Build a full-fledged ride-hailing app with OyeLabs’ Ola Clone. It’s fully customizable, supports Android, iOS & web, and includes real-time tracking, fare estimation, carpooling, driver wallet, and powerful admin tools — plus 2 months of post-launch support.
https://oyelabs.com/ola-cl...
#OlaClone #RideHailing #taxiapp #StartupTech #Mobility
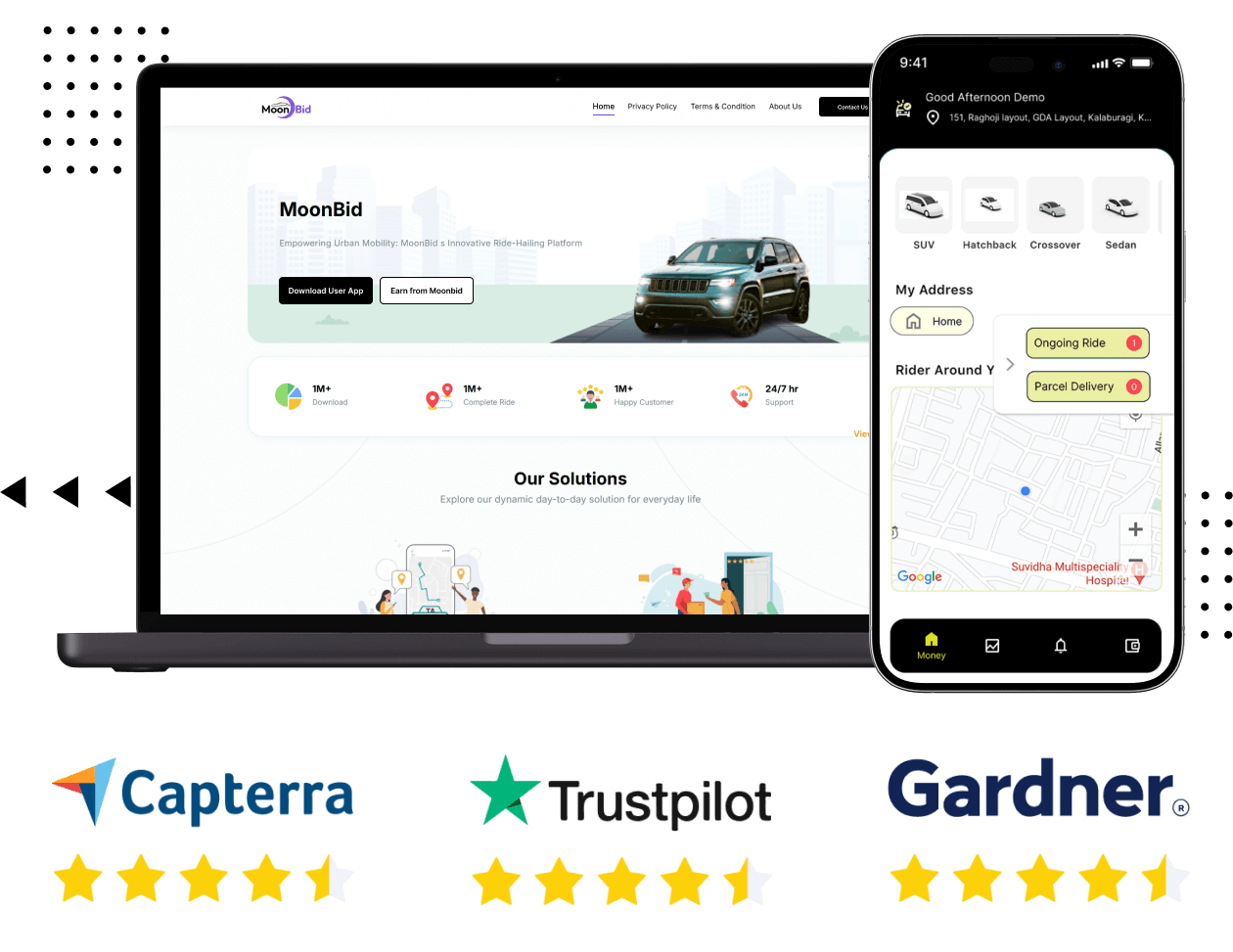
Ola Clone App- Launch Your On-Demand Taxi Booking Business in 7 Days
Ola Clone is a 100% customizable taxi booking app script with advanced features, fast deployment, and 60-day free support to launch your taxi business.
https://oyelabs.com/ola-cl...Build a full-fledged ride-hailing app with OyeLabs’ Ola Clone. It’s fully customizable, supports Android, iOS & web, and includes real-time tracking, fare estimation, carpooling, driver wallet, and powerful admin tools — plus 2 months of post-launch support.
https://oyelabs.com/ola-cl...
#OlaClone #RideHailing #taxiapp #StartupTech #Mobility
Start your own peer-to-peer carpooling app with OyeLabs’ BlaBlaCar Clone. It features trip matching, route optimization, dynamic pricing, passenger reviews, and a robust driver-rider dashboard — ideal for community ride-sharing startups.
#BlaBlaCarClone #ridesharing #Carpooling #StartupApp #Mobility
Launch a feature-rich ride-hailing platform with Oyelabs’ white-label Uber Clone. Enjoy real-time tracking, automated ride dispatch, advanced admin control, and complete source-code ownership — all designed to help you scale your mobility business seamlessly.
https://oyelabs.com/uber-c...
