Launch a handyman app like Uber with scalable features, real-time tracking, and custom branding. Perfect for startups and enterprises entering the on-demand service market. Visit our website for more Info: https://whitelabelfox.com/...
#UberforHandymanServicesApp #UberLikeAppForHandyman #handymanapplikeuber #UberForHandyman #HandymanCloneApp #ondemandhandymanapp #uberforhandymanservices #HandymanAppDevelopment #ondemandhandymanappdevelopment #handymanappdevelopmentservices #handymanhomeservicescloneapp #ondemandhandymanservicesapp
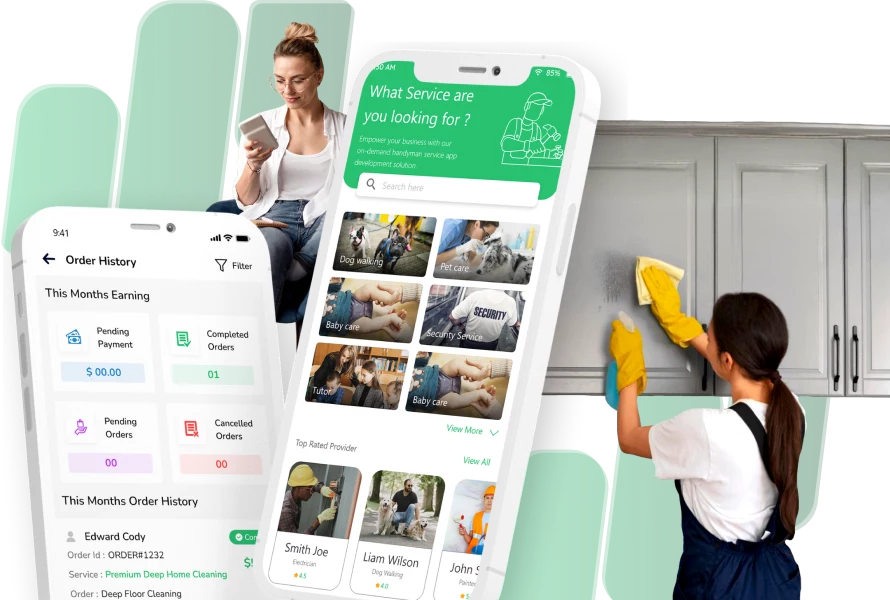
Handyman App Like Uber - Handyman Clone App for You
Looking for a handyman app like Uber? Get our ready-to-launch handyman clone app. All features included! Book a demo today and start your business!
https://whitelabelfox.com/on-demand-handyman-app-like-uber/The freelance economy is growing faster than ever, and businesses are looking for ways to tap into this booming market. Building a freelance marketplace from scratch can be time-consuming, expensive, and technically complex. That’s where Fiverr clone scripts come into play.
These ready-made solutions provide entrepreneurs with a quick and cost-effective way to launch their own freelance marketplace. But beyond speed, Fiverr clone scripts also bring flexibility, scalability, and user-friendly features that make them a smart choice for startups and enterprises alike.
How It Speeds Up Development
Pre-Built Features: Everything from dashboards to payment systems comes ready to use.
Customizable Design: Tailor the look and feel to match your brand identity.
Faster Launch Time: Get your marketplace up and running in weeks instead of months.
Cost-Effective: Save money on development and allocate more budget to marketing.
Scalable: Add new features as your platform grows without starting from scratch.
Use Cases of Fiverr Clone Solutions
Startups launching niche marketplaces (e.g., freelance designers, tutors, or consultants).
Enterprises are creating internal gig platforms for their workforce.
Agencies that want to build white-label freelance platforms for clients.
Final Thoughts
The demand for freelance platforms will only grow in 2025 and beyond. “When you use a Fiverr clone script, entrepreneurs can cut down development time, reduce costs, and still deliver a professional, feature-rich marketplace. Whether you’re building a Fiverr clone website or app, the right script can help you focus on what matters most - growing your business and serving your users.
https://www.logicspice.com...
Ever thought of building your own language-learning app like Duolingo? Check out OyeLabs’ Duolingo Clone — a white-label, fully customizable platform with source code ownership. It supports web, iOS & Android, offers gamified lessons, offline mode, AI-powered features (pronunciation coach, conversational tutor), and a powerful admin panel for course building. Starting at just US$ 2,998, you can brand it your way and go live fast. Perfect for EdTech startups, language academies, or corporate training.
Explore more & request a demo: oyelabs.com/duolingo-clone/
#EdTech #LanguageLearning #startup #WhiteLabelApp #AIinEducation
Start your own peer-to-peer carpooling app with OyeLabs’ BlaBlaCar Clone. It features trip matching, route optimization, dynamic pricing, passenger reviews, and a robust driver-rider dashboard — ideal for community ride-sharing startups.
#BlaBlaCarClone #ridesharing #Carpooling #StartupApp #Mobility
Build a powerful app like Gojek and enter the booming on-demand market. Our Gojek-like super app enables ride-hailing, food delivery, parcel, and more — helping startups and enterprises streamline operations and boost profitability with ease. Visit our website for more Info: https://applionsoft.com/go...
