Whether you’re a startup or an established brand, we deliver impactful digital strategies that boost your online presence and drive long-term growth. Choose Techfinad — your trusted digital growth partner in Noida.
Visit Us : https://techfinad.com/
, Payments Mafia appreciates how variables went with the limited conclude house previous time, and it should really contain optimum supporters bewildered around the coming marketing campaign. The exact is in all probability real of the vast receivers outdoors of Khalil Shakir. However which place between the 2 is Buffalo major speculate mark going into working out camp within just late July? Primarily based upon Reacts votes, vast recipient is the largest not known, with 71% of voters voting that route, When precisely 29% check out it restricted close as the largest speculate mark upon offense. It legitimate that the detail chart continues to be mostly unchanged at restricted conclude, however does the place actually
At EZ Rankings, our Performance Marketing Services are built to help businesses achieve measurable, results-oriented growth. Unlike traditional marketing, where success can be uncertain, performance marketing focuses on tangible outcomes whether it’s generating clicks, driving qualified leads, or boosting sales. You only pay for results, ensuring maximum return on every investment.
Visit us : https://www.ezrankings.com...
Turn your passion for photography into a business with essential tips on equipment, branding, marketing, and managing your services effectively.
For more information Read our blog
https://www.invoicetemple....

Essential Steps to Launch Your Photography Business
Turn your passion for photography into a business with essential tips on equipment, branding, marketing, and managing your services effectively.
https://www.invoicetemple.com/blog/how-to-launch-a-photography-business-essential-steps-to-begin/That’s how Google Analytics (GA4) comes into play. It’s not just a reporting tool it’s your window into user behavior, conversions, and the real impact of your SEO efforts.
In this article we get into the 10 reasons why seo specialists should master google analytics and also let’s quickly understand what Google Analytics is and why it matters for SEO. #seo #marketing #digitalmarketing #googleanalytics #analytics #article
https://pratsdigital.in/re...
What role should traditional medicine play in Nigeria's health system?
Traditional medicine (TM), often referred to as "African Traditional Medicine" (ATM) or "Alternative Medicine" (though the latter term can be broader), plays an incredibly significant, and often indispensable, role in Nigeria's health system, particularly given the challenges facing conventional Western medicine.
Over 70-80% of Nigerians, especially those in rural and low-income communities, rely on traditional medicine for their primary healthcare needs.
The role of traditional medicine should ideally be one of integration, regulation, and research, leveraging its strengths while mitigating its risks, to complement and enhance the formal healthcare system.
Here's a breakdown of its current and potential roles:
I. Current De Facto Role (Filling the Gaps):
Primary Healthcare Provider for the Underserved: In many rural areas where modern healthcare facilities are scarce or non-existent, traditional healers are often the only accessible and affordable source of healthcare. They serve as the first point of contact for a vast majority of the population.
Affordability and Accessibility: Traditional remedies and consultations are often cheaper than orthodox medicine, and payment in kind (e.g., farm produce) can be acceptable. Traditional practitioners are typically located within communities, making them highly accessible.
Cultural and Spiritual Resonance: Traditional medicine often takes a holistic approach, addressing not just physical ailments but also spiritual, psychological, and social dimensions of health. This resonates deeply with the cultural beliefs and worldview of many Nigerians regarding disease causation and healing.
Treatment of Specific Ailments: Traditional medicine has long been relied upon for managing certain conditions, such as:
Bone setting: Traditional bone setters (TBS) are popular for treating fractures and dislocations.
Mental health: Traditional healers often deal with mental illnesses, which are frequently attributed to spiritual causes in many Nigerian cultures.
Obstetrics and Gynecology: Traditional birth attendants (TBAs) play a significant role in maternal care, particularly in rural settings.
Herbal Remedies: A vast array of medicinal plants are used to treat common ailments like malaria, fever, skin infections, and digestive issues.
Source of New Drug Discovery: Many modern pharmaceutical drugs have their origins in traditional plant-based remedies (e.g., quinine from cinchona bark for malaria, artemisinin from Artemisia annua).
II. The Ideal and Future Role (Integration, Regulation, and Research):
Integration into Primary Healthcare:
Referral System: Traditional practitioners can be trained to recognize conditions beyond their scope and refer patients to modern health facilities. Conversely, orthodox doctors should be educated about common traditional practices to facilitate communication and understanding with patients.
Collaborative Care: For certain conditions, a collaborative approach could be beneficial, where traditional and modern practitioners work together, especially in areas like mental health, rehabilitation, and chronic disease management.
Community Health Workers: Traditional healers, with their deep community trust, could be integrated into community health worker networks for health promotion, disease prevention, and surveillance.
Standardization and Regulation:
National Policy and Legal Framework: Develop clear national policies and legal frameworks for the practice of traditional medicine, defining roles, responsibilities, and standards.
Registration and Licensing: Establish a robust system for the registration, licensing, and certification of traditional medicine practitioners (TMPs) to ensure they meet minimum standards of training and ethics.
Quality Control of Herbal Products: Implement strict regulations for the cultivation, harvesting, processing, packaging, labeling, and marketing of herbal remedies. NAFDAC (National Agency for Food and Drug Administration and Control) has a role here in ensuring safety, quality, and efficacy.
Code of Ethics: Develop and enforce a code of conduct and ethics for TMPs to curb quackery, exploitation, and harmful practices.
Scientific Research and Validation:
Efficacy and Safety Studies: Conduct rigorous scientific research, clinical trials, and toxicological studies on widely used traditional remedies to ascertain their efficacy, safety, active compounds, dosages, and potential side effects or drug interactions.
Preservation of Knowledge: Document and archive traditional medicinal knowledge (which is often oral and localized) to prevent its loss and facilitate scientific study. This also raises issues of intellectual property rights for traditional knowledge holders.
Drug Discovery: Invest in pharmaceutical research and development to identify new drug candidates from Nigeria's rich biodiversity, collaborating with traditional healers.
Education and Training:
Formal Training for TMPs: Develop formal training programs for TMPs that combine traditional knowledge with basic modern medical concepts (e.g., anatomy, physiology, hygiene, first aid, record-keeping, referral protocols).
Cross-Cultural Education: Incorporate elements of traditional medicine into the curriculum of modern medical and nursing schools to foster understanding, respect, and potential collaboration.
Public Education: Educate the public on the importance of seeking validated and regulated traditional medicines, and the dangers of harmful practices or unproven remedies.
III. Challenges to Integration:
Lack of Standardization: The diverse, often secretive, and undocumented nature of TM practices.
Safety and Efficacy Concerns: Issues with dosage, purity, potential toxicity, and lack of scientific evidence for many traditional remedies.
Quackery: The prevalence of charlatans and untrained individuals who exploit public trust.
Professional Skepticism: Resistance and distrust from some orthodox medical practitioners towards TM.
Spiritual vs. Scientific Divide: The challenge of reconciling spiritual and cultural aspects of TM with the scientific, evidence-based approach of modern medicine.
Despite these challenges, ignoring traditional medicine in Nigeria is not an option. Its widespread use and cultural significance necessitate its proper integration into the national healthcare system, ensuring safety, efficacy, and ultimately, better health outcomes for all Nigerians.
Why do so many Nigerians seek medical treatment abroad?
Nigerians, across various socioeconomic strata, frequently seek medical treatment abroad for a multitude of reasons, highlighting significant systemic issues within Nigeria's healthcare sector. This phenomenon, known as medical tourism, has a substantial economic drain on the country.
Here are the primary reasons why so many Nigerians opt for foreign medical care:
Inadequate Healthcare Infrastructure and Technology:
Obsolete Equipment: Many Nigerian hospitals, especially public ones, lack modern medical equipment (e.g., advanced MRI/CT scanners, specialized surgical tools, radiotherapy machines for cancer treatment). Where equipment exists, it's often poorly maintained or frequently breaks down.
Lack of Specialization: While Nigeria has many general practitioners, there's a severe shortage of highly specialized medical professionals in complex fields like oncology, neurosurgery, advanced cardiology, organ transplantation, and specialized orthopedics.
Dilapidated Facilities: Many hospitals suffer from poor maintenance, overcrowding, unreliable power supply (leading to dependence on expensive generators), and lack of basic amenities like clean water and proper waste disposal.
Shortage and Brain Drain of Medical Professionals:
Mass Exodus: Nigeria faces a severe "brain drain" of qualified doctors, nurses, and other healthcare professionals. Lured by better remuneration, working conditions, access to advanced technology, and professional development opportunities, many migrate to countries like the UK, USA, Canada, and Saudi Arabia.
High Patient-to-Doctor Ratio: The emigration of medical personnel exacerbates the existing shortage, leading to an extremely high patient-to-doctor ratio (far below WHO recommendations), overworking the remaining staff and compromising patient care.
Loss of Expertise: The departure of highly skilled specialists means that certain complex procedures or sophisticated diagnostic interpretations are simply not available in Nigeria.
Lack of Trust in the Local Healthcare System:
Perceived Low Quality of Care: Decades of underfunding and poor performance have eroded public confidence in the Nigerian healthcare system. Many Nigerians, including the elite, believe they will receive superior care, more accurate diagnoses, and better treatment outcomes abroad.
Fear of Misdiagnosis/Malpractice: There's a widespread fear of misdiagnosis, medical negligence, and inadequate follow-up care within Nigeria, prompting individuals to seek second opinions or primary treatment elsewhere.
High-Profile Cases: When prominent Nigerians (including politicians and government officials) consistently seek medical attention abroad, it further reinforces the perception that the local system is not good enough, even for the nation's leaders.
Poor Funding and High Out-of-Pocket Payments:
Low Budgetary Allocation: The Nigerian government's allocation to healthcare consistently falls far below international recommendations (e.g., the Abuja Declaration's 15% target). This limits investment in infrastructure, training, and research.
