1 hr. ago
#Netflix is not just a #streaming service it’s a global #entertainment powerhouse influencing #culture , #creativity , and viewing habits worldwide. But its success depends on more than #content and decisions made inside the company.
Netflix operates in a complex, fast-changing external environment, shaped by regulations, #technology , #market economics, consumer behaviour, and global challenges.
A #PESTLE #analysis helps us understand the macro-environmental factors that affect Netflix’s strategic decisions, risks, and long-term growth.
https://pratsdigital.in/ne...
Netflix operates in a complex, fast-changing external environment, shaped by regulations, #technology , #market economics, consumer behaviour, and global challenges.
A #PESTLE #analysis helps us understand the macro-environmental factors that affect Netflix’s strategic decisions, risks, and long-term growth.
https://pratsdigital.in/ne...
5 days ago
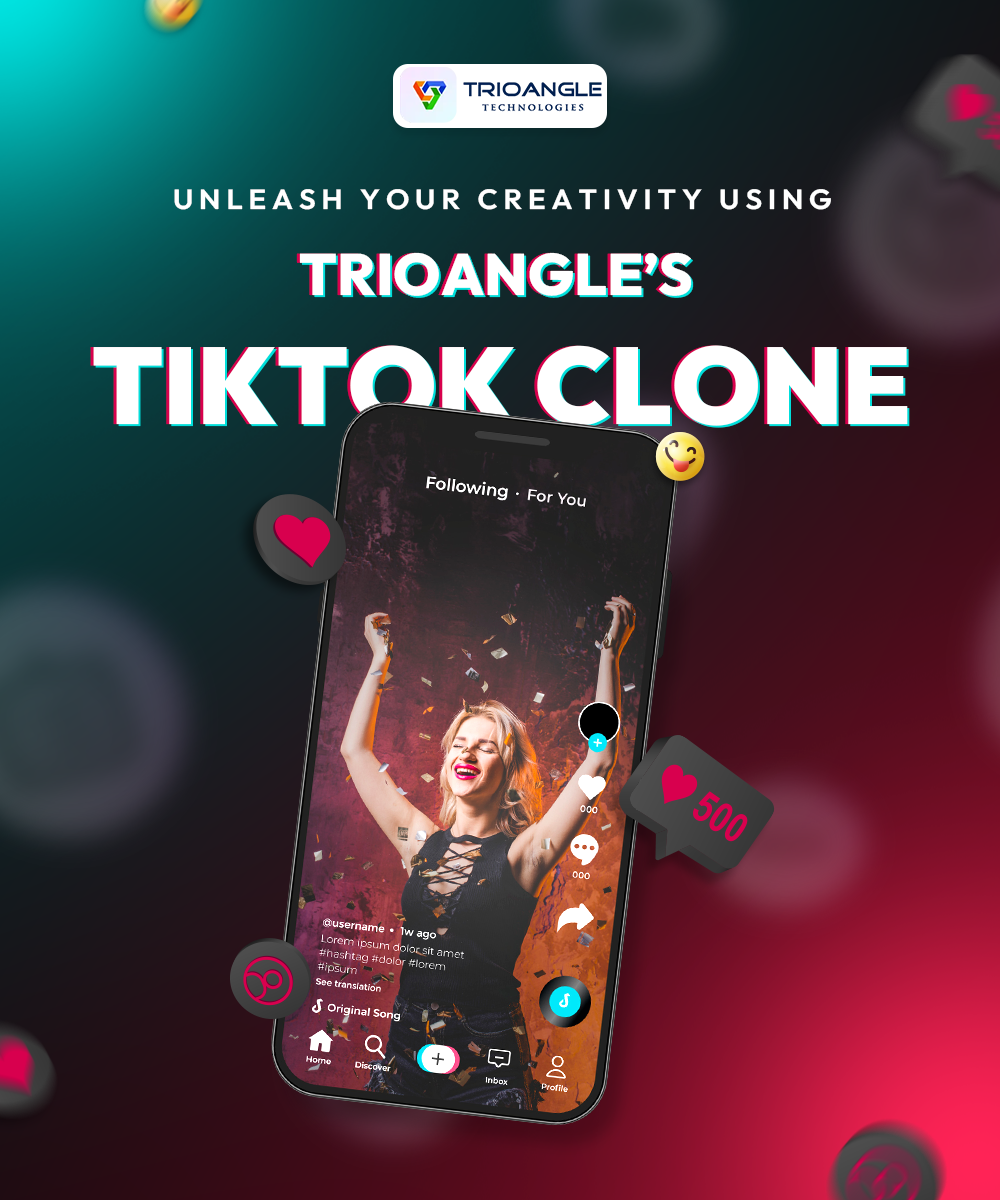
Unleash your creativity using Trioangle’s TikTok clone
Create, share, and monetize your passion with Trioangle’s TikTok clone app 🚀 that supports vivid video effects, trending challenges, and seamless social integration.
To Know More: https://www.trioangle.com/...
WhatsApp - +91 63796 30152
Email ID - salestrioangle.com
Telegram- https://t.me/Trioangle_Tec...
#tiktokclone #TikTokCloneApp #tiktokclonescript #TikTokLikeApp #ShortVideoApp #VideoSharingApp #SocialMediaApp #AppDevelopment #TikTokAlternative #creatorapp #VideoPlatform #MobileAppDevelopment
Create, share, and monetize your passion with Trioangle’s TikTok clone app 🚀 that supports vivid video effects, trending challenges, and seamless social integration.
To Know More: https://www.trioangle.com/...
WhatsApp - +91 63796 30152
Email ID - salestrioangle.com
Telegram- https://t.me/Trioangle_Tec...
#tiktokclone #TikTokCloneApp #tiktokclonescript #TikTokLikeApp #ShortVideoApp #VideoSharingApp #SocialMediaApp #AppDevelopment #TikTokAlternative #creatorapp #VideoPlatform #MobileAppDevelopment
2 months ago
2 months ago
Creativity has more to do with the elimination of the
inessential than with inventing something new.
- Helmut Jahn
inessential than with inventing something new.
- Helmut Jahn
2 months ago
May your mind whirl joyful cartwheels of creativity.
Asking "What IF" is the essence of creativity.
It Takes a Creative Mind to Ask the Right Questions.
- Jonathan Lockwood Huie
Asking "What IF" is the essence of creativity.
It Takes a Creative Mind to Ask the Right Questions.
- Jonathan Lockwood Huie
3 months ago
Decorate Naturally with Artistic Stone Garden Statues
Enhance the beauty of your outdoor space with artistic stone g arden statues that bring elegance, peace, and timeless charm to your surroundings. Handcrafted by skilled artisans at OdishaKraft, these statues add a natural touch while reflecting tradition and creativity. Whether for lawns, patios, or spiritual corners, stone statues create a serene atmosphere that blends perfectly with nature. Explore OdishaKraft’s wide collection of unique designs to elevate your garden. Add character and lasting beauty today with exquisite stone garden statues.
Shop now at- https://www.odishakraft.co...
#stonestatue , #gardenstatue , #stonegardenstatue
Enhance the beauty of your outdoor space with artistic stone g arden statues that bring elegance, peace, and timeless charm to your surroundings. Handcrafted by skilled artisans at OdishaKraft, these statues add a natural touch while reflecting tradition and creativity. Whether for lawns, patios, or spiritual corners, stone statues create a serene atmosphere that blends perfectly with nature. Explore OdishaKraft’s wide collection of unique designs to elevate your garden. Add character and lasting beauty today with exquisite stone garden statues.
Shop now at- https://www.odishakraft.co...
#stonestatue , #gardenstatue , #stonegardenstatue
3 months ago
Hiring a Dedicated Game Developer: Top Reasons and Complete Insights
Discover why hiring a dedicated game developer ensures faster development, cost savings, better creativity, and high-quality gameplay. for more: https://duplextech.com/blo...
Discover why hiring a dedicated game developer ensures faster development, cost savings, better creativity, and high-quality gameplay. for more: https://duplextech.com/blo...
3 months ago
From Strong Idea to Trusted Meme Coin - Beleaf Technologies
A successful meme coin blends creativity, strategy, and flawless execution. We provide everything you need to turn your concept into a trusted digital asset with lasting impact.
Our Services Include:
Innovative concept and tokenomics planning
Blockchain choice and smart contract creation
Secure wallet integration and liquidity setup
Distinctive branding, logo, and website design
Exchange listing assistance and community growth support
We make your meme coin unique, secure, and ready to capture attention.
Get a Free Consultation !
Visit Us >>>> https://www.beleaftechnolo...
Let’s Talk >>>> WhatsApp: +91 7904323274
Telegram: BeleafSoftTech
Email: businessbeleaftechnologies.com
A successful meme coin blends creativity, strategy, and flawless execution. We provide everything you need to turn your concept into a trusted digital asset with lasting impact.
Our Services Include:
Innovative concept and tokenomics planning
Blockchain choice and smart contract creation
Secure wallet integration and liquidity setup
Distinctive branding, logo, and website design
Exchange listing assistance and community growth support
We make your meme coin unique, secure, and ready to capture attention.
Get a Free Consultation !
Visit Us >>>> https://www.beleaftechnolo...
Let’s Talk >>>> WhatsApp: +91 7904323274
Telegram: BeleafSoftTech
Email: businessbeleaftechnologies.com
4 months ago
What They Don’t Teach You About Artificial Intelligence and Jobs
(Unspoken Truths | Future of Work, Adaptability & Economic Shifts)
They told you to get a degree, follow the rules, and climb the career ladder.
But they didn’t teach you how AI would reshape entire industries, shift job markets, and challenge everything we thought we knew about employment.
Let’s talk about what they don’t teach you:
The future of work isn’t about competing with AI — it’s about learning how to work with it.
WHAT THEY DON’T TEACH YOU:
1. AI Isn’t Coming for All Jobs — But It’s Reshaping Every Job
AI won’t replace everyone — but it will change:
-How we work
-What we value
-Who stays relevant
-Jobs won’t disappear overnight — they’ll evolve, or dissolve.
2. Routine Tasks Are the First to Go — Creativity and Empathy Are the Last to Fall
Jobs heavy in repetition are the most at risk:
-Data entry
-Basic coding
Customer service
But skills like problem-solving, creativity, emotional intelligence, and storytelling will stay in demand.
Soft skills are the new hard currency.
3. You’re Not Safe Just Because You Have a “Good Degree”
AI doesn’t care what school you went to.
It cares if you’re adaptable, tech-literate, and continuously learning.
Your real edge = human skills + tech fluency + reinvention.
4. Learning to Use AI Is More Valuable Than Fearing It
People who embrace tools like ChatGPT, automation platforms, and machine learning in their roles…
-Will outperform those who resist it.
-Become AI-assisted, not AI-replaced.
5. Being “Replaceable” Isn’t About the Job — It’s About the Mindset
If you stop growing, questioning, and upskilling — even a creative role becomes outdated.
Lifelong learning isn’t optional anymore — it’s survival.
6. New Careers Will Be Born That Don’t Exist Yet
Think of roles like:
-Prompt engineer
-AI ethicist
-Human-machine collaboration designer
-Disruption creates opportunity — if you stay curious and flexible.
7. The Future Isn’t Just Tech — It’s Human-Tech Balance
As AI takes over logic and speed, humans are needed for:
-Wisdom
-Context
-Emotion
-Ethics
In a world of machines, being deeply human becomes your superpower.
8. Governments and Schools Aren’t Preparing People Fast Enough
By the time many systems adjust, the workforce gap may already be wide.
Your education is your responsibility — don’t wait for the system to catch up.
- FUTURE-READY WORK MINDSET CHECKLIST:
Am I learning how to use AI in my field — not avoiding it?
-Do I focus on irreplaceable human skills (creativity, empathy, judgment)?
- Am I open to switching careers or reinventing myself if needed?
-Do I stay updated on tech trends and workforce shifts?
- Am I building a portfolio of skills, not just a resume of titles?
FINAL THOUGHT:
They didn’t teach you about the impact of AI on jobs — because they didn’t see it coming either.
But now you know:
Your job isn’t to fear AI. It’s to understand how to lead with what AI can’t replace.
The future doesn’t belong to machines. It belongs to those who learn to thrive alongside them.
(Unspoken Truths | Future of Work, Adaptability & Economic Shifts)
They told you to get a degree, follow the rules, and climb the career ladder.
But they didn’t teach you how AI would reshape entire industries, shift job markets, and challenge everything we thought we knew about employment.
Let’s talk about what they don’t teach you:
The future of work isn’t about competing with AI — it’s about learning how to work with it.
WHAT THEY DON’T TEACH YOU:
1. AI Isn’t Coming for All Jobs — But It’s Reshaping Every Job
AI won’t replace everyone — but it will change:
-How we work
-What we value
-Who stays relevant
-Jobs won’t disappear overnight — they’ll evolve, or dissolve.
2. Routine Tasks Are the First to Go — Creativity and Empathy Are the Last to Fall
Jobs heavy in repetition are the most at risk:
-Data entry
-Basic coding
Customer service
But skills like problem-solving, creativity, emotional intelligence, and storytelling will stay in demand.
Soft skills are the new hard currency.
3. You’re Not Safe Just Because You Have a “Good Degree”
AI doesn’t care what school you went to.
It cares if you’re adaptable, tech-literate, and continuously learning.
Your real edge = human skills + tech fluency + reinvention.
4. Learning to Use AI Is More Valuable Than Fearing It
People who embrace tools like ChatGPT, automation platforms, and machine learning in their roles…
-Will outperform those who resist it.
-Become AI-assisted, not AI-replaced.
5. Being “Replaceable” Isn’t About the Job — It’s About the Mindset
If you stop growing, questioning, and upskilling — even a creative role becomes outdated.
Lifelong learning isn’t optional anymore — it’s survival.
6. New Careers Will Be Born That Don’t Exist Yet
Think of roles like:
-Prompt engineer
-AI ethicist
-Human-machine collaboration designer
-Disruption creates opportunity — if you stay curious and flexible.
7. The Future Isn’t Just Tech — It’s Human-Tech Balance
As AI takes over logic and speed, humans are needed for:
-Wisdom
-Context
-Emotion
-Ethics
In a world of machines, being deeply human becomes your superpower.
8. Governments and Schools Aren’t Preparing People Fast Enough
By the time many systems adjust, the workforce gap may already be wide.
Your education is your responsibility — don’t wait for the system to catch up.
- FUTURE-READY WORK MINDSET CHECKLIST:
Am I learning how to use AI in my field — not avoiding it?
-Do I focus on irreplaceable human skills (creativity, empathy, judgment)?
- Am I open to switching careers or reinventing myself if needed?
-Do I stay updated on tech trends and workforce shifts?
- Am I building a portfolio of skills, not just a resume of titles?
FINAL THOUGHT:
They didn’t teach you about the impact of AI on jobs — because they didn’t see it coming either.
But now you know:
Your job isn’t to fear AI. It’s to understand how to lead with what AI can’t replace.
The future doesn’t belong to machines. It belongs to those who learn to thrive alongside them.
4 months ago
Focus Africa-
How does reliance on imports limit opportunities for youth entrepreneurship, innovation, and skills development?
Reliance on imports significantly limits opportunities for youth entrepreneurship, innovation, and skills development by eliminating the very sectors where these opportunities would naturally arise.
Instead of being creators and producers, young people are relegated to roles in retail and distribution, with far less potential for growth and advancement.
Impact on Entrepreneurship
A flood of cheap imports makes it incredibly difficult for young entrepreneurs to start businesses in manufacturing and production. The capital required to set up a factory or workshop can't compete with the massive economies of scale enjoyed by foreign producers. This discourages young people from even attempting to enter these sectors, as the risk of failure is too high. Instead, they are pushed into less productive sectors, like becoming distributors or retailers for the very goods that are undercutting local production.
Hindrance to Innovation
Innovation often stems from the practical challenges and opportunities within a production process. When there's no local manufacturing base, there are fewer problems to solve and fewer products to improve. This creates a knowledge gap, as young people don't get the hands-on experience of designing, building, and refining goods. The entire ecosystem for innovation—from product development to marketing—is outsourced, leaving little room for local creativity or technological advancement.
Stifled Skills Development
A strong industrial sector is a key driver of skills development. It provides opportunities for apprenticeships, on-the-job training, and the acquisition of technical skills like engineering, welding, and electronics repair. When these industries disappear due to import competition, so do the opportunities for young people to acquire these valuable skills. This creates a vicious cycle where a lack of skilled labor makes local production even less competitive, further reinforcing the reliance on imports.
How does reliance on imports limit opportunities for youth entrepreneurship, innovation, and skills development?
Reliance on imports significantly limits opportunities for youth entrepreneurship, innovation, and skills development by eliminating the very sectors where these opportunities would naturally arise.
Instead of being creators and producers, young people are relegated to roles in retail and distribution, with far less potential for growth and advancement.
Impact on Entrepreneurship
A flood of cheap imports makes it incredibly difficult for young entrepreneurs to start businesses in manufacturing and production. The capital required to set up a factory or workshop can't compete with the massive economies of scale enjoyed by foreign producers. This discourages young people from even attempting to enter these sectors, as the risk of failure is too high. Instead, they are pushed into less productive sectors, like becoming distributors or retailers for the very goods that are undercutting local production.
Hindrance to Innovation
Innovation often stems from the practical challenges and opportunities within a production process. When there's no local manufacturing base, there are fewer problems to solve and fewer products to improve. This creates a knowledge gap, as young people don't get the hands-on experience of designing, building, and refining goods. The entire ecosystem for innovation—from product development to marketing—is outsourced, leaving little room for local creativity or technological advancement.
Stifled Skills Development
A strong industrial sector is a key driver of skills development. It provides opportunities for apprenticeships, on-the-job training, and the acquisition of technical skills like engineering, welding, and electronics repair. When these industries disappear due to import competition, so do the opportunities for young people to acquire these valuable skills. This creates a vicious cycle where a lack of skilled labor makes local production even less competitive, further reinforcing the reliance on imports.
4 months ago
"What they don't teach you" on religion- For the general public: Why is religious literacy crucial for peaceful coexistence and informed civic engagement in a diverse world?
The question of "What they don't teach you" about religion, particularly for the general public, directly hits upon why religious literacy is not just a niche academic interest but an absolutely crucial skill for peaceful coexistence and informed civic engagement in our diverse, interconnected world.
Here's why:
1. Fostering Peaceful Coexistence: Bridging Divides and Reducing Conflict
Deconstructing Stereotypes and Prejudice:
What's Often Taught (or Inferred): Simplistic, often media-driven caricatures of religious groups (e.g., all Muslims are extremists, all Christians are judgmental, all atheists are immoral).
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The vast internal diversity within every major religion (different sects, denominations, interpretations, cultural expressions), the existence of peaceful and compassionate majority adherents, and the historical and political factors that often fuel extremism more than theology itself.
Why it's Crucial: Without this, the general public falls prey to misinformation and prejudice. Religious literacy allows individuals to look beyond headlines, challenge harmful stereotypes, and recognize the humanity in those with different beliefs. This directly reduces the likelihood of "othering," discrimination, and religiously-motivated violence or tension.
Understanding the Roots of Global Conflict:
What's Often Taught: Geopolitical conflicts are presented primarily through political, economic, or nationalistic lenses.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The deep and often complex ways religious identity, historical grievances, theological interpretations, and religious leadership intertwine with political and economic factors to drive or exacerbate conflicts globally (e.g., in the Middle East, South Asia, parts of Africa).
Why it's Crucial: To genuinely understand and respond to global crises, the public needs to grasp the religious dimensions at play. Ignoring them leads to ineffective policies, misjudged interventions, and a perpetuation of conflict due to a lack of fundamental understanding of the actors' motivations and worldviews.
Promoting Effective Interfaith Dialogue:
What's Often Taught: Little about other religions beyond basic facts, leading to a perception that different faiths are fundamentally incompatible.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The common ethical concerns, shared human experiences, and often similar underlying quests for meaning that exist across diverse religious and secular traditions. Also, how to engage in respectful dialogue without proselytizing or being dismissive.
Why it's Crucial: In pluralistic societies, friction is inevitable without dialogue. Religious literacy provides the tools to engage across belief systems, find common ground on shared values (e.g., justice, compassion, care for the environment), and work together on community issues, fostering social cohesion.
2. Informed Civic Engagement: Navigating a Complex Society
Understanding Domestic Politics and Policy Debates:
What's Often Taught: Political issues are framed as purely secular matters of policy and economics.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The powerful role of religious lobbying groups, the influence of faith-based organizations on social policy (e.g., healthcare, education, social welfare), and how religious values inform voters' choices and politicians' positions on a vast array of issues (e.g., abortion, LGBTQ+ rights, environmental regulations, foreign aid).
Why it's Crucial: A religiously illiterate public cannot fully grasp the motivations behind certain political movements or legislative efforts. They may misinterpret policy debates or be unable to critically evaluate the arguments presented, hindering their ability to vote and participate effectively in a democracy.
Navigating Rights and Responsibilities in a Pluralistic Society:
What's Often Taught: Basic concepts of freedom of speech and religion.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The complexities of religious freedom (e.g., balancing individual religious rights with public good, "reasonable accommodation" vs. discrimination), the historical evolution of church-state separation, and the diverse ways different societies approach religion in the public square.
Why it's Crucial: The general public needs to understand why certain religious groups act or advocate in particular ways, and how their rights intersect with the rights of others. This is essential for preventing clashes over public space, school curricula, workplace policies, and ultimately, for upholding a truly inclusive and equitable society.
Critical Media Literacy:
What's Often Taught: How to identify basic bias in news.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): How religious narratives are often oversimplified, sensationalized, or misinterpreted in media coverage; how to discern between genuine religious expression and the political manipulation of religious identity.
Why it's Crucial: In an age of widespread misinformation, religious literacy empowers individuals to critically evaluate news stories, recognize loaded language, and demand more nuanced reporting on religious issues, protecting them from being swayed by harmful narratives.
Appreciating Cultural Heritage and Diversity:
What's Often Taught: Culture is often presented broadly, without diving into its foundational elements.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The immense influence of religion on art, architecture, music, literature, holidays, and social customs around the world.
Why it's Crucial: Understanding this enriches cultural appreciation, whether visiting a historic site, reading a classic novel, or participating in a festival. It allows the public to appreciate the depth and beauty of human creativity and tradition, fostering a richer civic life and more respectful interactions with diverse communities.
In conclusion, for the general public, religious literacy moves beyond mere curiosity; it is a practical necessity for navigating the complexities of modern life. It equips individuals with the understanding, empathy, and critical thinking skills needed to contribute to a society that is not only tolerant but genuinely capable of peaceful coexistence and robust, informed democratic engagement in a truly diverse world.
The question of "What they don't teach you" about religion, particularly for the general public, directly hits upon why religious literacy is not just a niche academic interest but an absolutely crucial skill for peaceful coexistence and informed civic engagement in our diverse, interconnected world.