#uberclone #RideSharingApp #TaxiBusiness #WhiteLabelSolution #MobilityStartup
Kickstart your own taxi booking platform with the powerful, white-label Uber Clone App from Oyelabs. With real-time tracking, automated dispatch, multi-region scalability and full source-code ownership, you’re equipped to scale quickly into the mobility market.
https://oyelabs.com/uber-c...
#uberclone #TaxiAppDevelopment #RideHailingSolution #WhiteLabelApp #OnDemandMobility
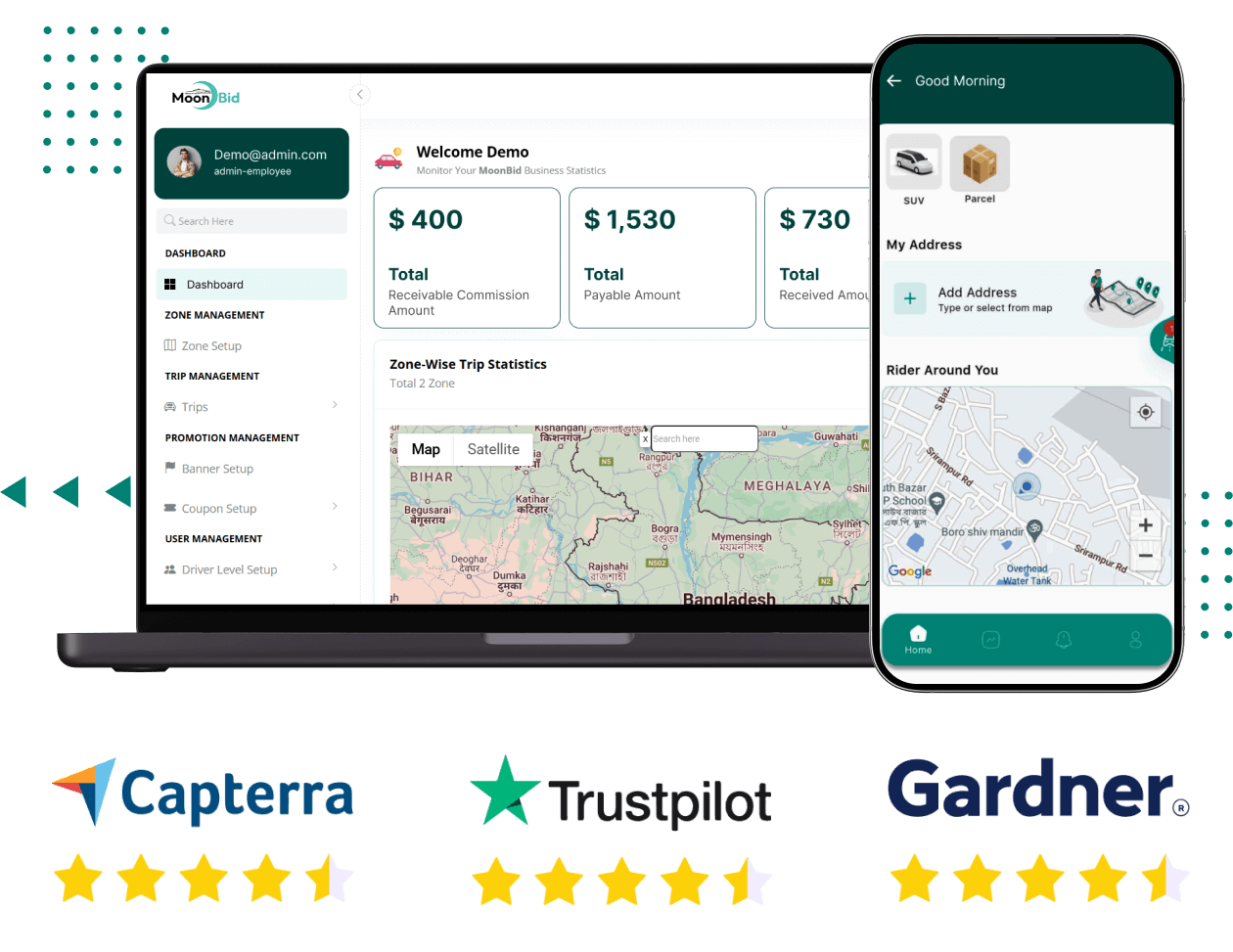
Uber Clone - Build Your Own Online Taxi Booking App
Build your own ride-sharing and taxi booking app with our Uber Clone solution. A customizable, scalable, and secure platform to launch your on-demand transportation business.
https://oyelabs.com/uber-clone/Transform the mobility market with Oyelabs’ Uber clone—live dispatch, GPS tracking, wallet & payments, driver & rider apps, and a powerful admin panel. Build your own branded ride-sharing solution today!
https://oyelabs.com/uber-c...