Out-of-Pocket Expenses: The vast majority of Nigerians pay for healthcare directly out of their pockets, as the National Health Insurance Scheme (NHIS) covers a very small percentage of the population. This means that even basic care can be financially burdensome. For complex treatments, the cost can be prohibitive, making the "all-inclusive" price for treatment abroad (which often seems high in Naira) sometimes comparable or even more appealing if it guarantees a better outcome.
Long Waiting Times and Bureaucracy:
Even when certain treatments are available, patients might face long waiting lists for appointments, diagnostic tests, or surgeries in public hospitals, leading them to seek faster access abroad.
Bureaucratic hurdles and administrative inefficiencies can also frustrate patients and their families.
Desire for Privacy and Confidentiality:
Some high-profile individuals or those seeking treatments for sensitive conditions may travel abroad for greater privacy and confidentiality, away from public scrutiny.
Aggressive Marketing by Foreign Hospitals:
Countries like India, Turkey, and some in the Middle East have developed robust medical tourism industries. They actively market their advanced facilities, specialized doctors, and relatively affordable (compared to Western countries) treatment packages directly to Nigerians.
The collective impact of this medical tourism is a significant drain on Nigeria's foreign exchange reserves (estimated to be billions of dollars annually), a disincentive for investment in local healthcare, and a perpetuation of a system where those who can afford it simply bypass local services, undermining efforts to improve the domestic health sector for the general populace.
How does reliance on imports limit opportunities for youth entrepreneurship, innovation, and skills development?
Reliance on imports significantly limits opportunities for youth entrepreneurship, innovation, and skills development by eliminating the very sectors where these opportunities would naturally arise.
Instead of being creators and producers, young people are relegated to roles in retail and distribution, with far less potential for growth and advancement.
Impact on Entrepreneurship
A flood of cheap imports makes it incredibly difficult for young entrepreneurs to start businesses in manufacturing and production. The capital required to set up a factory or workshop can't compete with the massive economies of scale enjoyed by foreign producers. This discourages young people from even attempting to enter these sectors, as the risk of failure is too high. Instead, they are pushed into less productive sectors, like becoming distributors or retailers for the very goods that are undercutting local production.
Hindrance to Innovation
Innovation often stems from the practical challenges and opportunities within a production process. When there's no local manufacturing base, there are fewer problems to solve and fewer products to improve. This creates a knowledge gap, as young people don't get the hands-on experience of designing, building, and refining goods. The entire ecosystem for innovation—from product development to marketing—is outsourced, leaving little room for local creativity or technological advancement.
Stifled Skills Development
A strong industrial sector is a key driver of skills development. It provides opportunities for apprenticeships, on-the-job training, and the acquisition of technical skills like engineering, welding, and electronics repair. When these industries disappear due to import competition, so do the opportunities for young people to acquire these valuable skills. This creates a vicious cycle where a lack of skilled labor makes local production even less competitive, further reinforcing the reliance on imports.
What if your app could predict what users want, before they even type in a search? That’s the power of AI recommendations. Do you want to know how to implement AI-powered product recommendations in your Amazon clone? Here are some steps. Let's dive in.
What is AI-Powered Recommendation?
An artificially intelligent system that makes real-time product recommendations to consumers based on their interests, behaviour, and previous purchases is known as an AI-powered recommendation system in e-commerce. AI customises the shopping experience to boost sales, engagement, and customer satisfaction rather than displaying the same product list to every user.
Types of recommendation strategies:
1. Collaborative Filtering
Collaborative Filtering is a recommendation strategy that recommends products based on user activity and preferences rather than product information in an Amazon-like app.
User-based collaborative filtering detects folks who share similar interests. If a user likes a product, it will be recommended to another person who shares their interests.
Item-based collaborative filtering: This type of filtering shows recommendations based on similarities. For example, it recommends a phone case to the people who purchased New phones.
2. Content-based Filtering:
Content-based filtering recommends products based on the traits or features that the customer has previously purchased. For example, if you frequently buy or see bags, the algorithm would suggest alternatives or products with comparable characteristics such as brand, style, price range, or material.
3. Hybrid Filtering:
Hybrid filtering blends collaborative filtering, which proposes products based on the preferences of other users, with content-based filtering, which recommends items similar to those a user has previously liked. This strategy takes advantage of both methods' strengths while correcting their faults, yielding more accurate and personalised recommendations.
4. Trending and popular items:
In an Amazon clone website, Trending or Popular Items recommendations highlight things that are currently best-sellers, most viewed, or highly rated throughout the platform or within a category. Helping consumers find popular, in-demand items while increasing interaction and revenue.
5. Personalized rankings:
Personalized rankings reorder the search results or other lists of items based on users' preferences and behaviour. Instead of showing the same products to every user, it improves the user experience and increases the platform engagement.
Implementing AI-powered recommendations in an Amazon clone app:
Implement AI-powered suggestions in your Amazon clone. You should concentrate on collecting data, selecting the best AI solution, and optimising recommendations.
1. Data Collection and analysis:
Collect vast data: Gather the users' purchase history, product preferences, browsing habits, and product interactions such as clicks, add to cart, and reviews. Collecting these diverse data points provides a detailed picture of each customer's interests and habits.
2. Choosing the Right AI Solution:
Utilise data points: Analyse individual consumer preferences, detect bigger trends across users, and create dynamic customer profiles that evolve as new data is received.
Ensure data privacy: When developing AI-powered product suggestions, you must protect the privacy and security of user data. Encryption, secure servers, and access controls can all help to protect user data from unauthorised access. This is especially important when dealing with sensitive information such as purchasing history, behaviour, or personal details.
Consider Your Needs: Before deciding on an AI recommendation, you should first understand your business goals, budget, and technical resources.
Investigate diverse AI models: There are several recommendation models, each with a unique function. There are three types of filtering: collaborative, content-based, and hybrid.
Look for user-friendly options: If you're not ready to start from scratch with an Amazon clone website, look for choices that are easy to use. Many e-commerce platforms have built-in AI recommendation algorithms or third-party applications.
3. Implementing and optimizing recommendations:
Integrate cross-platform: Ensure that your recommendations are consistent and personalised across all platforms, including the website, email marketing, mobile app, and even customer support chat. This will improve the user experience and maintain personalisation seamlessly.
Use various formats: Use several recommendation styles, such as pop-ups and inline sections, to keep shoppers' attention at different phases of their purchasing journey.
A/B testing and optimisation: Continuously monitor the performance of the recommendations and make improvements depending on data and user input.
Focus on user experience: Make sure that recommendations are not only appropriate but also easy to navigate, quick to load, and visually integrated on mobile sites.
Prioritise Explainability: Be open about how recommendations are made, and give users control over their preferences.
Begin small, then scale: Start with a pilot or test group to validate performance and get feedback. Use this feedback to develop and expand your recommendation system throughout the platform.
Benefits of AI-powered recommendations:
1. Improved conversion performance:
The AI algorithm examines clients' browsing histories and purchasing habits to help them get what they want without using their hands. This will boost your Amazon clone conversion rate.
2. Enhanced user experience:
This AI-powered customised suggestion saves users time and effort by guiding them to the proper products. The end outcome is customer satisfaction and a good purchasing experience.
3. Increased average order value:
AI-powered suggestions in your Amazon clone app encourage customers to buy complementary, upsell, and cross-sell items, which raises the overall order value.
4. Insights based on data:
Artificial intelligence (AI) recommendation systems gather and analyse consumer data to learn about preferences and purchasing habits. Businesses can use this to enhance their marketing, select better products to sell, and more effectively manage their inventory.
5. Improved customer retention:
When users consistently receive relevant product recommendations, they are more likely to return to the platform. This strengthens brand presence and generates recurring sales.
6. Enhanced marketing strategies:
AI-powered recommendations customize marketing strategies based on each customer’s individual preferences and behaviors. This personalized approach results in more relevant and engaging marketing campaigns that resonate better with customers, ultimately increasing their interest and likelihood to respond positively.
7. Reduced cart abandonment:
AI-powered recommendations lower cart abandonment by using personalized recommendations, timely reminders, and providing discounts or free shipping. These strategies help users complete their purchases and increase the overall sales rates in your Amazon clone website.
8. Real-time discovery:
This enables AI to make real-time product recommendations to users based on their interests, assisting consumers in finding things they may not have previously found. It is most helpful in vast product catalogues where customers may find manual searching daunting. AI speeds up, simplifies, and enhances the pleasure of shopping by providing timely and pertinent recommendations.
Summing up:
I hope this blog helps you understand the importance of Artificial Intelligence in product recommendations for your Amazon clone app.
It covers the implementation of AI-powered recommendation systems, different types of recommendation strategies, and their benefits.
Now is the perfect time to launch AI-powered recommendations in your Amazon clone app.
https://www.trioangle.com/...
#EcommercePlatform #TechForBusiness #AmazonCloneScript #USAeCommerce #EcommerceLondon #MiddleEastEcommerce #SAOnlineStore # OnlineMarketplace
#MultiVendorMarketplace #DigitalRetailUSA #UAEStartupScene #MarketplaceTrends
To protect and grow local manufacturing against cheap imports, governments can implement a mix of protectionist policies and incentives for domestic industries. These strategies aim to either make imports less competitive or boost the capabilities and competitiveness of local businesses.
Protectionist Policies
These policies directly address the challenge of low-priced imports by raising their cost or limiting their quantity.
Tariffs: A tariff is a tax on imported goods. By increasing the price of imports, tariffs make locally produced goods more attractive to consumers. Governments can use specific tariffs (a fixed fee per unit) or ad valorem tariffs (a percentage of the item's value).
Import Quotas: This is a non-tax barrier that sets a strict limit on the volume of a specific good that can be imported over a given period. Quotas reduce the supply of foreign goods, which drives up their price and creates a market for domestic producers to fill the gap.