Here's why:
1. Fostering Peaceful Coexistence: Bridging Divides and Reducing Conflict
Deconstructing Stereotypes and Prejudice:
What's Often Taught (or Inferred): Simplistic, often media-driven caricatures of religious groups (e.g., all Muslims are extremists, all Christians are judgmental, all atheists are immoral).
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The vast internal diversity within every major religion (different sects, denominations, interpretations, cultural expressions), the existence of peaceful and compassionate majority adherents, and the historical and political factors that often fuel extremism more than theology itself.
Why it's Crucial: Without this, the general public falls prey to misinformation and prejudice. Religious literacy allows individuals to look beyond headlines, challenge harmful stereotypes, and recognize the humanity in those with different beliefs. This directly reduces the likelihood of "othering," discrimination, and religiously-motivated violence or tension.
Understanding the Roots of Global Conflict:
What's Often Taught: Geopolitical conflicts are presented primarily through political, economic, or nationalistic lenses.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The deep and often complex ways religious identity, historical grievances, theological interpretations, and religious leadership intertwine with political and economic factors to drive or exacerbate conflicts globally (e.g., in the Middle East, South Asia, parts of Africa).
Why it's Crucial: To genuinely understand and respond to global crises, the public needs to grasp the religious dimensions at play. Ignoring them leads to ineffective policies, misjudged interventions, and a perpetuation of conflict due to a lack of fundamental understanding of the actors' motivations and worldviews.
Promoting Effective Interfaith Dialogue:
What's Often Taught: Little about other religions beyond basic facts, leading to a perception that different faiths are fundamentally incompatible.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The common ethical concerns, shared human experiences, and often similar underlying quests for meaning that exist across diverse religious and secular traditions. Also, how to engage in respectful dialogue without proselytizing or being dismissive.
Why it's Crucial: In pluralistic societies, friction is inevitable without dialogue. Religious literacy provides the tools to engage across belief systems, find common ground on shared values (e.g., justice, compassion, care for the environment), and work together on community issues, fostering social cohesion.
2. Informed Civic Engagement: Navigating a Complex Society
Understanding Domestic Politics and Policy Debates:
What's Often Taught: Political issues are framed as purely secular matters of policy and economics.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The powerful role of religious lobbying groups, the influence of faith-based organizations on social policy (e.g., healthcare, education, social welfare), and how religious values inform voters' choices and politicians' positions on a vast array of issues (e.g., abortion, LGBTQ+ rights, environmental regulations, foreign aid).
Why it's Crucial: A religiously illiterate public cannot fully grasp the motivations behind certain political movements or legislative efforts. They may misinterpret policy debates or be unable to critically evaluate the arguments presented, hindering their ability to vote and participate effectively in a democracy.
Navigating Rights and Responsibilities in a Pluralistic Society:
What's Often Taught: Basic concepts of freedom of speech and religion.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The complexities of religious freedom (e.g., balancing individual religious rights with public good, "reasonable accommodation" vs. discrimination), the historical evolution of church-state separation, and the diverse ways different societies approach religion in the public square.
Why it's Crucial: The general public needs to understand why certain religious groups act or advocate in particular ways, and how their rights intersect with the rights of others. This is essential for preventing clashes over public space, school curricula, workplace policies, and ultimately, for upholding a truly inclusive and equitable society.
Critical Media Literacy:
What's Often Taught: How to identify basic bias in news.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): How religious narratives are often oversimplified, sensationalized, or misinterpreted in media coverage; how to discern between genuine religious expression and the political manipulation of religious identity.
Why it's Crucial: In an age of widespread misinformation, religious literacy empowers individuals to critically evaluate news stories, recognize loaded language, and demand more nuanced reporting on religious issues, protecting them from being swayed by harmful narratives.
Appreciating Cultural Heritage and Diversity:
What's Often Taught: Culture is often presented broadly, without diving into its foundational elements.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The immense influence of religion on art, architecture, music, literature, holidays, and social customs around the world.
Why it's Crucial: Understanding this enriches cultural appreciation, whether visiting a historic site, reading a classic novel, or participating in a festival. It allows the public to appreciate the depth and beauty of human creativity and tradition, fostering a richer civic life and more respectful interactions with diverse communities.
In conclusion, for the general public, religious literacy moves beyond mere curiosity; it is a practical necessity for navigating the complexities of modern life. It equips individuals with the understanding, empathy, and critical thinking skills needed to contribute to a society that is not only tolerant but genuinely capable of peaceful coexistence and robust, informed democratic engagement in a truly diverse world.
4 months ago
How can Nigeria bridge the gap between education and employable skills?
Bridging the gap between education and employable skills in Nigeria is a critical challenge that requires a holistic and multi-pronged approach involving government, educational institutions, the private sector, and civil society.
The current system often produces graduates ill-equipped for the demands of the modern job market, leading to high youth unemployment.
Here's how Nigeria can effectively bridge this gap:
I. Curriculum Reform & Relevance:
Industry-Driven Curriculum Development:
Regular Review & Updates: Curricula at all levels (primary, secondary, tertiary, and TVET) must be regularly reviewed and updated in close collaboration with industry experts, employers, and professional bodies. This ensures that what is taught aligns directly with the skills demanded by the job market.
Competency-Based Learning: Shift the focus from rote memorization and theoretical knowledge to competency-based education. This means assessing students on their ability to apply knowledge and skills to real-world problems.
Inclusion of 21st-Century Skills: Integrate critical thinking, problem-solving, creativity, communication, collaboration, digital literacy, and data analysis across all disciplines. These "soft skills" are highly valued by employers.
Emphasis on STEM and Digital Skills:
Strengthen Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) Education: Invest heavily in STEM education from an early age, ensuring adequate laboratories, equipment, and qualified teachers.
Digital Literacy: Make digital literacy a foundational skill across all levels of education. Introduce coding, data analytics, cybersecurity, and AI/Machine Learning at appropriate stages. Initiatives like NITDA's 3MTT (Three Million Technical Talent) are good starts but need massive scaling.
Mandatory Entrepreneurship Education:
Integrate practical entrepreneurship education into all tertiary curricula. This should go beyond theoretical concepts to include business plan development, mentorship, access to seed funding (even if small), and incubation support. The goal is to produce job creators, not just job seekers.
II. Strengthen Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET):
Rebranding and Destigmatization:
Launch nationwide campaigns to change the societal perception of TVET. Highlight successful TVET graduates, showcase the lucrative nature of skilled trades (e.g., plumbing, welding, carpentry, ICT repairs), and emphasize their vital role in economic development. Combat the notion that TVET is for "school dropouts."
Increased Investment and Modernization:
Adequately fund TVET institutions with modern tools, equipment, workshops, and technology that reflect current industry standards.
Upgrade and maintain existing polytechnics, technical colleges, and vocational centers.
Industry-Led TVET:
Ensure that TVET programs are directly developed and run in partnership with industries. Companies should be involved in curriculum design, practical training, and certification.
Promote apprenticeships and on-the-job training programs, where students learn practical skills directly in a workplace setting.
III. Enhance Industry-Academia Collaboration:
Structured Partnerships:
MOU and Joint Projects: Facilitate Memoranda of Understanding (MOUs) between universities/polytechnics and industries for joint research projects, curriculum development, and student internships.
Research & Development (R&D): Encourage industries to fund university research that addresses their specific needs and challenges, creating a symbiotic relationship.
Advisory Boards: Establish industry advisory boards for academic departments to provide direct input on curriculum, necessary skills, and emerging trends.
Internship and Apprenticeship Programs:
Make internships (Industrial Attachment) mandatory, well-structured, and adequately supervised. Ensure students gain relevant, hands-on experience that aligns with their studies.
Incentivize companies (e.g., through tax breaks) to offer quality internships and apprenticeships.
Guest Lecturers and Adjunct Faculty:
Invite industry professionals to serve as guest lecturers, adjunct faculty, or mentors, bringing real-world experience into the classroom.
IV. Teacher Training and Professional Development:-
Skills-Focused Pedagogy:
Train educators at all levels to adopt practical, problem-solving, and project-based teaching methodologies that foster skill development rather than rote learning.
Equip teachers with the skills to integrate technology effectively into their teaching.
Continuous Professional Development:
Provide ongoing training for teachers and lecturers to keep them updated on industry trends, new technologies, and modern pedagogical approaches.
Encourage lecturers to undertake sabbaticals in relevant industries to gain practical experience.
Industry Experience for Educators:
Implement programs that allow academic staff to spend time in relevant industries, gaining practical experience that they can then bring back to the classroom.
V. Leverage Technology and Digital Learning:
E-Learning Platforms:
Invest in robust e-learning platforms and digital resources to complement traditional classroom learning, making education more accessible and flexible.
Promote blended learning models that combine online and in-person instruction.
Access to ICT Infrastructure:
Address the challenges of internet connectivity and reliable power supply, especially in rural areas, to ensure equitable access to digital learning tools.
Provide affordable digital devices to students and educators.
Virtual Labs and Simulations:
Utilize virtual laboratories and simulation software to provide practical experience where physical equipment is limited or too expensive.
VI. Government Policies & Funding:
Increased and Targeted Funding:
Significantly increase the budget allocation to education, specifically earmarking funds for curriculum reform, TVET modernization, industry collaboration initiatives, and teacher training.
Ensure transparent and accountable use of these funds.
Policy Cohesion:
Develop a coherent national education policy that links educational outcomes directly to labor market needs, with clear implementation strategies and monitoring mechanisms.
Avoid frequent policy changes that disrupt progress.
Incentives for Private Sector Engagement:
Offer tax incentives, grants, or subsidies to private companies that invest in skills development, apprenticeships, or collaborate with educational institutions.
Strengthen Career Guidance & Counseling:
Implement effective career guidance and counseling services in schools and universities to help students make informed choices about their academic and career paths, aligning their interests with market demands.
By addressing these areas comprehensively, Nigeria can transform its educational system into a powerful engine for skill development, producing a workforce that is not only educated but also highly employable and capable of driving economic growth and innovation.
Bridging the gap between education and employable skills in Nigeria is a critical challenge that requires a holistic and multi-pronged approach involving government, educational institutions, the private sector, and civil society.
The current system often produces graduates ill-equipped for the demands of the modern job market, leading to high youth unemployment.
Here's how Nigeria can effectively bridge this gap:
I. Curriculum Reform & Relevance:
Industry-Driven Curriculum Development:
Regular Review & Updates: Curricula at all levels (primary, secondary, tertiary, and TVET) must be regularly reviewed and updated in close collaboration with industry experts, employers, and professional bodies. This ensures that what is taught aligns directly with the skills demanded by the job market.
Competency-Based Learning: Shift the focus from rote memorization and theoretical knowledge to competency-based education. This means assessing students on their ability to apply knowledge and skills to real-world problems.
Inclusion of 21st-Century Skills: Integrate critical thinking, problem-solving, creativity, communication, collaboration, digital literacy, and data analysis across all disciplines. These "soft skills" are highly valued by employers.
Emphasis on STEM and Digital Skills:
Strengthen Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) Education: Invest heavily in STEM education from an early age, ensuring adequate laboratories, equipment, and qualified teachers.
Digital Literacy: Make digital literacy a foundational skill across all levels of education. Introduce coding, data analytics, cybersecurity, and AI/Machine Learning at appropriate stages. Initiatives like NITDA's 3MTT (Three Million Technical Talent) are good starts but need massive scaling.
Mandatory Entrepreneurship Education:
Integrate practical entrepreneurship education into all tertiary curricula. This should go beyond theoretical concepts to include business plan development, mentorship, access to seed funding (even if small), and incubation support. The goal is to produce job creators, not just job seekers.
II. Strengthen Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET):
Rebranding and Destigmatization:
Launch nationwide campaigns to change the societal perception of TVET. Highlight successful TVET graduates, showcase the lucrative nature of skilled trades (e.g., plumbing, welding, carpentry, ICT repairs), and emphasize their vital role in economic development. Combat the notion that TVET is for "school dropouts."
Increased Investment and Modernization:
Adequately fund TVET institutions with modern tools, equipment, workshops, and technology that reflect current industry standards.
Upgrade and maintain existing polytechnics, technical colleges, and vocational centers.
Industry-Led TVET:
Ensure that TVET programs are directly developed and run in partnership with industries. Companies should be involved in curriculum design, practical training, and certification.
Promote apprenticeships and on-the-job training programs, where students learn practical skills directly in a workplace setting.
III. Enhance Industry-Academia Collaboration:
Structured Partnerships:
MOU and Joint Projects: Facilitate Memoranda of Understanding (MOUs) between universities/polytechnics and industries for joint research projects, curriculum development, and student internships.
Research & Development (R&D): Encourage industries to fund university research that addresses their specific needs and challenges, creating a symbiotic relationship.
Advisory Boards: Establish industry advisory boards for academic departments to provide direct input on curriculum, necessary skills, and emerging trends.
Internship and Apprenticeship Programs:
Make internships (Industrial Attachment) mandatory, well-structured, and adequately supervised. Ensure students gain relevant, hands-on experience that aligns with their studies.
Incentivize companies (e.g., through tax breaks) to offer quality internships and apprenticeships.
Guest Lecturers and Adjunct Faculty:
Invite industry professionals to serve as guest lecturers, adjunct faculty, or mentors, bringing real-world experience into the classroom.
IV. Teacher Training and Professional Development:-
Skills-Focused Pedagogy:
Train educators at all levels to adopt practical, problem-solving, and project-based teaching methodologies that foster skill development rather than rote learning.
Equip teachers with the skills to integrate technology effectively into their teaching.
Continuous Professional Development:
Provide ongoing training for teachers and lecturers to keep them updated on industry trends, new technologies, and modern pedagogical approaches.
Encourage lecturers to undertake sabbaticals in relevant industries to gain practical experience.
Industry Experience for Educators:
Implement programs that allow academic staff to spend time in relevant industries, gaining practical experience that they can then bring back to the classroom.
V. Leverage Technology and Digital Learning:
E-Learning Platforms:
Invest in robust e-learning platforms and digital resources to complement traditional classroom learning, making education more accessible and flexible.
Promote blended learning models that combine online and in-person instruction.
Access to ICT Infrastructure:
Address the challenges of internet connectivity and reliable power supply, especially in rural areas, to ensure equitable access to digital learning tools.
Provide affordable digital devices to students and educators.
Virtual Labs and Simulations:
Utilize virtual laboratories and simulation software to provide practical experience where physical equipment is limited or too expensive.
VI. Government Policies & Funding:
Increased and Targeted Funding:
Significantly increase the budget allocation to education, specifically earmarking funds for curriculum reform, TVET modernization, industry collaboration initiatives, and teacher training.
Ensure transparent and accountable use of these funds.
Policy Cohesion:
Develop a coherent national education policy that links educational outcomes directly to labor market needs, with clear implementation strategies and monitoring mechanisms.
Avoid frequent policy changes that disrupt progress.
Incentives for Private Sector Engagement:
Offer tax incentives, grants, or subsidies to private companies that invest in skills development, apprenticeships, or collaborate with educational institutions.
Strengthen Career Guidance & Counseling:
Implement effective career guidance and counseling services in schools and universities to help students make informed choices about their academic and career paths, aligning their interests with market demands.
By addressing these areas comprehensively, Nigeria can transform its educational system into a powerful engine for skill development, producing a workforce that is not only educated but also highly employable and capable of driving economic growth and innovation.
8 months ago
💡 Creativity: The Rebellion That Sparks Innovation! 🔥
Creativity isn’t just thinking outside the box—it’s breaking the box entirely.
Yet, what holds most people back?
🚧 “What if I fail?”
🚧 “Is this even worth my time?”
The truth? Fear of failure kills more dreams than failure ever will.
💎 That’s why the wealthiest minds invest in art—the purest form of human expression.
🎨 The simplest ideas often hold the most value—because true creativity isn’t about complexity, but boldness.
Want to unlock your creative potential?
🧠 Step back from overthinking—the best ideas emerge when you least expect them.
💡 Embrace the weird & unexpected—innovation thrives where rules are rewritten.
🚀 Dare to take risks—every breakthrough starts with a leap into the unknown.
Creativity flourishes when you stop asking for permission.
💬 What’s your secret to unlocking creativity?
Drop a comment below!👇
Creativity isn’t just thinking outside the box—it’s breaking the box entirely.
Yet, what holds most people back?
🚧 “What if I fail?”
🚧 “Is this even worth my time?”
The truth? Fear of failure kills more dreams than failure ever will.
💎 That’s why the wealthiest minds invest in art—the purest form of human expression.
🎨 The simplest ideas often hold the most value—because true creativity isn’t about complexity, but boldness.
Want to unlock your creative potential?
🧠 Step back from overthinking—the best ideas emerge when you least expect them.
💡 Embrace the weird & unexpected—innovation thrives where rules are rewritten.
🚀 Dare to take risks—every breakthrough starts with a leap into the unknown.
Creativity flourishes when you stop asking for permission.
💬 What’s your secret to unlocking creativity?
Drop a comment below!👇
1 yr. ago
World Economy-
How do technological advancements, like AI and automation, shape economic structures and job markets?
By Hugo Keji
Technological advancements, particularly in artificial intelligence (AI) and automation, are profoundly reshaping economic structures and job markets.
These technologies bring significant benefits, such as increased productivity and efficiency, but also pose challenges, including job displacement and income inequality.
Here’s how AI and automation are influencing the economy and the labor market:
1. Transformation of Economic Structures
A. Increased Productivity and Efficiency
Automation of Repetitive Tasks: AI and automation can handle repetitive and routine tasks more efficiently than humans, leading to significant productivity gains across various industries.
For example, manufacturing processes, data entry, and customer service can be automated, reducing costs and increasing output.
Optimized Decision-Making: AI systems can analyze vast amounts of data to optimize business processes, improve decision-making, and predict market trends.
This leads to more efficient allocation of resources and better overall economic performance.
B. Shift in Industry Focus
Growth of Tech-Driven Sectors: Industries that develop, implement, or rely on AI and automation, such as tech, finance, healthcare, and logistics, are experiencing rapid growth.
This shift is leading to a reallocation of economic resources and investment towards these high-tech sectors.
Decline of Traditional Industries: Some traditional industries, particularly those relying heavily on manual labor, may decline as automation reduces the need for human workers. This can lead to economic shifts where regions and economies reliant on these industries face economic challenges.
C. Globalization and Supply Chain Transformation
Reshoring and Localization: Automation reduces the need for cheap labor, leading some companies to bring manufacturing back to their home countries (reshoring) or localize production closer to markets.
This shift can change global supply chains and reduce reliance on offshore production.
New Global Trade Dynamics: As AI and automation advance, countries with strong technological infrastructures may dominate global trade, leading to new economic power dynamics.
Developing nations that previously relied on low-cost labor may need to adapt by investing in education and technology.
2. Impact on Job Markets
A. Job Displacement and Creation
Displacement of Routine Jobs: Jobs that involve repetitive tasks, such as assembly line work, data entry, or basic customer service, are most at risk of being automated.
This can lead to significant job displacement, particularly for workers in low-skill positions.
Creation of New Jobs: While some jobs are lost, AI and automation also create new job opportunities in fields such as AI development, robotics, data science, and cybersecurity. Additionally, roles that require complex problem-solving, creativity, and human interaction are less likely to be automated and may see increased demand.
B. Skill Shifts and Workforce Adaptation
Demand for Tech Skills: As AI and automation become more prevalent, there is a growing demand for workers with skills in programming, machine learning, data analysis, and other technology-related fields.
This shift requires workers to continually upgrade their skills through education and training.
Lifelong Learning and Retraining: The rapid pace of technological change necessitates a focus on lifelong learning. Governments, educational institutions, and employers must invest in retraining programs to help workers transition to new roles that require different skills.
C. Polarization of the Labor Market
High-Skill, High-Pay Jobs: Automation tends to create a demand for highly skilled jobs, often in technology and management, which are well compensated.
This can lead to increased opportunities and income for those with the right skills and education.
Low-Skill, Low-Pay Jobs: On the other end, jobs that cannot be automated but require lower skills, such as personal care, cleaning, and some service roles, may experience stagnation or even decline in wages.
This polarization can exacerbate income inequality.
3. Socioeconomic and Cultural Impacts
A. Income Inequality
Widening Wealth Gap: As high-skilled workers in tech-driven sectors see increased earnings, while low-skilled workers face job insecurity and wage stagnation, income inequality is likely to grow. This disparity can lead to social and economic tensions.
Concentration of Wealth: Companies that successfully integrate AI and automation can achieve significant productivity gains and profitability, potentially leading to a concentration of wealth among business owners and shareholders, further widening the wealth gap.
B. Changing Work Dynamics
Gig Economy Expansion: AI and automation are facilitating the growth of the gig economy, where workers engage in short-term, flexible jobs often facilitated by digital platforms.
While this offers flexibility, it can also lead to job insecurity and a lack of traditional employment benefits.
Remote Work and Digital Nomadism:
The rise of AI-driven tools and automation makes remote work more
feasible and efficient, allowing workers to work from anywhere. This shift could lead to changes in urbanization patterns, with some workers relocating to less expensive or more desirable locations.
C. Social and Ethical Challenges
Job Loss and Social Unrest: Significant job displacement due to automation can lead to social unrest if large segments of the population are unable to find new employment.
Governments may need to implement policies like social safety nets, retraining programs, and perhaps even universal basic income to address these challenges.
Ethical Considerations: The widespread use of AI raises ethical concerns, such as biases in AI algorithms, privacy issues, and the potential for AI to be used in surveillance or other harmful ways. Addressing these concerns is crucial for ensuring that AI and automation are used for the benefit of society.
4. Policy and Regulatory Responses
A. Education and Workforce Development
Focus on STEM Education: Governments and educational institutions should prioritize STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education to prepare the workforce for the demands of a tech-driven economy. Additionally, emphasis on creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills is essential.
Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between governments, businesses, and educational institutions is vital for developing and implementing training programs that meet the needs of the evolving job market.
B. Regulation of AI and Automation
Labor Market Regulations: Governments may need to update labor laws to address the unique challenges posed by AI and automation, such as ensuring fair wages, protecting workers' rights, and regulating gig work.
Ethical AI Governance: Implementing frameworks for the ethical use of AI, including transparency, accountability, and bias mitigation, is essential to ensure that these technologies are used responsibly and fairly.
C. Social Safety Nets
Universal Basic Income (UBI): Some policymakers advocate for UBI as a way to provide financial security in an economy where automation may reduce the availability of traditional jobs.
Expanded Social Programs: Strengthening social safety nets, including unemployment benefits, healthcare, and retraining initiatives, can help mitigate the negative impacts of job displacement and income inequality.
Technological advancements in AI and automation are reshaping economic structures and job markets, bringing both opportunities and challenges.
While they drive productivity and innovation, they also lead to job displacement, skill shifts, and income inequality.
To ensure that the benefits of these technologies are widely shared, governments, businesses, and educational institutions must collaborate to develop policies that promote inclusive growth, provide retraining opportunities, and address the ethical and social implications of AI and automation.
How do technological advancements, like AI and automation, shape economic structures and job markets?
By Hugo Keji
Technological advancements, particularly in artificial intelligence (AI) and automation, are profoundly reshaping economic structures and job markets.