#gojekclone #gojekcloneapp #gojekcloneappdevelopment #gojekclonescript #gojekappclone #applikegojek #gojeklikeapp #gojekcloneappscript #gojekclonesolution #allinoneapp #multiservicesapp #gojekclonesoftware #appclonegojek
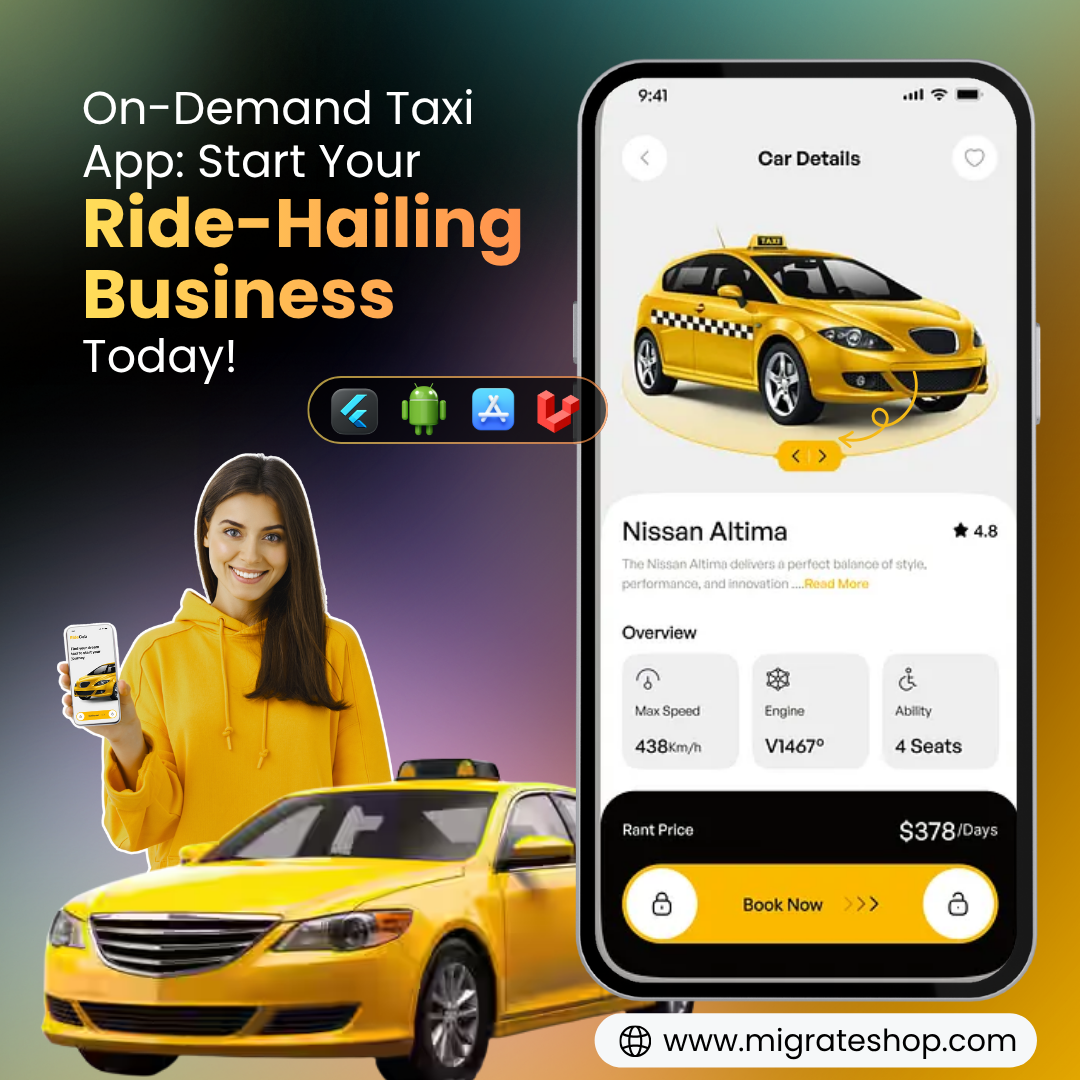
✨ Launch your app. Grow your brand. Drive your success.
Start Now: https://migrateshop.com/ub...