Anti-Dumping Duties: "Dumping" occurs when a foreign company sells its products in an export market at a price below its production cost to gain market share. Governments can impose special tariffs, known as anti-dumping duties, on these goods to level the playing field and prevent predatory pricing that could destroy local industries.
Local Content Requirements: This policy mandates that a certain percentage of a product's components or labor must be sourced locally. This measure is often used in sectors like automotive manufacturing or electronics to build a domestic supply chain and foster related industries.
Incentives and Support for Local Industry
Beyond restricting imports, governments can also take proactive steps to make local businesses more competitive.
Subsidies and Financial Support: Governments can provide financial assistance to local manufacturers through cash grants, low-interest loans, or tax breaks. These subsidies help reduce the cost of production, making local products more affordable and competitive without directly raising consumer prices.
Investment in Infrastructure and Technology: Improving a nation's infrastructure, such as power grids, transportation networks, and ports, can significantly lower the operational costs for local businesses. Governments can also fund research and development or offer tax credits for businesses that invest in new technology to improve efficiency and productivity.
Export Promotion: Policies that support local firms in selling their products abroad can help them achieve economies of scale. This includes government-sponsored trade missions, export subsidies, and assistance with marketing and logistics. A larger market allows companies to grow, become more efficient, and better withstand foreign competition at home.
"Buy Local" Campaigns: These are public awareness campaigns that encourage consumers and government agencies to prioritize purchasing locally made goods. For example, a "Buy Local" program for government procurement can guarantee a steady market for domestic producers, providing a stable foundation for growth.
Citadel CEO Ken Griffin says President Donald Trump’s tariff policy on China is misguided as the jobs it would “reshore” are mostly those making low-value items. “There’s no money in there for anybody, and there’s certainly no money for doing those jobs,” Griffin said at a forum in New York.
Ken Griffin, the founder and CEO of Citadel Securities who backed Donald Trump in 2024 election, is taking issue with the president’s tariff policy.
Griffin tore into Trump’s tariffs during an appearance Thursday at the Forbes Iconoclast Summit in New York, describing tariffs as “protectionist policy” that “comes at a great price to the U.S. consumer.”
The president’s shifting tariff policy has resulted, for now, in a 30% tariff on most imports from China and the end of ultra-cheap imports from the likes of fast-fashion label Shein and Temu. And that pain for the U.S. consumer isn’t helping the American worker, Griffin said.
“Americans want to wear Nikes, not make them,” he said, quoting criticism from New York University marketing professor Scott Galloway.
“I don’t know why we strive to bring back low value-added products to the United States,” Griffin continued. “There’s no money in there for anybody, and there’s certainly no money for doing those jobs… Jobs are actually walking out of China into lower-cost jurisdictions.
“Why are we aspiring to be the nation of the lowest-cost workforce in the world?”
In fact, China is asking the same question, according to Griffin. Speaking with Forbes editor-at-large Maneet Ahuja at the summit, Griffin recounted his trip to China in March, when he met with multiple government officials to discuss investing in the country.
“China dreams to be like the United States—a nation of very high value-added jobs, a nation rich in services, rich in high development…[with] a stunning GDP per capita,” Griffin said.
“‘China aspires to be like the United States,’”Griffin said a Chinese government official told him. The person said, “‘We want to be like you. Why are you trying to be like us?’” and gave “a look of befuddlement,” according to Griffin.
Griffin said he does support reshoring jobs—but for high-technology, high-value products.
“It’s one thing to make Nikes, it’s another thing to make F-35 fighters,” he said.
Russia is using a new Chinese laser system to shoot down Ukrainian drones, according to pro-Russian Telegram channels. The system seen in a video posted to Telegram on Thursday appears to be at least extremely similar to a system Beijing has apparently already provided to Iran, which you can read more about here.
The video, posted on the Military Information Telegram channel, opens with scenes of troops inside a vehicle, flicking switches and looking at heavily pixelated screens. The next scene shows the system rising out of the vehicle and then being rotated by a soldier in the vehicle using a joystick. It then cuts to small fiery holes being burned into a metal plate. A subsequent view shows the plate with four holes burned through it, apparently created by the laser.
The next scene shows several screens, with one displaying video of a drone catching fire and spinning out of control, with the implication that the damage was caused by the laser system. A second drone is shown being hit by what appears to be the laser. The video ends with recovered drone segments with burn marks that could be indicative of a laser engagement.
While we can’t say for certain what system this is, or where or when the video was taken, as noted earlier, it is very similar to a system China apparently provided to Iran. From our previous story about that: “… it has a single large aperture on the left side. In addition, there is an aperture with a more squared-off shape on the right side … A similar, if not identical arrangement is visible in Chinese marketing literature for another counter-drone laser weapon called the Shen Nung (also transliterated Shennong). Containerized and 4×4 Dongfeng Mengshi light tactical truck-mounted versions of the Shen Nung – the Shen Nung 5000 and 3000, respectively – have at least been pitched in the past. The pictures reportedly taken in Tehran last week show the system behind a blue tarp screen, but what is visible could point to a containerized variant.”
This is a conclusion also drawn by Fabian Hinz, a research fellow for Defense and Military Analysis at the International Institute for Strategic Studies.
“While the sensor arrangement seems to have been altered, the system observed in Russian service strongly resembles the Chinese Shen Nung 3000/5000 anti-drone laser,” Hinz noted on X.
Russian Telegram channels claim the system is already in use by the Nomad special forces unit and is a great improvement over earlier counter-drone laser designs.
“Previously, there was an opinion in the domestic information environment that combat lasers were useless and expensive toys,” wrote the Military Informant Telegram channel, which on Thursday was the first to publish the video.
“However, new threats identified during [the full-on invasion of Ukraine] forced the search for alternative methods of counteraction. Thanks to the development of new technologies, laser systems have become an effective tool for the destruction of Ukrainian UAVs.”
“It remains to be hoped that the topic of developing laser weapons in Russia will receive new impetus, and the experience of using lasers as air defense weapons will be scaled up throughout the country,” the channel added.
While Military Information did not explain what kind of system it was, the editor of a Russian military-themed magazine identified it as “the Chinese Low-Altitude Laser Defending System (LASS).”
It is used, “among others, by the People’s Armed Police of the People’s Republic of China,” wrote Kornev Dmitry, editor of the NOZS magazine and the MilitaryRussia.Ru website. “The developer and manufacturer of LASS is probably the Chinese Academy of Engineering Physics.”
Though we don’t know many details about this system, it certainly is not the first laser directed energy weapon to be used in combat against drones.
Earlier this week, Israeli officials disclosed that Jerusalem has used a new air defense laser to shoot down Hezbollah drones in the current conflict in the Middle East.
As we noted in our story: “What is described as an adapted version of the Iron Beam system made its combat debut last October, and the definitive version should be fielded by the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) later this year, joining an already formidable, layered air defense network, something you can read about in more detail here.”
The use of the Iron Beam — also known by its Hebrew name Magen Or — was announced by the IDF, Israeli Air Force (IAF), and defense contractor Rafael, in a joint statement. These three organizations, it is said, “executed an accelerated development program to deploy revolutionary interception systems,” as part of an effort that also involved Israel’s Directorate of Defense Research and Development.
A World First — Combat-Proven Laser Defense, Powered by Rafael
For the first time in history, high-power laser systems have been used to intercept aerial threats in combat.
This unprecedented breakthrough took place during the Swords of Iron War — with Rafael’s advanced… pic.twitter.com/B3D6UdCJvE
— Rafael Advanced Defense Systems (RAFAELdefense) May 28, 2025
The U.S. has similar lasers deployed in small numbers to forward locations and vessels for early operational use and evaluation. Multiple countries are working on developing similar systems. Although progress is being made on adapting laser weapons to operational military use, it has been far slower than many had predicted, including the Department of Defense. These systems also have key limitations in terms of their range and environmental factors significantly impacting their performance. Thermal limitations can also limit their engagement efficacy against multiple targets. They also use relatively delicate components that have to be hardened to the rigors of forward operations, often in remote locales, with limited external support.
While there is still much we don’t know about the system that emerged on social media, the fact that Iran has likely fielded a Chinese system that closely resembles is a sign that it is on the market. Russia, China and Iran have growing relations as they seek to challenge the United States and its allies on the world stage, which includes both China and Iran providing weapons or supporting technologies to Russia in its fight against Ukraine.
Contact us today to start your journey to success! https://www.minglemedias.c...
Quick Responce Whatsapp Chat: https://wa.me/7305249205
#topseoservices #professionalseoagency #seooptimizationcompany #expertseoprovider #affordableseoservices #leadingseofirm #seomanagementagency #seosolutionscompany #localseoservices #bestseoconsultants #searchengineoptimizationservices #seospecialists #seomarketingexperts #trustedseocompany #seoassistance #seostrategyservices #seoperformanceexperts #seorankingservices #seoconsultationfirm #seocampaignservices #seoanalysiscompany #seoauditservices #seoimplementationagency #customseosolutions #reliableseopartner
As Xtotech Nigeria embarks on an exciting expansion across Africa, launching in South Africa, Ghana, Kenya, and Ethiopia next year, we’re inviting passionate individuals to join us on this transformative journey! We’re looking for volunteers who are committed to our mission of empowering Africa through technology and innovation.
This is your chance to be part of an ambitious project from the ground up. As a volunteer, you’ll gain hands-on experience, collaborate with tech industry experts, and contribute to impactful projects in digital marketing, web development, graphic design, animation, and much more. Whether you bring a specific tech skill or simply a desire to make a difference, Xtotech has a place for you!
What You’ll Gain as a Volunteer:
- Practical Experience: Work on real projects and contribute to Xtotech’s impact across Africa.
- Professional Development: Build valuable connections, enhance your skill set, and deepen your
Much stronger global regulatory controls are urgently needed to curb the impact of commercial gambling on global health and wellbeing.
