported goods offer diversity and competitive pricing, locally produced items often provide higher consistency and consumer trust.
Ultimately, informed consumer choices and continuous efforts to enhance standards globally and locally are essential for ensuring the quality and safety of all products.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Quality and Standards: Comparing Imported and Locally Produced Goods:-
Introduction-
Brief overview of the importance of quality and safety standards in goods.
Mention the growing concern over the standards of imported vs. locally produced goods.
Regulatory Framework-
Imported Goods:
Discuss the international regulations and agreements governing quality and safety standards (e.g., WTO, ISO)
Explain the role of customs and border protection agencies in inspecting and enforcing standards
Locally Produced Goods:
Detail the national regulatory bodies and standards (e.g., FDA, USDA in the USA, EFSA in the EU)
Highlight how these agencies monitor and enforce standards within the country.
Quality Standards-
Imported Goods:
Potential variability in quality due to differences in manufacturing standards across countries.
Instances of high-quality imports meeting stringent international standards.
Examples of common quality issues with certain imported goods (e.g., counterfeit products, substandard materials).
Locally Produced Goods:
Typically higher consistency in quality due to uniform national standards.
Benefits of traceability and accountability in local production
Examples of high-quality locally produced goods (e.g., organic foods, artisanal products).
Safety Standards-
Imported Goods:
Risks associated with imports from countries with less stringent safety regulations.
The role of third-party testing and certification in ensuring safety.
Case studies of safety breaches in imported goods (e.g., lead in toys, contaminated food products)
Locally Produced Goods:
Generally stricter safety oversight and faster response to safety issues.
Advantages of shorter supply chains in maintaining safety standards.
Examples of safety recalls and how they are managed locally.
Consumer Perception and Trust-
Imported Goods:
Consumer concerns over the authenticity and safety of imported products.
Instances where imported goods are preferred due to perceived higher quality or lower cost.
Locally Produced Goods:
Higher consumer trust due to transparency and familiarity with local brands.
The trend towards supporting local economies and sustainable practices.
Economic and Environmental Impact-
Imported Goods:
Economic benefits of access to a broader range of goods and competitive pricing.
Environmental concerns related to long-distance transportation and carbon footprint.
Locally Produced Goods:
Positive impact on the local economy and job creation.
Environmental benefits of reduced transportation and support for local agriculture.
Summary of the key points comparing the quality and safety standards of imported and locally produced goods.
Final thoughts on the importance of informed consumer choices and ongoing efforts to enhance standards globally and locally.
References:-
List of sources and further reading on quality and safety standards in imported and locally produced goods.
Section 1: Introduction
Quality and safety standards play a crucial role in ensuring that goods meet certain benchmarks for consumer use. With the globalization of trade, consumers have access to a wide range of imported goods, which raises questions about how these products compare to those produced locally.
This article explores the regulatory frameworks, quality and safety standards, consumer perceptions, and economic impacts of imported versus locally produced goods.
Section 2: Regulatory Framework
Imported Goods-
Imported goods are subject to international regulations and agreements designed to maintain quality and safety standards. Organizations such as the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) establish guidelines that member countries are expected to follow.
Customs and border protection agencies play a critical role in inspecting imported goods and enforcing these standards to prevent substandard or unsafe products from entering the market.
Locally Produced Goods-
Locally produced goods are regulated by national bodies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) in the USA, or the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) in the EU.
These agencies ensure that goods produced within the country adhere to specific quality and safety standards, providing a consistent and reliable benchmark for consumers.
Section 3: Quality Standards-
Imported Goods:
The quality of imported goods can vary significantly depending on the country of origin and its manufacturing standards.
While many imported products meet or exceed international standards, there are instances where imports fall short, resulting in issues such as counterfeit products or the use of substandard materials.
Despite these challenges, there are also many examples of high-quality imports that are recognized for their excellence.
Locally Produced Goods-
Locally produced goods generally benefit from more consistent quality due to uniform national standards.
The ability to trace the origin and production process of local goods enhances accountability and trust.
For instance, locally produced organic foods and artisanal products often enjoy a reputation for higher quality due to stringent local standards and consumer trust in the local production process.
Section 4: Safety Standards-
Imported Goods:
The safety of imported goods can be compromised when they come from countries with less rigorous safety regulations.
Third-party testing and certification are crucial in ensuring that these products meet safety standards before reaching consumers.