These technologies bring significant benefits, such as increased productivity and efficiency, but also pose challenges, including job displacement and income inequality.
Here’s how AI and automation are influencing the economy and the labor market:
1. Transformation of Economic Structures
A. Increased Productivity and Efficiency
Automation of Repetitive Tasks: AI and automation can handle repetitive and routine tasks more efficiently than humans, leading to significant productivity gains across various industries.
For example, manufacturing processes, data entry, and customer service can be automated, reducing costs and increasing output.
Optimized Decision-Making: AI systems can analyze vast amounts of data to optimize business processes, improve decision-making, and predict market trends.
This leads to more efficient allocation of resources and better overall economic performance.
B. Shift in Industry Focus
Growth of Tech-Driven Sectors: Industries that develop, implement, or rely on AI and automation, such as tech, finance, healthcare, and logistics, are experiencing rapid growth.
This shift is leading to a reallocation of economic resources and investment towards these high-tech sectors.
Decline of Traditional Industries: Some traditional industries, particularly those relying heavily on manual labor, may decline as automation reduces the need for human workers. This can lead to economic shifts where regions and economies reliant on these industries face economic challenges.
C. Globalization and Supply Chain Transformation
Reshoring and Localization: Automation reduces the need for cheap labor, leading some companies to bring manufacturing back to their home countries (reshoring) or localize production closer to markets.
This shift can change global supply chains and reduce reliance on offshore production.
New Global Trade Dynamics: As AI and automation advance, countries with strong technological infrastructures may dominate global trade, leading to new economic power dynamics.
Developing nations that previously relied on low-cost labor may need to adapt by investing in education and technology.
2. Impact on Job Markets
A. Job Displacement and Creation
Displacement of Routine Jobs: Jobs that involve repetitive tasks, such as assembly line work, data entry, or basic customer service, are most at risk of being automated.
This can lead to significant job displacement, particularly for workers in low-skill positions.
Creation of New Jobs: While some jobs are lost, AI and automation also create new job opportunities in fields such as AI development, robotics, data science, and cybersecurity. Additionally, roles that require complex problem-solving, creativity, and human interaction are less likely to be automated and may see increased demand.
B. Skill Shifts and Workforce Adaptation
Demand for Tech Skills: As AI and automation become more prevalent, there is a growing demand for workers with skills in programming, machine learning, data analysis, and other technology-related fields.
This shift requires workers to continually upgrade their skills through education and training.
Lifelong Learning and Retraining: The rapid pace of technological change necessitates a focus on lifelong learning. Governments, educational institutions, and employers must invest in retraining programs to help workers transition to new roles that require different skills.
C. Polarization of the Labor Market
High-Skill, High-Pay Jobs: Automation tends to create a demand for highly skilled jobs, often in technology and management, which are well compensated.
This can lead to increased opportunities and income for those with the right skills and education.
Low-Skill, Low-Pay Jobs: On the other end, jobs that cannot be automated but require lower skills, such as personal care, cleaning, and some service roles, may experience stagnation or even decline in wages.
This polarization can exacerbate income inequality.
3. Socioeconomic and Cultural Impacts
A. Income Inequality
Widening Wealth Gap: As high-skilled workers in tech-driven sectors see increased earnings, while low-skilled workers face job insecurity and wage stagnation, income inequality is likely to grow. This disparity can lead to social and economic tensions.
Concentration of Wealth: Companies that successfully integrate AI and automation can achieve significant productivity gains and profitability, potentially leading to a concentration of wealth among business owners and shareholders, further widening the wealth gap.
B. Changing Work Dynamics
Gig Economy Expansion: AI and automation are facilitating the growth of the gig economy, where workers engage in short-term, flexible jobs often facilitated by digital platforms.
While this offers flexibility, it can also lead to job insecurity and a lack of traditional employment benefits.
Remote Work and Digital Nomadism:
The rise of AI-driven tools and automation makes remote work more
feasible and efficient, allowing workers to work from anywhere. This shift could lead to changes in urbanization patterns, with some workers relocating to less expensive or more desirable locations.
C. Social and Ethical Challenges
Job Loss and Social Unrest: Significant job displacement due to automation can lead to social unrest if large segments of the population are unable to find new employment.
Governments may need to implement policies like social safety nets, retraining programs, and perhaps even universal basic income to address these challenges.
Ethical Considerations: The widespread use of AI raises ethical concerns, such as biases in AI algorithms, privacy issues, and the potential for AI to be used in surveillance or other harmful ways. Addressing these concerns is crucial for ensuring that AI and automation are used for the benefit of society.
4. Policy and Regulatory Responses
A. Education and Workforce Development
Focus on STEM Education: Governments and educational institutions should prioritize STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education to prepare the workforce for the demands of a tech-driven economy. Additionally, emphasis on creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills is essential.
Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between governments, businesses, and educational institutions is vital for developing and implementing training programs that meet the needs of the evolving job market.
B. Regulation of AI and Automation
Labor Market Regulations: Governments may need to update labor laws to address the unique challenges posed by AI and automation, such as ensuring fair wages, protecting workers' rights, and regulating gig work.
Ethical AI Governance: Implementing frameworks for the ethical use of AI, including transparency, accountability, and bias mitigation, is essential to ensure that these technologies are used responsibly and fairly.
C. Social Safety Nets
Universal Basic Income (UBI): Some policymakers advocate for UBI as a way to provide financial security in an economy where automation may reduce the availability of traditional jobs.
Expanded Social Programs: Strengthening social safety nets, including unemployment benefits, healthcare, and retraining initiatives, can help mitigate the negative impacts of job displacement and income inequality.
Technological advancements in AI and automation are reshaping economic structures and job markets, bringing both opportunities and challenges.
While they drive productivity and innovation, they also lead to job displacement, skill shifts, and income inequality.
To ensure that the benefits of these technologies are widely shared, governments, businesses, and educational institutions must collaborate to develop policies that promote inclusive growth, provide retraining opportunities, and address the ethical and social implications of AI and automation.
1 yr. ago
What are some unique traditions or customs from various cultures that you find interesting or surprising?
By Hugo Keji
There are many unique and fascinating traditions and customs from cultures around the world. Here are a few that stand out:
1. La Tomatina (Spain)
Held annually in the town of Buñol, La Tomatina is a festival where participants engage in a massive tomato fight. This quirky tradition originated in 1945 and attracts thousands of people from around the world.
2. Kanamara Matsuri (Japan)
Known as the "Festival of the Steel Phallus," this annual celebration in Kawasaki is dedicated to a phallic-shaped shrine. It is believed to protect against sexually transmitted diseases, and the festival includes a parade with giant phallic symbols, crafts, and food.
3. Thaipusam (India and Malaysia)
During this Hindu festival, devotees pierce their bodies with hooks, skewers, and spears as acts of penance and devotion. The festival is marked by colorful processions and is a testament to the participants' faith and endurance.
4. Dia de los Muertos (Mexico)
The Day of the Dead is a vibrant celebration honoring deceased loved ones. Families create altars with offerings like food, drink, and photographs, and they visit graves to clean and decorate them with marigolds. The festival features lively parades, music, and dancing.
5. Up Helly Aa (Scotland)
This Shetland Islands festival celebrates Viking heritage with a spectacular torch-lit procession and the burning of a Viking longship. Participants dress in Viking attire, and the event includes music, dancing, and feasting.
6. Nyepi (Indonesia)
Nyepi, the Balinese Day of Silence, marks the Balinese New Year. On this day, the entire island of Bali comes to a standstill, with no travel, work, or entertainment allowed. The day is dedicated to self-reflection and meditation.
7. Holika Dahan and Holi (India)
Holi, the festival of colors, begins with Holika Dahan, a ritual bonfire symbolizing the victory of good over evil. The following day, people celebrate by throwing colored powders and water at each other, dancing, and enjoying festive foods.
8. Bastille Day (France)
France's national holiday, celebrated on July 14th, commemorates the French Revolution and the storming of the Bastille. The day features a grand military parade on the Champs-Élysées, fireworks, parties, and communal meals.
9. Monkey Buffet Festival (Thailand)
In the town of Lopburi, this festival is held to honor the local monkey population. Thousands of monkeys are treated to a buffet of fruits, vegetables, and sweets, attracting both locals and tourists to witness the spectacle.
10. Kavadi Attam (India and Sri Lanka)
Part of the Tamil festival of Thaipusam, Kavadi Attam involves devotees carrying elaborately decorated structures called kavadis on their shoulders. Some participants also engage in body piercing and other acts of physical endurance as offerings to Lord Murugan.
11. Inti Raymi (Peru)
The Festival of the Sun, held in Cusco, celebrates the Incan sun god Inti. The festival includes traditional music, dance, and elaborate reenactments of Incan ceremonies, attracting visitors from around the world.
12. Songkran (Thailand)
Celebrated as the Thai New Year, Songkran is known for its massive water fights. People pour water on each other to wash away bad luck and welcome the new year with joy and renewal.
13. Hanami (Japan)
Hanami, or flower viewing, is the traditional Japanese custom of enjoying the beauty of cherry blossoms. During sakura season, people gather in parks to have picnics under blooming cherry trees, celebrating nature's fleeting beauty.
These unique traditions and customs highlight the rich cultural diversity and creativity found around the world, offering fascinating insights into the values and history of different societies.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Be part of Health Data 101.... Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan. With servers in Asia, Europe and America. Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365 For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
There are many unique and fascinating traditions and customs from cultures around the world. Here are a few that stand out:
1. La Tomatina (Spain)
Held annually in the town of Buñol, La Tomatina is a festival where participants engage in a massive tomato fight. This quirky tradition originated in 1945 and attracts thousands of people from around the world.
2. Kanamara Matsuri (Japan)
Known as the "Festival of the Steel Phallus," this annual celebration in Kawasaki is dedicated to a phallic-shaped shrine. It is believed to protect against sexually transmitted diseases, and the festival includes a parade with giant phallic symbols, crafts, and food.
3. Thaipusam (India and Malaysia)
During this Hindu festival, devotees pierce their bodies with hooks, skewers, and spears as acts of penance and devotion. The festival is marked by colorful processions and is a testament to the participants' faith and endurance.
4. Dia de los Muertos (Mexico)
The Day of the Dead is a vibrant celebration honoring deceased loved ones. Families create altars with offerings like food, drink, and photographs, and they visit graves to clean and decorate them with marigolds. The festival features lively parades, music, and dancing.
5. Up Helly Aa (Scotland)
This Shetland Islands festival celebrates Viking heritage with a spectacular torch-lit procession and the burning of a Viking longship. Participants dress in Viking attire, and the event includes music, dancing, and feasting.
6. Nyepi (Indonesia)
Nyepi, the Balinese Day of Silence, marks the Balinese New Year. On this day, the entire island of Bali comes to a standstill, with no travel, work, or entertainment allowed. The day is dedicated to self-reflection and meditation.
7. Holika Dahan and Holi (India)
Holi, the festival of colors, begins with Holika Dahan, a ritual bonfire symbolizing the victory of good over evil. The following day, people celebrate by throwing colored powders and water at each other, dancing, and enjoying festive foods.
8. Bastille Day (France)
France's national holiday, celebrated on July 14th, commemorates the French Revolution and the storming of the Bastille. The day features a grand military parade on the Champs-Élysées, fireworks, parties, and communal meals.
9. Monkey Buffet Festival (Thailand)
In the town of Lopburi, this festival is held to honor the local monkey population. Thousands of monkeys are treated to a buffet of fruits, vegetables, and sweets, attracting both locals and tourists to witness the spectacle.
10. Kavadi Attam (India and Sri Lanka)
Part of the Tamil festival of Thaipusam, Kavadi Attam involves devotees carrying elaborately decorated structures called kavadis on their shoulders. Some participants also engage in body piercing and other acts of physical endurance as offerings to Lord Murugan.
11. Inti Raymi (Peru)
The Festival of the Sun, held in Cusco, celebrates the Incan sun god Inti. The festival includes traditional music, dance, and elaborate reenactments of Incan ceremonies, attracting visitors from around the world.
12. Songkran (Thailand)
Celebrated as the Thai New Year, Songkran is known for its massive water fights. People pour water on each other to wash away bad luck and welcome the new year with joy and renewal.
13. Hanami (Japan)
Hanami, or flower viewing, is the traditional Japanese custom of enjoying the beauty of cherry blossoms. During sakura season, people gather in parks to have picnics under blooming cherry trees, celebrating nature's fleeting beauty.
These unique traditions and customs highlight the rich cultural diversity and creativity found around the world, offering fascinating insights into the values and history of different societies.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Be part of Health Data 101.... Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan. With servers in Asia, Europe and America. Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365 For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
1 yr. ago
How does cultural diversity enrich a society?
By Hugo Keji
Cultural diversity enriches a society in numerous ways, contributing to its vibrancy, innovation, and resilience.
Benefits of cultural diversity:-
1. Enhanced Creativity and Innovation
Cultural diversity brings together different perspectives, ideas, and approaches, fostering creativity and innovation. When people from varied backgrounds collaborate, they can combine their unique viewpoints to create new solutions and drive progress.
2. Broader Skill Set-
A diverse society benefits from a wider range of skills and experiences. Different cultural groups may excel in various areas, bringing specialized knowledge and expertise that can enhance overall societal capabilities.
3. Economic Growth-
Cultural diversity can contribute to economic growth by attracting a global talent pool and creating a more dynamic workforce. Diverse teams can tap into different markets and understand consumer needs more effectively, leading to better business outcomes.
4. Social Enrichment-
Exposure to different cultures enriches social interactions and broadens individuals' horizons. It promotes mutual understanding, tolerance, and respect, helping to build cohesive communities.
5. Educational Benefits-
Cultural diversity in educational settings provides students with a richer learning environment. It encourages critical thinking, empathy, and cultural awareness, preparing students to thrive in a globalized world.
6. Cultural Exchange and Innovation-
Cultural exchange can lead to the fusion of different art forms, culinary traditions, music, and literature, creating new and exciting cultural expressions. This exchange enriches the cultural landscape of a society.
7. Resilience and Adaptability-
Diverse societies are often more resilient and adaptable in the face of challenges. The variety of perspectives and experiences can lead to more robust problem-solving and adaptability to change.
8. Enhanced Social Welfare-
Diverse societies tend to develop more inclusive policies and social programs that cater to the needs of different groups. This inclusivity can lead to improved social welfare and equity.
9. Global Competence-
In a globalized world, cultural diversity equips individuals and organizations with the skills and understanding necessary to operate effectively across different cultures. This competence is crucial for international relations and business.
10. Reduction of Prejudice and Discrimination-
Living in a culturally diverse society can help reduce prejudice and discrimination. When people interact with those from different backgrounds, they are more likely to challenge stereotypes and develop more inclusive attitudes.
Examples of Cultural Diversity's Impact:-
Urban Areas: Cities like New York, London, and Toronto thrive on cultural diversity, which is evident in their vibrant arts scenes, diverse culinary offerings, and dynamic economies.
Innovation Hubs: Silicon Valley's success is partly due to its cultural diversity, attracting talent from around the world and fostering an environment of innovation and entrepreneurship.
Cultural Festivals: Events like Carnival in Brazil, Diwali in India, and Chinese New Year celebrations showcase the richness of cultural traditions and bring communities together in celebration.
Cultural diversity is a source of strength and enrichment, enhancing every aspect of society from economic performance to social cohesion and cultural vitality.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Cultural diversity enriches a society in numerous ways, contributing to its vibrancy, innovation, and resilience.
Benefits of cultural diversity:-
1. Enhanced Creativity and Innovation
Cultural diversity brings together different perspectives, ideas, and approaches, fostering creativity and innovation. When people from varied backgrounds collaborate, they can combine their unique viewpoints to create new solutions and drive progress.
2. Broader Skill Set-
A diverse society benefits from a wider range of skills and experiences. Different cultural groups may excel in various areas, bringing specialized knowledge and expertise that can enhance overall societal capabilities.
3. Economic Growth-
Cultural diversity can contribute to economic growth by attracting a global talent pool and creating a more dynamic workforce. Diverse teams can tap into different markets and understand consumer needs more effectively, leading to better business outcomes.
4. Social Enrichment-
Exposure to different cultures enriches social interactions and broadens individuals' horizons. It promotes mutual understanding, tolerance, and respect, helping to build cohesive communities.
5. Educational Benefits-
Cultural diversity in educational settings provides students with a richer learning environment. It encourages critical thinking, empathy, and cultural awareness, preparing students to thrive in a globalized world.
6. Cultural Exchange and Innovation-
Cultural exchange can lead to the fusion of different art forms, culinary traditions, music, and literature, creating new and exciting cultural expressions. This exchange enriches the cultural landscape of a society.
7. Resilience and Adaptability-
Diverse societies are often more resilient and adaptable in the face of challenges. The variety of perspectives and experiences can lead to more robust problem-solving and adaptability to change.
8. Enhanced Social Welfare-
Diverse societies tend to develop more inclusive policies and social programs that cater to the needs of different groups. This inclusivity can lead to improved social welfare and equity.
9. Global Competence-
In a globalized world, cultural diversity equips individuals and organizations with the skills and understanding necessary to operate effectively across different cultures. This competence is crucial for international relations and business.
10. Reduction of Prejudice and Discrimination-
Living in a culturally diverse society can help reduce prejudice and discrimination. When people interact with those from different backgrounds, they are more likely to challenge stereotypes and develop more inclusive attitudes.
Examples of Cultural Diversity's Impact:-
Urban Areas: Cities like New York, London, and Toronto thrive on cultural diversity, which is evident in their vibrant arts scenes, diverse culinary offerings, and dynamic economies.
Innovation Hubs: Silicon Valley's success is partly due to its cultural diversity, attracting talent from around the world and fostering an environment of innovation and entrepreneurship.
Cultural Festivals: Events like Carnival in Brazil, Diwali in India, and Chinese New Year celebrations showcase the richness of cultural traditions and bring communities together in celebration.
Cultural diversity is a source of strength and enrichment, enhancing every aspect of society from economic performance to social cohesion and cultural vitality.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
1 yr. ago
How do different cultures define identity, and what elements (e.g., language, traditions, values) are most important in shaping it?
By Hugo Keji
Cultural definitions of identity vary widely across different societies, influenced by a range of factors including history, geography, and social norms.
Key elements that shape identity in different cultures:
1. Language-
Language is a primary means of communication and a crucial component of cultural identity. It reflects and shapes our thoughts, values, and perceptions. In many cultures, language is closely tied to a sense of belonging and community.
2. Traditions and Customs-
Traditions, rituals, and customs play a significant role in defining identity. These practices often have historical significance and are passed down through generations, helping to maintain a sense of continuity and connection to the past.
3. Values and Beliefs-
Cultural values and belief systems, including religious and moral principles, are foundational to a person’s identity. These values dictate social norms and behaviors, influencing how individuals see themselves and their place in the world.
4. Social Structures-
Family, community, and social hierarchies are crucial in shaping identity. Different cultures place varying degrees of importance on family ties, social status, and community involvement.
5. History and Heritage-
A shared history, including historical events, legends, and collective memories, contributes to a sense of identity. This can include everything from national history to local folklore.
6. Art and Literature-
Cultural expressions through art, music, literature, and other forms of creativity reflect and shape identity. They offer insights into the collective consciousness and values of a society.
7. Geography and Environment-
The physical environment and geographical location of a culture can influence its identity. For example, island cultures might have different identities compared to continental cultures, shaped by their interaction with the natural world.
Examples of Cultural Identity Definitions-
Western Cultures: Often emphasize individualism, where personal achievements and autonomy are key aspects of identity.
Eastern Cultures: Tend to emphasize collectivism, where group harmony, family, and community are paramount in defining identity.
Indigenous Cultures: Frequently define identity in relation to the land, ancestors, and traditional ecological knowledge, emphasizing a deep connection to nature and community.
Intersectionality:-
Identity is multifaceted and can intersect with various factors such as gender, race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and more. This intersectionality means that an individual’s identity is shaped by multiple, overlapping social categories, each influencing their experience and self-conception.
Understanding identity within different cultural contexts requires a nuanced approach, recognizing the unique combination of elements that define each culture's sense of self and community.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Cultural definitions of identity vary widely across different societies, influenced by a range of factors including history, geography, and social norms.
Key elements that shape identity in different cultures:
1. Language-
Language is a primary means of communication and a crucial component of cultural identity. It reflects and shapes our thoughts, values, and perceptions. In many cultures, language is closely tied to a sense of belonging and community.
2. Traditions and Customs-
Traditions, rituals, and customs play a significant role in defining identity. These practices often have historical significance and are passed down through generations, helping to maintain a sense of continuity and connection to the past.
3. Values and Beliefs-
Cultural values and belief systems, including religious and moral principles, are foundational to a person’s identity. These values dictate social norms and behaviors, influencing how individuals see themselves and their place in the world.
4. Social Structures-
Family, community, and social hierarchies are crucial in shaping identity. Different cultures place varying degrees of importance on family ties, social status, and community involvement.
5. History and Heritage-
A shared history, including historical events, legends, and collective memories, contributes to a sense of identity. This can include everything from national history to local folklore.
6. Art and Literature-
Cultural expressions through art, music, literature, and other forms of creativity reflect and shape identity. They offer insights into the collective consciousness and values of a society.
7. Geography and Environment-
The physical environment and geographical location of a culture can influence its identity. For example, island cultures might have different identities compared to continental cultures, shaped by their interaction with the natural world.
Examples of Cultural Identity Definitions-
Western Cultures: Often emphasize individualism, where personal achievements and autonomy are key aspects of identity.
Eastern Cultures: Tend to emphasize collectivism, where group harmony, family, and community are paramount in defining identity.
Indigenous Cultures: Frequently define identity in relation to the land, ancestors, and traditional ecological knowledge, emphasizing a deep connection to nature and community.
Intersectionality:-
Identity is multifaceted and can intersect with various factors such as gender, race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and more. This intersectionality means that an individual’s identity is shaped by multiple, overlapping social categories, each influencing their experience and self-conception.
Understanding identity within different cultural contexts requires a nuanced approach, recognizing the unique combination of elements that define each culture's sense of self and community.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
1 yr. ago
How can the young and youths of Africa secure a better future for Africa?
By Hugo Keji
Securing a better future for Africa involves proactive steps by the youth in various areas such as education, entrepreneurship, governance, social inclusion, and sustainable development.
Here are several strategies that young Africans can adopt to contribute to a brighter future for the continent:
1. Education and Skills Development
Lifelong Learning: Commit to continuous learning and skill development to stay competitive in the global job market.
STEM Focus: Pursue education in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) fields to drive technological and industrial advancements.
Critical Thinking and Problem Solving: Develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills to innovate and address local and global challenges.
2. Entrepreneurship and Innovation
Startups and SMEs: Establish startups and small-to-medium enterprises (SMEs) to create jobs and stimulate economic growth.
Innovation Hubs: Participate in innovation hubs and tech incubators to foster creativity and develop solutions to local problems.
Social Enterprises: Launch social enterprises that address societal issues such as education, health, and environmental sustainability.