#uberclone #RideSharingApp #TaxiStartup #OnDemandTransport #MobilitySolution
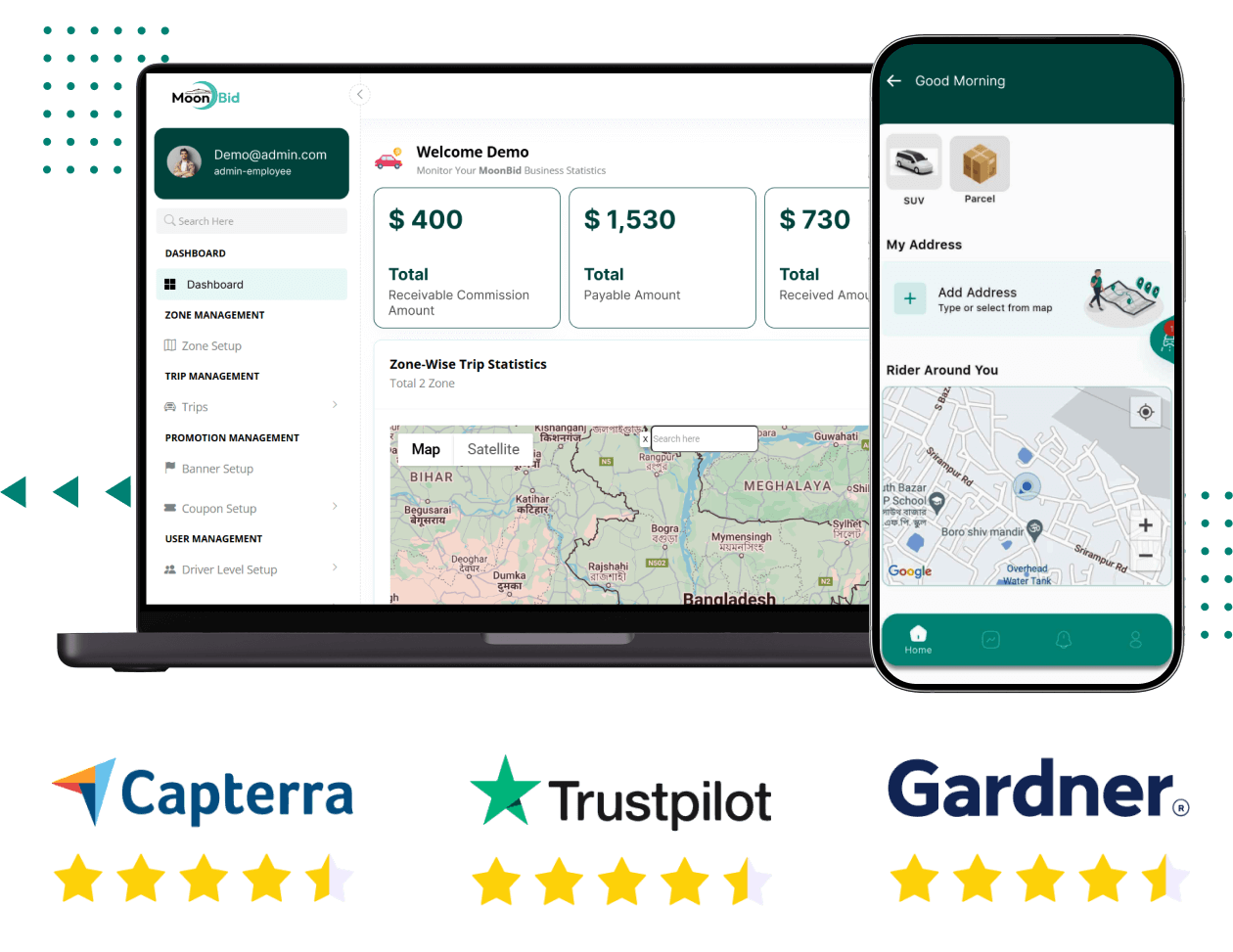
Uber Clone - Build Your Own Online Taxi Booking App
Build your own ride-sharing and taxi booking app with our Uber Clone solution. A customizable, scalable, and secure platform to launch your on-demand transportation business.
https://oyelabs.com/uber-clone/Discover more: https://www.spotnrides.com...
Whatsapp: https://wa.me/919600695595
#watertaxiapp #AustralianWaterTaxiapp #taxibookingapp #WaterTaxibookingApp #WaterTaxibookingAppinAustralia #Watertaxibusiness #WaterTaxiinAustralia #TaxiAppDevelopment #eatertaxiscript #taxibookingsoftware #TaxiBusiness #taximanagementsoftware #taxicloneapp #uberclone #ubercloneapp

Rise of Aquatic Ride with Water Taxi booking App in Australia - SpotnRides - AI Powered Taxi Booking App
Overview of the Australian Water Taxi Sector The craze of water transport is always the same from historic periods. Even before the hundreds of years when proper bridges were not in use, water transportation played a major role. Days have changed but the method of transportation is still in practice..
https://www.spotnrides.com/blog/rise-of-aquatic-ride-with-water-taxi-booking-app-in-australia/Well, the on-demand taxi booking app plays a crucial role in urban mobility. If you’re an entrepreneur curious about launching a profitable platform, choosing the best taxi app development solution is key. It enables your business to reach users, streamline operations, and customize efficiently.
With numerous solutions available in the market, considering the cost factors becomes essential to make the best choice.
It’s not a big deal!. Here’s a closer look at some major cost-effective characteristics.
User Interface & Design
Interface speaks volumes about how effectively your app will perform. An eye-catching and appealing design matters in selecting the best taxi booking app development solution, as it directly enhances user experience and overall satisfaction.
A clean and intuitive design enables the user to book a taxi while the driver manages the trip smoothly.
Compared to a basic design with simpler buttons, colors, and layouts, the advanced UI with animation-rich design elements impacts cost.
End Note
Do you know that success relies on how wisely you manage costs?
We're sure. By carefully evaluating these cost factors, you can select the right taxi booking app development solution within your budget. This provides financial efficiency, great performance, and scalability.
Partner with us to create a profitable and future-ready platform.
https://www.trioangle.com/...