However, there have been notable safety breaches in imported goods, such as the presence of lead in toys or contaminated food products, highlighting the risks involved.
Locally Produced Goods-
Local products typically undergo stricter safety oversight, with faster response times to address any safety issues that arise. Shorter supply chains also contribute to maintaining higher safety standards.
Local authorities can quickly implement recalls and corrective actions, as seen in various instances where local products were swiftly removed from shelves to protect consumers.
Section 5: Consumer Perception and Trust-
Imported Goods:
Consumers often harbor concerns about the authenticity and safety of imported products, particularly from regions known for lower standards. However, imported goods can also be favored for their perceived higher quality or lower cost, depending on the product category and origin.
Locally Produced Goods:
Locally produced goods generally enjoy higher consumer trust due to greater transparency and familiarity with local brands. There is a growing trend towards supporting local economies and sustainable practices, which boosts the reputation and appeal of locally produced goods.
Section 6: Economic and Environmental Impact:-
Imported Goods-
The importation of goods provides economic benefits by offering a wider range of products and fostering competitive pricing. However, the environmental impact of long-distance transportation and the associated carbon footprint are significant concerns that need to be addressed.
Locally Produced Goods-
Producing goods locally supports the local economy and creates jobs, contributing to economic stability. Environmentally, local production reduces transportation emissions and supports sustainable practices, making it a favorable option for eco-conscious consumers.
In conclusion, both imported and locally produced goods have their advantages and challenges in terms of quality and safety standards.
While imported goods offer diversity and competitive pricing, locally produced items often provide higher consistency and consumer trust.
Ultimately, informed consumer choices and continuous efforts to enhance standards globally and locally are essential for ensuring the quality and safety of all products.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
1 yr. ago
What role does consumer preference play in the balance between imported and locally produced goods?
By Hugo Keji
Role of Consumer Preference in the Balance Between Imported and Locally Produced Goods.
Price Sensitivity:-
Cost-Conscious Choices: Consumers often opt for imported goods if they are cheaper than locally produced alternatives.
Value for Money: Consumers weigh the cost against perceived value, often choosing products that offer better quality or features for the same price.
Quality Perception:-
Brand Reputation: Imported goods from established international brands are often perceived as higher quality.
Consistency: Consumers might prefer imported goods if they believe they offer more consistent quality compared to local products.
Cultural and Social Influences:-
Cultural Affinity: Consumers may prefer local products due to cultural significance or a sense of national pride.
Social Trends: Trends and social influences, including endorsements by celebrities or influencers, can sway consumer preferences towards either imported or local goods.
Product Availability and Variety:
Wide Selection: Imported goods often increase the variety of available products, attracting consumers looking for unique or niche items not produced locally.
Seasonal Availability: Some imported goods fill gaps in seasonal availability, making them preferred choices at certain times of the year.
Environmental and Ethical Considerations:-
Sustainability: Environmentally conscious consumers may prefer locally produced goods to reduce their carbon footprint.
Fair Trade: Ethical considerations, such as fair trade practices, can influence consumers to choose local products that support fair labor conditions and community development.
Marketing and Branding:-
Effective Advertising: Strong marketing campaigns by international brands can influence consumer preferences towards imported goods.
Local Branding: Effective local branding that emphasizes unique aspects and benefits of local products can attract consumers.
Impact on Local and Imported Goods Balance:-
Demand Shifts:
Economic Fluctuations: During economic downturns, consumers may shift towards cheaper imported goods. Conversely, in times of economic growth, there may be a stronger preference for higher-quality local products.
Income Levels: Higher income levels can increase demand for premium imported goods, while lower income levels might boost demand for affordable local alternatives.
Market Dynamics:
Competitive Pressure: High consumer preference for imported goods can pressure local industries to improve quality and reduce prices.
Niche Markets: Local producers can carve out niche markets by catering to specific consumer preferences, such as organic or artisanal products.
Policy and Regulation:
Government Support: Policies such as subsidies for local industries, tariffs on imports, and promotion of local goods can influence consumer preferences towards locally produced items.
Trade Agreements: Trade policies and agreements can affect the availability and pricing of imported goods, thereby influencing consumer choices.
Innovation and Adaptation:
Product Development: Local industries may innovate and adapt to changing consumer preferences by developing new products or improving existing ones.
Service Excellence: Providing superior customer service and building strong customer relationships can enhance consumer loyalty to local brands.
Consumer preference plays a crucial role in balancing the demand between imported and locally produced goods.