#migrateshop #uberclone #ubercloneapp #OnDemandTaxiApp #OnDemandServices #TaxiAppDevelopment #RideHailing #taxiapp #entreprenure #business #apps
Kickstart your on-demand business with our Gojek Clone Script. A robust and scalable solution that lets startups and enterprises offer taxi rides, food and grocery delivery, courier services, and more — all within one unified super app platform. Visit our website for more info: https://gojekcloneapp.com/
#gojekclone #gojekcloneapp #gojekcloneappdevelopment #gojekclonescript #gojekappclone #applikegojek #gojeklikeapp #gojekcloneappscript #gojekclonesolution #allinoneapp #multiservicesapp #gojekclonesoftware #appclonegojek
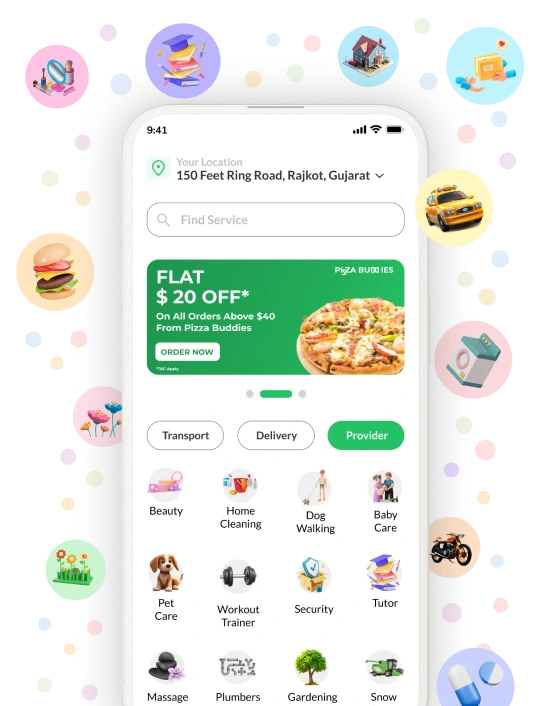
Get a Gojek Clone App Script for Multi-Service Business
The Gojek Clone is a smart and efficient on-demand multiservice platform offering 130+ online services. Get a demo of the Gojek Clone script to start your business today.
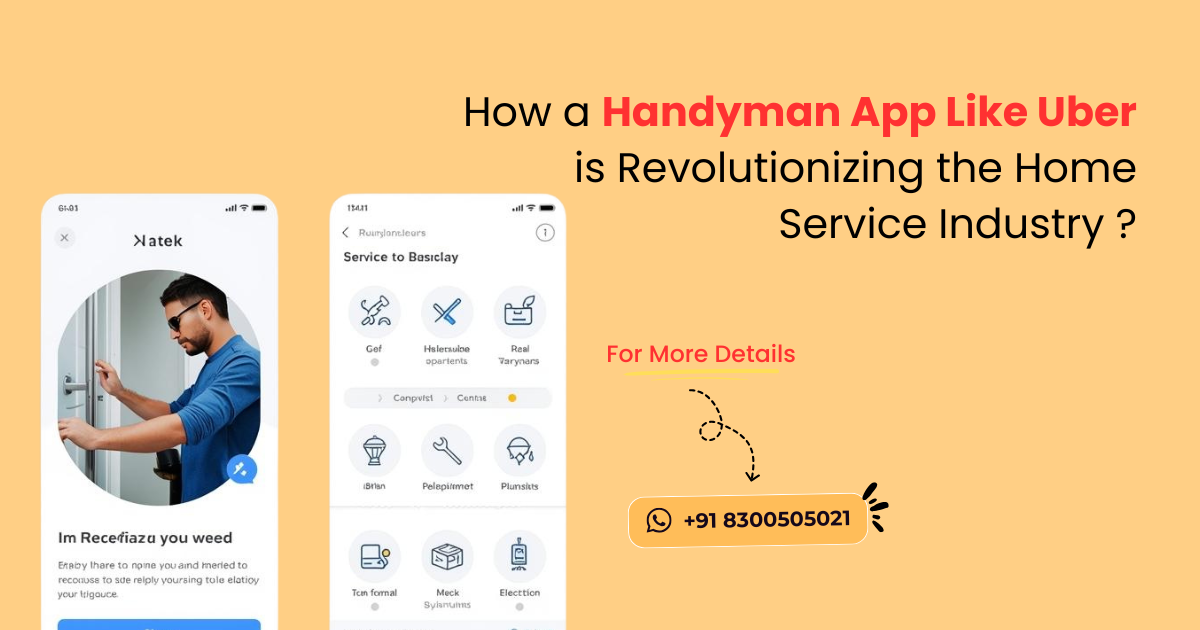
https://gojekcloneapp.com/Tired of searching for a reliable handyman? A Handyman App Like Uber connects you with skilled professionals for quick home repairs, installations, and maintenance — anytime, anywhere!
👉 Explore more at - https://sangvish.com/handy...
#HandymanApp #handymanservice #applikeuber #handymen #business #startups
Create your own scalable Upwork clone platform featuring gig posting, secure escrow payments, real-time chat, service bundles, skill-based filtering, ratings & reviews, and a powerful admin panel. Fully white-label and customizable with full source code access — ideal for startups, agencies, and niche freelance markets.
🔗 https://oyelabs.com/upwork...