#TaxiAppUSA #CabAppUK #RideHailingAfrica #GulfTaxiApp #TaxiAppDevelopment #UberLikeApp #DigitalTaxiSolution #OnDemandTaxiApp #TaxiAppSolutions #CustomTaxiApp #AppDevelopmentCompany
The taxi sector is flourishing like never before, allowing businesses to expand, develop, and capture new market possibilities.
Have you ever thought about how the cab booking software can transform your business? It helps you streamline bookings, optimize driver management, and enhance customer satisfaction. Don’t get stressed.
This brief blog outlines critical factors to consider when selecting cab booking software that drives growth and profitability.
Get started now!
What is Cab Booking Software?
A cab booking software is a built-in technology solution with core functionalities designed to power an on-demand mobility app. It facilitates urban users to book a cab or taxi ride with a single tap using mobile or web platforms.
The global taxi market is expected to reach $592.96 billion by 2033, up from $274.6 billion in 2024, boasting a CAGR of 8.93% from 2025 to 2033.
In a Nutshell
Hurray! We’ve reached the end. This is the moment to build your online cab booking app and transform your taxi service into a smart and highly profitable venture.
The right cab booking software can accelerate your launch, streamline operations, and stand out in a rapidly expanding industry.
Don't wait, ride the wave of innovation today!
https://www.trioangle.com/...
#TaxiSoftwareUSA #USATaxiTech #DispatchSoftwareUK #UKTransportTech #TaxiAppCanada #RideshareAU #TaxiSoftwareGermany #FleetManagementSoftware #RideshareTechnology #taxidispatchsoftware
Let us look at the two Russia-origin systems.
S-400 Missile System “Sudarshan Chakra”
The S-400 is a Russian mobile SAM system developed in the 1990s by Russia’s NPO Almaz as an upgrade to the S-300 family of missiles.
The S-400 joined the Russian armed forces in 2007. The system is complemented by its successor, the S-500. The S-400 system has four radars and four sets of missiles covering different ranges and vertical bubbles.
The maximum target detection range is 600 kilometres, and targets can be engaged as far as 400 kilometres. The five S-400 batteries contracted by India in 2018 cost $5.43 billion, including reserve missiles.
All the sub-units are data-linked and controlled by a central command and control system with sufficient redundancy. The system is capable of layered defence and integrates with other Indian air defences.
One system can control 72 launchers, with a maximum of 384 missiles. All missiles are equipped with directed explosion warheads, which increases the probability of complete destruction of aerial targets.
The system is designed to destroy aircraft, cruise, and ballistic missiles, and can also be used against ground targets. It can engage targets up to 17,000 km/h or Mach 14. It can intercept low-flying cruise missiles at a range of about 40 km due to the line-of-sight requirement. The anti-ballistic missile (ABM) capabilities of the S-400 system are near the maximum allowed under the (now void) Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty. The number of simultaneously engaged targets by the full system is 36.
The system ground mobility speed is close to 60 km/h on roads and 25 km/h cross-country. It takes 5 minutes to be operational and fire when ordered while driving. Otherwise, the system response time is just 10 seconds. The time between major overhauls is 10,000 hours. The Service life is at least 20 years.
In Russia, the system was made operational around Moscow in 2007. Russia reportedly deployed S-400 in Syria. The system has been widely used in the ongoing conflict in Ukraine, and it is claimed to have shot down many aircraft.
Meanwhile, Ukraine has reportedly used Western weapons, mainly U.S.-made ATACMS missiles, to hit S-400 units on the ground.
Belarus has unspecified numbers of S-400 units. Deliveries to China, of the six batteries ordered, began in January 2018. Four batteries consisting of 36 fire units and 192 or more missiles were delivered to Turkey.
Algeria is another operator. Some other countries, like Iran, Egypt, Iraq, and Serbia, have also shown interest. South Korea is developing the KM-SAM, a medium-range SAM system based on technology from S-400 missiles, with assistance from NPO Almaz.
Three of the five batteries have arrived in India. India took deliveries despite the American threat of CAATSA (Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act).
The remaining two are expected in 2025/26. The recent conflict has revealed the rough location of two systems, one each in Punjab and Gujarat. As per open sources, the third is somewhere in the east. The systems have been tested in various Indian military exercises.
BrahMos
The BrahMos is a long-range ramjet supersonic cruise missile that can be launched from land, submarines, ships, and fighter aircraft. It is a joint venture between the Indian Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and the Russian Federation’s NPO Mashinostroyeniya, which together have formed BrahMos Aerospace.
The missile is based on Russian P-800 Oniks. The name BrahMos is a portmanteau formed from the names of two rivers, the Brahmaputra of India and the Moskva of Russia. India holds 50.5 percent share of the joint venture. 75 percent of the missile is manufactured in India and there are plans to increase this to 85 percent.
Large numbers of land-launched, ship-launched as well as air-launched versions have been inducted and are in service with the Indian armed forces.
The missile guidance has been developed by BrahMos Aerospace. In 2016, after India became a member of the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR), India and Russia gradually increased the range of the missile to 800 km. The latest deliveries to the Indian Navy are of this type.
The cruise missile has anti-ship and land-attack roles, and has been in service since June 2007. The other operator is the Philippine Marine Corps. The unit cost is around $ 3.5 million.
The extended range variant costs around $4.85 million. Many futuristic variants are evolving. The BrahMos-A is a modified air-launched variant of the missile with a reduced size and weight (2.55 tons). It has a range of 500 km when launched from Su-30 MKI, and it can carry only one BrahMos missile.