Factors such as price sensitivity, quality perception, cultural influences, product availability, environmental considerations, and marketing strategies significantly impact consumer choices. These preferences, in turn, shape market dynamics, influence policy decisions, and drive local industries to innovate and adapt to meet evolving consumer demands. Balancing consumer preferences effectively can help sustain both local industries and the availability of diverse imported goods.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$5 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Role of Consumer Preference in the Balance Between Imported and Locally Produced Goods.
Price Sensitivity:-
Cost-Conscious Choices: Consumers often opt for imported goods if they are cheaper than locally produced alternatives.
Value for Money: Consumers weigh the cost against perceived value, often choosing products that offer better quality or features for the same price.
Quality Perception:-
Brand Reputation: Imported goods from established international brands are often perceived as higher quality.
Consistency: Consumers might prefer imported goods if they believe they offer more consistent quality compared to local products.
Cultural and Social Influences:-
Cultural Affinity: Consumers may prefer local products due to cultural significance or a sense of national pride.
Social Trends: Trends and social influences, including endorsements by celebrities or influencers, can sway consumer preferences towards either imported or local goods.
Product Availability and Variety:
Wide Selection: Imported goods often increase the variety of available products, attracting consumers looking for unique or niche items not produced locally.
Seasonal Availability: Some imported goods fill gaps in seasonal availability, making them preferred choices at certain times of the year.
Environmental and Ethical Considerations:-
Sustainability: Environmentally conscious consumers may prefer locally produced goods to reduce their carbon footprint.
Fair Trade: Ethical considerations, such as fair trade practices, can influence consumers to choose local products that support fair labor conditions and community development.
Marketing and Branding:-
Effective Advertising: Strong marketing campaigns by international brands can influence consumer preferences towards imported goods.
Local Branding: Effective local branding that emphasizes unique aspects and benefits of local products can attract consumers.
Impact on Local and Imported Goods Balance:-
Demand Shifts:
Economic Fluctuations: During economic downturns, consumers may shift towards cheaper imported goods. Conversely, in times of economic growth, there may be a stronger preference for higher-quality local products.
Income Levels: Higher income levels can increase demand for premium imported goods, while lower income levels might boost demand for affordable local alternatives.
Market Dynamics:
Competitive Pressure: High consumer preference for imported goods can pressure local industries to improve quality and reduce prices.
Niche Markets: Local producers can carve out niche markets by catering to specific consumer preferences, such as organic or artisanal products.
Policy and Regulation:
Government Support: Policies such as subsidies for local industries, tariffs on imports, and promotion of local goods can influence consumer preferences towards locally produced items.
Trade Agreements: Trade policies and agreements can affect the availability and pricing of imported goods, thereby influencing consumer choices.
Innovation and Adaptation:
Product Development: Local industries may innovate and adapt to changing consumer preferences by developing new products or improving existing ones.
Service Excellence: Providing superior customer service and building strong customer relationships can enhance consumer loyalty to local brands.
Consumer preference plays a crucial role in balancing the demand between imported and locally produced goods.
Factors such as price sensitivity, quality perception, cultural influences, product availability, environmental considerations, and marketing strategies significantly impact consumer choices. These preferences, in turn, shape market dynamics, influence policy decisions, and drive local industries to innovate and adapt to meet evolving consumer demands. Balancing consumer preferences effectively can help sustain both local industries and the availability of diverse imported goods.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$5 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
1 yr. ago
How does mass importation affect the competitiveness of local industries?
By Hugo Keji
Impact of Mass Importation on the Competitiveness of Local Industries.
Positive Impacts:-
Cost Efficiency:
Lower Production Costs: Importing cheaper raw materials and intermediate goods can reduce production costs for local industries, enabling them to offer competitive pricing.
Higher Profit Margins: Cost savings from imports can translate into higher profit margins, allowing for reinvestment in business improvements and innovation.
Access to Advanced Technologies:-
Technology Transfer: Importation can facilitate the transfer of advanced technologies and manufacturing techniques, improving local production capabilities.
Innovation Boost: Exposure to international markets and products can inspire innovation, leading to better quality and more diverse offerings.
Enhanced Product Diversity:-
Broader Product Range: Access to a variety of imported goods allows local industries to expand their product lines, meeting diverse consumer demands.
Market Expansion: The ability to offer a wider range of products can help local businesses expand their market reach, both domestically and internationally.