About 450 million people have at least one behavioural symptom or have experienced a harmful personal, social or health consequence of gambling.
80 million people suffer from gambling disorder, a mental health condition identified by a pattern of repeated and continuous betting despite negative consequences on a person’s life.
Incredibly sophisticated marketing, ever-widening easy access to the internet and mobile phones are enabling the gambling industry to reach more people than ever before. These included adolescents and younger children who were routinely exposed to advertising of gambling products in ways that were unprecedented before the digital revolutio

How do you manage communication challenges with marketing and sales...
Managing communication challenges between marketing and sales teams is crucial for ensuring project success, as these teams have distinct but interdependent roles. Here are some strategies to manage these challenges effectively: 1. Establish Clear Goals and Objectives Align both teams on the...
https://afriprime.net/blogs/54289/How-do-you-manage-communication-challenges-with-marketing-and-salesBy Hugo Keji
Community-driven initiatives can significantly enhance the competitiveness of local products by fostering collaboration, leveraging local resources, and creating a supportive ecosystem for local businesses.
1. Collaborative Efforts and Networks
Cooperatives and Collectives: Forming cooperatives allows local producers to pool resources, share knowledge, and increase bargaining power. This can lead to better pricing, improved quality, and more efficient distribution.
Business Networks: Establishing local business networks can facilitate knowledge sharing, mentorship, and collaboration. Businesses can learn from each other’s successes and challenges, leading to overall improvement.
2. Local Branding and Marketing
Community Branding: Creating a strong local brand that emphasizes the unique qualities and cultural significance of local products can differentiate them from imported goods. Community branding can foster a sense of pride and loyalty among consumers.
Local Campaigns: Grassroots marketing campaigns that promote local products within the community can raise awareness and encourage local consumption. These campaigns can include events, social media promotion, and local media coverage.
3. Shared Resources and Infrastructure
Shared Facilities: Community-driven initiatives can establish shared production facilities, such as kitchens, workshops, or processing plants. This can lower costs for individual businesses and allow them to focus on quality and innovation.
Distribution Networks: Developing local distribution networks, such as farmers' markets, local stores, and online platforms, can make it easier for consumers to access local products and increase their market reach.
4. Education and Training
Skill Development: Organizing workshops, training sessions, and educational programs can help local producers improve their skills, adopt new technologies, and enhance product quality.
Entrepreneurship Programs: Supporting local entrepreneurs with business training, mentorship, and access to resources can foster innovation and competitiveness within the community.
5. Community Engagement and Support
Buy Local Campaigns: Encouraging community members to support local businesses through buy-local campaigns can increase demand for local products and strengthen the local economy.
Customer Feedback: Engaging the community in providing feedback can help local businesses understand consumer preferences and make improvements that increase competitiveness.
6. Access to Funding and Resources
Crowdfunding and Grants: Community-driven crowdfunding campaigns and local grants can provide much-needed capital for local businesses to expand, innovate, and improve their offerings.
Microloans and Financial Support: Establishing community-based microloan programs can help small businesses access the funds they need to grow and compete.
7. Promoting Sustainability and Ethical Practices
Sustainability Initiatives: Community-driven efforts to promote sustainable and ethical production practices can attract eco-conscious consumers and create a competitive edge.
Certifications and Standards: Developing and promoting local certifications for quality, sustainability, and ethical practices can enhance the credibility and appeal of local products.
8. Enhancing Visibility and Market Access
Local Events and Markets: Organizing local events, fairs, and markets provides platforms for local producers to showcase their products and connect with consumers directly.
Tourism and Culture: Promoting local products as part of the cultural and tourist experience can increase their visibility and appeal to a broader audience, including tourists.
9. Community Advocacy and Policy Support
Advocacy Groups: Forming community advocacy groups to lobby for policies that support local industries can lead to favorable conditions for local businesses, such as tax incentives and infrastructure development.
Partnerships with Local Government: Collaborating with local government authorities can lead to initiatives that support local businesses, such as improved transportation infrastructure, business development programs, and promotional campaigns.
In summary, community-driven initiatives enhance the competitiveness of local products by fostering collaboration, leveraging collective resources, promoting local branding, providing education and training, and advocating for supportive policies.
These efforts create a robust ecosystem that supports local businesses and helps them thrive in the face of competition from imported goods.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Be part of Health Data 101.... Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan. With servers in Asia, Europe and America. Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365 For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Public awareness campaigns play a crucial role in supporting local industries by influencing consumer behavior, fostering community support, and driving economic growth.
Here are several ways in which these campaigns contribute:
1. Educating Consumers
Informing About Benefits: Campaigns can educate consumers on the economic, environmental, and social benefits of supporting local industries, such as job creation, reducing carbon footprints, and sustaining local communities.
Highlighting Quality and Uniqueness: By showcasing the quality, craftsmanship, and unique aspects of local products, campaigns can help differentiate them from imported goods.
2. Building Emotional Connections
Storytelling: Sharing stories about the people behind local businesses, their history, and cultural significance can create an emotional connection with consumers, encouraging them to support local industries.
Community Pride: Campaigns can foster a sense of pride in local products and industries, encouraging community members to support their local economy.
3. Shaping Consumer Preferences
Changing Purchasing Habits: Awareness campaigns can influence purchasing habits by highlighting the advantages of buying local, such as fresher produce or unique artisan goods.
Promoting Sustainability: Emphasizing the environmental benefits of supporting local businesses can appeal to eco-conscious consumers and encourage sustainable consumption patterns.
4. Strengthening Local Economies
Economic Impact Awareness: By making the economic impact of buying local more visible, campaigns can help consumers understand how their spending supports local jobs and services.
Increasing Demand: Successful campaigns can increase demand for local products, leading to business growth and more robust local economies.
5. Encouraging Local Innovation
Showcasing Success Stories: Highlighting successful local businesses can inspire other entrepreneurs and encourage innovation within the community.
Fostering Competitiveness: Awareness campaigns can motivate local businesses to improve their products and services to meet the growing demand for quality local goods.
6. Building Partnerships and Networks
Collaborative Efforts: Campaigns can foster collaborations between local businesses, government agencies, and community organizations, creating a supportive network for local industries.
Engaging Influencers: Partnering with local influencers, celebrities, and community leaders can amplify the reach and impact of awareness campaigns.
7. Policy Support
Advocating for Policies: Public awareness campaigns can build support for policies that benefit local industries, such as tax incentives, subsidies, or regulatory changes.
Public Pressure: Increased public awareness can lead to greater public pressure on policymakers to support local industries through favorable policies and infrastructure investments.
8. Enhancing Visibility and Accessibility
Marketing and Promotion: Campaigns can enhance the visibility of local products through various marketing channels, making them more accessible to consumers.
Creating Platforms: Initiatives like local marketplaces, fairs, and online platforms can be promoted through awareness campaigns, making it easier for consumers to find and purchase local products.
9. Promoting Cultural Heritage
Cultural Preservation: Campaigns can emphasize the importance of preserving cultural heritage by supporting local artisans and traditional industries.
Tourism and Culture: By promoting local industries, campaigns can also boost cultural tourism, attracting visitors interested in authentic local experiences and products.
In summary, public awareness campaigns are vital for supporting local industries by educating consumers, building emotional connections, shaping purchasing habits, and fostering a supportive environment for local economic growth and cultural preservation.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Be part of Health Data 101.... Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan. With servers in Asia, Europe and America. Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365 For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Local industries can adopt various strategies to promote culturally significant products in the face of mass importation:
1. Leveraging Cultural Heritage
Storytelling and Branding: Highlight the cultural significance and unique stories behind local products. This can create an emotional connection with consumers and differentiate local products from imported ones.
Heritage Certification: Develop certification programs that authenticate and promote products with cultural and historical significance. Labels like “Protected Designation of Origin” (PDO) or “Geographical Indication” (GI) can enhance credibility and appeal.
2. Quality and Innovation
Quality Assurance: Ensure high-quality standards for local products. Quality can be a strong selling point, especially when competing with mass-produced imports.
Innovation in Design and Packaging: Innovate in design, packaging, and presentation to make local products more attractive and competitive. Incorporating modern aesthetics while retaining cultural elements can appeal to a broader audience.
3. Marketing and Promotion
Digital Marketing: Utilize social media and digital marketing to reach a wider audience. Share content that showcases the uniqueness and cultural value of local products.
Collaborations and Partnerships: Partner with influencers, celebrities, and cultural ambassadors to promote local products. Collaborations with well-known personalities can boost visibility and credibility.
4. Community Engagement
Local Festivals and Events: Participate in and sponsor local festivals, fairs, and cultural events to showcase products. These events provide a platform to reach potential customers and build brand awareness.
Community Support Programs: Engage in community development programs that support local culture and traditions. This can foster goodwill and loyalty among consumers.
Government Support and Policy
Government Subsidies and Grants: Advocate for government support in the form of subsidies, grants, and incentives for local industries. This financial support can help local businesses compete with imported goods.
Regulatory Support: Work with government agencies to implement policies that protect and promote local products, such as import tariffs on certain goods or tax incentives for local businesses.
5. Sustainable Practices
Sustainability and Ethical Practices: Promote the sustainable and ethical production practices of local products. Consumers are increasingly interested in products that are environmentally friendly and ethically produced.
Local Sourcing: Emphasize the use of locally sourced materials and traditional methods, which can appeal to consumers looking for authentic and eco-friendly products.
6. Education and Awareness
Consumer Education: Educate consumers about the benefits of buying local products, such as supporting the local economy, preserving cultural heritage, and reducing environmental impact.
Workshops and Demonstrations: Organize workshops and demonstrations that showcase the making of culturally significant products. This can create a deeper appreciation and understanding among consumers.
7. Export and Global Markets
Export Promotion: Explore opportunities to export culturally significant products to international markets. Niche markets abroad may have a strong interest in authentic cultural products.