50 IAF SU-30MKI were modified to carry the BrahMos-A missile. Smaller-sized variants like BrahMos-NG could be carried on more types of aircraft, even on LCA. Additionally, the BrahMos-NG will have an AESA radar rather than the current mechanically scanned one.
The Sukhoi Su-30MKI will carry three NG missiles, while other IAF fighters will carry one. The BrahMos-NG will be ready by the end of 2025. BrahMos-II will be a hypersonic cruise missile. A UCAV variant is planned.
This solid propellant missile can carry a 200–300 kg warhead that could be nuclear or conventional semi-armour-piercing. Max operational ranges are up to 8-900 kilometres. Export variants are currently restricted to 290 kilometres.
The BrahMos is generally considered the world’s fastest supersonic cruise missile. Currently, the missile speed is Mach 3. Later variants will be hypersonic (M 5+). The missile is very accurate with a CEP of less than one metre.
BrahMos was first test-fired on 12 June 2001 from the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur, in a vertical launch configuration. The September 2010 test of BrahMos created a world record for being the first cruise missile to be tested at supersonic speeds in a steep-dive mode.
BrahMos was tested with an Indian seeker for the first time in March 2018, and was tested with an India-developed propulsion system, airframe, and power supply in September 2019. On 30 September 2020, India successfully test-fired an extended-range BrahMos, offering a range of around 350 km, at speeds up to Mach 2.8.
The submarine-launched variant of BrahMos was test-fired successfully for the first time from a submerged pontoon on 20 March 2013. Even BrahMos Block III land-attack variants are operational. There are plans to have missiles with a range of 1500 km or more.
BrahMos is operationally deployed in large numbers by the three services. Additional missile orders have been recently placed for extended-range variants.
The Philippines has placed a substantial order for their services, and deliveries began in 2024. Russia, too, has plans to buy many missiles. Brazil has shown interest in the missile system. Vietnam and Indonesia have already signed deals.
Sky Is Not The Limit
Resolute political will, choice of targets, weapon matching and accuracy, actionable intelligence, strong Indian air defences, and great IAF professionals. and hitting strategic targets in depth were the clear clinchers.
Aerospace has become the primary means of prosecuting war. India-Russia relations are time-tested. Nearly 60 percent of IAF aircraft are of Russian origin.
Russian platforms and weapons with the Indian armed forces have performed exceedingly well for many decades, since the MiG-21s of the 1960s. The S-400 and Su-30MKI-BrahMos combination have excelled in Op Sindoor.
Could S-500 (600 km) be the next acquisition? Will India select the Su-57 fifth-generation aircraft and Make in India? Can Russia help accelerate the Indian nuclear submarine program? Should India acquire the “AWACS Killer” Russian R-37M AAM and collaborate on developing futuristic long-range aerial missiles?
Should there be more work together on the Su-30MKI upgrade? Can the two enter into a joint venture for Kamikaze drones required by both sides in large numbers, and India can help scale up production?
The Sky is NO more the limit!
Nowadays, traditional taxi services are being replaced with tech-enabled ride-hailing systems.
Car Rental App
Create a taxi app that allows consumers to select a diverse range of vehicles and book their rental on an hourly, daily, or weekly basis.
Fleet Management App
A fleet management app can help you streamline diverse fleet operations. It meets all of your particular service requirements.
Corporate Taxi App
Provide a dedicated corporate taxi app for employee transportation with scheduled rides, expense tracking, and billing management for businesses of any size.
Wrapping Up
Trioangle offers a robust taxi app development solution with advanced features, easy navigation, intuitive design, and scalable architecture. It's aimed to fulfil modern mobility demands while streamlining operations.
https://www.trioangle.com/...
#TaxiAppUSA #CabAppUK #RideHailingAfrica #GulfTaxiApp #TaxiAppDevelopment #UberLik
India's commerce minister said his country's startups needed to emulate China by focusing on high-end tech and not quick grocery deliveries or fancy ice cream - harsh criticism that had entrepreneurs quickly pointing out the government's shortcomings.
Piyush Goyal told a startup event in New Delhi late on Thursday that too many were offering food delivery so that "the rich can get their meals without moving out of their house" and were "turning unemployed youth into cheap labour."
"Are we going to be happy being delivery boys and girls? (Making) fancy ice cream and cookies ... is that the destiny of India?" he said, showing a slide titled "India vs. China. The Startup Reality Check".
"What do the Chinese startups do? Work on developing electric mobility, battery technology ... look at what the other side is doing - robotics, automation, machine learning, preparing themselves for 3D manufacturing," Goyal said.
About 10,000 employees of the United States Agency for International Development, excluding essential personnel, were notified Tuesday they will be placed on administrative leave at the end of Friday as President Donald Trump moves to dismantle the foreign aid agency.
A State Department notice to USAID employees ‒ two-thirds of whom work overseas across 60 countries ‒ said all USAID "direct hire personnel" across the world will be placed on administrative leave effective Friday, Feb. 7
The State Department is working on a plan to arrange and pay for the return of USAID employees living overseas back to the United States within 30 days and to terminate contracts not deemed essential, the notice reads. Extensions for their return to the United States will be considered "based on personal or family hardship, mobility or safety concerns, or other reasons."
The Tomahawk cruise missiles in the launchers can hit targets in both China and Russia from the Philippines; the SM-6 missiles it also carries can strike air or sea targets more than 200 km (165 miles) away.