Increased Efficiency:-
Process Improvement: Competitive pressure from imported goods can drive local industries to improve their processes, increase efficiency, and reduce waste.
Benchmarking: Local industries can benchmark against international standards, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Stimulated Economic Growth:-
Job Creation: While some sectors may suffer, mass importation can create jobs in logistics, retail, and distribution.
Increased Competition: A competitive market can lead to better services and products for consumers, stimulating economic activity.
Negative Impacts:
Market Saturation and Competition:-
Domestic Market Saturation: An influx of imported goods can saturate the market, making it difficult for local products to compete.
Price Wars: Local industries may be forced into price wars with cheaper imported alternatives, leading to reduced profitability.
Threat to Local Businesses:-
Business Closures: Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) may struggle to survive against the competition from large-scale international companies.
Loss of Market Share: Established local brands may lose market share to more competitively priced or higher-quality imported goods.
Dependence on Imports:-
Supply Chain Vulnerability: Heavy reliance on imports can make local industries vulnerable to global supply chain disruptions and price volatility.
Economic Vulnerability: Dependence on imported goods can lead to economic instability, especially if trade relations become strained.
Quality Control Issues:
Variable Quality: Imported goods may vary in quality, posing challenges for local industries that rely on consistent input standards.
Regulatory Challenges: Ensuring that imported goods meet local regulatory standards can be complex and costly.
Environmental Concerns:-
Increased Carbon Footprint: Importing goods from distant locations contributes to carbon emissions, conflicting with sustainable practices.
Resource Depletion: Excessive reliance on imported goods can lead to over-exploitation of resources in exporting countries, causing long-term sustainability issues.
Mass importation has a dual impact on the competitiveness of local industries.
On the positive side, it can drive cost efficiency, technology transfer, product diversity, and overall economic growth. However, it also poses significant challenges, including market saturation, threats to local businesses, supply chain vulnerabilities, quality control issues, and environmental concerns.
Balancing these factors is crucial for local industries to maintain and enhance their competitiveness in a global market.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$5 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Impact of Mass Importation on the Competitiveness of Local Industries.
Positive Impacts:-
Cost Efficiency:
Lower Production Costs: Importing cheaper raw materials and intermediate goods can reduce production costs for local industries, enabling them to offer competitive pricing.
Higher Profit Margins: Cost savings from imports can translate into higher profit margins, allowing for reinvestment in business improvements and innovation.
Access to Advanced Technologies:-
Technology Transfer: Importation can facilitate the transfer of advanced technologies and manufacturing techniques, improving local production capabilities.
Innovation Boost: Exposure to international markets and products can inspire innovation, leading to better quality and more diverse offerings.
Enhanced Product Diversity:-
Broader Product Range: Access to a variety of imported goods allows local industries to expand their product lines, meeting diverse consumer demands.
Market Expansion: The ability to offer a wider range of products can help local businesses expand their market reach, both domestically and internationally.
Increased Efficiency:-
Process Improvement: Competitive pressure from imported goods can drive local industries to improve their processes, increase efficiency, and reduce waste.
Benchmarking: Local industries can benchmark against international standards, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Stimulated Economic Growth:-
Job Creation: While some sectors may suffer, mass importation can create jobs in logistics, retail, and distribution.
Increased Competition: A competitive market can lead to better services and products for consumers, stimulating economic activity.
Negative Impacts:
Market Saturation and Competition:-
Domestic Market Saturation: An influx of imported goods can saturate the market, making it difficult for local products to compete.
Price Wars: Local industries may be forced into price wars with cheaper imported alternatives, leading to reduced profitability.
Threat to Local Businesses:-
Business Closures: Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) may struggle to survive against the competition from large-scale international companies.
Loss of Market Share: Established local brands may lose market share to more competitively priced or higher-quality imported goods.
Dependence on Imports:-
Supply Chain Vulnerability: Heavy reliance on imports can make local industries vulnerable to global supply chain disruptions and price volatility.
Economic Vulnerability: Dependence on imported goods can lead to economic instability, especially if trade relations become strained.
Quality Control Issues:
Variable Quality: Imported goods may vary in quality, posing challenges for local industries that rely on consistent input standards.
Regulatory Challenges: Ensuring that imported goods meet local regulatory standards can be complex and costly.
Environmental Concerns:-
Increased Carbon Footprint: Importing goods from distant locations contributes to carbon emissions, conflicting with sustainable practices.