#UpworkClone #FreelanceMarketplace #GigEconomyApp #ServicePlatform #oyelabs #WhiteLabelSolution #SecurePayments #CustomCloneScript
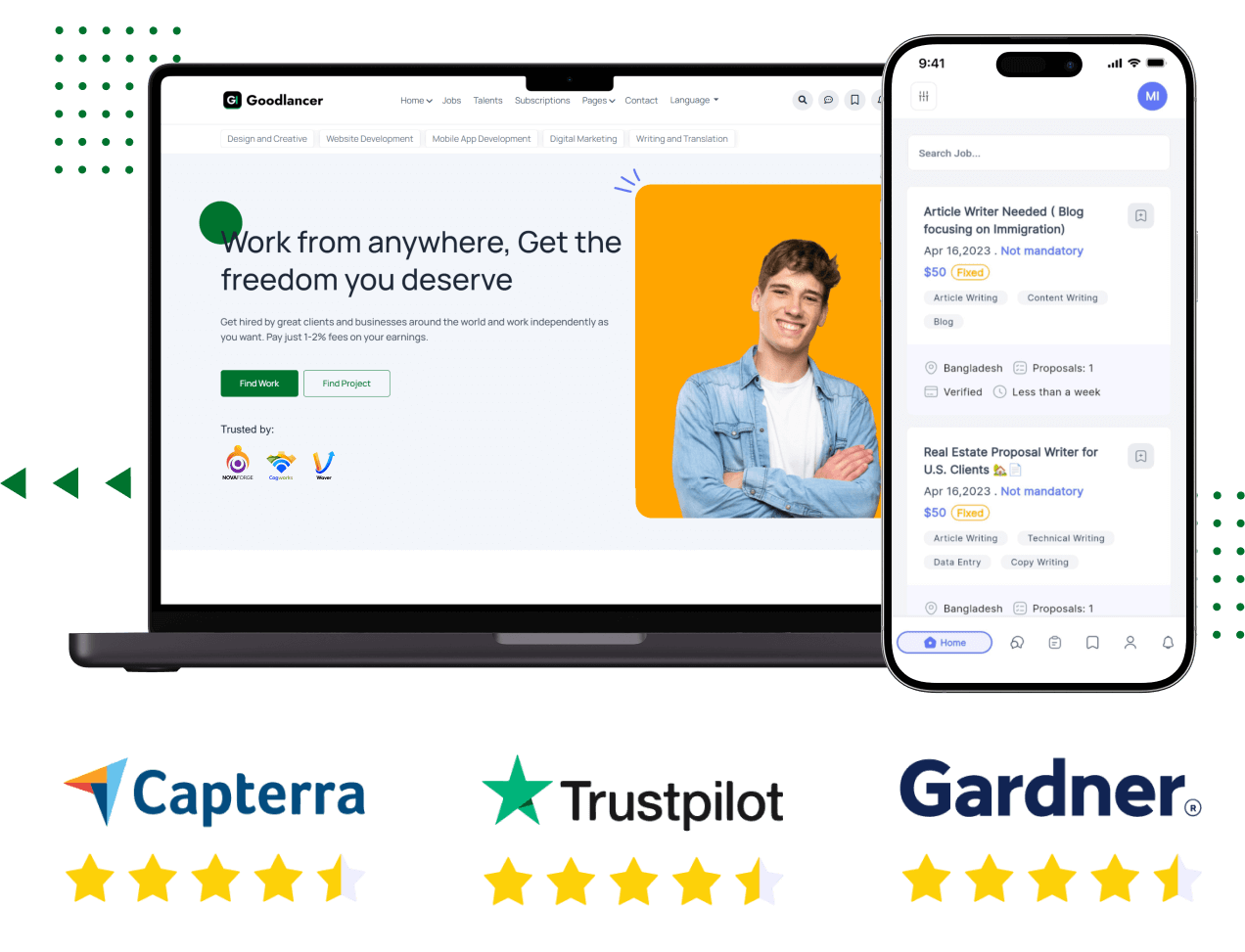
Upwork Clone - Launch Global Freelance Marketplace Platform
Launch your own customizable Upwork clone app with all the basic & advanced features. Build your freelance job marketplace platform now!
https://oyelabs.com/upwork-clone/Step into the short-video realm with Oyelabs’ powerful TikTok clone app. Packed with features like trending feed algorithms, video editing tools, duet/stitch modes, monetization options (ads, virtual gifts), and full source code ownership—this white-label solution lets startups and creators build custom video platforms fast and brand boldly.
https://oyelabs.com/tiktok...
#tiktokclone #ShortVideoApp #CreatorMonetization #VideoSocialPlatform #oyelabs #WhiteLabelApp #ViralVideoApp #CustomVideoScript
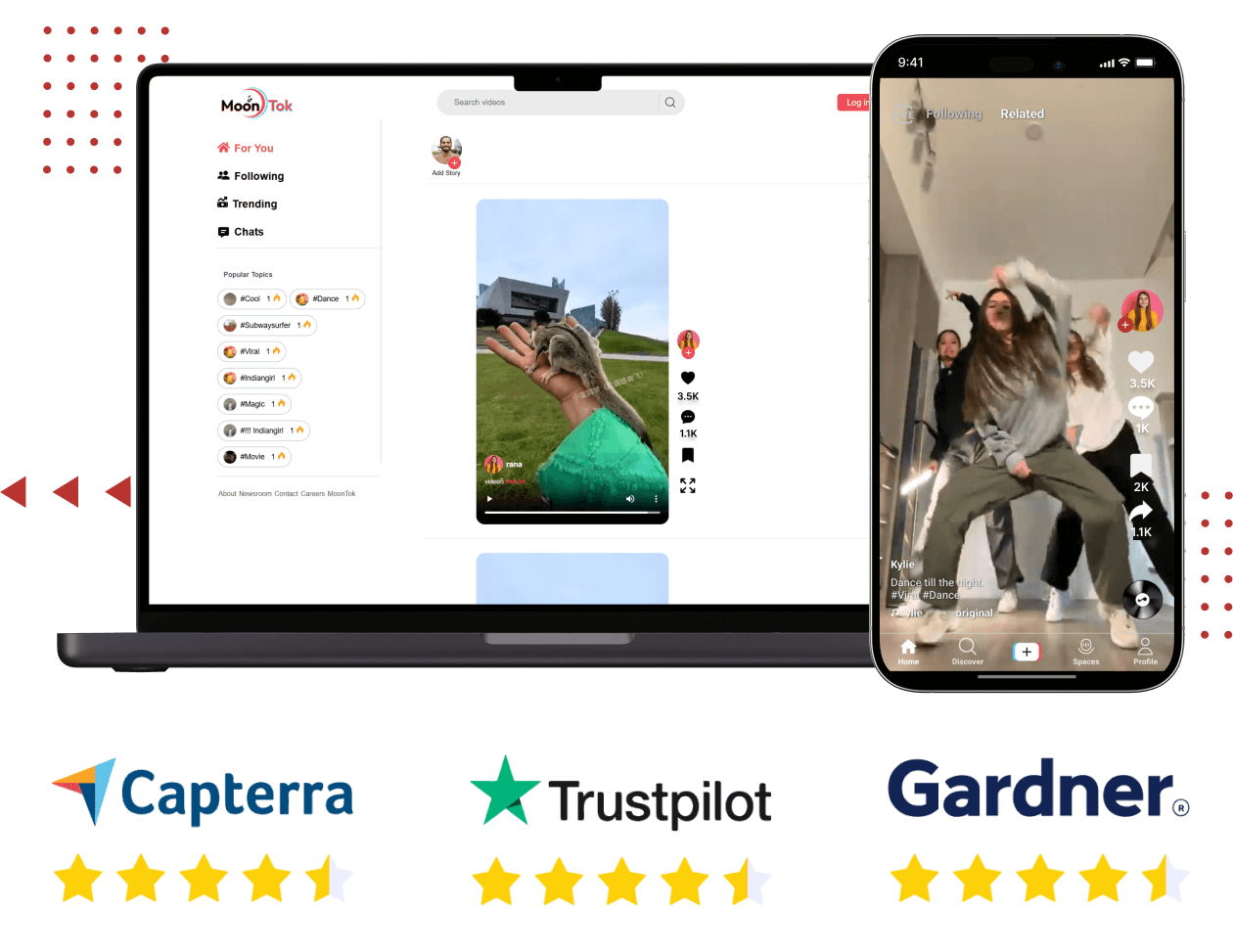
TikTok Clone - Launch Your Own TikTok Like App 2025
TikTok Clone is a 100% customizable, feature-rich solution to launch a video dubbing and video-sharing platform like TikTok, Dubsmash, Musical.ly in 7 days only.
https://oyelabs.com/tiktok-clone/Kickstart your global food delivery business with our ready-made DoorDash Clone App, built for startups & small businesses at a low cost.
🚀 Features include
✅ Real-Time Order Tracking
✅ Secure Local Payments
✅ Easy Admin Panel
✅ Multi-Service Ready.
🔥 Special Offer: Launch at 50% OFF + Free Demo! Don’t wait — start your food delivery app today.
🌐 Free Demo: https://www.trioangle.com/...
📲 WhatsApp: +91 6379630152 | 📩 salestrioangle.com
#fooddeliveryapp #doordashclone #DeliveryApp #RestaurantDeliveryApp #FastFoodDelivery #GroceryDeliveryApp #StartupApp #EntrepreneurApp #OnlineDeliveryApp #MultiServiceDelivery #DeliveryTrackingApp #LowCostApp #AffordableApp #Delivery Business #Delivery Startup
The eCommerce industry has witnessed immersive growth, fueled by new technology innovations and evolving user demands.