The senior Philippine government source said the redeployment would help determine where and how fast the missile battery could be moved to a new firing position. That mobility is seen as a way to make them more survivable during a conflict
Satellite images showed the batteries and their associated gear being loaded onto C-17 transport aircraft at Laoag International Airport in recent weeks, said Jeffrey Lewis of the Middlebury Institute of International Studies. The Typhon system is part of a U.S. drive to amass a variety of anti-ship weapons
India, known for its massive pool of IT professionals, many of whom work across the world, accounts for the bulk of such visas issued by the United States.
"Our countries have a strong and growing economic and technological partnership and within this ambit, mobility of skilled professionals is an important component," India's foreign ministry spokesperson, Randhir Jaiswal, told a press conference when asked about the H1B visa discussions in the U.S.
"India-U.S economic ties benefit a lot from the technical expertise provided by skilled professionals, with both sides leveraging their strengths and competitive value. We look forward to further deepening India-U.S economic ties which are to our mutual benefit."
The assistance will include Stinger missiles, ammunition for High Mobility Artillery Rocket Systems (HIMARS), drones and land mines, among other items, Blinken said in a statement.
Reuters reported last week that the Biden administration planned to provide the equipment, much of it anti-tank weapons, to ward off Russia's attacking forces.
Moscow's troops have been capturing village after village in Ukraine's east, part of a drive to seize the industrial Donbas region, while Russian airstrikes target a hobbled Ukrainian energy grid.
"The United States and more than 50 nations stand united to ensure Ukraine has the capabilities it needs to defend itself against Russian aggression,"
The Presidential Drawdown Authority (PDA) package is estimated to hold a value of about $425 million and will provide Ukraine with the ability to meet its most urgent needs in terms of air defense, air-to-ground weapons, rocket systems and artillery munitions, armored vehicles and anti-tank weapons.
U.S. included additional munitions for National Advanced Surface-to-Air Missile Systems (NASAMS); RIM-7 missiles and support for air defense; Stinger anti-aircraft missiles; ammunition for High Mobility Artillery Rocket Systems (HIMARS); air-to-ground munitions; 150mm and 105mm artillery ammunition; tube-launched, optically-tracked, wire-guided (TOW) missiles; Javelin and AT-4 anti-armor systems; High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicles (HMMWVs); small arms and ammunition; grenades, thermals and training equipment; demolitions equipment and munitions;.....
By Hugo Keji
The gig economy, characterized by short-term, flexible jobs often facilitated by digital platforms, is reshaping the traditional employment landscape.
While it offers opportunities for flexibility and independence, it also poses challenges to traditional employment structures and labor rights.
Here are the potential long-term impacts:
1. Shift in Employment Models
A. Rise of Freelancing and Independent Contracting
Decline of Full-Time Employment: As gig work becomes more prevalent, there may be a decline in traditional full-time jobs with stable income and benefits. Companies might prefer hiring gig workers to reduce costs associated with salaries, benefits, and long-term commitments.
Increased Job Flexibility: Gig work offers more flexibility, allowing individuals to work multiple jobs or pursue personal interests. This flexibility can be attractive to workers seeking work-life balance, but it also comes with trade-offs in job security and benefits.
B. Blurring of Employment Boundaries
Erosion of Employer-Employee Relationship: The gig economy often blurs the line between employers and independent contractors, leading to ambiguity in employment rights and responsibilities. This can weaken the traditional employer-employee relationship and reduce workers' bargaining power.
Rise of Platform Dependence: Workers may become increasingly dependent on digital platforms (e.g., Uber, TaskRabbit) for income. This dependence can lead to power imbalances, where platforms dictate terms and conditions, often at the expense of workers' rights.
2. Impact on Labor Rights and Protections
A. Challenges to Traditional Labor Protections
Lack of Benefits: Gig workers often do not receive traditional employment benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave, or unemployment insurance. This can lead to increased financial insecurity and reduced access to essential services.
Limited Legal Protections: Gig workers may not be covered by labor laws that protect traditional employees, such as minimum wage laws, overtime pay, and workplace safety regulations. This can lead to exploitation and unsafe working conditions.
B. Unionization and Collective Bargaining
Difficulty in Organizing: The gig economy's decentralized and dispersed nature makes it challenging for workers to organize and form unions. Without collective bargaining power, gig workers may struggle to negotiate better pay and working conditions.
Emergence of New Forms of Worker Advocacy: Despite challenges, new forms of worker advocacy are emerging, such as digital unions and worker cooperatives. These organizations aim to represent gig workers' interests and push for better labor protections.
3. Economic Inequality and Social Implications
A. Widening Income Inequality
Polarization of Income: The gig economy may contribute to widening income inequality, as high-skilled workers (e.g., freelance consultants, developers) command higher pay, while low-skilled gig workers (e.g., delivery drivers) face low wages and precarious work conditions.
Reduced Social Mobility: The instability and lack of benefits in gig work can hinder long-term financial planning, making it difficult for workers to achieve upward social mobility.
B. Impact on Social Safety Nets
Strain on Public Resources: As more workers engage in gig work without employer-provided benefits, there may be increased reliance on public resources, such as healthcare and social welfare programs. This could strain government budgets and require policy adjustments.
Redefinition of Social Contracts: The rise of the gig economy may necessitate a rethinking of the social contract between workers, employers, and the state. This could lead to policy reforms, such as the introduction of universal basic income, portable benefits, or new labor classifications that better reflect the realities of gig work.
4. Future of Work and Employment Norms
A. Technological Disruption
Automation and AI: The gig economy is closely linked to technological advancements. As automation and AI continue to evolve, some gig jobs may be replaced by machines, leading to further disruption in the labor market.