Resource Depletion: Excessive reliance on imported goods can lead to over-exploitation of resources in exporting countries, causing long-term sustainability issues.
Mass importation has a dual impact on the competitiveness of local industries.
On the positive side, it can drive cost efficiency, technology transfer, product diversity, and overall economic growth. However, it also poses significant challenges, including market saturation, threats to local businesses, supply chain vulnerabilities, quality control issues, and environmental concerns.
Balancing these factors is crucial for local industries to maintain and enhance their competitiveness in a global market.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$5 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com

Health Data 101 - App on Amazon Appstore
Healthdata101-Manage Hospital and Health data.
https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B0D514TH5S
1 yr. ago
What are the key challenges and opportunities for startups and entrepreneurs in Africa?
By Hugo Keji
Startups and entrepreneurs in Africa face a unique set of challenges and opportunities.
Challenges:-
Access to Funding:
Limited Venture Capital: There is a scarcity of venture capital and angel investors compared to other regions, making it difficult for startups to secure funding.
High Interest Rates: Loans from traditional financial institutions often come with high interest rates and stringent repayment terms.
Informal Sector: A large portion of economic activity occurs in the informal sector, which is less accessible to formal funding mechanisms.
Infrastructure:
Internet and Connectivity: While improving, internet access and broadband connectivity remain inconsistent and expensive in many areas.
Electricity Supply: Frequent power outages and unreliable electricity supply can disrupt business operations.
Transport and Logistics: Poor transportation networks and logistical challenges can hinder the distribution of goods and services.
Regulatory Environment:
Bureaucracy: Complex and opaque regulatory processes can slow down business operations and increase costs.
Corruption: Corruption and lack of transparency can pose significant barriers to business development.
Policy Uncertainty: Frequent changes in government policies can create an unstable business environment.
Talent and Skills:
Skills Gap: There is often a mismatch between the skills available in the workforce and the needs of startups, particularly in tech and specialized fields.
Brain Drain: Skilled professionals may emigrate in search of better opportunities, depleting the local talent pool.
Market Access:
Fragmented Markets: The continent consists of 54 countries with diverse regulatory, economic, and cultural environments, complicating market entry and expansion.
Consumer Trust: Building trust among consumers can be challenging, particularly for new brands or innovative products.
Opportunities
Growing Youth Population:
Demographic Dividend: Africa has a large and growing young population, providing a dynamic and potentially innovative workforce.
Digital Natives: The youth are increasingly tech-savvy, driving demand for digital products and services.
Mobile Technology:
Mobile Penetration: High mobile phone penetration offers a platform for innovative mobile-based solutions, particularly in fintech, health tech, and edtech.
Leapfrogging: There is an opportunity to bypass traditional stages of development through mobile technologies, such as mobile banking.
Untapped Markets:
Under-served Needs: Many sectors, including healthcare, education, agriculture, and financial services, have significant unmet needs.
Rural Markets: Rural areas present opportunities for new business models that cater to unique local needs.
Innovation and Entrepreneurship:
Tech Hubs: Emerging tech hubs and incubators in cities like Lagos, Nairobi, Cape Town, and Accra support a growing startup ecosystem.
Social Entrepreneurship: There is a strong focus on solving social issues through innovative business models, which attracts impact investors.
Government and Policy Support:
Entrepreneurial Policies: Some governments are recognizing the importance of startups and are introducing supportive policies and incentives.
Trade Agreements: Regional trade agreements, such as the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), aim to reduce barriers and create larger markets for businesses.
Access to Global Markets:
Diaspora Networks: African entrepreneurs can leverage diaspora networks for investment, mentorship, and market access.
E-commerce: Growing internet penetration and mobile adoption are facilitating access to global markets through e-commerce platforms.
Navigating these challenges and leveraging the opportunities, startups and entrepreneurs in Africa can create impactful and sustainable businesses.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$5 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Startups and entrepreneurs in Africa face a unique set of challenges and opportunities.
Challenges:-
Access to Funding:
Limited Venture Capital: There is a scarcity of venture capital and angel investors compared to other regions, making it difficult for startups to secure funding.
High Interest Rates: Loans from traditional financial institutions often come with high interest rates and stringent repayment terms.
Informal Sector: A large portion of economic activity occurs in the informal sector, which is less accessible to formal funding mechanisms.
Infrastructure:
Internet and Connectivity: While improving, internet access and broadband connectivity remain inconsistent and expensive in many areas.