International Exhibitions: Participate in international trade fairs and exhibitions to showcase local products to a global audience. This can open up new markets and create global recognition.
Adopting these strategies, local industries can effectively promote their culturally significant products, build a strong brand identity, and compete with mass importation.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Be part of Health Data 101.... Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan. With servers in Asia, Europe and America. Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365 For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Vocational training and education can play a pivotal role in supporting local industries against the challenges posed by mass importation.
These initiatives can help:
Enhancing Workforce Competence:-
Skill Development:
Industry-Relevant Skills: Vocational training provides workers with specific skills that are directly applicable to local industries, improving their productivity and efficiency.
Advanced Techniques: Education programs can introduce workers to advanced manufacturing techniques, new technologies, and best practices.
Adaptability:
Retraining Programs: Offer retraining for workers whose jobs are displaced by import competition, enabling them to transition to new roles within local industries.
Lifelong Learning: Encourage continuous education to help workers stay current with industry changes and technological advancements.
Promoting Innovation and Quality-
Research and Development:
Innovation Hubs: Establish partnerships with local educational institutions to create innovation hubs where new ideas and technologies can be developed.
R&D Training: Provide training in research and development to foster a culture of innovation within the workforce.
Quality Improvement:
Quality Control Training: Educate workers on quality control processes and standards, helping local industries produce higher-quality goods that can compete with imports.
Customer Satisfaction: Training programs focused on customer service and product quality can help local businesses build a loyal customer base.
Boosting Productivity and Efficiency-
Lean Manufacturing:
Process Optimization: Teach workers lean manufacturing principles to streamline production processes, reduce waste, and increase efficiency.
Efficiency Tools: Train employees to use tools and techniques such as Six Sigma and Total Quality Management (TQM) to enhance productivity.
Technological Proficiency:
Digital Skills: Equip workers with digital skills to leverage modern manufacturing technologies, such as automation, robotics, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Software Training: Provide training on industry-specific software for design, production management, and inventory control.
Supporting Business Growth-
Entrepreneurial Skills:
Business Development: Offer education in business management, marketing, and finance to help local entrepreneurs grow their businesses and compete more effectively.
Start-Up Support: Provide resources and training for start-ups, including access to incubators and accelerators.
Market Expansion:
Export Training: Educate local businesses on how to enter and compete in international markets, helping them diversify their revenue streams.
E-commerce Skills: Train businesses in e-commerce and digital marketing to reach broader markets and reduce reliance on traditional retail channels.
Enhancing Economic Resilience-
Economic Diversification:
Multi-Sector Training: Offer vocational training across various industries to diversify the local economy and reduce dependence on a single sector.
Resource Management: Educate workers on sustainable resource management to ensure long-term viability of local industries.
Community Development:
Local Employment: Vocational training can help ensure that local industries have access to a skilled workforce, reducing unemployment and supporting community development.
Social Stability: Providing education and job opportunities can enhance social stability and economic resilience in the face of global competition.
Government and Policy Support-
Incentive Programs:
Training Grants: Government incentives and grants for vocational training programs can help offset costs for businesses and encourage participation.
Tax Benefits: Offer tax benefits to companies that invest in employee training and development.
Public-Private Partnerships:
Collaborative Efforts: Foster partnerships between the government, educational institutions, and local industries to develop comprehensive training programs that meet industry needs.
Shared Resources: Utilize shared resources and facilities for training programs, reducing costs and increasing access.
Implementing robust vocational training and education programs, local industries can build a more skilled, adaptable, and innovative workforce capable of competing effectively against imported goods.
This not only supports business growth and economic resilience but also contributes to the overall development of the community.
By Hugo Keji
Local industries can create job opportunities despite the influx of imported goods by adopting several strategies aimed at enhancing competitiveness, innovation, and market adaptation.
Enhancing Competitiveness:-
Improving Quality and Differentiation:
Product Innovation: Focus on creating unique, high-quality products that differentiate from imported goods.
Brand Building: Develop strong brand identities to build customer loyalty and emphasize local heritage.
Cost Efficiency:
Streamlining Operations: Implement lean manufacturing and other efficiency-enhancing processes to reduce costs.
Economies of Scale: Increase production volumes to reduce per-unit costs.
Leveraging Technology:-
Adopting Advanced Technologies:
Automation and AI: Use automation and artificial intelligence to enhance productivity and reduce labor costs.
Digital Transformation: Invest in digital tools for better inventory management, supply chain optimization, and customer relationship management.
E-commerce and Digital Marketing:-
Online Sales Channels: Develop robust online sales platforms to reach a broader audience and reduce dependency on traditional retail channels.
Digital Marketing: Utilize digital marketing strategies to target specific customer segments more effectively.
Fostering Innovation
Research and Development (R&D):-
Innovation Hubs: Establish innovation hubs and collaborate with research institutions to develop new products and processes.
Continuous Improvement: Encourage a culture of continuous improvement and innovation within the workforce.
Customization and Flexibility:-
Custom Products: Offer customized products tailored to the specific needs and preferences of local customers.
Agile Production: Adopt agile manufacturing techniques to quickly respond to market changes and customer demands.
Strengthening Local Supply Chains:-
Local Sourcing:
Supporting Local Suppliers: Create a robust local supply chain to reduce dependency on imports and support local businesses.
Vertical Integration: Integrate vertically to control more stages of the production process, reducing costs and improving quality control.
Collaborations and Partnerships:-
Strategic Alliances: Form strategic alliances with other local businesses to share resources, knowledge, and markets.
Industry Clusters: Develop industry clusters where businesses can collaborate, share infrastructure, and foster innovation.
Government and Community Engagement:-
Advocacy and Policy:
Lobbying for Support: Advocate for government policies that support local industries, such as favorable trade policies, subsidies, and tax incentives.
Community Initiatives: Engage in community initiatives to build goodwill and promote the benefits of supporting local businesses.
Education and Training:
Workforce Development: Invest in training and development programs to enhance the skills of the local workforce.
Apprenticeships and Internships: Create apprenticeship and internship programs to attract young talent and provide hands-on training.
Promoting Sustainability:-
Sustainable Practices:
Eco-Friendly Products: Develop eco-friendly products and sustainable practices to attract environmentally conscious consumers.
Energy Efficiency: Invest in energy-efficient technologies to reduce costs and environmental impact.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):-
Community Projects: Engage in CSR projects that benefit the local community, improving the company's image and building local support.
Sustainability Certifications: Obtain sustainability certifications to appeal to a growing market of eco-conscious consumers.
Diversification:-
New Markets and Products:
Exploring New Markets: Identify and enter new markets, both locally and internationally, to diversify revenue streams.
Product Line Expansion: Expand product lines to cater to different customer segments and reduce reliance on a single product.
By implementing these strategies, local industries can not only create job opportunities but also build resilience against the challenges posed by the influx of imported goods.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Be part of Health Data 101.... Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan. With servers in Asia, Europe and America. Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365 For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Local industries can leverage technology and innovation to compete with imported goods in several ways:
1. Adopting Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Automation and Robotics: Implementing automation and robotics can increase production efficiency and reduce costs.
3D Printing: Utilizing 3D printing for rapid prototyping and custom manufacturing can reduce time-to-market and cater to specific customer needs.
2. Enhancing Product Quality and Customization
Smart Manufacturing: Using IoT (Internet of Things) to monitor and optimize production processes ensures high-quality products.
Customization: Employing digital tools to offer personalized products that meet local consumer preferences can differentiate local goods from imports.
3. Implementing Digital Transformation
ERP Systems: Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems can streamline operations, improve supply chain management, and reduce operational costs.
E-commerce Platforms: Leveraging online sales channels to reach a broader customer base and offering superior customer service through digital tools.
4. Fostering Innovation and R&D
Collaborative Innovation: Partnering with local universities and research institutions to develop new technologies and innovative products.
R&D Investment: Investing in research and development to create unique products and improve existing ones.
5. Utilizing Data Analytics
Consumer Insights: Analyzing customer data to understand market trends and consumer preferences helps in developing products that meet local demand.
Operational Efficiency: Using data analytics to optimize production processes and supply chains.
6. Promoting Sustainability
Eco-friendly Practices: Adopting sustainable manufacturing practices and using renewable energy sources can appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
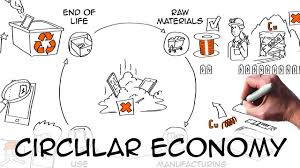
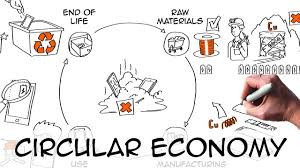
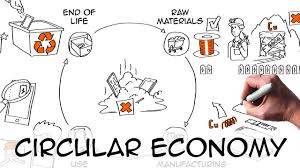
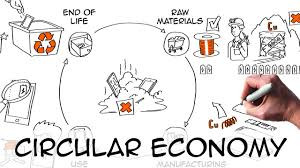
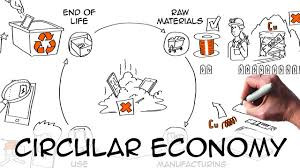
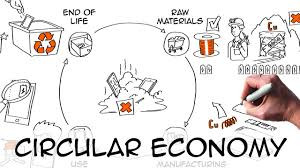
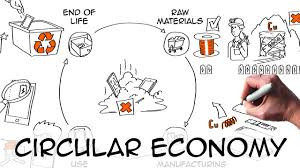
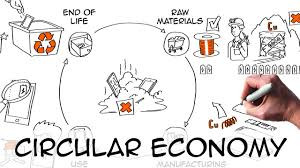
Circular Economy: Implementing circular economy principles such as recycling and reusing materials can reduce costs and waste.
7. Enhancing Supply Chain Management
Local Sourcing: Reducing dependency on imported raw materials by sourcing locally to decrease lead times and transportation costs.