Continuous Learning and Skill Development: To stay competitive, gig workers may need to engage in continuous learning and skill development. This could lead to a shift in education and training systems, with a focus on lifelong learning.
B. Cultural and Social Changes
Changing Perceptions of Work: The gig economy may lead to a cultural shift in how work is perceived, with greater emphasis on flexibility, entrepreneurship, and work-life balance. However, this could also contribute to the normalization of precarious work and job insecurity.
Redefinition of Career Paths: Traditional career paths, characterized by long-term employment and progression within a single company, may give way to more fragmented and non-linear career trajectories. Workers may need to adapt to frequent job changes and the need to continually re-skill.
The gig economy has the potential to significantly reshape traditional employment and labor rights. While it offers opportunities for flexibility and independence, it also raises concerns about job security, income inequality, and the erosion of labor protections.
The long-term impact will depend on how governments, businesses, and workers respond to these challenges, potentially leading to new labor policies, social safety nets, and employment norms.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
By Hugo Keji
Key Challenges in Higher Education and Research in Africa:-
1. Limited Funding and Resources
Inadequate Infrastructure: Many institutions lack sufficient infrastructure, including modern classrooms, laboratories, and libraries.
Insufficient Research Funding: Limited financial resources for research and development hinder academic progress and innovation.
High Student-to-Teacher Ratios: Overcrowded classrooms and insufficient faculty members affect the quality of education.
2. Brain Drain
Talent Migration: Many highly skilled professionals and academics leave Africa for better opportunities abroad, resulting in a loss of talent and expertise.
3. Quality and Relevance of Education
Curriculum Misalignment: Curricula often do not align with the needs of the job market or local contexts, leading to graduates who are ill-prepared for employment.
Quality Assurance: Ensuring consistent quality and standards across institutions is challenging due to varying levels of resources and oversight.
4. Access and Equity
Limited Access: Higher education is often inaccessible to many due to financial, geographical, and social barriers.
Gender Disparities: Women are underrepresented in higher education, particularly in STEM fields.
5. Governance and Management
Institutional Weaknesses: Inefficient governance structures and management practices hinder the effectiveness of higher education institutions.
Corruption: Corruption and lack of transparency can affect admissions, funding allocations, and academic integrity.
6. Technology and Digital Divide
Limited ICT Infrastructure: Inadequate internet connectivity and access to digital tools impede the integration of technology in education.
Digital Literacy: Many students and faculty members lack the digital skills needed to fully utilize e-learning and digital research tools.
7. Research Capacity and Collaboration
Fragmented Efforts: Research efforts are often fragmented and lack coordination, limiting their impact.
Low Publication Rates: African researchers face challenges in publishing their work in international journals, partly due to limited support and resources.
Key Opportunities in Higher Education and Research in Africa:-
1. Technological Advancements
E-Learning and Distance Education: Technology can expand access to higher education through online courses and remote learning platforms.
Digital Research Tools: Digital tools and platforms can enhance research capabilities and collaboration across institutions.
2. Partnerships and Collaboration
International Collaboration: Partnerships with international institutions can provide funding, expertise, and opportunities for joint research projects.
Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration with the private sector can bring in additional resources and ensure that education and research are aligned with industry needs.
3. Policy and Reform
Education Policy Reforms: Governments can implement policies that prioritize higher education and research, increase funding, and improve governance.
Regional Integration: Regional cooperation can facilitate resource sharing, standardization of qualifications, and mobility of students and researchers.
4. Focus on STEM and Innovation
STEM Education: Emphasizing science, technology, engineering, and mathematics can drive innovation and address critical developmental challenges.
Innovation Hubs: Establishing innovation hubs and incubators can support entrepreneurship and practical applications of research.
5. Harnessing Demographic Dividend
Youth Engagement: Africa’s large youth population can be a driving force for higher education and research if adequately educated and empowered.
Skill Development: Focusing on skills development and vocational training can enhance employability and economic growth.
6. Improving Quality and Relevance
Curriculum Reform: Aligning curricula with local needs and global standards can enhance the relevance and impact of higher education.
Quality Assurance Mechanisms: Strengthening quality assurance mechanisms can ensure consistent standards and improve educational outcomes.
7. Enhancing Research Capacity
Capacity Building: Investing in the professional development of researchers and academic staff can improve research output and quality.
Research Networks: Establishing and supporting research networks can facilitate collaboration, knowledge sharing, and large-scale projects.
Strategic Recommendations:-
1. Increase Investment
Government Funding: Increase public investment in higher education and research infrastructure.
Diversified Funding: Encourage private sector investment and international donor support.
2. Foster Innovation and Entrepreneurship
Innovation Ecosystems: Develop ecosystems that support research commercialization and entrepreneurship.
Incubation Programs: Establish incubation and accelerator programs to support startups and innovations from academic research.
3. Strengthen Governance and Management
Capacity Building: Provide training and support for university administrators to improve governance and management practices.
Transparency and Accountability: Implement measures to reduce corruption and increase transparency in higher education institutions.
4. Promote Equity and Inclusion
Scholarships and Financial Aid: Provide scholarships and financial aid to underrepresented groups, including women and rural students.
Inclusive Policies: Develop policies that promote gender equality and inclusion of marginalized communities in higher education.
By addressing these challenges and leveraging the opportunities, African countries can significantly improve their higher education and research sectors, contributing to broader socio-economic development across the continent.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$5 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com

Health Data 101 - App on Amazon Appstore
Healthdata101-Manage Hospital and Health data.
https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B0D514TH5SBy Hugo Keji
Addressing the Challenges of Rapid Urbanization in African Countries:-
Introduction-
Rapid urbanization presents significant challenges for African countries, including inadequate infrastructure, housing shortages, and increased pressure on social services.