Electricity Supply: Frequent power outages and unreliable electricity supply can disrupt business operations.
Transport and Logistics: Poor transportation networks and logistical challenges can hinder the distribution of goods and services.
Regulatory Environment:
Bureaucracy: Complex and opaque regulatory processes can slow down business operations and increase costs.
Corruption: Corruption and lack of transparency can pose significant barriers to business development.
Policy Uncertainty: Frequent changes in government policies can create an unstable business environment.
Talent and Skills:
Skills Gap: There is often a mismatch between the skills available in the workforce and the needs of startups, particularly in tech and specialized fields.
Brain Drain: Skilled professionals may emigrate in search of better opportunities, depleting the local talent pool.
Market Access:
Fragmented Markets: The continent consists of 54 countries with diverse regulatory, economic, and cultural environments, complicating market entry and expansion.
Consumer Trust: Building trust among consumers can be challenging, particularly for new brands or innovative products.
Opportunities
Growing Youth Population:
Demographic Dividend: Africa has a large and growing young population, providing a dynamic and potentially innovative workforce.
Digital Natives: The youth are increasingly tech-savvy, driving demand for digital products and services.
Mobile Technology:
Mobile Penetration: High mobile phone penetration offers a platform for innovative mobile-based solutions, particularly in fintech, health tech, and edtech.
Leapfrogging: There is an opportunity to bypass traditional stages of development through mobile technologies, such as mobile banking.
Untapped Markets:
Under-served Needs: Many sectors, including healthcare, education, agriculture, and financial services, have significant unmet needs.
Rural Markets: Rural areas present opportunities for new business models that cater to unique local needs.
Innovation and Entrepreneurship:
Tech Hubs: Emerging tech hubs and incubators in cities like Lagos, Nairobi, Cape Town, and Accra support a growing startup ecosystem.
Social Entrepreneurship: There is a strong focus on solving social issues through innovative business models, which attracts impact investors.
Government and Policy Support:
Entrepreneurial Policies: Some governments are recognizing the importance of startups and are introducing supportive policies and incentives.
Trade Agreements: Regional trade agreements, such as the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), aim to reduce barriers and create larger markets for businesses.
Access to Global Markets:
Diaspora Networks: African entrepreneurs can leverage diaspora networks for investment, mentorship, and market access.
E-commerce: Growing internet penetration and mobile adoption are facilitating access to global markets through e-commerce platforms.
Navigating these challenges and leveraging the opportunities, startups and entrepreneurs in Africa can create impactful and sustainable businesses.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$5 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
1 yr. ago
The EU has just put its car industry on the road to destruction....
The timing, to put it mildly, is slightly odd.
Any of us watching the start of the Euro 2024 football tournament this weekend may well have noticed the logo of the Chinese electric vehicle manufacturer BYD plastered everywhere in its role both as one of its main sponsors and as the “mobility partner” for matches staged across German cities.
In the same week, the European Union slapped punitive tariffs on imports of Chinese EVs. On the one hand Europe is welcoming the Chinese brands, and on the other it is telling them to get lost.
These mixed messages are typical of the EU’s hopelessly mismanaged response to electric vehicles. Its war on cheap Chinese imports is going to misfire spectacularly – and all it will do is end up destroying its once-mighty auto industry.
It has certainly been a tough few days for the Chinese electric vehicle giants planning to bring their brands to Europe. On Wednesday, the EU announced that it would impose extra tariffs on imports of up to 38pc, on top of the existing 10pc levies, putting almost 50pc in taxes on any cars Chinese brands bring into the bloc.
It follows a decision by US President Joe Biden to impose tariffs of 100pc.
At a stroke, the price advantage that the likes of BYD, Geely and Nio planned to use to force the market open and to start building a presence on the Continent has been wiped out. Chinese EVs will end up being a lot more expensive and the EU will rake in huge levies on each sale.
It is not hard to understand why the decision was made. Officials in Brussels are terrified that the Chinese EV manufacturers will wipe out the European auto industry, which still employs an estimated 13.8 million people, or 6pc of the total workforce, and generates €150bn (£130bn) of annual exports.
We can argue about whether the Chinese cars are subsidised by the state or are simply manufactured more efficiently by companies that have brilliantly mastered the technology in a very short space of time (the truth is probably somewhere between the two).
And yet leaving that aside, one point is certain: it will stall their advance. It is hard to compete when you face a 50pc tax on each car you sell.