Supply Chain Resilience: Using technology to build more resilient supply chains that can adapt to disruptions.
8. Improving Marketing and Brand Positioning
Digital Marketing: Utilizing social media, content marketing, and SEO to build a strong online presence and connect with local customers.
Brand Loyalty: Creating strong brand loyalty through customer engagement, superior service, and community involvement.
9. Accessing Financial Innovations
Fintech Solutions: Leveraging financial technology to access funding, manage finances efficiently, and provide flexible payment options to customers.
Crowdfunding: Using crowdfunding platforms to raise capital for innovative projects and gauge market interest.
10. Training and Workforce Development
Skill Development: Investing in training programs to upskill employees and ensure they are proficient with the latest technologies.
Talent Attraction: Attracting and retaining top talent through competitive wages, benefits, and a positive work environment.
Integrating these strategies, local industries can enhance their competitiveness, improve operational efficiencies, and better meet the needs of their customers, making their products more attractive compared to imported goods.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
By Hugo Keji
Section 1: Introduction
Consumer perceptions and trust play a crucial role in influencing purchasing decisions between imported and locally produced goods.
Understanding these factors is essential for local industries to effectively compete with high-quality imports and for imported goods to maintain their market presence.
This article delves into the various aspects of consumer perceptions and trust and their impact on the preference for imported versus local goods.
Section 2: Factors Influencing Consumer Perceptions
Quality Perception
Consumers often perceive imported goods as higher quality due to the reputation of certain countries for specific products. For instance:
Electronics from Japan: Known for precision, innovation, and reliability, Japanese electronics are often preferred for their perceived superior quality.
Luxury Goods from Europe: European brands like Louis Vuitton and Gucci have built a global reputation for craftsmanship and exclusivity, leading to a perception of high quality.
Marketing and branding significantly shape these perceptions. Effective campaigns that highlight the quality and heritage of imported products can enhance their appeal to consumers.
Price Perception-
Price perception is a critical factor in consumer preference. Imported goods can be seen as offering better value for money, especially when produced in countries with lower production costs. For example:
Textiles from Southeast Asia: These are often more affordable due to lower labor and production costs in the region.
On the other hand, local goods may be perceived as more expensive, but they often justify this with arguments around superior quality, freshness, or ethical production practices.
Cultural Influence-
Cultural factors also play a significant role. The desire for exotic or foreign products can drive consumer preference for imports. Conversely, national pride and a desire to support the local economy can lead to a preference for local goods. For instance:
French Wines vs. Local Wines: While French wines are often revered for their heritage and quality, local wines can appeal to consumers who value supporting regional producers.
Availability and Accessibility-
The ease of accessing products influences consumer preferences. Imported goods might be more readily available through global retail chains and e-commerce platforms.
In contrast, locally produced goods might benefit from shorter supply chains, leading to fresher products, particularly in the food sector.
Section 3: The Role of Trust
Product Safety and Reliability-
Trust in product safety and reliability is paramount. Products from countries with stringent safety standards, such as Germany for machinery, often enjoy high trust levels.
Local products may also be trusted more due to familiarity and the ability to directly address any issues with the producer.
Brand Reputation-
Strong brand reputation is crucial for building consumer trust. Established foreign brands leverage their global reputation, while local brands can capitalize on their deep understanding of local market needs and community connections. For example:
Apple (USA): Known for its innovation and quality, Apple enjoys a strong global reputation.
Patagonia (USA): This local brand is trusted for its commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Transparency and Traceability-
Consumers increasingly value transparency in production processes. Imported goods with clear traceability can build trust, as can local producers who provide detailed information about their supply chain. Blockchain technology is one tool being used to enhance traceability and transparency.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations-
Ethical production practices and sustainability are key to building trust. Consumers are often wary of imported goods from countries with poor labor practices or environmental records.
Local goods, on the other hand, benefit from perceptions of being more sustainable and ethically produced, which aligns with the values of environmentally conscious consumers.
Section 4: Case Studies:
Imported Goods-
Electronics from Japan: Renowned for innovation and reliability, Japanese electronics are trusted and preferred by many consumers globally.
Luxury Goods from Europe: European luxury brands like Louis Vuitton and Gucci are perceived as high-quality and exclusive, attracting consumers looking for premium products.
Local Goods-
Organic Foods: Locally sourced organic foods are trusted for their freshness and traceability, appealing to health-conscious consumers.
Handicrafts and Artisanal Products: Local craftspeople often garner trust and preference for their unique, handmade items that reflect cultural heritage and craftsmanship.
Section 5: Strategies for Local Industries to Build Perceptions and Trust:
Quality Assurance and Certification-
Obtaining and prominently displaying certifications that attest to the quality and safety of local products is crucial. Local industries should:
Ensure continuous improvement and quality control to maintain high standards.
Highlight these certifications in marketing materials to build consumer trust.
Effective Branding and Marketing-
Developing strong local brands that emphasize quality, reliability, and cultural value is essential. This includes:
Investing in marketing campaigns that tell the story of the local product and its benefits.
Using storytelling to connect with consumers emotionally, emphasizing unique aspects such as local heritage or sustainability.
Engagement and Transparency-
Direct engagement with consumers through social media, community events, and transparent business practices fosters trust. Local industries can:
Provide detailed information about sourcing, production processes, and sustainability efforts.
Engage in open dialogues with consumers to address concerns and gather feedback.
Leveraging Local Advantages-
Highlighting the advantages of local production, such as freshness, support for the local economy, and reduced environmental impact, can attract consumers. Strategies include:
Collaborating with local influencers and advocates to promote the benefits of buying local.
Emphasizing the unique qualities of local products in marketing efforts.
Section 6: Conclusion
Consumer perceptions and trust significantly impact the preference for imported versus local goods.
By understanding and strategically addressing these factors, local industries can enhance their competitiveness and build strong relationships with consumers.
Improving product quality, effective branding, transparency, and leveraging local advantages are key strategies for local industries to succeed in a global market.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Be part of Health Data 101.... Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan. With servers in Asia, Europe and America. Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365 For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/... https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
The Role of Consumer Perceptions and Trust in the Preference for Imported Versus Local Goods.
Overview of the influence of consumer perceptions and trust on purchasing decisions.
Importance of understanding these factors in the competition between imported and local goods.
Factors Influencing Consumer Perceptions:-
Quality Perception-
Consumers often perceive imported goods as higher quality due to the reputation of certain countries for specific products (e.g., electronics from Japan, luxury goods from Europe).
Marketing and branding play significant roles in shaping these perceptions.
Price Perception-
Imported goods can be perceived as more affordable or offering better value for money, particularly when produced in countries with lower production costs.
Conversely, local goods may be seen as more expensive due to smaller economies of scale.
Cultural Influence-
Cultural factors influence consumer preferences, such as the desire for exotic or foreign products.
National pride and the desire to support the local economy can drive preference for locally produced goods.
Availability and Accessibility-
The ease of accessing imported versus local goods affects consumer preference. Imports might be more readily available through global retail chains.
Locally produced goods might benefit from shorter supply chains, leading to fresher products, especially in the case of food items.
The Role of Trust:
Product Safety and Reliability-
Trust in product safety and reliability significantly impacts consumer preference. Products from countries with stringent safety standards are often trusted more.
Local products might be trusted more due to familiarity and easier recourse in case of issues.
Brand Reputation-
Strong brands, whether local or international, build consumer trust through consistent quality and effective marketing.
Established foreign brands can leverage their global reputation to gain trust, while local brands can capitalize on local market knowledge and community ties.
Transparency and Traceability-
Consumers are increasingly valuing transparency in production processes and supply chains. Imported goods with clear traceability can build trust.
Local producers often have an advantage in transparency, being closer to the market and more accountable to local consumers.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations-
Ethical production practices and sustainability influence consumer trust. Imported goods may suffer from perceptions of unethical labor practices or environmental harm.
Local goods often benefit from a perception of being more sustainable and ethically produced, aligning with consumers' values.
Case Studies:-
Imported Goods-
Electronics from Japan: Known for innovation and reliability, Japanese electronics are trusted and preferred by many consumers globally.
Luxury Goods from Europe: European luxury brands like Louis Vuitton and Gucci are perceived as high-quality and exclusive.
Local Goods-
Organic Foods: Locally sourced organic foods are trusted for their freshness and traceability.
Handicrafts and Artisanal Products: Local craftspeople often garner trust and preference for their unique, handmade items that reflect cultural heritage.
Strategies for Local Industries to Build Perceptions and Trust:
Quality Assurance and Certification-
Obtain and prominently display certifications that attest to the quality and safety of local products.
Engage in continuous improvement and quality control to ensure consistent product quality.
Effective Branding and Marketing-
Develop strong local brands that emphasize quality, reliability, and cultural value.
Use storytelling to connect with consumers on an emotional level, highlighting the benefits and uniqueness of local products.
Engagement and Transparency-
Foster direct engagement with consumers through social media, community events, and transparency in business practices.
Provide detailed information about sourcing, production processes, and sustainability efforts.
Leveraging Local Advantages-
Highlight the advantages of local production, such as freshness, support for the local economy, and reduced environmental impact.
Collaborate with local influencers and advocates to promote the benefits of buying local.
Summary of the significant role of consumer perceptions and trust in shaping preferences for imported versus local goods.
Emphasis on the need for local industries to strategically build and maintain trust and positive perceptions to compete effectively.

Health Data 101 - App on Amazon Appstore
Healthdata101-Manage Hospital and Health data.
https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B0D514TH5SBy Hugo Keji
Detailed Section:-
Section 1: Introduction
In the face of increasing globalization, local industries must focus on enhancing product quality to remain competitive against high-quality imports.
Improving product quality not only boosts competitiveness but also fosters customer loyalty and drives sustainable growth.
This article explores strategies that local industries can employ to elevate their product quality and compete effectively in the global market.