3. Civic Engagement and Governance
Political Participation: Engage in political processes, vote, and run for public office to influence policies that affect the future of the continent.
Advocacy and Activism: Advocate for transparent, accountable governance and fight against corruption to build trust in institutions.
Youth Councils: Join or establish youth councils to ensure that young people’s voices are heard in decision-making processes.
4. Sustainable Development
Environmental Stewardship: Promote and practice sustainable environmental practices to protect natural resources for future generations.
Renewable Energy: Advocate for and invest in renewable energy sources to combat climate change and promote sustainable development.
Sustainable Agriculture: Engage in sustainable agricultural practices to ensure food security and support rural economies.
5. Health and Wellbeing
Healthcare Access: Work towards improving access to quality healthcare services, especially in underserved areas.
Mental Health Awareness: Promote mental health awareness and support systems to address the mental health needs of the population.
Preventive Measures: Advocate for and participate in preventive health measures to reduce the burden of diseases.
6. Technology and Digital Transformation
Digital Literacy: Improve digital literacy to harness the power of technology for education, business, and social impact.
E-Government Services: Advocate for the development of e-government services to improve public service delivery and transparency.
Tech Innovation: Develop and adopt tech innovations to solve local problems and improve living standards.
7. Cultural Preservation and Promotion
Cultural Heritage: Preserve and promote African cultural heritage through arts, music, and traditional practices.
Creative Industries: Engage in and support creative industries such as film, fashion, and music to drive cultural and economic growth.
Cultural Exchange: Participate in cultural exchange programs to foster mutual understanding and global appreciation of African culture.
8. Economic Empowerment
Financial Literacy: Improve financial literacy to make informed financial decisions and manage personal and business finances effectively.
Access to Finance: Seek and advocate for better access to financial resources for young entrepreneurs and small businesses.
Inclusive Growth: Promote inclusive economic growth that benefits all segments of society, including marginalized groups.
9. Peace and Social Cohesion
Conflict Resolution: Engage in and promote conflict resolution and peacebuilding initiatives to ensure stable and peaceful communities.
Social Inclusion: Advocate for social inclusion and equality, ensuring that all individuals, regardless of background, have opportunities to succeed.
Volunteerism: Participate in volunteer activities to support community development and foster a sense of unity and purpose.
10. Global Engagement
Global Networks: Build and leverage global networks to exchange ideas, resources, and best practices.
International Collaboration: Collaborate with international organizations and partners to address global challenges and harness opportunities for development.
Diaspora Engagement: Engage with the African diaspora to tap into their expertise, resources, and networks for the continent's development.
By actively participating in these areas, African youths can secure a better future for the continent, driving progress, innovation, and sustainable development.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$5 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Securing a better future for Africa involves proactive steps by the youth in various areas such as education, entrepreneurship, governance, social inclusion, and sustainable development.
Here are several strategies that young Africans can adopt to contribute to a brighter future for the continent:
1. Education and Skills Development
Lifelong Learning: Commit to continuous learning and skill development to stay competitive in the global job market.
STEM Focus: Pursue education in Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) fields to drive technological and industrial advancements.
Critical Thinking and Problem Solving: Develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills to innovate and address local and global challenges.
2. Entrepreneurship and Innovation
Startups and SMEs: Establish startups and small-to-medium enterprises (SMEs) to create jobs and stimulate economic growth.
Innovation Hubs: Participate in innovation hubs and tech incubators to foster creativity and develop solutions to local problems.
Social Enterprises: Launch social enterprises that address societal issues such as education, health, and environmental sustainability.
3. Civic Engagement and Governance
Political Participation: Engage in political processes, vote, and run for public office to influence policies that affect the future of the continent.
Advocacy and Activism: Advocate for transparent, accountable governance and fight against corruption to build trust in institutions.
Youth Councils: Join or establish youth councils to ensure that young people’s voices are heard in decision-making processes.
4. Sustainable Development
Environmental Stewardship: Promote and practice sustainable environmental practices to protect natural resources for future generations.
Renewable Energy: Advocate for and invest in renewable energy sources to combat climate change and promote sustainable development.
Sustainable Agriculture: Engage in sustainable agricultural practices to ensure food security and support rural economies.
5. Health and Wellbeing
Healthcare Access: Work towards improving access to quality healthcare services, especially in underserved areas.
Mental Health Awareness: Promote mental health awareness and support systems to address the mental health needs of the population.
Preventive Measures: Advocate for and participate in preventive health measures to reduce the burden of diseases.
6. Technology and Digital Transformation
Digital Literacy: Improve digital literacy to harness the power of technology for education, business, and social impact.
E-Government Services: Advocate for the development of e-government services to improve public service delivery and transparency.
Tech Innovation: Develop and adopt tech innovations to solve local problems and improve living standards.
7. Cultural Preservation and Promotion
Cultural Heritage: Preserve and promote African cultural heritage through arts, music, and traditional practices.
Creative Industries: Engage in and support creative industries such as film, fashion, and music to drive cultural and economic growth.
Cultural Exchange: Participate in cultural exchange programs to foster mutual understanding and global appreciation of African culture.
8. Economic Empowerment
Financial Literacy: Improve financial literacy to make informed financial decisions and manage personal and business finances effectively.
Access to Finance: Seek and advocate for better access to financial resources for young entrepreneurs and small businesses.
Inclusive Growth: Promote inclusive economic growth that benefits all segments of society, including marginalized groups.
9. Peace and Social Cohesion
Conflict Resolution: Engage in and promote conflict resolution and peacebuilding initiatives to ensure stable and peaceful communities.
Social Inclusion: Advocate for social inclusion and equality, ensuring that all individuals, regardless of background, have opportunities to succeed.
Volunteerism: Participate in volunteer activities to support community development and foster a sense of unity and purpose.
10. Global Engagement
Global Networks: Build and leverage global networks to exchange ideas, resources, and best practices.
International Collaboration: Collaborate with international organizations and partners to address global challenges and harness opportunities for development.
Diaspora Engagement: Engage with the African diaspora to tap into their expertise, resources, and networks for the continent's development.
By actively participating in these areas, African youths can secure a better future for the continent, driving progress, innovation, and sustainable development.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$5 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
1 yr. ago
How can African youths drive global growth?
By Hugo Keji
African youths can drive global growth through various avenues, leveraging their talents, creativity, and the continent's unique opportunities.
Entrepreneurship and Innovation:-
Startups: By creating and scaling startups, African youths can introduce innovative products and services to global markets.
Tech Hubs: Participation in tech hubs and innovation centers can lead to the development of cutting-edge technologies and solutions.
E-commerce: Leveraging e-commerce platforms to sell African products globally, contributing to the digital economy.
Education and Skills Development:-
STEM Education: Pursuing STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) education to contribute to global advancements in these fields.
Upskilling: Continuously updating skills to match global industry trends, making African youths competitive in the international job market.
Research and Development: Engaging in research and development projects that address global challenges such as health, energy, and sustainability.
Digital Economy:-
Remote Work: Taking advantage of remote work opportunities to provide services to companies worldwide.
Freelancing: Offering freelance services in areas such as software development, graphic design, and digital marketing.
Content Creation: Using platforms like YouTube, TikTok, and blogs to create content that can attract global audiences and advertisers.
Agribusiness and Sustainability:-
Sustainable Agriculture: Implementing sustainable agricultural practices that can be models for other regions facing similar challenges.
Exporting Goods: Engaging in agribusiness and exporting high-quality agricultural products to international markets.
Green Technologies: Innovating in renewable energy and green technologies to contribute to global sustainability efforts.
Cultural Influence:-
Creative Industries: Participating in the creative industries (music, film, fashion) to influence global culture and create economic value.
Cultural Exchange: Promoting African culture through international collaborations and exchanges.
Tourism Promotion: Leveraging digital platforms to promote African tourism, attracting visitors and investment.
Leadership and Advocacy:-
Global Forums: Participating in global forums and organizations to influence policy and advocate for issues affecting young people and the continent.
Social Entrepreneurship: Launching social enterprises that address global social issues such as poverty, education, and health.
Climate Action: Leading climate action initiatives and participating in international climate negotiations.
Networking and Collaboration:-
Diaspora Engagement: Collaborating with the African diaspora to build networks that can facilitate investment, knowledge transfer, and market access.
Global Partnerships: Forming partnerships with international organizations, NGOs, and businesses to drive development projects and innovations.
Knowledge Sharing: Participating in global knowledge-sharing platforms to exchange ideas and best practices.
Technology and Digital Transformation:-
Tech Startups: Developing tech startups that can scale globally, providing innovative solutions to worldwide problems.
AI and Data Science: Engaging in AI and data science projects to contribute to global advancements in these fields.
Blockchain and Fintech: Innovating in blockchain and fintech to provide financial solutions that can be adopted globally.
Health and Biotechnology:-
Medical Research: Engaging in medical research and developing health solutions that can address global health challenges.
Biotech Startups: Creating biotech startups that can innovate in areas such as pharmaceuticals, diagnostics, and agriculture.
Advancing Democracy and Governance:-
Civic Engagement: Promoting democracy, transparency, and good governance in African countries, serving as a model for other regions.
Policy Innovation: Innovating in public policy to address global challenges such as migration, urbanization, and human rights.
Leveraging these strategies, African youths can not only drive growth within the continent but also contribute significantly to global economic, social, and technological progress.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$5 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
African youths can drive global growth through various avenues, leveraging their talents, creativity, and the continent's unique opportunities.
Entrepreneurship and Innovation:-
Startups: By creating and scaling startups, African youths can introduce innovative products and services to global markets.
Tech Hubs: Participation in tech hubs and innovation centers can lead to the development of cutting-edge technologies and solutions.
E-commerce: Leveraging e-commerce platforms to sell African products globally, contributing to the digital economy.
Education and Skills Development:-
STEM Education: Pursuing STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) education to contribute to global advancements in these fields.
Upskilling: Continuously updating skills to match global industry trends, making African youths competitive in the international job market.
Research and Development: Engaging in research and development projects that address global challenges such as health, energy, and sustainability.
Digital Economy:-
Remote Work: Taking advantage of remote work opportunities to provide services to companies worldwide.
Freelancing: Offering freelance services in areas such as software development, graphic design, and digital marketing.
Content Creation: Using platforms like YouTube, TikTok, and blogs to create content that can attract global audiences and advertisers.
Agribusiness and Sustainability:-
Sustainable Agriculture: Implementing sustainable agricultural practices that can be models for other regions facing similar challenges.
Exporting Goods: Engaging in agribusiness and exporting high-quality agricultural products to international markets.
Green Technologies: Innovating in renewable energy and green technologies to contribute to global sustainability efforts.
Cultural Influence:-
Creative Industries: Participating in the creative industries (music, film, fashion) to influence global culture and create economic value.
Cultural Exchange: Promoting African culture through international collaborations and exchanges.
Tourism Promotion: Leveraging digital platforms to promote African tourism, attracting visitors and investment.
Leadership and Advocacy:-
Global Forums: Participating in global forums and organizations to influence policy and advocate for issues affecting young people and the continent.
Social Entrepreneurship: Launching social enterprises that address global social issues such as poverty, education, and health.
Climate Action: Leading climate action initiatives and participating in international climate negotiations.
Networking and Collaboration:-
Diaspora Engagement: Collaborating with the African diaspora to build networks that can facilitate investment, knowledge transfer, and market access.
Global Partnerships: Forming partnerships with international organizations, NGOs, and businesses to drive development projects and innovations.
Knowledge Sharing: Participating in global knowledge-sharing platforms to exchange ideas and best practices.
Technology and Digital Transformation:-
Tech Startups: Developing tech startups that can scale globally, providing innovative solutions to worldwide problems.
AI and Data Science: Engaging in AI and data science projects to contribute to global advancements in these fields.
Blockchain and Fintech: Innovating in blockchain and fintech to provide financial solutions that can be adopted globally.
Health and Biotechnology:-
Medical Research: Engaging in medical research and developing health solutions that can address global health challenges.
Biotech Startups: Creating biotech startups that can innovate in areas such as pharmaceuticals, diagnostics, and agriculture.
Advancing Democracy and Governance:-
Civic Engagement: Promoting democracy, transparency, and good governance in African countries, serving as a model for other regions.
Policy Innovation: Innovating in public policy to address global challenges such as migration, urbanization, and human rights.
Leveraging these strategies, African youths can not only drive growth within the continent but also contribute significantly to global economic, social, and technological progress.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$5 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
1 yr. ago
How can the business environment be improved to foster innovation and growth?
By Hugo Keji
Improving the business environment to foster innovation and growth in Africa involves a multi-faceted approach that addresses existing challenges and leverages opportunities.
Enhancing Access to Funding:-
Encouraging Investment:
Venture Capital and Angel Networks: Support the growth of venture capital and angel investor networks through tax incentives, regulatory ease, and government-backed matching funds.
Crowdfunding Platforms: Promote and regulate crowdfunding platforms to make it easier for startups to access capital.
Microfinance and Impact Investing: Expand microfinance and impact investment initiatives that target underfunded sectors and regions.
Public-Private Partnerships:
Government Grants and Subsidies: Implement grants, subsidies, and innovation funds specifically targeted at startups and small businesses.
Financial Literacy Programs: Provide training programs to enhance financial literacy and business acumen among entrepreneurs.
Improving Infrastructure:-
Digital Infrastructure:
Broadband Expansion: Invest in expanding broadband infrastructure to improve internet connectivity, especially in rural areas.
Affordable Data: Implement policies to reduce the cost of data and improve access to affordable internet services.
Energy Solutions:
Renewable Energy: Promote renewable energy solutions to provide reliable electricity, such as solar power in off-grid areas.
Infrastructure Investment: Invest in modernizing and expanding electricity grids to reduce outages and increase reliability.
Transport and Logistics:
Improving Roads and Ports: Upgrade transportation infrastructure to facilitate smoother logistics and supply chains.
Smart Logistics Solutions: Encourage the development and adoption of smart logistics and supply chain management solutions.
Streamlining Regulatory Environment:-
Simplifying Bureaucracy:
E-Government Services: Implement e-government services to streamline business registration, licensing, and compliance processes.
One-Stop Shops: Establish one-stop shops for business services to reduce administrative burdens and processing times.
Anti-Corruption Measures:
Transparency Initiatives: Increase transparency in government transactions and procurement processes.
Whistleblower Protection: Strengthen laws to protect whistleblowers and encourage reporting of corrupt practices.
Stable Policy Environment:
Long-Term Policies: Develop and adhere to long-term economic policies that provide stability and predictability for businesses.
Public Consultation: Engage in regular dialogue with the business community to ensure policies are supportive and conducive to growth.
Building Talent and Skills:-
Education and Training:
STEM Education: Invest in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) education from primary through tertiary levels.
Vocational Training: Expand vocational training programs to provide practical skills that meet market demands.
Entrepreneurship Programs: Implement entrepreneurship education in schools and universities to foster a culture of innovation.
Attracting Talent:
Incentives for Returnees: Create incentives for skilled professionals in the diaspora to return and contribute to the local economy.
Talent Exchange Programs: Establish exchange programs with other countries to allow for knowledge transfer and skill development.
Enhancing Market Access:-
Regional Integration:
Trade Agreements: Strengthen regional trade agreements to create larger and more accessible markets for businesses.
Cross-Border Initiatives: Develop cross-border initiatives to reduce trade barriers and facilitate easier movement of goods and services.
Consumer Trust:
Quality Standards: Implement and enforce quality standards to build consumer trust in locally produced goods and services.
Consumer Protection: Strengthen consumer protection laws to ensure fair practices and build a reliable market environment.
Supporting Innovation Ecosystems:-
Tech Hubs and Incubators:
Funding for Incubators: Provide funding and support for tech hubs, incubators, and accelerators to nurture startups.
Networking Opportunities: Facilitate networking events and platforms for entrepreneurs to connect with investors, mentors, and peers.
Innovation Challenges and Competitions:
Hackathons and Competitions: Organize hackathons, innovation challenges, and competitions to spur creativity and problem-solving.
Showcasing Success Stories: Highlight and celebrate successful startups and entrepreneurs to inspire others and attract attention.
Promoting Sustainable Business Practices:-
Green Economy:
Environmental Incentives: Provide incentives for businesses to adopt sustainable and environmentally friendly practices.
Circular Economy: Promote the concept of a circular economy to reduce waste and increase resource efficiency.
Social Entrepreneurship:
Impact Metrics: Encourage businesses to measure and report on their social and environmental impact.
Support for Social Enterprises: Provide support for social enterprises that address local challenges through innovative business models.
By addressing these areas, the business environment in Africa can be significantly improved to foster innovation, attract investment, and promote sustainable economic growth.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$5 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Improving the business environment to foster innovation and growth in Africa involves a multi-faceted approach that addresses existing challenges and leverages opportunities.
Enhancing Access to Funding:-
Encouraging Investment:
Venture Capital and Angel Networks: Support the growth of venture capital and angel investor networks through tax incentives, regulatory ease, and government-backed matching funds.
Crowdfunding Platforms: Promote and regulate crowdfunding platforms to make it easier for startups to access capital.
Microfinance and Impact Investing: Expand microfinance and impact investment initiatives that target underfunded sectors and regions.
Public-Private Partnerships:
Government Grants and Subsidies: Implement grants, subsidies, and innovation funds specifically targeted at startups and small businesses.
Financial Literacy Programs: Provide training programs to enhance financial literacy and business acumen among entrepreneurs.
Improving Infrastructure:-
Digital Infrastructure:
Broadband Expansion: Invest in expanding broadband infrastructure to improve internet connectivity, especially in rural areas.
Affordable Data: Implement policies to reduce the cost of data and improve access to affordable internet services.
Energy Solutions:
Renewable Energy: Promote renewable energy solutions to provide reliable electricity, such as solar power in off-grid areas.
Infrastructure Investment: Invest in modernizing and expanding electricity grids to reduce outages and increase reliability.
Transport and Logistics:
Improving Roads and Ports: Upgrade transportation infrastructure to facilitate smoother logistics and supply chains.
Smart Logistics Solutions: Encourage the development and adoption of smart logistics and supply chain management solutions.
Streamlining Regulatory Environment:-
Simplifying Bureaucracy:
E-Government Services: Implement e-government services to streamline business registration, licensing, and compliance processes.
One-Stop Shops: Establish one-stop shops for business services to reduce administrative burdens and processing times.
Anti-Corruption Measures:
Transparency Initiatives: Increase transparency in government transactions and procurement processes.
Whistleblower Protection: Strengthen laws to protect whistleblowers and encourage reporting of corrupt practices.
Stable Policy Environment:
Long-Term Policies: Develop and adhere to long-term economic policies that provide stability and predictability for businesses.
Public Consultation: Engage in regular dialogue with the business community to ensure policies are supportive and conducive to growth.
Building Talent and Skills:-
Education and Training:
STEM Education: Invest in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) education from primary through tertiary levels.
Vocational Training: Expand vocational training programs to provide practical skills that meet market demands.
Entrepreneurship Programs: Implement entrepreneurship education in schools and universities to foster a culture of innovation.
Attracting Talent:
Incentives for Returnees: Create incentives for skilled professionals in the diaspora to return and contribute to the local economy.
Talent Exchange Programs: Establish exchange programs with other countries to allow for knowledge transfer and skill development.
Enhancing Market Access:-
Regional Integration:
Trade Agreements: Strengthen regional trade agreements to create larger and more accessible markets for businesses.
Cross-Border Initiatives: Develop cross-border initiatives to reduce trade barriers and facilitate easier movement of goods and services.
Consumer Trust:
Quality Standards: Implement and enforce quality standards to build consumer trust in locally produced goods and services.
Consumer Protection: Strengthen consumer protection laws to ensure fair practices and build a reliable market environment.
Supporting Innovation Ecosystems:-
Tech Hubs and Incubators:
Funding for Incubators: Provide funding and support for tech hubs, incubators, and accelerators to nurture startups.
Networking Opportunities: Facilitate networking events and platforms for entrepreneurs to connect with investors, mentors, and peers.
Innovation Challenges and Competitions:
Hackathons and Competitions: Organize hackathons, innovation challenges, and competitions to spur creativity and problem-solving.
Showcasing Success Stories: Highlight and celebrate successful startups and entrepreneurs to inspire others and attract attention.
Promoting Sustainable Business Practices:-
Green Economy:
Environmental Incentives: Provide incentives for businesses to adopt sustainable and environmentally friendly practices.
Circular Economy: Promote the concept of a circular economy to reduce waste and increase resource efficiency.
Social Entrepreneurship:
Impact Metrics: Encourage businesses to measure and report on their social and environmental impact.
Support for Social Enterprises: Provide support for social enterprises that address local challenges through innovative business models.
By addressing these areas, the business environment in Africa can be significantly improved to foster innovation, attract investment, and promote sustainable economic growth.
SHARE YOUR COMMENTS AND QUESTIONS........
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$5 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com

Health Data 101 - App on Amazon Appstore
Healthdata101-Manage Hospital and Health data.
https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B0D514TH5S
1 yr. ago
What measures can be taken to boost India's economic growth sustainably?
By Ugo Ikeji
To boost India's economic growth sustainably, a multifaceted approach is required, focusing on key areas such as infrastructure development, education, healthcare, environmental sustainability, and governance.
1. Infrastructure Development
Transportation Networks: Improve road, rail, air, and waterway connectivity to facilitate trade and reduce logistics costs.
Urban Infrastructure: Develop smart cities with robust public transport, waste management systems, and sustainable housing.
Rural Infrastructure: Enhance rural roads, electrification, and internet connectivity to integrate rural areas into the economic mainstream.
2. Education and Skill Development
Quality Education: Reform the education system to focus on critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills.
Vocational Training: Expand vocational training programs to equip the workforce with industry-relevant skills.
Higher Education: Invest in research and development (R&D) and promote higher education institutions to foster innovation.
3. Healthcare Improvements
Universal Healthcare: Implement universal healthcare schemes to ensure access to medical services for all citizens.
Preventive Healthcare: Promote preventive healthcare measures to reduce the burden of diseases.
Healthcare Infrastructure: Build more hospitals, especially in rural and underserved areas, and ensure they are well-equipped and staffed.
4. Environmental Sustainability
Renewable Energy: Invest in renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power.
Sustainable Agriculture: Promote sustainable farming practices to increase productivity without degrading the environment.
Climate Change Mitigation: Implement policies to reduce carbon emissions and enhance climate resilience.
5. Governance and Policy Reforms
Ease of Doing Business: Simplify regulations to attract domestic and foreign investment.
Tax Reforms: Create a fair and efficient tax system to increase compliance and revenue.
Corruption Reduction: Strengthen anti-corruption measures to improve transparency and accountability.
6. Financial Inclusion and Innovation
Banking Access: Ensure that banking services are accessible to all, including in remote areas.
Digital Economy: Promote digital payments and financial technologies (FinTech) to streamline financial transactions.
Start-up Ecosystem: Support start-ups and small businesses through funding, mentorship, and incubation programs.