The trouble is the policy is going to backfire spectacularly on the EU and of course on the UK if we are foolish enough to impose similar levies. There are three reasons for that.
First, anyone who thinks the Chinese will simply shrug their shoulders is simply kidding themselves. It will inevitably mean retaliation. There are already reports that China will respond with tariffs on large-engine imports from the EU, specifically targeting the high-end, luxury vehicles that sell best in that country.
Given that the EU exports €18bn of vehicles to China every year, and has even more money tied up in local joint-venture operations, that is going to be very painful for European manufacturers.
Tariffs may well be targeted at other EU goods as well. It is not as if China does not have a robust trade policy or that it is ever slow to defend its industries. In the wake of the announcement, €4.5bn was wiped off the value of the major German auto manufacturers as investors braced themselves for the inevitable response.
With grim inevitability, the EU’s giants will end up paying a high price and will end up locked out of what will soon be the world’s largest market. It is hard to see that as a great victory for anyone.
Next, the European manufacturers will inevitably grow flabby behind tariff walls. We have a long history of trade wars, tariffs and protectionism to teach us that the result is always the same. The protected industry does not have to compete anymore, it doesn’t bother to innovate and it simply puts up prices to milk easy profits out of customers who no longer have the choice of going elsewhere.
EVs are still a new technology, and there need to be huge improvements in driving range, battery life, vehicle weight and most of all price if they are to become the standard way of getting around.
That is only going to happen with ferocious competition between lots of different companies. Once a cosy cartel is established, they will just stagnate. The result? Even if they are protected at home, the European manufacturers will be steadily less competitive on the global market where they can’t hide behind tariff walls.
Finally, it is a tax that will be paid by European consumers. Some of us heard a rumour that governments across Europe were encouraging us all to switch to electric vehicles to help curb carbon emissions and hit our net zero targets. Now it turns out that they are also imposing massive levies on them.
All the mandates and quotas will still be in place, but the cars will be far more expensive, draining spending power out of the economy and taxing the transition to green energies. It would be hard to think of a more comically mismanaged policy, or one that is likely to do more damage.
In reality, even by the standards of incompetent officials in Brussels, it is a mess. The EU should have made sure it was competitive in EVs before imposing quotas and targets on the industry.
It should have made sure its own industry was ahead in technology and had worked out how to scale up production to deliver the low-cost cars that could take on the world.
It is too late to fix any of that now with tariffs. All it will end up doing is making a bad situation a whole lot worse. The EU will end up destroying one of its biggest and most strategic industries – and it will only have itself to blame.
Scholz hopes to avoid EU punitive tariffs on China's electric cars.....
German Chancellor Olaf Scholz is hoping that that punitive tariffs the EU has threatened to slap on Chinese electric vehicles can still be prevented in negotiations with Beijing.
Scholz said he had been "firmly promised" that the EU's talks with Beijing would take place with this goal in mind, and that it was "the right way to go."
He said the dispute could be resolved by the end of the month if all goes well.
The European Commission, the EU's executive arm, threatened on Wednesday to impose import tariffs on Chinese electric vehicles of up to 38.1%, after an investigation found evidence of illegal support from subsidies.
The higher import duties will only be applied if the EU and China cannot find a solution to the issue, and would come into force from July 4.
According to the commission, Chinese electric cars are normally around 20% cheaper than models built in the EU.
The German automotive industry has come out against the higher tariffs. It fears that the government in China, a key market, could impose retaliatory duties on electric cars imported from Europe.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
The timing, to put it mildly, is slightly odd.
Any of us watching the start of the Euro 2024 football tournament this weekend may well have noticed the logo of the Chinese electric vehicle manufacturer BYD plastered everywhere in its role both as one of its main sponsors and as the “mobility partner” for matches staged across German cities.
In the same week, the European Union slapped punitive tariffs on imports of Chinese EVs. On the one hand Europe is welcoming the Chinese brands, and on the other it is telling them to get lost.
These mixed messages are typical of the EU’s hopelessly mismanaged response to electric vehicles. Its war on cheap Chinese imports is going to misfire spectacularly – and all it will do is end up destroying its once-mighty auto industry.
It has certainly been a tough few days for the Chinese electric vehicle giants planning to bring their brands to Europe. On Wednesday, the EU announced that it would impose extra tariffs on imports of up to 38pc, on top of the existing 10pc levies, putting almost 50pc in taxes on any cars Chinese brands bring into the bloc.