Section 2: Investment in Research and Development (R&D)
Innovation and Product Improvement-
Investing in R&D is crucial for local industries to innovate and enhance their product offerings. This includes:
Allocating resources to develop new technologies and improve existing processes.
Fostering a culture of innovation within the organization to continuously generate new ideas.
Collaboration with Research Institutions-
Partnering with universities and research centers provides access to expertise and advanced research facilities. Local industries should:
Engage in joint research projects and leverage government-funded programs.
Stay updated on the latest industry trends and technological advancements through these collaborations.
Section 3: Quality Management Systems
Adoption of International Standards-
Implementing quality management systems like ISO 9001 helps local industries align with international best practices. This involves:
Regularly updating and maintaining certifications to ensure compliance with global standards.
Conducting internal audits to identify and address areas for improvement.
Continuous Improvement Processes-
Employing methodologies such as Six Sigma and Total Quality Management (TQM) helps streamline processes and eliminate defects. Key steps include:
Training employees in these methodologies to build internal capabilities.
Establishing a continuous improvement culture that encourages proactive problem-solving.
Section 4: Skilled Workforce Development
Training and Education
Investing in employee training programs enhances skills and knowledge. This can be achieved by:
Offering regular workshops and courses on the latest industry practices and technologies.
Encouraging employees to pursue higher education and professional certifications.
Attracting and Retaining Talent-
Creating an attractive work environment and competitive compensation packages helps attract and retain skilled workers. This includes:
Implementing career development plans and offering growth opportunities within the organization.
Fostering a positive workplace culture that values employee contributions.
Section 5: Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Automation and Robotics
Investing in automation and robotics increases precision and consistency in manufacturing processes. This involves:
Utilizing advanced machinery to reduce human error and improve efficiency.
Integrating robotics into production lines to enhance product quality.
Industry 4.0-
Adopting Industry 4.0 technologies such as IoT, AI, and data analytics optimizes production processes. Steps to implement these technologies include:
Utilizing IoT devices to monitor and control manufacturing processes in real-time.
Applying AI and data analytics to identify and address production inefficiencies.
Section 6: Supply Chain Optimization
Supplier Quality Management
Establishing strict quality standards for suppliers ensures that raw materials and components meet high standards. This includes:
Conducting regular audits of suppliers to verify compliance with quality standards.
Developing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers to ensure consistent quality.
Lean Manufacturing-
Implementing lean manufacturing principles reduces waste and improves efficiency. Key practices include:
Focusing on value-added activities that enhance product quality.
Continuously identifying and eliminating non-value-added processes.
Section 7: Customer Feedback and Engagement
Listening to Customers
Actively seeking and analyzing customer feedback helps identify areas for improvement. This involves:
Conducting surveys, focus groups, and monitoring social media to gather customer insights.
Using feedback to drive product and service enhancements.
Responsive Customer Service
Providing excellent customer service addresses issues promptly and effectively. Key actions include:
Establishing a responsive customer service team to handle inquiries and complaints.
Using customer feedback to inform continuous improvement efforts.
Section 8: Branding and Marketing Strategies
Building a Strong Brand
Developing a strong brand identity that emphasizes quality and reliability enhances market competitiveness. This involves:
Investing in marketing campaigns that highlight the unique qualities of local products.
Creating a brand story that resonates with consumers and builds trust.
Market Differentiation-
Differentiating products by focusing on unique selling points such as sustainability, local craftsmanship, and superior customer service. Strategies include:
Tailoring marketing efforts to target specific consumer segments.
Highlighting the benefits and unique attributes of local products in marketing materials.
Section 9: Government and Industry Support
Policy and Incentives
Advocating for government policies that support local industries, such as tax incentives and subsidies. This includes:
Participating in industry associations to influence policy decisions and share best practices.
Collaborating with government bodies to develop supportive regulations.
Export Promotion
Utilizing government and industry programs to promote local products in international markets. Key actions include:
Participating in trade shows and international exhibitions to showcase local products.
Leveraging export promotion initiatives to expand market reach.
Section 10:
Improving product quality is essential for local industries to compete with high-quality imports. By investing in R&D, implementing quality management systems, developing a skilled workforce, adopting advanced manufacturing technologies, optimizing supply chains, engaging with customers, building strong brands, and leveraging government and industry support, local industries can enhance their competitiveness and achieve sustainable growth.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
How Local Industries Can Improve Product Quality to Compete with High-Quality Imports.
Introduction-
Importance of product quality in global competitiveness
Challenges local industries face in competing with high-quality imports.
Investment in Research and Development (R&D).
Innovation and Product Improvement:
Invest in R&D to innovate and enhance product offerings.
Develop new technologies and processes to improve product quality and efficiency.
Collaboration with Research Institutions:
Partner with universities and research centers to leverage expertise and resources.
Participate in industry research initiatives and government-funded programs.
Quality Management Systems
Adoption of International Standards:
Implement quality management systems such as ISO 9001.
Regularly update and maintain certification to ensure continuous improvement.
Continuous Improvement Processes:
Employ methodologies like Six Sigma and Total Quality Management (TQM) to streamline processes and eliminate defects.
Foster a culture of continuous improvement within the organization.
Skilled Workforce Development
Training and Education:
Invest in regular training programs for employees to enhance their skills and knowledge.
Encourage higher education and professional development in relevant fields.
Attracting and Retaining Talent:
Create attractive work environments and competitive compensation packages to attract skilled workers.
Implement career development plans to retain top talent.
Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Automation and Robotics:
Invest in automation and robotics to increase precision and consistency in manufacturing.
Utilize advanced machinery to reduce errors and improve efficiency.
Industry 4.0:
Adopt Industry 4.0 technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics.
Implement smart manufacturing practices to optimize production processes.
Supply Chain Optimization
Supplier Quality Management:
Establish strict quality standards for suppliers and conduct regular audits.
Develop long-term relationships with reliable and high-quality suppliers.
Lean Manufacturing:
Implement lean manufacturing principles to reduce waste and improve efficiency.
Focus on value-added activities to enhance product quality.
Customer Feedback and Engagement
Listening to Customers:
Actively seek and analyze customer feedback to identify areas for improvement.
Engage with customers through surveys, focus groups, and social media.
Responsive Customer Service:
Provide excellent customer service to address issues promptly and effectively.
Use customer feedback to drive product and service enhancements.
Branding and Marketing Strategies
Building a Strong Brand:
Develop a strong brand identity that emphasizes quality and reliability.
Invest in marketing campaigns that highlight the unique qualities and benefits of local products.
Market Differentiation:
Differentiate products by focusing on unique selling points such as sustainability, local craftsmanship, and superior customer service.
Tailor marketing strategies to target specific consumer segments.
Government and Industry Support
Policy and Incentives:
Advocate for government policies that support local industries, such as tax incentives and subsidies.
Participate in industry associations to influence policy decisions and share best practices.
Export Promotion:
Utilize government and industry programs to promote local products in international markets.
Participate in trade shows and international exhibitions to showcase local products.
Summary of key strategies for improving product quality in local industries
Emphasis on the need for a comprehensive approach involving innovation, workforce development, advanced technologies, supply chain optimization, customer engagement, branding, and support from government and industry bodies.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Balancing the need for imports with the promotion of local industries is a complex task that requires a combination of policies and strategies to ensure sustainable economic growth and development.
Governments can employ various approaches to achieve this balance:
1. Trade Policies
Tariffs and Quotas: Implementing moderate tariffs and quotas on certain imports can protect nascent and strategic domestic industries from overwhelming foreign competition while still allowing essential imports.
Trade Agreements: Negotiating trade agreements that provide favorable terms for both imports and exports can enhance market access for local industries while ensuring the availability of necessary imports.
2. Incentives for Local Industries
Subsidies and Grants: Providing financial support, such as subsidies and grants, to local industries can help them compete with imported goods and services.
Tax Incentives: Offering tax breaks or credits to domestic manufacturers and producers can reduce their operational costs and enhance competitiveness.
3. Investment in Infrastructure and Technology
Infrastructure Development: Investing in infrastructure such as transportation, energy, and communication networks can lower production and logistics costs for local industries.
Technology Upgradation: Supporting the adoption of advanced technologies through funding, tax incentives, and partnerships can improve the productivity and quality of local industries.
4. Support for Research and Development
Innovation Grants: Providing grants and funding for research and development can drive innovation in local industries, making them more competitive globally.
Collaboration with Academia: Encouraging collaboration between industry and academic institutions can foster innovation and the development of new technologies and products.
5. Skill Development and Education
Vocational Training: Investing in vocational training programs can equip the workforce with the necessary skills to meet the demands of modern industries.
Higher Education: Enhancing higher education systems to produce skilled graduates in fields relevant to key industries can support the growth and competitiveness of local businesses.
6. Promotion of Export-Oriented Industries
Export Incentives: Providing incentives for export-oriented industries can help local businesses access global markets and reduce trade deficits.
Market Access: Assisting local companies in gaining access to international markets through trade missions, marketing support, and diplomatic efforts can boost exports.
7. Quality Standards and Certification
Quality Control: Implementing and enforcing high-quality standards and certification processes can ensure that local products meet international standards, making them more competitive.
Branding and Marketing: Supporting branding and marketing initiatives to promote local products can increase their appeal in both domestic and international markets.
8. Balancing Import and Local Production
Selective Import Substitution: Encouraging the production of certain goods domestically while importing those that are not feasible to produce locally can strike a balance.
Strategic Reserves: Building strategic reserves of essential goods can provide a buffer against supply chain disruptions while supporting local production in other areas.
9. Public-Private Partnerships
Collaboration: Encouraging public-private partnerships can leverage the strengths of both sectors to support local industries and manage imports effectively.
Investment: Facilitating joint investments in critical industries can enhance their growth and sustainability.