AliExpress Clone is one of the top on-demand platforms with a scalable architecture, unique layouts, and standard vendor management. It opens a new opportunity for startups to stand out in a competitive marketplace.
This blog provides a complete guide to building a multi-vendor app using an AliExpress clone script. We covered its essential features, development steps, and latest trends.
Dive in.
Aliexpress Clone: An Introduction
Don’t you know what an AliExpress clone is? Here’s a short overview of it. Let’s check in.
An AliExpress clone is a ready-made solution inspired by the original AliExpress business model, designed with its core functionalities intact. This connects every single user who wants to order products through an online medium. They can compare prices across multiple vendors and finally buy a product from a preferred store. It increases user convenience and satisfaction.
This eCommerce clone script streamlines the complete end-to-end purchasing process with advanced features, including user registration, multiple delivery addresses, shipment tracking, and secure payments.
Partner With Trioangle and Start Today!
Obviously, you are at the right place to start and implement your multi-vendor marketplace idea.
Trioangle's AliExpress Clone Script can help you turn your idea into a robust and revenue-generating eCommerce platform.
Connect with our experts to acknowledge business goals and craft solutions that meet your target audience's needs.
Subscribe now!
https://www.trioangle.com/...
#AliExpressClone #AliExpressCloneScript #AliExpressLikeApp #MultiVendorEcommerce #MarketplaceSoftware #EcommerceScript #ReadymadeEcommerce #B2BMarketplace #OnlineMarketplace
Greetings, taxi startups!
The taxi industry is gaining momentum with the emergence of on-demand transportation. But stepping into the market through taxi booking app development isn’t easy. That’s where taxi dispatch software comes in. It enables you to automate bookings, streamline operations, and manage the platform efficiently.