It follows a decision by US President Joe Biden to impose tariffs of 100pc.
At a stroke, the price advantage that the likes of BYD, Geely and Nio planned to use to force the market open and to start building a presence on the Continent has been wiped out. Chinese EVs will end up being a lot more expensive and the EU will rake in huge levies on each sale.
It is not hard to understand why the decision was made. Officials in Brussels are terrified that the Chinese EV manufacturers will wipe out the European auto industry, which still employs an estimated 13.8 million people, or 6pc of the total workforce, and generates €150bn (£130bn) of annual exports.
We can argue about whether the Chinese cars are subsidised by the state or are simply manufactured more efficiently by companies that have brilliantly mastered the technology in a very short space of time (the truth is probably somewhere between the two).
And yet leaving that aside, one point is certain: it will stall their advance. It is hard to compete when you face a 50pc tax on each car you sell.
The trouble is the policy is going to backfire spectacularly on the EU and of course on the UK if we are foolish enough to impose similar levies. There are three reasons for that.
First, anyone who thinks the Chinese will simply shrug their shoulders is simply kidding themselves. It will inevitably mean retaliation. There are already reports that China will respond with tariffs on large-engine imports from the EU, specifically targeting the high-end, luxury vehicles that sell best in that country.
Given that the EU exports €18bn of vehicles to China every year, and has even more money tied up in local joint-venture operations, that is going to be very painful for European manufacturers.
Tariffs may well be targeted at other EU goods as well. It is not as if China does not have a robust trade policy or that it is ever slow to defend its industries. In the wake of the announcement, €4.5bn was wiped off the value of the major German auto manufacturers as investors braced themselves for the inevitable response.
With grim inevitability, the EU’s giants will end up paying a high price and will end up locked out of what will soon be the world’s largest market. It is hard to see that as a great victory for anyone.
Next, the European manufacturers will inevitably grow flabby behind tariff walls. We have a long history of trade wars, tariffs and protectionism to teach us that the result is always the same. The protected industry does not have to compete anymore, it doesn’t bother to innovate and it simply puts up prices to milk easy profits out of customers who no longer have the choice of going elsewhere.
EVs are still a new technology, and there need to be huge improvements in driving range, battery life, vehicle weight and most of all price if they are to become the standard way of getting around.
That is only going to happen with ferocious competition between lots of different companies. Once a cosy cartel is established, they will just stagnate. The result? Even if they are protected at home, the European manufacturers will be steadily less competitive on the global market where they can’t hide behind tariff walls.
Finally, it is a tax that will be paid by European consumers. Some of us heard a rumour that governments across Europe were encouraging us all to switch to electric vehicles to help curb carbon emissions and hit our net zero targets. Now it turns out that they are also imposing massive levies on them.
All the mandates and quotas will still be in place, but the cars will be far more expensive, draining spending power out of the economy and taxing the transition to green energies. It would be hard to think of a more comically mismanaged policy, or one that is likely to do more damage.
In reality, even by the standards of incompetent officials in Brussels, it is a mess. The EU should have made sure it was competitive in EVs before imposing quotas and targets on the industry.
It should have made sure its own industry was ahead in technology and had worked out how to scale up production to deliver the low-cost cars that could take on the world.
It is too late to fix any of that now with tariffs. All it will end up doing is making a bad situation a whole lot worse. The EU will end up destroying one of its biggest and most strategic industries – and it will only have itself to blame.
Scholz hopes to avoid EU punitive tariffs on China's electric cars.....
German Chancellor Olaf Scholz is hoping that that punitive tariffs the EU has threatened to slap on Chinese electric vehicles can still be prevented in negotiations with Beijing.
Scholz said he had been "firmly promised" that the EU's talks with Beijing would take place with this goal in mind, and that it was "the right way to go."
He said the dispute could be resolved by the end of the month if all goes well.
The European Commission, the EU's executive arm, threatened on Wednesday to impose import tariffs on Chinese electric vehicles of up to 38.1%, after an investigation found evidence of illegal support from subsidies.
The higher import duties will only be applied if the EU and China cannot find a solution to the issue, and would come into force from July 4.
According to the commission, Chinese electric cars are normally around 20% cheaper than models built in the EU.
The German automotive industry has come out against the higher tariffs. It fears that the government in China, a key market, could impose retaliatory duties on electric cars imported from Europe.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...