10. Regulatory and Institutional Support
Ease of Doing Business: Improving the regulatory environment to make it easier to start and operate businesses can attract investment and support local industries.
Institutional Frameworks: Establishing institutions and agencies that support industry development, trade promotion, and innovation can create a conducive environment for local businesses.
Balancing the need for imports with the promotion of local industries requires a multi-faceted approach that includes trade policies, incentives, infrastructure investment, support for R&D, skill development, export promotion, quality standards, selective import substitution, public-private partnerships, and regulatory support.
By implementing these strategies, governments can create a sustainable and competitive economic environment that supports both imports and the growth of local industries.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Strategies for Local Industries to Compete with Imported Products.
1. Enhancing Product Quality and Innovation:
Continuous Improvement: Implement regular quality checks and upgrades to ensure products meet or exceed international standards.
Innovation: Invest in research and development to create innovative products that cater to local tastes and preferences, offering unique features that imported goods may lack.
2. Cost Efficiency:
Operational Efficiency: Streamline production processes to reduce costs without compromising quality. This could involve adopting lean manufacturing techniques or automating certain production stages.
Local Sourcing: Source raw materials locally when possible to reduce transportation costs and support the local economy.
3. Strong Branding and Marketing:
Brand Identity: Develop a strong brand identity that emphasizes the unique qualities of local products, such as cultural heritage, craftsmanship, and community support.
Marketing Campaigns: Create effective marketing campaigns that resonate with local consumers, highlighting the benefits of choosing local products over imported ones.
4. Customer Engagement and Loyalty Programs:
Customer Feedback: Actively seek and incorporate customer feedback to improve products and services.
Loyalty Programs: Implement loyalty programs that reward repeat customers, fostering a strong connection and encouraging long-term patronage.
5. Leveraging Local Advantage:
Cultural Relevance: Produce goods that are culturally relevant and tailored to the local market, capitalizing on knowledge of local traditions and preferences.
Speed to Market: Utilize proximity to the market to quickly respond to changing consumer demands and trends, offering faster turnaround times than international competitors.
6. Strategic Partnerships and Alliances:
Collaboration: Partner with other local businesses to share resources, knowledge, and technologies, creating synergies that can enhance competitiveness.
Joint Ventures: Form joint ventures with international companies to combine local market knowledge with global expertise and technology.
7. Sustainability and Ethical Practices:
Sustainable Practices: Adopt environmentally friendly practices to appeal to the growing segment of eco-conscious consumers.
Ethical Standards: Ensure fair labor practices and ethical sourcing to build a positive brand image and attract ethically minded consumers.
8. Government and Policy Support:
Advocacy: Work with government bodies to advocate for policies that support local industries, such as subsidies, tax incentives, and protective tariffs.
Grants and Funding: Utilize available government grants and funding programs to invest in technology upgrades, workforce training, and market expansion initiatives.
9. Digital Transformation:
E-commerce: Develop robust online sales channels to reach a wider audience, including tech-savvy consumers who prefer shopping online.
Digital Marketing: Leverage digital marketing tools and social media platforms to increase brand visibility and engage with consumers directly.
10. Product Differentiation:
Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Identify and promote unique aspects of local products that set them apart from imported goods, such as superior craftsmanship, local flavors, or traditional methods.
Customization: Offer customization options that cater to specific consumer needs and preferences, providing a personalized experience that imported goods may not offer.
Local industries can effectively compete with imported products by focusing on enhancing product quality, achieving cost efficiency, and leveraging their unique cultural and market advantages. Strong branding, strategic partnerships, customer engagement, and sustainability practices also play crucial roles. Additionally, advocating for supportive government policies and embracing digital transformation can further strengthen the competitive position of local industries.
By adopting these strategies, local businesses can not only withstand the pressure from imported goods but also thrive and grow in a competitive market environment.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$5 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Role of Consumer Preference in the Balance Between Imported and Locally Produced Goods.
Price Sensitivity:-
Cost-Conscious Choices: Consumers often opt for imported goods if they are cheaper than locally produced alternatives.
Value for Money: Consumers weigh the cost against perceived value, often choosing products that offer better quality or features for the same price.
Quality Perception:-
Brand Reputation: Imported goods from established international brands are often perceived as higher quality.
Consistency: Consumers might prefer imported goods if they believe they offer more consistent quality compared to local products.
Cultural and Social Influences:-
Cultural Affinity: Consumers may prefer local products due to cultural significance or a sense of national pride.
Social Trends: Trends and social influences, including endorsements by celebrities or influencers, can sway consumer preferences towards either imported or local goods.
Product Availability and Variety:
Wide Selection: Imported goods often increase the variety of available products, attracting consumers looking for unique or niche items not produced locally.
Seasonal Availability: Some imported goods fill gaps in seasonal availability, making them preferred choices at certain times of the year.
Environmental and Ethical Considerations:-
Sustainability: Environmentally conscious consumers may prefer locally produced goods to reduce their carbon footprint.
Fair Trade: Ethical considerations, such as fair trade practices, can influence consumers to choose local products that support fair labor conditions and community development.
Marketing and Branding:-
Effective Advertising: Strong marketing campaigns by international brands can influence consumer preferences towards imported goods.
Local Branding: Effective local branding that emphasizes unique aspects and benefits of local products can attract consumers.
Impact on Local and Imported Goods Balance:-
Demand Shifts:
Economic Fluctuations: During economic downturns, consumers may shift towards cheaper imported goods. Conversely, in times of economic growth, there may be a stronger preference for higher-quality local products.
Income Levels: Higher income levels can increase demand for premium imported goods, while lower income levels might boost demand for affordable local alternatives.
Market Dynamics:
Competitive Pressure: High consumer preference for imported goods can pressure local industries to improve quality and reduce prices.
Niche Markets: Local producers can carve out niche markets by catering to specific consumer preferences, such as organic or artisanal products.
Policy and Regulation:
Government Support: Policies such as subsidies for local industries, tariffs on imports, and promotion of local goods can influence consumer preferences towards locally produced items.
Trade Agreements: Trade policies and agreements can affect the availability and pricing of imported goods, thereby influencing consumer choices.
Innovation and Adaptation:
Product Development: Local industries may innovate and adapt to changing consumer preferences by developing new products or improving existing ones.
Service Excellence: Providing superior customer service and building strong customer relationships can enhance consumer loyalty to local brands.
Consumer preference plays a crucial role in balancing the demand between imported and locally produced goods.
Factors such as price sensitivity, quality perception, cultural influences, product availability, environmental considerations, and marketing strategies significantly impact consumer choices. These preferences, in turn, shape market dynamics, influence policy decisions, and drive local industries to innovate and adapt to meet evolving consumer demands. Balancing consumer preferences effectively can help sustain both local industries and the availability of diverse imported goods.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$5 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
African youths can drive global growth through various avenues, leveraging their talents, creativity, and the continent's unique opportunities.
Entrepreneurship and Innovation:-
Startups: By creating and scaling startups, African youths can introduce innovative products and services to global markets.
Tech Hubs: Participation in tech hubs and innovation centers can lead to the development of cutting-edge technologies and solutions.
E-commerce: Leveraging e-commerce platforms to sell African products globally, contributing to the digital economy.
Education and Skills Development:-
STEM Education: Pursuing STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) education to contribute to global advancements in these fields.
Upskilling: Continuously updating skills to match global industry trends, making African youths competitive in the international job market.
Research and Development: Engaging in research and development projects that address global challenges such as health, energy, and sustainability.
Digital Economy:-
Remote Work: Taking advantage of remote work opportunities to provide services to companies worldwide.
Freelancing: Offering freelance services in areas such as software development, graphic design, and digital marketing.
Content Creation: Using platforms like YouTube, TikTok, and blogs to create content that can attract global audiences and advertisers.
Agribusiness and Sustainability:-
Sustainable Agriculture: Implementing sustainable agricultural practices that can be models for other regions facing similar challenges.
Exporting Goods: Engaging in agribusiness and exporting high-quality agricultural products to international markets.
Green Technologies: Innovating in renewable energy and green technologies to contribute to global sustainability efforts.
Cultural Influence:-
Creative Industries: Participating in the creative industries (music, film, fashion) to influence global culture and create economic value.
Cultural Exchange: Promoting African culture through international collaborations and exchanges.
Tourism Promotion: Leveraging digital platforms to promote African tourism, attracting visitors and investment.
Leadership and Advocacy:-
Global Forums: Participating in global forums and organizations to influence policy and advocate for issues affecting young people and the continent.
Social Entrepreneurship: Launching social enterprises that address global social issues such as poverty, education, and health.
Climate Action: Leading climate action initiatives and participating in international climate negotiations.
Networking and Collaboration:-
Diaspora Engagement: Collaborating with the African diaspora to build networks that can facilitate investment, knowledge transfer, and market access.
Global Partnerships: Forming partnerships with international organizations, NGOs, and businesses to drive development projects and innovations.
Knowledge Sharing: Participating in global knowledge-sharing platforms to exchange ideas and best practices.
Technology and Digital Transformation:-
Tech Startups: Developing tech startups that can scale globally, providing innovative solutions to worldwide problems.
AI and Data Science: Engaging in AI and data science projects to contribute to global advancements in these fields.
Blockchain and Fintech: Innovating in blockchain and fintech to provide financial solutions that can be adopted globally.
Health and Biotechnology:-
Medical Research: Engaging in medical research and developing health solutions that can address global health challenges.
Biotech Startups: Creating biotech startups that can innovate in areas such as pharmaceuticals, diagnostics, and agriculture.
Advancing Democracy and Governance:-
Civic Engagement: Promoting democracy, transparency, and good governance in African countries, serving as a model for other regions.
Policy Innovation: Innovating in public policy to address global challenges such as migration, urbanization, and human rights.
Leveraging these strategies, African youths can not only drive growth within the continent but also contribute significantly to global economic, social, and technological progress.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$5 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com