Here, we list the major challenges of taxi app startups and how a dispatch solution effectively addresses them.
Let’s find it clearly!
Slow Manual Dispatch
In the early stages, taxi startups can depend on phone calls or spreadsheets to assign taxis. It leads to delays, lost business trust, mismatched driver-passenger pairings, and frustrated customers. This challenge is addressed by,
Automated GPS-based trip assignment matches riders with the nearest available driver based on their pickup location.
Cab booking software with AI features simplifies the matching within seconds, far more efficient than map-based coordination.
This also predicts demand surges during local events or peak hours, helping manage driver allocation and increase earnings.
By utilizing these capabilities, you can reduce wait times, provide faster rides, and extend cab bookings without any bottlenecks.
Summing Up
Nowadays, standing out in a competitive taxi marketplace is critical. If you’re an entrepreneur ready to launch or already running a business, it’s important to take note of the challenges and solutions mentioned above.
Consider these points, and start choosing a taxi dispatch software with these functionalities to ensure instant success and growth.
Subscribe for more updates. Thank you for reading!
https://www.trioangle.com/...
#TaxiSoftwareUSA #USATaxiTech #DispatchSoftwareUK #UKTransportTech #TaxiAppCanada #RideshareAU #TaxiSoftwareGermany #FleetManagementSoftware #RideshareTechnology #taxidispatchsoftware
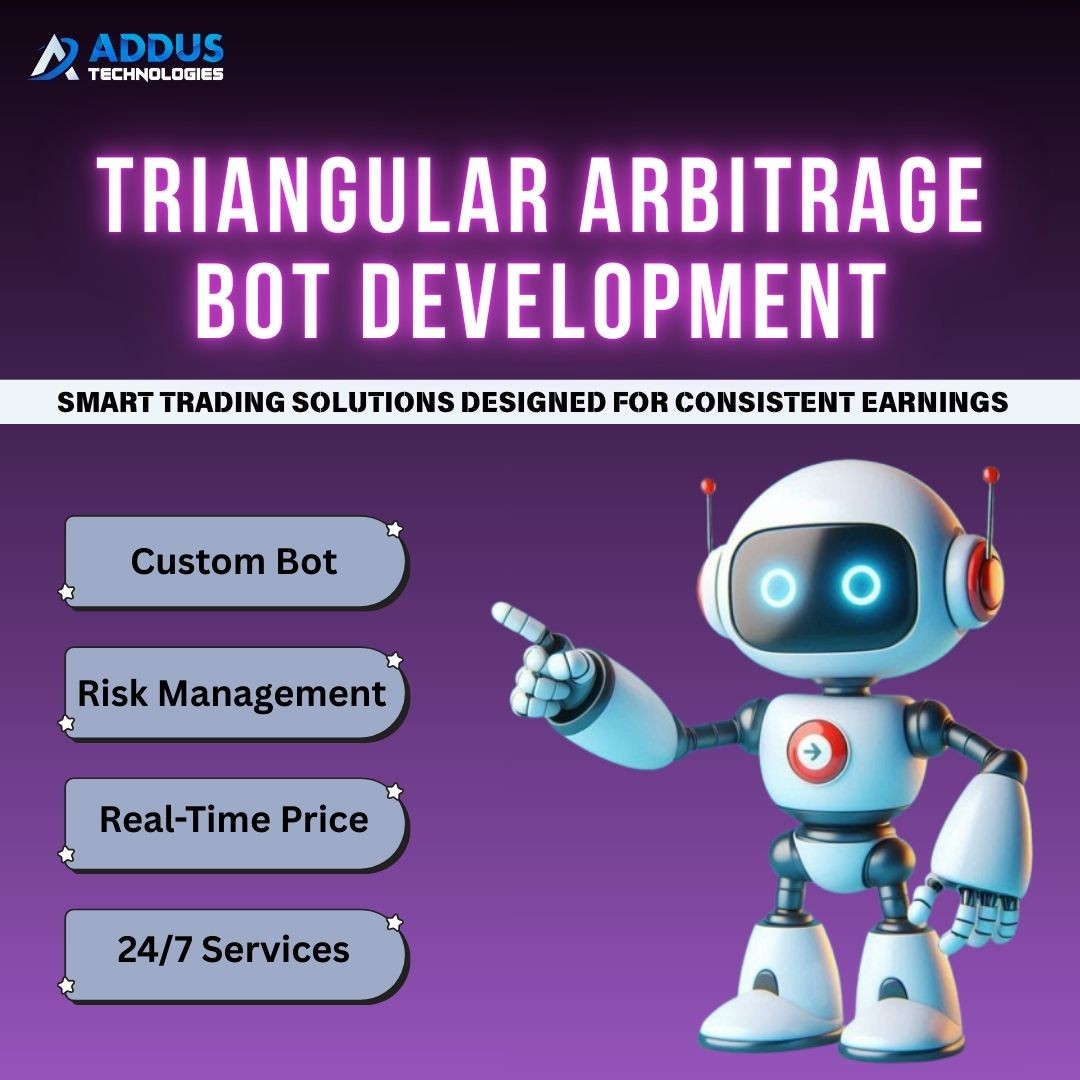
To More Information : https://www.addustechnolog...