7. Trade and Industry
Export Promotion: Develop policies to boost exports and reduce trade deficits.
Industrial Policy: Encourage manufacturing and industrialization with incentives for sectors like electronics, automobiles, and textiles.
Research and Development: Increase investment in R&D to drive innovation and industrial growth.
8. Social Equity and Inclusion
Poverty Alleviation: Implement targeted programs to lift people out of poverty.
Gender Equality: Promote gender equality in education, employment, and entrepreneurship.
Social Security: Strengthen social security nets to protect vulnerable populations.
Conclusion
To ensure sustainable economic growth, India needs to adopt a holistic approach addressing infrastructure, education, healthcare, environmental sustainability, governance, financial inclusion, trade, industry, and social equity.
Collaborative efforts between the government, private sector, and civil society are essential to implement these measures effectively and build a resilient and inclusive economy.
By Ugo Ikeji
To boost India's economic growth sustainably, a multifaceted approach is required, focusing on key areas such as infrastructure development, education, healthcare, environmental sustainability, and governance.
1. Infrastructure Development
Transportation Networks: Improve road, rail, air, and waterway connectivity to facilitate trade and reduce logistics costs.
Urban Infrastructure: Develop smart cities with robust public transport, waste management systems, and sustainable housing.
Rural Infrastructure: Enhance rural roads, electrification, and internet connectivity to integrate rural areas into the economic mainstream.
2. Education and Skill Development
Quality Education: Reform the education system to focus on critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills.
Vocational Training: Expand vocational training programs to equip the workforce with industry-relevant skills.
Higher Education: Invest in research and development (R&D) and promote higher education institutions to foster innovation.
3. Healthcare Improvements
Universal Healthcare: Implement universal healthcare schemes to ensure access to medical services for all citizens.
Preventive Healthcare: Promote preventive healthcare measures to reduce the burden of diseases.
Healthcare Infrastructure: Build more hospitals, especially in rural and underserved areas, and ensure they are well-equipped and staffed.
4. Environmental Sustainability
Renewable Energy: Invest in renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power.
Sustainable Agriculture: Promote sustainable farming practices to increase productivity without degrading the environment.
Climate Change Mitigation: Implement policies to reduce carbon emissions and enhance climate resilience.
5. Governance and Policy Reforms
Ease of Doing Business: Simplify regulations to attract domestic and foreign investment.
Tax Reforms: Create a fair and efficient tax system to increase compliance and revenue.
Corruption Reduction: Strengthen anti-corruption measures to improve transparency and accountability.
6. Financial Inclusion and Innovation
Banking Access: Ensure that banking services are accessible to all, including in remote areas.
Digital Economy: Promote digital payments and financial technologies (FinTech) to streamline financial transactions.
Start-up Ecosystem: Support start-ups and small businesses through funding, mentorship, and incubation programs.
7. Trade and Industry
Export Promotion: Develop policies to boost exports and reduce trade deficits.
Industrial Policy: Encourage manufacturing and industrialization with incentives for sectors like electronics, automobiles, and textiles.
Research and Development: Increase investment in R&D to drive innovation and industrial growth.
8. Social Equity and Inclusion
Poverty Alleviation: Implement targeted programs to lift people out of poverty.
Gender Equality: Promote gender equality in education, employment, and entrepreneurship.
Social Security: Strengthen social security nets to protect vulnerable populations.
Conclusion
To ensure sustainable economic growth, India needs to adopt a holistic approach addressing infrastructure, education, healthcare, environmental sustainability, governance, financial inclusion, trade, industry, and social equity.
Collaborative efforts between the government, private sector, and civil society are essential to implement these measures effectively and build a resilient and inclusive economy.
1 yr. ago
RESILIENCE-
Cultivating Resilience: The Interplay of Dread and Hope.
Holding on to hope requires resilience and self-compassion.
KEY POINTS-
In chronic and acute traumatic events, dread and fear can lead to a sense of being frozen and immobilized.
Joyful moments can exist even amid despair. If savored, they can invite hope.
Dread and hope, though seemingly contradictory, can coexist in a complex way that shapes the human experience.
People often ask me how it is possible to celebrate amid deep suffering and life-altering, traumatic events that shatter any sense of safety or security and leave us in confusion and the unknown.
In the face of our unbearable reality, complex trauma, shock, and uncertainty foreclose any vestige of imagination, creativity, play, and reverie. (Steve Mitchell, 1993). A malignant reality becomes pervasive and normative; the lived present is then filled with the torture of suffering while compromising any felt sense of safety or security. (Lifton, J., 1992). Time has no meaning in trauma, past, present, or future. Fear and dread become shadows that accompany and hold us hostage.
Dread often arises from anticipating negative outcomes, representing fear and anxiety about the unknown or inevitable challenges. It can be paralyzing, casting a shadow over our thoughts and actions.
Both fear and dread involve a sense of apprehension. Fear is a direct response to present and identifiable, whereas dread is more generalized, long-term, intense, and existential.
Dread can be a crippling emotion. It holds us captive in fear as long as we give it power. Both fear and dread can render us immobile, and when we fixate on dread, it consumes our thoughts. In many situations, experiencing dread is a natural part of coping with what's ahead in certain situations. It could be a severe medical diagnosis or the loss of a loved one.
It's fitting and necessary to feel that dread, move through it, and emerge on the other side (Mcfee, 2017).
So, how is it possible to play with dread and hope simultaneously?
Lord Jonathan Sacks' words have given me a perspective that I find comforting and hopeful. They are a balm to ease suffering amid despair.
"Happiness is something you can feel alone, but joy is something you share with others. Happiness is about a lifetime, but joy lives in the moment. Happiness tends to be a cool emotion, but joy makes you want to dance and sing. It's hard to feel happiness amid chaos and uncertainty. But you can still feel joy.” (Sacks, 2010 P.50)
Joyful moments can exist even amid despair. When they appear, if savored, they can invite hope. Dread and hope, though seemingly contradictory, can coexist in a complex dance that shapes human experience. This intricate interplay can be seen in various aspects of life, reflecting the duality of our emotions.
The belief in positive outcomes and the possibility of improvement or success is a source of motivation, strength, and connectivity. Safety and security can be found in our connection to ourselves and other people. After all, we are born to connect. It is our birthright!
Holding onto hope in the presence of dread can be a significant challenge, but it's also a fundamental aspect of resilience and coping with difficult situations. Here are some strategies to help maintain hope: I have found these coping strategies highly effective. Please remember that the more you practice, the easier it becomes to absorb and apply.
1. Acknowledge your feelings: Recognizing and validating your feelings of dread is essential. Ignoring or suppressing them can make it harder to move forward. Accept that it's okay to feel this way.
2. Focus on the present moment: Instead of dwelling on the future or past events contributing to your dread, try to focus on the present moment. Mindfulness techniques such as deep breathing or meditation can help anchor you in the here and now.
3. Seek support: Talking to friends, family, or a therapist about your feelings can provide comfort and perspective. Sharing your worries with others can lighten the burden and remind you that you're not alone.
4. Find meaning: Look for meaning or purpose in your experiences, even in difficult times, and reflect on what you can learn from the situation or how it can lead to personal growth.
5. Practice gratitude: Cultivating a sense of appreciation for the positive aspects of your life, no matter how small, can help counteract feelings of dread. Keeping a gratitude journal or taking a few moments each day to appreciate what you have can shift your focus toward the positive.
6. Focus on what you can control: While worrying about things beyond your control is natural, shift your focus toward what you can influence or change. Taking proactive steps, no matter how small, can help restore a sense of agency and empowerment.
7. Find sources of inspiration, whether it's through books, music, art, nature, or spiritual practices. Seek out sources that uplift and motivate you. Surrounding yourself with positivity can help counteract feelings of dread.
Conclusion
When dread invites hope to dance, they join together and move as one. Together, they create a third space; ultimately, holding onto hope requires resilience, self-compassion, and a willingness to cultivate optimism despite uncertainty. It's a process that takes time and effort, but it can make a significant difference in navigating challenging or traumatic circumstances.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Cultivating Resilience: The Interplay of Dread and Hope.
Holding on to hope requires resilience and self-compassion.
KEY POINTS-
In chronic and acute traumatic events, dread and fear can lead to a sense of being frozen and immobilized.
Joyful moments can exist even amid despair. If savored, they can invite hope.
Dread and hope, though seemingly contradictory, can coexist in a complex way that shapes the human experience.
People often ask me how it is possible to celebrate amid deep suffering and life-altering, traumatic events that shatter any sense of safety or security and leave us in confusion and the unknown.
In the face of our unbearable reality, complex trauma, shock, and uncertainty foreclose any vestige of imagination, creativity, play, and reverie. (Steve Mitchell, 1993). A malignant reality becomes pervasive and normative; the lived present is then filled with the torture of suffering while compromising any felt sense of safety or security. (Lifton, J., 1992). Time has no meaning in trauma, past, present, or future. Fear and dread become shadows that accompany and hold us hostage.
Dread often arises from anticipating negative outcomes, representing fear and anxiety about the unknown or inevitable challenges. It can be paralyzing, casting a shadow over our thoughts and actions.
Both fear and dread involve a sense of apprehension. Fear is a direct response to present and identifiable, whereas dread is more generalized, long-term, intense, and existential.
Dread can be a crippling emotion. It holds us captive in fear as long as we give it power. Both fear and dread can render us immobile, and when we fixate on dread, it consumes our thoughts. In many situations, experiencing dread is a natural part of coping with what's ahead in certain situations. It could be a severe medical diagnosis or the loss of a loved one.
It's fitting and necessary to feel that dread, move through it, and emerge on the other side (Mcfee, 2017).
So, how is it possible to play with dread and hope simultaneously?
Lord Jonathan Sacks' words have given me a perspective that I find comforting and hopeful. They are a balm to ease suffering amid despair.
"Happiness is something you can feel alone, but joy is something you share with others. Happiness is about a lifetime, but joy lives in the moment. Happiness tends to be a cool emotion, but joy makes you want to dance and sing. It's hard to feel happiness amid chaos and uncertainty. But you can still feel joy.” (Sacks, 2010 P.50)
Joyful moments can exist even amid despair. When they appear, if savored, they can invite hope. Dread and hope, though seemingly contradictory, can coexist in a complex dance that shapes human experience. This intricate interplay can be seen in various aspects of life, reflecting the duality of our emotions.
The belief in positive outcomes and the possibility of improvement or success is a source of motivation, strength, and connectivity. Safety and security can be found in our connection to ourselves and other people. After all, we are born to connect. It is our birthright!
Holding onto hope in the presence of dread can be a significant challenge, but it's also a fundamental aspect of resilience and coping with difficult situations. Here are some strategies to help maintain hope: I have found these coping strategies highly effective. Please remember that the more you practice, the easier it becomes to absorb and apply.
1. Acknowledge your feelings: Recognizing and validating your feelings of dread is essential. Ignoring or suppressing them can make it harder to move forward. Accept that it's okay to feel this way.
2. Focus on the present moment: Instead of dwelling on the future or past events contributing to your dread, try to focus on the present moment. Mindfulness techniques such as deep breathing or meditation can help anchor you in the here and now.
3. Seek support: Talking to friends, family, or a therapist about your feelings can provide comfort and perspective. Sharing your worries with others can lighten the burden and remind you that you're not alone.
4. Find meaning: Look for meaning or purpose in your experiences, even in difficult times, and reflect on what you can learn from the situation or how it can lead to personal growth.
5. Practice gratitude: Cultivating a sense of appreciation for the positive aspects of your life, no matter how small, can help counteract feelings of dread. Keeping a gratitude journal or taking a few moments each day to appreciate what you have can shift your focus toward the positive.
6. Focus on what you can control: While worrying about things beyond your control is natural, shift your focus toward what you can influence or change. Taking proactive steps, no matter how small, can help restore a sense of agency and empowerment.
7. Find sources of inspiration, whether it's through books, music, art, nature, or spiritual practices. Seek out sources that uplift and motivate you. Surrounding yourself with positivity can help counteract feelings of dread.
Conclusion
When dread invites hope to dance, they join together and move as one. Together, they create a third space; ultimately, holding onto hope requires resilience, self-compassion, and a willingness to cultivate optimism despite uncertainty. It's a process that takes time and effort, but it can make a significant difference in navigating challenging or traumatic circumstances.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
1 yr. ago
STRESS-
The Art of Inner Tension.
Creative solutions to stress.
KEY POINTS-
The traditional approach to stress management leaves many feeling like failures.
Psychologists have routinely linked creativity and stress.
The art of inner tension is to take ownership of stress and its management.
“I merely took the energy it takes to pout and wrote some blues.” — Duke Ellington
Psychologists have routinely linked creativity and stress and the list of people whose lives were filled with challenges includes Vincent Van Gogh, Issac Newton, Virginia Woolf, Sylvia Plath, and Beethoven. While the debate over whether these geniuses created because of their inner tension or in spite of it continues, what is certain is that the rest of us can turn things around by bringing creativity into how we manage stress. By becoming artists whose muse is none other than life’s frustrations, worries, and anxieties we can create masterpieces of peace-filled lives or simply doodles of not overreacting to life’s difficulties.
I think of stress as the felt tension arising from a misalignment between our expectations and experiences. Eckhard Tolle put it more simply: “Stress is having this but wanting that.”
It's often a hard sell to suggest to people that they are the creators of their inner tension but with just a few examples, most will have the “aha” moment of realization that it's their interpretations of the happenings in their lives that bring it to life. When the self-blame factor is removed by demonstrating that, in most cases, this response was reflexive and habitual, taking ownership allows for new creative methods for coping with what some refer to as “the silent killer.”
The traditional approach to stress management that encourages getting quality sleep, healthy eating, exercise and relaxation leaves most of the clients I work with feeling like they are failing in their efforts to feel better. They point out that it is the very stress they are experiencing that makes the items on that list feel more like a Bucket List than a prescription for a more relaxed life.
I’ve learned that encouraging an artistic view of how one both experiences and expresses the stressors in one’s life taps into a deeply innate desire for imaginative endeavors—to stand back and proudly state, “Look what I’ve done.”
Thoreau wrote, “To affect the quality of the day, that is the highest of arts.” In this sense, everyone is engaged in an artistic undertaking, although the “quality” of that expressionism is colored by troublesome thoughts and emotions. Stress is a picture that paints itself in the absence of our conscious presence. It’s no wonder many clients look quizzically at me and ask, who did this?
In her book, The Artist’s Way, Julia Cameron states, “Creativity requires activity… and most of us hate to do something when we can obsess about something else instead.” This idea of obsessing-over-doing came to me as I was heading to a stress-management training. I was pondering why intelligent adults would continue to wallow in their worries rather than do something about them. It occurred to me, and I later shared my epiphany with the group I was leading, that it’s because many people think that “stressing out” is managing their stress.
To direct clients back toward “doing” mode, I offer these tips for unleashing the artist within:
Add some color. Too often, when stressed, the world appears only as black and white. One is either up or down, happy or sad. The pictures these clients paint of their current situations are dark and heavy. Using the therapeutic tool of challenging irrational beliefs, clients can draw from the Crayola box of emotions, thoughts, and behaviors to challenge the notion that life is simply dull shades of grey.
Switch media. Many people I work with are only able to list four or five coping skills, with at least two of them no longer working. I counter this by handing them the “Pleasant Events List," created by Marsha Linehan, which includes 225 activities one can engage in to emotionally regulate, and asking them to pick at least three to broaden their palette.
Ignore the critics. People are often discouraged from new endeavors by the opinions of others, some of whom use criticism as their own coping skill. Artists from across the creative spectrum have faced criticism of their works. Georgia O’Keefe wrote, “I have already settled it for myself, so flattery and criticism go down the same drain and I am quite free.”
Be a surrealist. Surrealism seeks to challenge reality and there is no better stress-busting technique than to take conventional thinking head-on. Liberating oneself from old ideas gives way to what the psychologist Kelly McGonical refers to as “the upside of stress.”
Reframe it. Many people box themselves in by assuming that they are limited in their abilities to cope with the strains of modern life. They have firm boundaries regarding what is acceptable and anything outside of those limits leads to stress.
Many people adopt a paint-by-numbers approach which boxes them in and stifles creativity. Reframing, in the artistic sense, is to work outside the lines of these limitations—to experience true freedom. Psychological reframing is simply seeing things in a new way—turning a negative on its head to find its opposite of positivity.
The beauty of the art of inner tension is that one does not need to be Mozart, Picasso, or Hemingway to benefit from redirecting their reactive energy toward a creative process.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
The Art of Inner Tension.
Creative solutions to stress.
KEY POINTS-
The traditional approach to stress management leaves many feeling like failures.
Psychologists have routinely linked creativity and stress.
The art of inner tension is to take ownership of stress and its management.
“I merely took the energy it takes to pout and wrote some blues.” — Duke Ellington
Psychologists have routinely linked creativity and stress and the list of people whose lives were filled with challenges includes Vincent Van Gogh, Issac Newton, Virginia Woolf, Sylvia Plath, and Beethoven. While the debate over whether these geniuses created because of their inner tension or in spite of it continues, what is certain is that the rest of us can turn things around by bringing creativity into how we manage stress. By becoming artists whose muse is none other than life’s frustrations, worries, and anxieties we can create masterpieces of peace-filled lives or simply doodles of not overreacting to life’s difficulties.
I think of stress as the felt tension arising from a misalignment between our expectations and experiences. Eckhard Tolle put it more simply: “Stress is having this but wanting that.”
It's often a hard sell to suggest to people that they are the creators of their inner tension but with just a few examples, most will have the “aha” moment of realization that it's their interpretations of the happenings in their lives that bring it to life. When the self-blame factor is removed by demonstrating that, in most cases, this response was reflexive and habitual, taking ownership allows for new creative methods for coping with what some refer to as “the silent killer.”
The traditional approach to stress management that encourages getting quality sleep, healthy eating, exercise and relaxation leaves most of the clients I work with feeling like they are failing in their efforts to feel better. They point out that it is the very stress they are experiencing that makes the items on that list feel more like a Bucket List than a prescription for a more relaxed life.
I’ve learned that encouraging an artistic view of how one both experiences and expresses the stressors in one’s life taps into a deeply innate desire for imaginative endeavors—to stand back and proudly state, “Look what I’ve done.”
Thoreau wrote, “To affect the quality of the day, that is the highest of arts.” In this sense, everyone is engaged in an artistic undertaking, although the “quality” of that expressionism is colored by troublesome thoughts and emotions. Stress is a picture that paints itself in the absence of our conscious presence. It’s no wonder many clients look quizzically at me and ask, who did this?
In her book, The Artist’s Way, Julia Cameron states, “Creativity requires activity… and most of us hate to do something when we can obsess about something else instead.” This idea of obsessing-over-doing came to me as I was heading to a stress-management training. I was pondering why intelligent adults would continue to wallow in their worries rather than do something about them. It occurred to me, and I later shared my epiphany with the group I was leading, that it’s because many people think that “stressing out” is managing their stress.
To direct clients back toward “doing” mode, I offer these tips for unleashing the artist within:
Add some color. Too often, when stressed, the world appears only as black and white. One is either up or down, happy or sad. The pictures these clients paint of their current situations are dark and heavy. Using the therapeutic tool of challenging irrational beliefs, clients can draw from the Crayola box of emotions, thoughts, and behaviors to challenge the notion that life is simply dull shades of grey.
Switch media. Many people I work with are only able to list four or five coping skills, with at least two of them no longer working. I counter this by handing them the “Pleasant Events List," created by Marsha Linehan, which includes 225 activities one can engage in to emotionally regulate, and asking them to pick at least three to broaden their palette.
Ignore the critics. People are often discouraged from new endeavors by the opinions of others, some of whom use criticism as their own coping skill. Artists from across the creative spectrum have faced criticism of their works. Georgia O’Keefe wrote, “I have already settled it for myself, so flattery and criticism go down the same drain and I am quite free.”
Be a surrealist. Surrealism seeks to challenge reality and there is no better stress-busting technique than to take conventional thinking head-on. Liberating oneself from old ideas gives way to what the psychologist Kelly McGonical refers to as “the upside of stress.”
Reframe it. Many people box themselves in by assuming that they are limited in their abilities to cope with the strains of modern life. They have firm boundaries regarding what is acceptable and anything outside of those limits leads to stress.
Many people adopt a paint-by-numbers approach which boxes them in and stifles creativity. Reframing, in the artistic sense, is to work outside the lines of these limitations—to experience true freedom. Psychological reframing is simply seeing things in a new way—turning a negative on its head to find its opposite of positivity.
The beauty of the art of inner tension is that one does not need to be Mozart, Picasso, or Hemingway to benefit from redirecting their reactive energy toward a creative process.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
1 yr. ago
MOTIVATION-
Mastering the Mindset of High Performers.
Here are some effective real-life practices to cultivate professional success.
KEY POINTS-
Understanding these foundational mental habits is crucial for achieving sustained success.
High performers embody resilience and a growth mindset, both of which are crucial for navigating challenges.
Practices like meditation and mindfulness can enhance mental discipline and cognitive abilities.
Mastering the mindset of success involves understanding the fundamental mental frameworks and habits that support sustained achievement. To accomplish this, professionals, entrepreneurs, and leaders can find inspiration from a diverse range of accomplished figures across various fields.
For example, Jeff Bezos and Robert Smith exemplify resilience and innovation, attributes that have enabled them to accumulate substantial wealth and profoundly influence the world. Meanwhile, leaders like Oprah Winfrey, Barack Obama, and LeBron James embody discipline, determination, and the capacity to turn adversity into opportunities for growth. By embracing these diverse viewpoints, one can foster a resilient mindset that effectively navigates challenges and seizes opportunities.
In preparation for this post, I recently had the privilege of interviewing successful entrepreneur Iman Gadzhi, who shared invaluable insights on navigating the complexities of entrepreneurship and maintaining peak performance.
The High Performer’s Mindset
High performers exhibit a distinct set of characteristics that propel their success. Experts highlight resilience as a foundational trait, crucial for navigating setbacks and maintaining unwavering focus amidst challenges. For instance, Elon Musk, known for his resilience in the face of numerous setbacks with SpaceX and Tesla, once remarked, “Failure is an option here. If things are not failing, you are not innovating enough.” This mindset not only underscores the importance of resilience but also reflects a growth-oriented approach that embraces learning from failures to drive progress.
KEY POINTS
Understanding these foundational mental habits is crucial for achieving sustained success.
High performers embody resilience and a growth mindset, both of which are crucial for navigating challenges.
Practices like meditation and mindfulness can enhance mental discipline and cognitive abilities.
Iman Gadzhi / Used With Permission
Source: Iman Gadzhi / Used With Permission
This post is Part 7 of a series in which I gather insights from leadership, diversity, and wellness experts.
Mastering the mindset of success involves understanding the fundamental mental frameworks and habits that support sustained achievement. To accomplish this, professionals, entrepreneurs, and leaders can find inspiration from a diverse range of accomplished figures across various fields.