#CryptoTrading #ArbitrageBot #CryptoProfits #BlockchainSolutions #TradingAutomation #CryptoInvestment #CryptoBusiness #FinTechSolutions #CryptoMarket
Koinkart is a reputed Sports Betting Game Development Company that offers full services for startups and businesses. We provide custom Sports Betting Software, Prediction Game Development, and solutions using blockchain & AI. Our expert team builds easy-to-use, secure, and scalable betting games to help your business succeed in the fast-growing sports betting market.
Whatsapp: +91 93842 63771
Website: https://www.koinkart.org/s...
Mail: businesskoinkart.org
Don't miss out—read more here: What Makes Monthly Subscription Services Attractive for Taxi Startups?
Mail ID:hellospotnrides.comSpotnRides
WhatsApp: https://wa.me/919600695595
#TaxiSolutions #AIAdvancements #SubscriptionModel #SpotnRides #SmartMobility #TechInnovation #StartupGrowth #DigitalTransformation #RideHailing #BusinessModel #Entrepreneurship #UrbanTransport #MobilityTech #FutureOfTransport #AIApplications #SustainableTransport #SmartCities #DataDrivenDecisions #uberclone #uberclonescript #aipoweredtaxiappsolution #aipowereduberclone
Find out the real cost to create an app like Uber for startups. Explore key features, development stages, and budget insights to build a successful ride-hailing app.
for more: https://duplextech.com/blo...
#taskrabbitclone #OnDemandApp #HandymanApp #AppDevelopment #gigmarketplace #startups #oyelabs
https://oyelabs.com/taskra...
#onlyfansclone #clone #AppDevelopment #app
https://oyelabs.com/onlyfa...
#taskrabbitclone #OnDemandApp #HandymanApp #AppDevelopment #gigmarketplace #startups
https://oyelabs.com/taskra...
#taskrabbitclone #OnDemandApp #HandymanApp #AppDevelopment #gigmarketplace #startups #oyelabs
https://oyelabs.com/taskra...
#taskrabbitclone #OnDemandApp #HandymanApp #AppDevelopment #gigmarketplace #startups #oyelabs
https://oyelabs.com/taskra...
#taskrabbitclone #OnDemandApp #HandymanApp #AppDevelopment #gigmarketplace #startups #oyelabs
https://oyelabs.com/taskra...
#onlyfansclone #clone #AppDevelopment #app #onlyfansclonescript #clonescript
https://oyelabs.com/onlyfa...
OnlyFans Clone | Launch Subscription-Based Content App in 7 Days
OnlyFans clone to launch your censor-free subscription-based creator community platform with our new age 100% customizable script loaded with latest features.
https://oyelabs.com/onlyfans-clone/In 2025, super app development is a tremendous opportunity for startups and businesses seeking to dominate the digital multi-service industry.
To Know More: https://medium.com/rosyam...
WhatsApp: +91 6379630152
Mail: salestrioangle.com
Telegram: https://t.me/Trioangle_Tec...
#gojekclone #allinoneapp #multiservice #OnDemandApp #ondemandappdevelopment #ondemandserviceapp

How to Build a Super Clone App in 2025: The Ultimate Guide | by Rosyamra | Jul, 2025 | Medium
In a world where convenience defines success, super apps are revolutionizing on-demand services by streamlining user experiences and unlocking higher profits and operational efficiency for…
https://medium.com/@rosyamra9/how-to-build-a-super-clone-app-in-2025-the-ultimate-guide-3d692ddd5b54Critical minerals are finally getting the attention they deserve. This year, rare earth elements have dominated headlines, whether because of geopolitical tensions in Greenland and Ukraine or escalating trade disputes with China. They loomed large in U.S.-China trade talks this week, allowing China to drive a hard bargain.
The 17 rare earth elements (REEs) are indispensable. They exhibit unique electromagnetic properties that make numerous technologies function—think smartphones, electric vehicles, artificial intelligence, humanoid robotics, advanced defense systems, and more.
The Trump administration seems to understand this. Recent actions by President Donald Trump—including his executive order “Immediate Measures to Increase American Mineral Production” and his use of Section 232—have made clear America’s interest in rare earths. Indeed, long before this administration, bipartisan recognition of these minerals’ strategic value already existed, for national security and a vast array of advanced technologies.
China dominates in rare earth elements-
As has been widely reported, China currently controls around 90% of global REE production. Its dominance is so strong that even some Western companies must send their rare earth materials to China for processing. Now, with Beijing imposing export controls on key elements and rare earths having been a central focus during this week’s U.S.-China trade talks, the challenge has been further amplified for America.
China’s grip is the result of decades of long-term investment, aggressive policy, and an economic playbook designed to corner the market. Processing rare earths is also notoriously dirty, which is something China has historically been less concerned about.
A 4-point fast-track program-
If the U.S. is serious about building a resilient, domestic REE supply chain, it must act with urgency. Here’s how we can do it, and do it fast:
Inject capital at scale-
The U.S. must follow China’s lead by strategically funding and investing in rare earth producers and infrastructure. Rare earth development, particularly refining, requires significant capital, unless the asset is already advanced and leverages existing infrastructure. That is rarely the case in the U.S., and while both private and public companies are raising funds, significant federal support is essential to compete with China at scale. America’s late start means we must move faster and spend smarter. We can’t afford to wait.