For example, Jeff Bezos and Robert Smith exemplify resilience and innovation, attributes that have enabled them to accumulate substantial wealth and profoundly influence the world. Meanwhile, leaders like Oprah Winfrey, Barack Obama, and LeBron James embody discipline, determination, and the capacity to turn adversity into opportunities for growth. By embracing these diverse viewpoints, one can foster a resilient mindset that effectively navigates challenges and seizes opportunities.
In preparation for this post, I recently had the privilege of interviewing successful entrepreneur Iman Gadzhi, who shared invaluable insights on navigating the complexities of entrepreneurship and maintaining peak performance.
The High Performer’s Mindset
High performers exhibit a distinct set of characteristics that propel their success. Experts highlight resilience as a foundational trait, crucial for navigating setbacks and maintaining unwavering focus amidst challenges. For instance, Elon Musk, known for his resilience in the face of numerous setbacks with SpaceX and Tesla, once remarked, “Failure is an option here. If things are not failing, you are not innovating enough.” This mindset not only underscores the importance of resilience but also reflects a growth-oriented approach that embraces learning from failures to drive progress.
article continues after advertisement
Discipline is foundational for high achievers, who are defined by their intense commitment to goals and the rigorous routines that uphold them. One example of a professional who embodies this trait is Ken Chenault, the former CEO of American Express. Throughout his tenure, Chenault demonstrated exceptional discipline in navigating challenges and steering the company to sustained growth and innovation in the financial services industry. His commitment to strategic vision and operational excellence illustrates how discipline contributes to long-term success in corporate leadership.
Additionally, high performers embody a growth mindset, believing in their capacity for continual personal development and the ability to glean valuable lessons from every experience. As former President Barack Obama once stated, “Change will not come if we wait for some other person or some other time. We are the ones we’ve been waiting for. We are the change that we seek.”
Key Habits of High Performers
Exploring the essential habits of high performers provides critical insights into the factors that drive sustained success and exceptional achievement. Here are some key habits that highlight the foundational practices essential for achieving these goals:
1. Meditation and Mindfulness
“If you can learn to control your mind, you can control your reality,” emphasizes Gadzhi, highlighting the transformative power of mental discipline. Daily meditation plays a crucial role in enhancing mental discipline, improving concentration, and effectively managing stress. Experts suggest that just 10 minutes of mindfulness practice each day can significantly enhance one’s ability to remain composed and focused during challenging situations.
Scientific studies, such as those by Tang, Friston, & Tang (2020), indicate that mindfulness meditation promotes the growth of gray matter in the brain, thereby enhancing emotional regulation and cognitive abilities. Cultivating a regular meditation practice not only supports immediate mental well-being but also contributes to long-term cognitive resilience and emotional stability.
2. Quality Sleep
Quality sleep is essential for high performers, who typically aim for 7-9 hours of restful sleep per night to facilitate recovery from intense work phases. Maintaining good sleep hygiene, such as ensuring a dark and cool sleeping environment and minimizing screen time before bed, significantly enhances sleep quality. Interestingly, research suggests that exposure to natural light during the day can improve sleep quality and duration (Blume, Garbazza, & Spitschan, 2019). This emphasizes the importance of both environmental factors and daily routines in promoting optimal sleep among high performers.
3. Substance Moderation
Avoiding or moderating the intake of substances like alcohol and caffeine requires a mindset that values long-term benefits over short-term gratification. High performers recognize that while these substances may offer immediate boosts in alertness or relaxation, they can also disrupt sleep patterns and impair cognitive function with prolonged use.
Instead of relying on substances for temporary effects, high performers prioritize sustainable practices that enhance overall well-being and performance. They recognize that activities such as regular exercise and meditation foster enduring energy levels, sharpened focus, and mental clarity, all without the negative side effects associated with substances. Gadzhi succinctly encapsulates this approach with his mantra, “Sleep, Lift, Meditate, Work, Repeat,” illustrating a disciplined daily routine that supports a high-performance lifestyle.
Iman Gadzhi: A Case Study
Iman Gadzhi, founder of IAG Media and a self-made millionaire, embodies the mindset and discipline of high achievers. Beginning in post-Soviet Russia, he forged a successful digital marketing empire through mental resilience and self-confidence. Gadzhi maintains his performance edge through daily meditation for clarity, rigorous exercise for physical and mental fitness, and strategic relaxation for creativity and decision-making.
Key to Gadzhi’s philosophy is the belief that individuals can transcend their thoughts and empower themselves through positive self-belief. He emphasizes overcoming challenges with inner strength, which is essential for success in business and personal life. As Gadzhi wisely advises, “Realize that you are not your thoughts, and you don’t have to be a prisoner of them,” highlighting the importance of challenging unhelpful thinking patterns.
In today’s competitive world, embracing Gadzhi’s principles fosters resilience and perseverance, paving the way for lasting success. His journey inspires aspiring entrepreneurs and individuals striving to achieve their fullest potential.
Implementing Strategies for Success-
Implementing strategies for success involves structuring your daily routine to optimize productivity and well-being. Gadzhi and experts recommend several key practices:
1. Plan Your Day: Allocate dedicated time slots for work and relaxation to prevent burnout and maintain productivity. Gadzhi emphasizes the importance of strategic relaxation periods, balancing intense work with rejuvenation to sustain long-term effectiveness. Set clear objectives for both work and relaxation phases to maintain focus and ensure that each activity contributes meaningfully to your overall goals.
2. Conduct Regular Health Checks: Monitor the impact of your daily routines, including meditation and exercise, on your physical and mental well-being.
3. Connect With Social Supports: Surround yourself with a supportive network that encourages a balanced lifestyle, providing both emotional encouragement and practical advice to navigate challenges effectively.
Bottom Line
Overall, achieving a success-oriented mindset requires adopting foundational habits and approaches that promote sustained achievement. Inspirational figures from various fields who showcase resilience, innovation, discipline, and the capacity to transform challenges into opportunities play a pivotal role in cultivating this resilient mindset. Practical strategies like daily meditation for mental clarity, establishing clear goals, and prioritizing self-care enhance productivity, creativity, and overall well-being.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Mastering the Mindset of High Performers.
Here are some effective real-life practices to cultivate professional success.
KEY POINTS-
Understanding these foundational mental habits is crucial for achieving sustained success.
High performers embody resilience and a growth mindset, both of which are crucial for navigating challenges.
Practices like meditation and mindfulness can enhance mental discipline and cognitive abilities.
Mastering the mindset of success involves understanding the fundamental mental frameworks and habits that support sustained achievement. To accomplish this, professionals, entrepreneurs, and leaders can find inspiration from a diverse range of accomplished figures across various fields.
For example, Jeff Bezos and Robert Smith exemplify resilience and innovation, attributes that have enabled them to accumulate substantial wealth and profoundly influence the world. Meanwhile, leaders like Oprah Winfrey, Barack Obama, and LeBron James embody discipline, determination, and the capacity to turn adversity into opportunities for growth. By embracing these diverse viewpoints, one can foster a resilient mindset that effectively navigates challenges and seizes opportunities.
In preparation for this post, I recently had the privilege of interviewing successful entrepreneur Iman Gadzhi, who shared invaluable insights on navigating the complexities of entrepreneurship and maintaining peak performance.
The High Performer’s Mindset
High performers exhibit a distinct set of characteristics that propel their success. Experts highlight resilience as a foundational trait, crucial for navigating setbacks and maintaining unwavering focus amidst challenges. For instance, Elon Musk, known for his resilience in the face of numerous setbacks with SpaceX and Tesla, once remarked, “Failure is an option here. If things are not failing, you are not innovating enough.” This mindset not only underscores the importance of resilience but also reflects a growth-oriented approach that embraces learning from failures to drive progress.
KEY POINTS
Understanding these foundational mental habits is crucial for achieving sustained success.
High performers embody resilience and a growth mindset, both of which are crucial for navigating challenges.
Practices like meditation and mindfulness can enhance mental discipline and cognitive abilities.
Iman Gadzhi / Used With Permission
Source: Iman Gadzhi / Used With Permission
This post is Part 7 of a series in which I gather insights from leadership, diversity, and wellness experts.
Mastering the mindset of success involves understanding the fundamental mental frameworks and habits that support sustained achievement. To accomplish this, professionals, entrepreneurs, and leaders can find inspiration from a diverse range of accomplished figures across various fields.
For example, Jeff Bezos and Robert Smith exemplify resilience and innovation, attributes that have enabled them to accumulate substantial wealth and profoundly influence the world. Meanwhile, leaders like Oprah Winfrey, Barack Obama, and LeBron James embody discipline, determination, and the capacity to turn adversity into opportunities for growth. By embracing these diverse viewpoints, one can foster a resilient mindset that effectively navigates challenges and seizes opportunities.
In preparation for this post, I recently had the privilege of interviewing successful entrepreneur Iman Gadzhi, who shared invaluable insights on navigating the complexities of entrepreneurship and maintaining peak performance.
The High Performer’s Mindset
High performers exhibit a distinct set of characteristics that propel their success. Experts highlight resilience as a foundational trait, crucial for navigating setbacks and maintaining unwavering focus amidst challenges. For instance, Elon Musk, known for his resilience in the face of numerous setbacks with SpaceX and Tesla, once remarked, “Failure is an option here. If things are not failing, you are not innovating enough.” This mindset not only underscores the importance of resilience but also reflects a growth-oriented approach that embraces learning from failures to drive progress.
article continues after advertisement
Discipline is foundational for high achievers, who are defined by their intense commitment to goals and the rigorous routines that uphold them. One example of a professional who embodies this trait is Ken Chenault, the former CEO of American Express. Throughout his tenure, Chenault demonstrated exceptional discipline in navigating challenges and steering the company to sustained growth and innovation in the financial services industry. His commitment to strategic vision and operational excellence illustrates how discipline contributes to long-term success in corporate leadership.
Additionally, high performers embody a growth mindset, believing in their capacity for continual personal development and the ability to glean valuable lessons from every experience. As former President Barack Obama once stated, “Change will not come if we wait for some other person or some other time. We are the ones we’ve been waiting for. We are the change that we seek.”
Key Habits of High Performers
Exploring the essential habits of high performers provides critical insights into the factors that drive sustained success and exceptional achievement. Here are some key habits that highlight the foundational practices essential for achieving these goals:
1. Meditation and Mindfulness
“If you can learn to control your mind, you can control your reality,” emphasizes Gadzhi, highlighting the transformative power of mental discipline. Daily meditation plays a crucial role in enhancing mental discipline, improving concentration, and effectively managing stress. Experts suggest that just 10 minutes of mindfulness practice each day can significantly enhance one’s ability to remain composed and focused during challenging situations.
Scientific studies, such as those by Tang, Friston, & Tang (2020), indicate that mindfulness meditation promotes the growth of gray matter in the brain, thereby enhancing emotional regulation and cognitive abilities. Cultivating a regular meditation practice not only supports immediate mental well-being but also contributes to long-term cognitive resilience and emotional stability.
2. Quality Sleep
Quality sleep is essential for high performers, who typically aim for 7-9 hours of restful sleep per night to facilitate recovery from intense work phases. Maintaining good sleep hygiene, such as ensuring a dark and cool sleeping environment and minimizing screen time before bed, significantly enhances sleep quality. Interestingly, research suggests that exposure to natural light during the day can improve sleep quality and duration (Blume, Garbazza, & Spitschan, 2019). This emphasizes the importance of both environmental factors and daily routines in promoting optimal sleep among high performers.
3. Substance Moderation
Avoiding or moderating the intake of substances like alcohol and caffeine requires a mindset that values long-term benefits over short-term gratification. High performers recognize that while these substances may offer immediate boosts in alertness or relaxation, they can also disrupt sleep patterns and impair cognitive function with prolonged use.
Instead of relying on substances for temporary effects, high performers prioritize sustainable practices that enhance overall well-being and performance. They recognize that activities such as regular exercise and meditation foster enduring energy levels, sharpened focus, and mental clarity, all without the negative side effects associated with substances. Gadzhi succinctly encapsulates this approach with his mantra, “Sleep, Lift, Meditate, Work, Repeat,” illustrating a disciplined daily routine that supports a high-performance lifestyle.
Iman Gadzhi: A Case Study
Iman Gadzhi, founder of IAG Media and a self-made millionaire, embodies the mindset and discipline of high achievers. Beginning in post-Soviet Russia, he forged a successful digital marketing empire through mental resilience and self-confidence. Gadzhi maintains his performance edge through daily meditation for clarity, rigorous exercise for physical and mental fitness, and strategic relaxation for creativity and decision-making.
Key to Gadzhi’s philosophy is the belief that individuals can transcend their thoughts and empower themselves through positive self-belief. He emphasizes overcoming challenges with inner strength, which is essential for success in business and personal life. As Gadzhi wisely advises, “Realize that you are not your thoughts, and you don’t have to be a prisoner of them,” highlighting the importance of challenging unhelpful thinking patterns.
In today’s competitive world, embracing Gadzhi’s principles fosters resilience and perseverance, paving the way for lasting success. His journey inspires aspiring entrepreneurs and individuals striving to achieve their fullest potential.
Implementing Strategies for Success-
Implementing strategies for success involves structuring your daily routine to optimize productivity and well-being. Gadzhi and experts recommend several key practices:
1. Plan Your Day: Allocate dedicated time slots for work and relaxation to prevent burnout and maintain productivity. Gadzhi emphasizes the importance of strategic relaxation periods, balancing intense work with rejuvenation to sustain long-term effectiveness. Set clear objectives for both work and relaxation phases to maintain focus and ensure that each activity contributes meaningfully to your overall goals.
2. Conduct Regular Health Checks: Monitor the impact of your daily routines, including meditation and exercise, on your physical and mental well-being.
3. Connect With Social Supports: Surround yourself with a supportive network that encourages a balanced lifestyle, providing both emotional encouragement and practical advice to navigate challenges effectively.
Bottom Line
Overall, achieving a success-oriented mindset requires adopting foundational habits and approaches that promote sustained achievement. Inspirational figures from various fields who showcase resilience, innovation, discipline, and the capacity to transform challenges into opportunities play a pivotal role in cultivating this resilient mindset. Practical strategies like daily meditation for mental clarity, establishing clear goals, and prioritizing self-care enhance productivity, creativity, and overall well-being.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
1 yr. ago
COGNITION-
Want to Transform Your Life? Reclaim Floodlight Thinking.
Reconnect regularly with your deeper values in the age of distraction.
KEY POINTS-
Seeing a phone or laptop reduces our learning and that of the people around us.
Through floodlight thinking, we can see the entire picture.
When we don't acknowledge the people around us, they feel more disconnected from society.
At a recent two-day conference I taught to more than 50 leaders in Amsterdam, we began with participants reading the Ground Rules. They expressed surprise at the fourth and most controversial rule of our collective engagement:
Your phone, laptop, tablet or other digital device must be switched off during the sessions. A phone ringing during a session will be considered disruptive and we will ask you to put it away if you are using it during a session. There will be time during breaks for you to answer messages. All digital devices must be turned off as they are disruptive to the learning of others. Please bring a paper and pen to take notes.
A Controversial Rule
I reassured participants, as I always do in all of my leadership programs and courses, that if they need to use their phone at any time, they can—outside of the classroom.
“No judgment,” I shared. “I know that there is more to your life than this program. You may have a sick child, or an elderly parent, or a struggling coworker who needs to reach you. If you need to use your phone, just step outside, do what you need to do, and return.”
Based on more than 10 years of research I reviewed for my book Screened In: The Art of Living Free in the Digital Age, I cite studies that the mere presence of a phone or laptop in a learning environment obstructs genuine learning for three primary reasons.
First, as a Stanford University study discovered, seeing a phone or laptop causes stress as it’s a reminder of everything you still need to do outside of the room. Second, it reduces your learning by damaging your cognitive capacity—even if it’s turned off.
Finally, using your phone, tablet, or laptop also decreases the learning—even if it’s just used for taking notes—of the people around you. Hence, allowing screens into a learning environment should not just be an individual decision, as most of us assume, but a collective decision—as screens affect everyone present.
You’ve Got to Be Kidding
After the usual incredulous glances around the room, the participants grudgingly settled in. Over the next two days, we engaged in screen-free discussions about leadership, how to manage anxiety and loneliness in oneself and one’s team members, work-life balance, the role of gender in leadership, and everything in between.
After the conference, I received many messages from participants thanking me and the other professors. They especially emphasized the fourth ground rule. It was the “first step to rehab,” shared one leader.
“What a gift the past two days were,” another expressed. “A break from the everyday madness (and our devices!) with inspiring sessions and encounters.”
“It was wonderful and a great gift to myself,” proclaimed another leader. “At least you know how to reach me. But beware since these two days I will not be so much on my phone as before.”
From Flashlight to Floodlight
These three reasons aside, there is another that, as an educator grappling with these issues every day, I must add. An idea I derived from Alan Watts’ interpretation of Zen Buddhism, I consider there to be two types of thinking.
The first is what I call “flashlight thinking.” If you turn off all the lights in a room and shine a flashlight on the wall, you will see a small disk of light. This disk is your next email, text, meeting, or phone call.
The other type of thinking I call “floodlight thinking.” If you again turn off the lights and this time place a floodlight on the floor, it will illuminate the entire wall. It is through this type of thinking that we are able to see the entire picture, our holistic vision of whatever issue we are grappling with.
Our screens constantly pull us out of floodlight thinking and into flashlight thinking. Yet it is floodlight thinking where our transformational potential lies. It enables us to access our deepest creativity and to view the same issue we’ve been looking at for months, perhaps even years, from a new angle. We may even make a breakthrough.
I consider my role as a leadership educator to be to facilitate a collective search for truth in relation to whatever topic I am teaching: leadership, work-life balance, emotion management, interpersonal communication. As we can see from the research, the mere presence of a phone or laptop in the room renders floodlight thinking elusive, not only for its owner but also for others in their vicinity.
Just Presence
For educators and facilitators in our current age of distraction, just as important as having knowledge to share may be the ability to be fully present with their students, clients, or participants. Creating such an environment is virtually impossible (pun intended) unless it’s screen-free.
The reason is that we educators are not the only ones tasked with providing presence in the collective search for truth that is a high-quality learning encounter: so is each and every student. Why?
A brilliant study asked participants to pass people on the street while refusing to make eye contact or acknowledge them so they feel what is referred to in Germany as wie Luft behandeln, which means “to be looked at as though air.” The result? The people they passed expressed a few minutes later that they felt more disconnected from society.
Each time we have the opportunity to bring people together for a shared learning experience, it is incumbent on us as educators to create a nonjudgmental, accepting environment conducive to everyone being fully present and comfortable with the prospect of sharing their professional and life challenges, dreams, and experiences.
If we are going to ask people to leave their phones at the door in the third millennium in order to learn, we can offer no less.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Want to Transform Your Life? Reclaim Floodlight Thinking.
Reconnect regularly with your deeper values in the age of distraction.
KEY POINTS-
Seeing a phone or laptop reduces our learning and that of the people around us.
Through floodlight thinking, we can see the entire picture.
When we don't acknowledge the people around us, they feel more disconnected from society.
At a recent two-day conference I taught to more than 50 leaders in Amsterdam, we began with participants reading the Ground Rules. They expressed surprise at the fourth and most controversial rule of our collective engagement:
Your phone, laptop, tablet or other digital device must be switched off during the sessions. A phone ringing during a session will be considered disruptive and we will ask you to put it away if you are using it during a session. There will be time during breaks for you to answer messages. All digital devices must be turned off as they are disruptive to the learning of others. Please bring a paper and pen to take notes.
A Controversial Rule
I reassured participants, as I always do in all of my leadership programs and courses, that if they need to use their phone at any time, they can—outside of the classroom.
“No judgment,” I shared. “I know that there is more to your life than this program. You may have a sick child, or an elderly parent, or a struggling coworker who needs to reach you. If you need to use your phone, just step outside, do what you need to do, and return.”
Based on more than 10 years of research I reviewed for my book Screened In: The Art of Living Free in the Digital Age, I cite studies that the mere presence of a phone or laptop in a learning environment obstructs genuine learning for three primary reasons.
First, as a Stanford University study discovered, seeing a phone or laptop causes stress as it’s a reminder of everything you still need to do outside of the room. Second, it reduces your learning by damaging your cognitive capacity—even if it’s turned off.
Finally, using your phone, tablet, or laptop also decreases the learning—even if it’s just used for taking notes—of the people around you. Hence, allowing screens into a learning environment should not just be an individual decision, as most of us assume, but a collective decision—as screens affect everyone present.
You’ve Got to Be Kidding
After the usual incredulous glances around the room, the participants grudgingly settled in. Over the next two days, we engaged in screen-free discussions about leadership, how to manage anxiety and loneliness in oneself and one’s team members, work-life balance, the role of gender in leadership, and everything in between.
After the conference, I received many messages from participants thanking me and the other professors. They especially emphasized the fourth ground rule. It was the “first step to rehab,” shared one leader.
“What a gift the past two days were,” another expressed. “A break from the everyday madness (and our devices!) with inspiring sessions and encounters.”
“It was wonderful and a great gift to myself,” proclaimed another leader. “At least you know how to reach me. But beware since these two days I will not be so much on my phone as before.”
From Flashlight to Floodlight
These three reasons aside, there is another that, as an educator grappling with these issues every day, I must add. An idea I derived from Alan Watts’ interpretation of Zen Buddhism, I consider there to be two types of thinking.
The first is what I call “flashlight thinking.” If you turn off all the lights in a room and shine a flashlight on the wall, you will see a small disk of light. This disk is your next email, text, meeting, or phone call.
The other type of thinking I call “floodlight thinking.” If you again turn off the lights and this time place a floodlight on the floor, it will illuminate the entire wall. It is through this type of thinking that we are able to see the entire picture, our holistic vision of whatever issue we are grappling with.
Our screens constantly pull us out of floodlight thinking and into flashlight thinking. Yet it is floodlight thinking where our transformational potential lies. It enables us to access our deepest creativity and to view the same issue we’ve been looking at for months, perhaps even years, from a new angle. We may even make a breakthrough.
I consider my role as a leadership educator to be to facilitate a collective search for truth in relation to whatever topic I am teaching: leadership, work-life balance, emotion management, interpersonal communication. As we can see from the research, the mere presence of a phone or laptop in the room renders floodlight thinking elusive, not only for its owner but also for others in their vicinity.
Just Presence
For educators and facilitators in our current age of distraction, just as important as having knowledge to share may be the ability to be fully present with their students, clients, or participants. Creating such an environment is virtually impossible (pun intended) unless it’s screen-free.
The reason is that we educators are not the only ones tasked with providing presence in the collective search for truth that is a high-quality learning encounter: so is each and every student. Why?
A brilliant study asked participants to pass people on the street while refusing to make eye contact or acknowledge them so they feel what is referred to in Germany as wie Luft behandeln, which means “to be looked at as though air.” The result? The people they passed expressed a few minutes later that they felt more disconnected from society.
Each time we have the opportunity to bring people together for a shared learning experience, it is incumbent on us as educators to create a nonjudgmental, accepting environment conducive to everyone being fully present and comfortable with the prospect of sharing their professional and life challenges, dreams, and experiences.