Establish price stability-
Once U.S. producers are operational, price volatility becomes the next major hurdle. China can manipulate the global market by flooding it with underpriced material, undermining U.S. startups before they can gain traction. A temporary pricing floor or purchase guarantee for U.S.-sourced rare earths would help stabilize the market and protect domestic growth. The U.S. has implemented similar pricing strategies to support other foundational industries, including oil and agriculture. America’s emerging rare earth industry is critical and could benefit from these types of pricing initiatives.
Streamline permitting-
While the U.S. rightly values environmental protection and community impact, permitting delays are hampering progress. Responsible, low-impact projects are waiting in line, when they should be fast-tracked. We must retain environmental oversight but remove unnecessary bureaucratic barriers that stifle innovation and increase costs. China has little to no concern with environmental protection in regard to REEs, so removing these roadblocks in the short term will not only allow U.S. companies to get set up to compete, but will also be better for the environment in the long term, all while delivering significant value for American stakeholders.
Create a centralized refining hub-
The rare earth bottleneck isn’t mining—it’s refining. Processing capacity outside China is severely limited. The U.S. needs a centralized, government-backed refinery that serves multiple companies, enabling cost-effective and collaborative scaling. This shared facility would accelerate production, reduce risk, and mark a crucial step toward independence from China’s stranglehold. I believe this effort is the best path forward for Americans to unite and build the industrial infrastructure required to combat the big bully in the rare earth space.
The power of a public-private partnership-
With government support and private-sector innovation, we can build a fully integrated rare earth supply chain. Doing so would neutralize one of China’s most powerful economic weapons and create a strategic advantage for the U.S. in critical industries. It’s also a smart investment in America’s long-term manufacturing future.
This isn’t just about minerals. It’s about national security, technological leadership, and economic resilience. The time to act and join forces is now.
Kickstart your online education business with our Udemy clone script at 50% OFF – exclusively for startups! Create your own eLearning platform with powerful features like course creation, video streaming, secure payments, and instructor dashboards. Perfect for entrepreneurs aiming to enter the booming edtech market. Don’t miss your chance to build the next big learning platform at half the cost!
To Know More: https://www.trioangle.com/...
WhatsApp: +91 6379630152
Mail: salestrioangle.com
Telegram: https://t.me/Trioangle_Tec...
#udemyclone #education #elearning #udemycloneapp
India's commerce minister said his country's startups needed to emulate China by focusing on high-end tech and not quick grocery deliveries or fancy ice cream - harsh criticism that had entrepreneurs quickly pointing out the government's shortcomings.
Piyush Goyal told a startup event in New Delhi late on Thursday that too many were offering food delivery so that "the rich can get their meals without moving out of their house" and were "turning unemployed youth into cheap labour."
"Are we going to be happy being delivery boys and girls? (Making) fancy ice cream and cookies ... is that the destiny of India?" he said, showing a slide titled "India vs. China. The Startup Reality Check".
"What do the Chinese startups do? Work on developing electric mobility, battery technology ... look at what the other side is doing - robotics, automation, machine learning, preparing themselves for 3D manufacturing," Goyal said.
European Union is expected to vote to finalize new tariffs on Chinese-made electric vehicles, after European officials accused Chinese EV companies of benefiting from an unfair level of state support.
Yet the CEO of one of China’s leading EV startups argues that the industry’s success is due to intense local competition, not state support. “There were rumored to be close to 500 [Chinese] EV startups, probably seven to eight years ago. Now, [we’re] left with less than 10% of those names still in business,” Brian Gu, co-president at Chinese EV startup Xpeng
Chinese domestic competition created a “highly efficient” and “highly innovative” industry, Gu claimed, that’s now thriving in global markets
As developed markets in Europe and North America consider new tariffs and controls on Chinese-made EVs, Gu said Xpeng wanted a fair level playing field for it
By Hugo Keji
Improving the business environment to foster innovation and growth requires a multiple approach that addresses various aspects of the ecosystem. Here are several strategies that can be implemented:
1. Policy and Regulatory Framework
Streamline Regulations: Simplify business regulations to reduce the administrative burden on startups and established companies. Clear, predictable, and transparent regulations can encourage entrepreneurship.
Tax Incentives: Offer tax breaks and incentives for companies investing in research and development (R&D) and innovative projects.
Intellectual Property Protection: Strengthen intellectual property rights to protect innovations and encourage investment in new technologies.
2. Access to Finance
Funding Mechanisms: Establish funding mechanisms such as grants, loans, and venture capital funds specifically targeting innovative startups and small businesses.
Public-Private Partnerships: Encourage partnerships between the government, private sector, and academic institutions to pool resources and share risks.
Microfinance and Crowdfunding: Promote alternative financing options like microfinance and crowdfunding to support early-stage entrepreneurs.
3. Infrastructure Development
Digital Infrastructure: Invest in high-speed internet and other digital infrastructure to support tech-based startups and businesses.
Innovation Hubs: Develop innovation hubs, tech parks, and co-working spaces to create collaborative environments.