If we are going to ask people to leave their phones at the door in the third millennium in order to learn, we can offer no less.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
1 yr. ago
ATTENTION-
Convergent Attention, Divergent Consciousness.
Since consciousness is private, attention is needed for communication.
KEY POINTS-
Phenomenal consciousness cannot be the sole source of intelligent capacities.
Attention is required for creating a common world, or communicative background.
The divergence of conscious experiences, however, can offer a diversity of perspectives and creativity.
In this blog series, for the last 9 years, we have explored the implications of the differences between consciousness and attention. One difference is about the divergent paths taken by species towards intersubjective communication (fueled by competition, cooperation, and joint attention) and towards a radical kind of subjectivity that eventually led to cognitive individuality and uniqueness, at least in humans (and perhaps close relatives of humans).
While cognitive uniqueness (what in philosophy is called “phenomenal consciousness” or “what it is like” to be you, from the point of view of your awareness) naturally builds on organismic autonomy, it is in considerable tension with cognition and intelligence in general, because of the radically private nature of consciousness. For instance, the set of possible kinds of radical subjectivity are less constrained by the environment than the constraints on the types of attention routines that animals can use.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
The evolution of complex communication, in particular, enriches attention in ways that allow for marked increases in intelligence. On the other hand, consciousness makes subjects diverge from a common or standard type of mentality. The difference between consciousness and attention is, therefore, more complicated than the simple necessity or sufficiency claims that are frequently discussed in the literature, namely, whether attention is necessary or necessary and sufficient for consciousness (or other combinations of this relation). So-called “access consciousness”, or the reportable kind of consciousness we use in action and decision-making, may just be attention, while phenomenal consciousness may be a graded phenomenon, some aspects of it more homeostatic than others, others more formatted through language (e.g., introspection).
A consequence of the difference between consciousness and attention for future research is that we need to focus on how consciousness radically diverges among individuals, and how this phenomenal divergence is modulated and tempered by the convergence of joint attention and language (or not, as might be the case of introspection and inner narrative). This is a dynamic relation, rather than a static dependence relation. We call this thesis: “divergent consciousness, convergent attention.”
Views that propose that consciousness is fundamental and immediate, and that it provides a unique kind of knowledge, get something right, which is that consciousness is a unique connection that brings familiarity to our cognitive capacities. But these views are wrong in proposing that this is our only way to connect with the world and, in particular, to communicate. For this, attention is needed. An implication of this conclusion, which we have explored in other posts, is that consciousness is not the same as intelligence, including artificial intelligence. Attention is essential for intelligence, which is a publicly available good and stands in contrast to your private conscious awareness, which is uniquely valuable to you.
With respect to contemporary theories of consciousness, the Integrated Information Theory (IIT) has the consequence that radical divergence (unique to an individual) is compatible with convergence with other individuals, through evolution (this seems to be a unique feature of IIT). But more needs to be said about how attention is involved here. Other theories of consciousness, such as the Global Neuronal Network Theory (GNWT) may explain convergence simply through information processing and neural activation, but might find it difficult to explain radical divergence. Is this the main difference between access and phenomenal consciousness? Is GNWT better suited at explaining access consciousness and IIT better suited at explaining phenomenal consciousness?
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
This point is so important that it can be made independently of the empirical literature, which favors the dissociation between consciousness and attention. If phenomenal intelligence is radically private, then it cannot be publicly assessable or communicable. Since phenomenal consciousness is radically private, we cannot create a common world through it alone. Phenomenal consciousness cannot be the sole source of intelligent capacities. Thus, phenomenal consciousness is not necessarily a source of convergence.
A slightly stronger claim is that phenomenal consciousness is a source of divergence. When combined with language, for instance, the contribution of language as conscious inner dialogue is divergent. Spontaneous and intrusive thoughts or memories can become a source of divergence. In this way, one could even classify certain costs of consciousness, such as inner distraction through introspection, and an obsession with inner language.
With regard to attention, the environment itself is not sufficient to explain the whole range of intersubjective coordination. Agents with capacities for attention are crucial to explain salient constancies for the action perception loop. Phenomenal consciousness itself is not sufficient to explain success in communication and action. Therefore, phenomenal consciousness is not a source of convergence. Attention is needed to explain convergence, both in the form of binding properties mapped from external information and also in terms of intersubjective attention that allows for communication and joint action. If phenomenal consciousness is a source of convergence, it is very important to explain how something radically private could achieve this without the involvement of the convergence functions of attention.
Are there advantages to being conscious? Clearly there are! Dreams are radical departures from environmental constraints, and provide fertile ground for the exploration of artistic and spiritual experiences. Art, our familiarity with the world, the immediacy of our biological needs, and our sense of embodiment, they all seem to depend fundamentally on phenomenal consciousness.
It is perhaps through this divergence of conscious experience that we find diversity in perspectives and creativity. The question now emerges: is this divergence an evolutionary advantage for conscious complex organisms? Or is this divergences detrimental to the survival of species with extreme versions of it?
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Convergent Attention, Divergent Consciousness.
Since consciousness is private, attention is needed for communication.
KEY POINTS-
Phenomenal consciousness cannot be the sole source of intelligent capacities.
Attention is required for creating a common world, or communicative background.
The divergence of conscious experiences, however, can offer a diversity of perspectives and creativity.
In this blog series, for the last 9 years, we have explored the implications of the differences between consciousness and attention. One difference is about the divergent paths taken by species towards intersubjective communication (fueled by competition, cooperation, and joint attention) and towards a radical kind of subjectivity that eventually led to cognitive individuality and uniqueness, at least in humans (and perhaps close relatives of humans).
While cognitive uniqueness (what in philosophy is called “phenomenal consciousness” or “what it is like” to be you, from the point of view of your awareness) naturally builds on organismic autonomy, it is in considerable tension with cognition and intelligence in general, because of the radically private nature of consciousness. For instance, the set of possible kinds of radical subjectivity are less constrained by the environment than the constraints on the types of attention routines that animals can use.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
The evolution of complex communication, in particular, enriches attention in ways that allow for marked increases in intelligence. On the other hand, consciousness makes subjects diverge from a common or standard type of mentality. The difference between consciousness and attention is, therefore, more complicated than the simple necessity or sufficiency claims that are frequently discussed in the literature, namely, whether attention is necessary or necessary and sufficient for consciousness (or other combinations of this relation). So-called “access consciousness”, or the reportable kind of consciousness we use in action and decision-making, may just be attention, while phenomenal consciousness may be a graded phenomenon, some aspects of it more homeostatic than others, others more formatted through language (e.g., introspection).
A consequence of the difference between consciousness and attention for future research is that we need to focus on how consciousness radically diverges among individuals, and how this phenomenal divergence is modulated and tempered by the convergence of joint attention and language (or not, as might be the case of introspection and inner narrative). This is a dynamic relation, rather than a static dependence relation. We call this thesis: “divergent consciousness, convergent attention.”
Views that propose that consciousness is fundamental and immediate, and that it provides a unique kind of knowledge, get something right, which is that consciousness is a unique connection that brings familiarity to our cognitive capacities. But these views are wrong in proposing that this is our only way to connect with the world and, in particular, to communicate. For this, attention is needed. An implication of this conclusion, which we have explored in other posts, is that consciousness is not the same as intelligence, including artificial intelligence. Attention is essential for intelligence, which is a publicly available good and stands in contrast to your private conscious awareness, which is uniquely valuable to you.
With respect to contemporary theories of consciousness, the Integrated Information Theory (IIT) has the consequence that radical divergence (unique to an individual) is compatible with convergence with other individuals, through evolution (this seems to be a unique feature of IIT). But more needs to be said about how attention is involved here. Other theories of consciousness, such as the Global Neuronal Network Theory (GNWT) may explain convergence simply through information processing and neural activation, but might find it difficult to explain radical divergence. Is this the main difference between access and phenomenal consciousness? Is GNWT better suited at explaining access consciousness and IIT better suited at explaining phenomenal consciousness?
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
This point is so important that it can be made independently of the empirical literature, which favors the dissociation between consciousness and attention. If phenomenal intelligence is radically private, then it cannot be publicly assessable or communicable. Since phenomenal consciousness is radically private, we cannot create a common world through it alone. Phenomenal consciousness cannot be the sole source of intelligent capacities. Thus, phenomenal consciousness is not necessarily a source of convergence.
A slightly stronger claim is that phenomenal consciousness is a source of divergence. When combined with language, for instance, the contribution of language as conscious inner dialogue is divergent. Spontaneous and intrusive thoughts or memories can become a source of divergence. In this way, one could even classify certain costs of consciousness, such as inner distraction through introspection, and an obsession with inner language.
With regard to attention, the environment itself is not sufficient to explain the whole range of intersubjective coordination. Agents with capacities for attention are crucial to explain salient constancies for the action perception loop. Phenomenal consciousness itself is not sufficient to explain success in communication and action. Therefore, phenomenal consciousness is not a source of convergence. Attention is needed to explain convergence, both in the form of binding properties mapped from external information and also in terms of intersubjective attention that allows for communication and joint action. If phenomenal consciousness is a source of convergence, it is very important to explain how something radically private could achieve this without the involvement of the convergence functions of attention.
Are there advantages to being conscious? Clearly there are! Dreams are radical departures from environmental constraints, and provide fertile ground for the exploration of artistic and spiritual experiences. Art, our familiarity with the world, the immediacy of our biological needs, and our sense of embodiment, they all seem to depend fundamentally on phenomenal consciousness.
It is perhaps through this divergence of conscious experience that we find diversity in perspectives and creativity. The question now emerges: is this divergence an evolutionary advantage for conscious complex organisms? Or is this divergences detrimental to the survival of species with extreme versions of it?
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
1 yr. ago
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE-
AI—the Transformation From Mechanical to Cognitive Advantage.
AI's secret power is amplifying human ingenuity.
KEY POINTS-
AI amplifies human ingenuity, optimizing routine tasks and pushing boundaries in complex domains.
AI transforms innovation into an iterative, collaborative, and adaptive process, democratizing progress.
As the ultimate catalyst, AI propels us into a future limited only by our imagination.
We look for the news—the big idea. We often focus on the groundbreaking ideas, the disruptive technologies, and the visionary leaders. But what if the true driver of innovation in our era is not any single invention, but rather a force that makes every invention better? Enter artificial intelligence (AI)—the ultimate catalyst for human innovation.
Amplifying Human Ingenuity
From the mundane to the sophisticated, AI is transforming every field it touches, not by replacing human ingenuity, but by amplifying it. It's a universal accelerant, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and creativity across the board. With AI, good ideas become great, and great ideas become revolutionary. In simple terms, AI is the evolution of the mechanical advantage—"mechanistic gears" are becoming "thought gears" that place us squarely in the Cognitive Age.
Optimizing the Mundane
Consider even the most routine tasks, such as scheduling meetings or sorting emails. AI-powered assistants can now handle these jobs with ease, not only saving time but optimizing the process. By learning our preferences and predicting our needs, these tools don't just automate work, but also improve how it's done. And as they free us from the tyranny of small decisions, they open up mental space for higher-order thinking and innovation.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Pushing the Boundaries of Possibility
Now imagine that same catalytic effect applied to more complex domains. In healthcare, AI is not just helping doctors read X-rays faster, but also enabling them to spot patterns they might have missed, leading to earlier and more accurate diagnoses. In manufacturing, AI is not just automating assembly lines, but also optimizing supply chains and predicting maintenance needs, leading to new levels of efficiency and reliability.
And in fields like scientific research and technological development, AI is truly pushing the boundaries of what's possible. By crunching vast datasets, generating novel hypotheses, and simulating complex systems, AI is accelerating the pace of discovery and invention. It's helping us design more effective drugs, develop more sustainable materials, and engineer more intelligent machines. In essence, AI is a catalyst for breakthrough innovations that might have otherwise remained as nascent thoughts trapped without connectivity.
Transforming the Nature of Innovation
But AI's impact goes beyond enhancing individual ideas or processes. It's fundamentally changing the nature of innovation itself. Traditionally, innovation has been a linear and often siloed endeavor—a flash of insight, followed by a lengthy process of development and deployment. But with AI, innovation becomes more iterative, collaborative, and adaptive.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
By enabling rapid prototyping, real-time feedback, and continuous learning, AI turns innovation into an agile and evolutionary process. Ideas can be tested and refined at an unprecedented pace, with insights from one domain readily applied to another. This creates a flywheel effect, where each innovation catalyzed by AI enables even more innovations down the line. In fact, the very nature of innovation is being transformed as large language models (LLMs) can now become both scientist and subject performing self-contained research.
Democratizing Innovation
Moreover, by lowering the barriers to entry and democratizing access to powerful tools and insights, AI is broadening the pool of potential innovators. No longer is breakthrough thinking confined to the expert few in select labs or Silicon Valley garages. With AI at their fingertips, students, entrepreneurs, and citizen scientists around the world can contribute to the cutting edge. AI thus becomes a great leveler and accelerator, unlocking the innovative potential of people and ideas that might have otherwise been overlooked.
Our Cognitive Catalyst
If we can harness this catalytic power wisely, the potential is immense. By making every good idea better, every process more efficient, and every person more empowered to create, AI could usher in a new golden age of innovation. It could help us tackle the grand challenges we face, from energy exploration and curing disease to exploring the cosmos and understanding our own minds.
In this sense, AI is not just another invention, but rather the invention that accelerates all others. It's the ultimate inflection point, the catalyst that could propel us into a future limited only by the stretch of our imaginations. So as we navigate this pivotal moment, let us not fear the rise of AI, but instead embrace it as the catalyst for our highest aspirations and our boldest innovations. For with AI as our partner, there's no telling how far or how fast we can go.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
AI—the Transformation From Mechanical to Cognitive Advantage.
AI's secret power is amplifying human ingenuity.
KEY POINTS-
AI amplifies human ingenuity, optimizing routine tasks and pushing boundaries in complex domains.
AI transforms innovation into an iterative, collaborative, and adaptive process, democratizing progress.
As the ultimate catalyst, AI propels us into a future limited only by our imagination.
We look for the news—the big idea. We often focus on the groundbreaking ideas, the disruptive technologies, and the visionary leaders. But what if the true driver of innovation in our era is not any single invention, but rather a force that makes every invention better? Enter artificial intelligence (AI)—the ultimate catalyst for human innovation.
Amplifying Human Ingenuity
From the mundane to the sophisticated, AI is transforming every field it touches, not by replacing human ingenuity, but by amplifying it. It's a universal accelerant, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and creativity across the board. With AI, good ideas become great, and great ideas become revolutionary. In simple terms, AI is the evolution of the mechanical advantage—"mechanistic gears" are becoming "thought gears" that place us squarely in the Cognitive Age.
Optimizing the Mundane
Consider even the most routine tasks, such as scheduling meetings or sorting emails. AI-powered assistants can now handle these jobs with ease, not only saving time but optimizing the process. By learning our preferences and predicting our needs, these tools don't just automate work, but also improve how it's done. And as they free us from the tyranny of small decisions, they open up mental space for higher-order thinking and innovation.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Pushing the Boundaries of Possibility
Now imagine that same catalytic effect applied to more complex domains. In healthcare, AI is not just helping doctors read X-rays faster, but also enabling them to spot patterns they might have missed, leading to earlier and more accurate diagnoses. In manufacturing, AI is not just automating assembly lines, but also optimizing supply chains and predicting maintenance needs, leading to new levels of efficiency and reliability.
And in fields like scientific research and technological development, AI is truly pushing the boundaries of what's possible. By crunching vast datasets, generating novel hypotheses, and simulating complex systems, AI is accelerating the pace of discovery and invention. It's helping us design more effective drugs, develop more sustainable materials, and engineer more intelligent machines. In essence, AI is a catalyst for breakthrough innovations that might have otherwise remained as nascent thoughts trapped without connectivity.
Transforming the Nature of Innovation
But AI's impact goes beyond enhancing individual ideas or processes. It's fundamentally changing the nature of innovation itself. Traditionally, innovation has been a linear and often siloed endeavor—a flash of insight, followed by a lengthy process of development and deployment. But with AI, innovation becomes more iterative, collaborative, and adaptive.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
By enabling rapid prototyping, real-time feedback, and continuous learning, AI turns innovation into an agile and evolutionary process. Ideas can be tested and refined at an unprecedented pace, with insights from one domain readily applied to another. This creates a flywheel effect, where each innovation catalyzed by AI enables even more innovations down the line. In fact, the very nature of innovation is being transformed as large language models (LLMs) can now become both scientist and subject performing self-contained research.
Democratizing Innovation
Moreover, by lowering the barriers to entry and democratizing access to powerful tools and insights, AI is broadening the pool of potential innovators. No longer is breakthrough thinking confined to the expert few in select labs or Silicon Valley garages. With AI at their fingertips, students, entrepreneurs, and citizen scientists around the world can contribute to the cutting edge. AI thus becomes a great leveler and accelerator, unlocking the innovative potential of people and ideas that might have otherwise been overlooked.
Our Cognitive Catalyst
If we can harness this catalytic power wisely, the potential is immense. By making every good idea better, every process more efficient, and every person more empowered to create, AI could usher in a new golden age of innovation. It could help us tackle the grand challenges we face, from energy exploration and curing disease to exploring the cosmos and understanding our own minds.
In this sense, AI is not just another invention, but rather the invention that accelerates all others. It's the ultimate inflection point, the catalyst that could propel us into a future limited only by the stretch of our imaginations. So as we navigate this pivotal moment, let us not fear the rise of AI, but instead embrace it as the catalyst for our highest aspirations and our boldest innovations. For with AI as our partner, there's no telling how far or how fast we can go.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
1 yr. ago
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE-
Collectors' Dreams: AI-Enhanced Sculptural Masterpieces.
AI's integration into sculpting opens up novel avenues for creativity.
KEY POINTS-
Sculpture (along with ceramics) consists of 57 percent of the objects within collections.
Today, AI-generated as well as traditional sculptures are produced.
The interaction between artists and AI provides new perspectives on creativity and human expression.
Sculpture (along with ceramics) consists of 57 percent of the objects within collections (Artsy’s Art Collector Insights 2023 report). Despite this, it is a lower-priority art form for some. A new field, however, is about to change that. Enter AI. Its integration into sculpting preserves its essence while at the same time opening up new avenues for creativity and innovation and, thus, new interpretations.
Traditional Sculpture Meets AI
Traditionally, sculptors sketch their ideas on paper or create small-scale models before embarking on the piece. AI tools, however, offer new possibilities for generating and refining concepts. Algorithms can analyze vast historical and contemporary sculpture datasets, identifying patterns and suggesting innovative designs that blend different styles and techniques. The results can be anything the sculptor or collector can imagine.
Generative adversarial networks (GANs)
Generative adversarial networks (GANs), a type of AI, have been particularly influential in the art world. GANs consist of two neural networks—a generator and a discriminator—that work together to create new data resembling the input data. In sculpture, GANs can generate novel designs by learning from existing sculptures, pushing the boundaries of traditional aesthetics.
Robotics Enter the Picture
AI is transforming the design phase and the actual sculpting process. Robotic sculptors equipped with AI capabilities can carve materials with precision and efficiency unmatched by human hands. For instance, the Robotor, an AI-driven robot, can sculpt intricate designs from marble, traditionally associated with classical sculpture. These robots use advanced algorithms to translate digital models into physical forms, ensuring accuracy and detail.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Moreover, AI can assist in physically demanding or hazardous tasks for human sculptors. By automating these aspects, artists can focus more on their work's creative and conceptual elements. This collaboration between human creativity and machine precision exemplifies the potential of AI to enhance, rather than replace, traditional sculptural practices.
Ethical and Philosophical Considerations
The integration of AI into sculpture raises several ethical and philosophical questions. One major concern is the authorship and originality of AI-generated artworks. Who should be credited as the artist if a machine creates a sculpture based on algorithms and data? This question challenges traditional notions of creativity and authorship, prompting a reevaluation of what it means to be an artist in the age of AI.
Additionally, there is the question of AI-generated sculptures' emotional and cultural significance. Art has always been a deeply human endeavor, reflecting its creators' emotions, experiences, and cultural contexts. Can a machine, devoid of human consciousness, produce works that resonate on the same emotional level? While AI can mimic styles and generate aesthetically pleasing designs, the depth of human experience and expression remains a unique aspect of traditional sculpture.
Contemporary Examples
Several contemporary artists and institutions are exploring the intersection of AI and sculpture. For example, the artist Sougwen Chung uses AI to collaborate with robotic arms to create intricate sculptures and installations. Her work blurs the lines between human and machine, emphasizing AI's collaborative potential in art.
Another notable example is the AI-driven project "DREAM," which uses neural networks to analyze dreams and translate them into sculptural forms. This project explores the subconscious mind's creativity, merging it with AI's computational power to create unique, dream-inspired sculptures.
The Future
As AI technology advances, its impact on sculpture will likely grow. Future developments may include more sophisticated AI algorithms capable of understanding and replicating complex artistic nuances. Additionally, advancements in materials science could lead to new mediums for AI-driven sculptures, further expanding the possibilities for artistic expression and thereby giving new opportunities for psychological interpretation.
While AI offers exciting innovation opportunities, preserving the human elements that make art meaningful is essential. The future of sculpture will likely be a harmonious blend of tradition and technology, where human creativity and machine precision coexist.
Summary
AI's ability to enhance the conceptualization, design, and execution of sculptures opens up novel avenues for artistic exploration. As this evolving landscape is navigated, it is essential to strike a balance that honors the rich heritage of sculpture while embracing the transformative potential of AI. Through this synergy, the future of sculpture promises to be even more exciting than before.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Collectors' Dreams: AI-Enhanced Sculptural Masterpieces.
AI's integration into sculpting opens up novel avenues for creativity.
KEY POINTS-
Sculpture (along with ceramics) consists of 57 percent of the objects within collections.
Today, AI-generated as well as traditional sculptures are produced.
The interaction between artists and AI provides new perspectives on creativity and human expression.
Sculpture (along with ceramics) consists of 57 percent of the objects within collections (Artsy’s Art Collector Insights 2023 report). Despite this, it is a lower-priority art form for some. A new field, however, is about to change that. Enter AI. Its integration into sculpting preserves its essence while at the same time opening up new avenues for creativity and innovation and, thus, new interpretations.
Traditional Sculpture Meets AI
Traditionally, sculptors sketch their ideas on paper or create small-scale models before embarking on the piece. AI tools, however, offer new possibilities for generating and refining concepts. Algorithms can analyze vast historical and contemporary sculpture datasets, identifying patterns and suggesting innovative designs that blend different styles and techniques. The results can be anything the sculptor or collector can imagine.
Generative adversarial networks (GANs)
Generative adversarial networks (GANs), a type of AI, have been particularly influential in the art world. GANs consist of two neural networks—a generator and a discriminator—that work together to create new data resembling the input data. In sculpture, GANs can generate novel designs by learning from existing sculptures, pushing the boundaries of traditional aesthetics.
Robotics Enter the Picture
AI is transforming the design phase and the actual sculpting process. Robotic sculptors equipped with AI capabilities can carve materials with precision and efficiency unmatched by human hands. For instance, the Robotor, an AI-driven robot, can sculpt intricate designs from marble, traditionally associated with classical sculpture. These robots use advanced algorithms to translate digital models into physical forms, ensuring accuracy and detail.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Moreover, AI can assist in physically demanding or hazardous tasks for human sculptors. By automating these aspects, artists can focus more on their work's creative and conceptual elements. This collaboration between human creativity and machine precision exemplifies the potential of AI to enhance, rather than replace, traditional sculptural practices.
Ethical and Philosophical Considerations
The integration of AI into sculpture raises several ethical and philosophical questions. One major concern is the authorship and originality of AI-generated artworks. Who should be credited as the artist if a machine creates a sculpture based on algorithms and data? This question challenges traditional notions of creativity and authorship, prompting a reevaluation of what it means to be an artist in the age of AI.
Additionally, there is the question of AI-generated sculptures' emotional and cultural significance. Art has always been a deeply human endeavor, reflecting its creators' emotions, experiences, and cultural contexts. Can a machine, devoid of human consciousness, produce works that resonate on the same emotional level? While AI can mimic styles and generate aesthetically pleasing designs, the depth of human experience and expression remains a unique aspect of traditional sculpture.
Contemporary Examples
Several contemporary artists and institutions are exploring the intersection of AI and sculpture. For example, the artist Sougwen Chung uses AI to collaborate with robotic arms to create intricate sculptures and installations. Her work blurs the lines between human and machine, emphasizing AI's collaborative potential in art.
Another notable example is the AI-driven project "DREAM," which uses neural networks to analyze dreams and translate them into sculptural forms. This project explores the subconscious mind's creativity, merging it with AI's computational power to create unique, dream-inspired sculptures.
The Future
As AI technology advances, its impact on sculpture will likely grow. Future developments may include more sophisticated AI algorithms capable of understanding and replicating complex artistic nuances. Additionally, advancements in materials science could lead to new mediums for AI-driven sculptures, further expanding the possibilities for artistic expression and thereby giving new opportunities for psychological interpretation.
While AI offers exciting innovation opportunities, preserving the human elements that make art meaningful is essential. The future of sculpture will likely be a harmonious blend of tradition and technology, where human creativity and machine precision coexist.
Summary
AI's ability to enhance the conceptualization, design, and execution of sculptures opens up novel avenues for artistic exploration. As this evolving landscape is navigated, it is essential to strike a balance that honors the rich heritage of sculpture while embracing the transformative potential of AI. Through this synergy, the future of sculpture promises to be even more exciting than before.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
1 yr. ago
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE-
Chatbots Could Start Shaping How We Trust and Who We Trust.
Like other technology, generative AI effects on our values may be profound.
KEY POINTS-
Trust is a keystone of social morality; it signals respect when a person trusts someone else.
People find humans "trustworthy," but machines are "reliable." What happens if chatbots outperform humans?
As we integrate generative AI into our lives, trusting humans "may be seen as unnecessary and discardable."
Are chatbots changing social morality?
Changes in social morality refer to changes in what people believe to be good and bad or right and wrong. Among the many ethical questions raised by chatbot development and use is their potential to influence social morality.
We know that technologies such as robots, computer interfaces, and algorithmic systems can have various psychological effects on us. They can cause us to lower our guard, make us feel less alone, and lead us to make all kinds of assumptions about reliability and value. But they can also have deeper, more long-lasting psychological effects that we usually don’t think about.
We know that technology has served as a “mediator” of moral change in many different ways, as Peter Verbeek (2012, 2013) and others have detailed. The smartphone is a common example. Its proliferation has shifted the value of our everyday experiences: Once, our social interactions with friends and colleagues were largely valuable in and of themselves, but now those interactions also have widely recognized instrumental value as content to be recorded, shared, and even monetized.
The presence of the smartphone has, in many ways, disrupted shared moral norms and expectations that previously defined everyday activities. “The technology has enabled this reinterpretation of the moral value of everyday experiences,” as some theorists describe it (Danaher & Sætra, 2022, p. 35).
Are chatbots poised to shift social morality in subtle but significant ways? Very possibly.
Consider the concept of trust. Can we only trust other humans? We typically judge machines based on reliability, but what if we decide that a machine—a chatbot—is trustworthy? Dozens of books and articles have been written on how trust functions in a moral system.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Most recently, in 2022 (before the rollout of OpenAI’s ChatGPT), two technology theorists, John Danaher and Skaug Sætra, addressed the issue of how technology can affect our understanding of trust and its function in our social lives. Trust, they wrote, “is the keystone in our broader value system by facilitating productive cooperation and coordination. If we can trust others, we can enhance our autonomy, happiness, mental well-being, health, relationships, and so on….Trust is a way of signaling respect to another person. If we trust someone, we are respecting their honesty, their competence, and their status as a co-equal moral citizen” (2022, p. 35).
They identify several ways in which technology can influence or even undermine trust and the important role it plays in our social lives. Drawing from their analysis, we should all consider how chatbot development and use may, even now, be influencing our sense of trust.
Chatbots may be exploiting our tendency to over-trust machines with social features. With its conversational interface, we are invited to assign more competence and veracity than generative AI models so far deserve and rely on them with insufficient justification (i.e., Sundar et al., 2015). We make assumptions about their intelligence, autonomy, and even their capacity for creativity. This is especially likely when we wrongly assume that they work like a Google search when, in reality, they are not designed for facticity retrieval but instead are word-sequence probability systems. This is why errors and misinformation remain common.
Chatbots could disrupt longstanding patterns of interpersonal trusting relationships because, in many ways, AI is perceived as more capable than humans at providing valuable information quickly and efficiently. This could result in a “redistribution” of trust away from human interlocutors if AI systems are widely perceived as more reliable. “We have always known that humans are fallible, but there is a difference between being the best there is, but fallible, and simply being the best human, when machines exceed our capabilities,” Danaher and Sætra write.
We typically judge machines based on the notion of reliability and generally reserve trust for human relationships. But as we integrate generative AI tools more deeply into our everyday lives, we may end up marginalizing the value of trust itself. “Rather than trust being seen as an essential or core instrumental social value (the glue that binds together cooperative relations), it may be seen as unnecessary and discardable,” Danaher and Sætra write (p. 47). This, in turn, could begin eroding respect for others since trusting someone is an elemental gesture of respect.
Increasing reliance on chatbots could invite a “robotomorphic” effect by subtly influencing our moral perception of others.
Whereas anthropomorphism refers to how we assign human attributes to animals and things, robotomorphy refers to how we can attribute robot qualities to human beings. It has a long history that includes the claims of Thomas Hobbes; today, neural network theorists liken the human brain to a computer. But the more such metaphors take root—the more we see ourselves as machine-like—the less valuable the concept of trust becomes. “Increased robotomorphy might…change trust in human beings into something more akin to a question of whether or not we can rely on each other just as we rely on a car or a dishwasher,” Danaher and Sætra write (p. 47-48).
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Chatbots Could Start Shaping How We Trust and Who We Trust.
Like other technology, generative AI effects on our values may be profound.
KEY POINTS-
Trust is a keystone of social morality; it signals respect when a person trusts someone else.
People find humans "trustworthy," but machines are "reliable." What happens if chatbots outperform humans?
As we integrate generative AI into our lives, trusting humans "may be seen as unnecessary and discardable."
Are chatbots changing social morality?
Changes in social morality refer to changes in what people believe to be good and bad or right and wrong. Among the many ethical questions raised by chatbot development and use is their potential to influence social morality.
We know that technologies such as robots, computer interfaces, and algorithmic systems can have various psychological effects on us. They can cause us to lower our guard, make us feel less alone, and lead us to make all kinds of assumptions about reliability and value. But they can also have deeper, more long-lasting psychological effects that we usually don’t think about.
We know that technology has served as a “mediator” of moral change in many different ways, as Peter Verbeek (2012, 2013) and others have detailed. The smartphone is a common example. Its proliferation has shifted the value of our everyday experiences: Once, our social interactions with friends and colleagues were largely valuable in and of themselves, but now those interactions also have widely recognized instrumental value as content to be recorded, shared, and even monetized.
The presence of the smartphone has, in many ways, disrupted shared moral norms and expectations that previously defined everyday activities. “The technology has enabled this reinterpretation of the moral value of everyday experiences,” as some theorists describe it (Danaher & Sætra, 2022, p. 35).
Are chatbots poised to shift social morality in subtle but significant ways? Very possibly.
Consider the concept of trust. Can we only trust other humans? We typically judge machines based on reliability, but what if we decide that a machine—a chatbot—is trustworthy? Dozens of books and articles have been written on how trust functions in a moral system.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Most recently, in 2022 (before the rollout of OpenAI’s ChatGPT), two technology theorists, John Danaher and Skaug Sætra, addressed the issue of how technology can affect our understanding of trust and its function in our social lives. Trust, they wrote, “is the keystone in our broader value system by facilitating productive cooperation and coordination. If we can trust others, we can enhance our autonomy, happiness, mental well-being, health, relationships, and so on….Trust is a way of signaling respect to another person. If we trust someone, we are respecting their honesty, their competence, and their status as a co-equal moral citizen” (2022, p. 35).
They identify several ways in which technology can influence or even undermine trust and the important role it plays in our social lives. Drawing from their analysis, we should all consider how chatbot development and use may, even now, be influencing our sense of trust.
Chatbots may be exploiting our tendency to over-trust machines with social features. With its conversational interface, we are invited to assign more competence and veracity than generative AI models so far deserve and rely on them with insufficient justification (i.e., Sundar et al., 2015). We make assumptions about their intelligence, autonomy, and even their capacity for creativity. This is especially likely when we wrongly assume that they work like a Google search when, in reality, they are not designed for facticity retrieval but instead are word-sequence probability systems. This is why errors and misinformation remain common.
Chatbots could disrupt longstanding patterns of interpersonal trusting relationships because, in many ways, AI is perceived as more capable than humans at providing valuable information quickly and efficiently. This could result in a “redistribution” of trust away from human interlocutors if AI systems are widely perceived as more reliable. “We have always known that humans are fallible, but there is a difference between being the best there is, but fallible, and simply being the best human, when machines exceed our capabilities,” Danaher and Sætra write.
We typically judge machines based on the notion of reliability and generally reserve trust for human relationships. But as we integrate generative AI tools more deeply into our everyday lives, we may end up marginalizing the value of trust itself. “Rather than trust being seen as an essential or core instrumental social value (the glue that binds together cooperative relations), it may be seen as unnecessary and discardable,” Danaher and Sætra write (p. 47). This, in turn, could begin eroding respect for others since trusting someone is an elemental gesture of respect.
Increasing reliance on chatbots could invite a “robotomorphic” effect by subtly influencing our moral perception of others.
Whereas anthropomorphism refers to how we assign human attributes to animals and things, robotomorphy refers to how we can attribute robot qualities to human beings. It has a long history that includes the claims of Thomas Hobbes; today, neural network theorists liken the human brain to a computer. But the more such metaphors take root—the more we see ourselves as machine-like—the less valuable the concept of trust becomes. “Increased robotomorphy might…change trust in human beings into something more akin to a question of whether or not we can rely on each other just as we rely on a car or a dishwasher,” Danaher and Sætra write (p. 47-48).
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
2 yr. ago
MOTIVATION-
When the Search for a Sense of Purpose Turns on You.
Purpose has benefits, but it can also become just another form of striving.
KEY POINTS-
There are real benefits to a sense of life-purpose—health, meaning, focus—but there are also drawbacks.
Enjoying the world is as good a purpose as serving the world.
Our fitful and purpose-driven world makes it hard to step away from the relentless pursuit of life-purpose.
Recently a friend of mine in her 60s declared that she was “over” the need for a sense of purpose in her life. This triggered in me both skepticism and envy because, on the one hand, I’ve devoted much of my career to helping people find passion and purpose, and, on the other hand, because I recently retired from that career, and the internal pressure to forge a renewed sense of purpose has begun feeling like just another to-do list item.
At first, I thought she was over just the sense of purpose that drives people to fulfill their personal potential—achieving goals, maximizing strengths, composing a life—and that she would now be turning her attentions toward a “higher” or more spiritual sense of purpose.
But my friend said she was over that as well, done with the general neediness and drive behind striving itself, whether on behalf of self or other. And despite my intellectual alarm at this idea—Is the sense of purpose something one can outgrow?—her disavowal of the driving force of purpose, and the fact that she seemed not unmoored but grounded, struck me as an enviable attainment in serenity and nonattachment, skills the aging process is insisting I learn.
Corkroo Android Web View app link on Amazon app store..... https://rb.gy/4cpidu
Adapting to Changes
There’s great emphasis in the purpose literature on its health-giving benefits, its importance in guiding our energies and giving our lives meaning, and how it leads us to serve “the greater good.” But folks at the Greater Good Science Center at the University of California, Berkeley, suggest that purpose seems to have been selected for by evolution as a way to help humans work together, and, like all things that evolve, it has to be adaptable to changing environments, circumstances, and mindsets. “We cannot live the afternoon of life according to the program of life’s morning,” said psychologist Carl Jung, “for what in the morning was true will in evening become a lie.”
Back in my 30s, I read a book called The Path, by Laurie Beth Jones, about how to craft a personal mission statement, not just for one’s career, but one’s life. What I came up with was this: “My mission is to educate and model passion and authenticity for those searching for their sense of calling and vitality.” This captured (1) what actions I would take, (2) what purpose or values motivate those actions, and (3) who I’d be serving. And it served me well, for decades.
But in retirement, I find myself backing off the need (or desire) to consciously serve anyone with all my educating and modeling, or even make good on the supposedly primary developmental task of elderhood, which Jung called generativity. That is, helping the generations coming up behind me. But I’ve been doing that all along; half my career was spent in university settings.
Corkroo Android Web View app link on Amazon app store..... https://rb.gy/4cpidu
Living One's Mission
This doesn’t mean I’m abandoning my mission. I’m just choosing to live it rather than teach it, though by most accounts living it is the best way to teach it. And it’s not that I’m bereft of a sense of purpose in this phase; it’s that my sense of purpose is changing, and I’m not so much retiring as reordering my priorities, and loosening my grip on the lifelong demand for results. I’m less interested in serving the world or changing the world than enjoying the world. Perhaps it’s the difference between “Why am I here?’ and “How am I here?”
It’s also dawning on me that enjoying life is as exalted a purpose—and every bit as aspirational and challenging—as any purpose devoted to career, community, or service. And as far as transcending the self goes, I’m happy just getting a little distance from (rising above, you might say) all my assumptions about what a passionate, productive, and meaningful life looks like, all the operating instructions I inherited for how to construct and maintain a proper sense of self.
A colleague of mine, Richard Leider, author of The Power of Purpose, says that purpose is composed of three ingredients: your gifts, passions, and values. But these drivers don’t have to be aimed at making a living, crafting a career, changing the world, or being of service to the greater good. If you have a gift and passion for painting, and you value creativity, you could spend all your time painting alone in a room and never show your work to a soul and still have a life propelled by purpose.
Similarly, when I apply Leider’s principle to my own nascent retirement, I see that my gifts, passions, and values all coalesce around the activities in which I now find myself spending the bulk of my time: writing, relationship-building, wellness, music, adventure, the appreciation of nature, and regular gratitude for this precious and fleeting life. And though these activities may spin off inspiration or usefulness for others, that’s welcome but ancillary. Bettering humanity is not my intention or purpose.
Besides, what counts as a contribution to the world and, by extension, a good-enough purpose? Are monks and nuns who sit in caves meditating and praying for humanity any less impactful on the greater good, any less socially useful or involved in moral action, than those who sit at the computer day after day cranking out manifestos, or heading down to the sit-in with placards?
Perhaps ideally, a sense of purpose should be deeper than any individual goal or intention or calling. Not so much a reason for doing what you do as a reason for being, what the French call your raison d’etre, and what the business world calls your why. Some overarching principle or ideal you devote yourself to: creating beauty, empowering people, cultivating relationships, creating solutions, encouraging self-awareness, stewarding the Earth.
Corkroo Android Web View app link on Amazon app store..... https://rb.gy/4cpidu
And these deeper purposes don't have singular strategies, but multitudes of them, and won’t end even if your work does. A few years ago, I consulted with a woman who was convinced she was called to quit her job, move to LA, and become an actress—but wanted a “reality check.” It turns out the call wasn’t to quit her life and move to LA to be an actress; it was to be more expressive in her life. Her mind simply conjured up what she thought was the epitome of an expressive life: being an actress. I suggested an assignment: Take six months and experiment with the following question: “In how many ways can I practice being more expressive in my life?”
Neal Allen, author of Better Days, writes
“I’m constantly told I’ll be happier if I find meaning, or purpose, or value, in my work-life. Be of service. Establish a purposeful life. Set intentions and stick to them. Better yourself. But maybe we’ve got it backwards, and our point isn’t productivity, communication, agreement, social welfare, but satisfaction. Attending to productivity can be a distraction from love and fascination. Which would you rather be? Of value to the world through achieving your purpose, or basking in a persistent field of love? What if appreciation of the world as it is—a form of contentment that is self-contained—is my purpose?”
When the Search for a Sense of Purpose Turns on You.
Purpose has benefits, but it can also become just another form of striving.
KEY POINTS-
There are real benefits to a sense of life-purpose—health, meaning, focus—but there are also drawbacks.
Enjoying the world is as good a purpose as serving the world.
Our fitful and purpose-driven world makes it hard to step away from the relentless pursuit of life-purpose.
Recently a friend of mine in her 60s declared that she was “over” the need for a sense of purpose in her life. This triggered in me both skepticism and envy because, on the one hand, I’ve devoted much of my career to helping people find passion and purpose, and, on the other hand, because I recently retired from that career, and the internal pressure to forge a renewed sense of purpose has begun feeling like just another to-do list item.
At first, I thought she was over just the sense of purpose that drives people to fulfill their personal potential—achieving goals, maximizing strengths, composing a life—and that she would now be turning her attentions toward a “higher” or more spiritual sense of purpose.
But my friend said she was over that as well, done with the general neediness and drive behind striving itself, whether on behalf of self or other. And despite my intellectual alarm at this idea—Is the sense of purpose something one can outgrow?—her disavowal of the driving force of purpose, and the fact that she seemed not unmoored but grounded, struck me as an enviable attainment in serenity and nonattachment, skills the aging process is insisting I learn.
Corkroo Android Web View app link on Amazon app store..... https://rb.gy/4cpidu
Adapting to Changes
There’s great emphasis in the purpose literature on its health-giving benefits, its importance in guiding our energies and giving our lives meaning, and how it leads us to serve “the greater good.” But folks at the Greater Good Science Center at the University of California, Berkeley, suggest that purpose seems to have been selected for by evolution as a way to help humans work together, and, like all things that evolve, it has to be adaptable to changing environments, circumstances, and mindsets. “We cannot live the afternoon of life according to the program of life’s morning,” said psychologist Carl Jung, “for what in the morning was true will in evening become a lie.”
Back in my 30s, I read a book called The Path, by Laurie Beth Jones, about how to craft a personal mission statement, not just for one’s career, but one’s life. What I came up with was this: “My mission is to educate and model passion and authenticity for those searching for their sense of calling and vitality.” This captured (1) what actions I would take, (2) what purpose or values motivate those actions, and (3) who I’d be serving. And it served me well, for decades.
But in retirement, I find myself backing off the need (or desire) to consciously serve anyone with all my educating and modeling, or even make good on the supposedly primary developmental task of elderhood, which Jung called generativity. That is, helping the generations coming up behind me. But I’ve been doing that all along; half my career was spent in university settings.
Corkroo Android Web View app link on Amazon app store..... https://rb.gy/4cpidu
Living One's Mission
This doesn’t mean I’m abandoning my mission. I’m just choosing to live it rather than teach it, though by most accounts living it is the best way to teach it. And it’s not that I’m bereft of a sense of purpose in this phase; it’s that my sense of purpose is changing, and I’m not so much retiring as reordering my priorities, and loosening my grip on the lifelong demand for results. I’m less interested in serving the world or changing the world than enjoying the world. Perhaps it’s the difference between “Why am I here?’ and “How am I here?”
It’s also dawning on me that enjoying life is as exalted a purpose—and every bit as aspirational and challenging—as any purpose devoted to career, community, or service. And as far as transcending the self goes, I’m happy just getting a little distance from (rising above, you might say) all my assumptions about what a passionate, productive, and meaningful life looks like, all the operating instructions I inherited for how to construct and maintain a proper sense of self.
A colleague of mine, Richard Leider, author of The Power of Purpose, says that purpose is composed of three ingredients: your gifts, passions, and values. But these drivers don’t have to be aimed at making a living, crafting a career, changing the world, or being of service to the greater good. If you have a gift and passion for painting, and you value creativity, you could spend all your time painting alone in a room and never show your work to a soul and still have a life propelled by purpose.
Similarly, when I apply Leider’s principle to my own nascent retirement, I see that my gifts, passions, and values all coalesce around the activities in which I now find myself spending the bulk of my time: writing, relationship-building, wellness, music, adventure, the appreciation of nature, and regular gratitude for this precious and fleeting life. And though these activities may spin off inspiration or usefulness for others, that’s welcome but ancillary. Bettering humanity is not my intention or purpose.
Besides, what counts as a contribution to the world and, by extension, a good-enough purpose? Are monks and nuns who sit in caves meditating and praying for humanity any less impactful on the greater good, any less socially useful or involved in moral action, than those who sit at the computer day after day cranking out manifestos, or heading down to the sit-in with placards?
Perhaps ideally, a sense of purpose should be deeper than any individual goal or intention or calling. Not so much a reason for doing what you do as a reason for being, what the French call your raison d’etre, and what the business world calls your why. Some overarching principle or ideal you devote yourself to: creating beauty, empowering people, cultivating relationships, creating solutions, encouraging self-awareness, stewarding the Earth.
Corkroo Android Web View app link on Amazon app store..... https://rb.gy/4cpidu
And these deeper purposes don't have singular strategies, but multitudes of them, and won’t end even if your work does. A few years ago, I consulted with a woman who was convinced she was called to quit her job, move to LA, and become an actress—but wanted a “reality check.” It turns out the call wasn’t to quit her life and move to LA to be an actress; it was to be more expressive in her life. Her mind simply conjured up what she thought was the epitome of an expressive life: being an actress. I suggested an assignment: Take six months and experiment with the following question: “In how many ways can I practice being more expressive in my life?”
Neal Allen, author of Better Days, writes
“I’m constantly told I’ll be happier if I find meaning, or purpose, or value, in my work-life. Be of service. Establish a purposeful life. Set intentions and stick to them. Better yourself. But maybe we’ve got it backwards, and our point isn’t productivity, communication, agreement, social welfare, but satisfaction. Attending to productivity can be a distraction from love and fascination. Which would you rather be? Of value to the world through achieving your purpose, or basking in a persistent field of love? What if appreciation of the world as it is—a form of contentment that is self-contained—is my purpose?”