This article explores strategies that can help African nations manage and mitigate the impacts of urbanization, ensuring sustainable and inclusive urban growth.
1. Urban Planning and Infrastructure Development-
1.1. Comprehensive Urban Planning
Develop and implement long-term urban plans that anticipate future growth and needs.
Incorporate land use zoning, public transportation, and green spaces into urban designs.
1.2. Infrastructure Investment
Invest in the construction and maintenance of essential infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and public transportation.
Upgrade existing infrastructure to accommodate increased urban populations.
2. Affordable Housing Solutions
2.1. Expanding Affordable Housing
Promote the development of affordable housing through public-private partnerships.
Implement housing policies that encourage the construction of low-cost homes.
2.2. Upgrading Informal Settlements
Regularize and upgrade informal settlements to improve living conditions.
Provide basic services such as water, sanitation, and electricity in these areas.
3. Enhancing Public Services
3.1. Improving Healthcare and Education
Expand healthcare facilities and ensure they are well-equipped to handle urban populations.
Increase access to quality education by building more schools and training teachers.
3.2. Strengthening Social Services
Enhance social safety nets to support vulnerable urban populations.
Develop community centers that provide various services, including job training and childcare.
4. Sustainable Economic Development
4.1. Creating Job Opportunities
Promote economic diversification to create a range of job opportunities in urban areas.
Support the growth of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) through access to finance and training.
4.2. Encouraging Innovation and Technology
Foster innovation hubs and technology parks to attract startups and tech companies.
Invest in digital infrastructure to support the growth of a knowledge-based economy.
5. Environmental Sustainability
5.1. Promoting Green Urban Development
Incorporate sustainable building practices and materials in urban construction.
Develop green spaces and urban parks to improve air quality and provide recreational areas.
5.2. Addressing Waste Management
Implement comprehensive waste management systems that include recycling and waste-to-energy initiatives.
Encourage community participation in waste reduction and recycling programs.
6. Enhancing Governance and Community Participation
6.1. Strengthening Local Governance
Empower local governments to manage urban development effectively.
Ensure transparency and accountability in urban planning and resource allocation.
6.2. Promoting Community Involvement
Encourage community participation in urban planning and decision-making processes.
Support local initiatives that address urban challenges and improve living conditions.
7. Transportation and Mobility
7.1. Developing Public Transportation Systems
Invest in efficient and affordable public transportation networks, including buses, trains, and metro systems.
Promote non-motorized transportation options such as cycling and walking paths.
7.2. Reducing Traffic Congestion
Implement traffic management systems to reduce congestion and improve mobility.
Encourage carpooling and the use of public transportation to decrease the number of private vehicles on the roads.
8. Addressing Social Inequality
8.1. Promoting Inclusive Development
Ensure that urban development projects benefit all residents, including marginalized and low-income groups.
Implement policies that address social inequalities and promote equitable access to resources and opportunities.
8.2. Supporting Vulnerable Populations
Develop targeted programs to support vulnerable populations such as migrants, refugees, and the homeless.
Provide access to affordable healthcare, education, and social services for these groups.
Managing rapid urbanization in African countries requires a multifaceted approach that includes comprehensive urban planning, infrastructure development, affordable housing, enhanced public services, sustainable economic growth, environmental sustainability, effective governance, and community participation.
By implementing these strategies, African nations can create vibrant, sustainable, and inclusive cities that improve the quality of life for all urban residents.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan.
With servers in Asia, Europe and America.
Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365
For ONLY USD$5 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download... App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
By Hugo Keji
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) plays a crucial role in economic development by providing capital, creating jobs, and facilitating technology transfer. Attracting more FDI requires a multi-faceted approach involving economic, legal, and social policies.
Here are several policies that can be implemented to attract more FDI:
Economic Policies:-
1. Stable Macroeconomic Environment
Maintain low inflation rates.
Ensure stable exchange rates.
Implement sound fiscal policies.
2. Tax Incentives
Offer tax holidays or reduced tax rates for foreign investors.
Implement double taxation avoidance agreements.
Provide tax credits for specific sectors or regions.
3. Investment in Infrastructure
Develop and upgrade transportation networks (roads, ports, airports).
Enhance telecommunications and internet connectivity.
Ensure reliable power and water supply.
4. Legal and Regulatory Framework
Ease of Doing Business-
Simplify business registration and licensing processes.
Reduce bureaucratic red tape and corruption.
Streamline customs procedures.
5. Protection of Property Rights
Enforce strong intellectual property laws.
Ensure transparent and fair legal processes.
Provide mechanisms for dispute resolution.
6. Flexible Labor Laws
Implement labor laws that balance worker protection with flexibility.
Promote labor market efficiency and mobility.
Provide incentives for skill development and training.
7. Financial and Trade Policies:-
Access to Finance-
Develop a robust financial sector.
Provide credit facilities and loans to foreign investors.
Facilitate public-private partnerships.
8. Trade Liberalization
Reduce tariffs and non-tariff barriers.
Enter into free trade agreements.
Promote export incentives and schemes.
9. Social and Political Stability:-
Political Stability-
Ensure stable governance and political continuity.
Promote democratic processes and reduce political risks.
Engage in active diplomacy to build investor confidence.
10. Social Infrastructure
Invest in healthcare and education.
Promote a skilled and healthy workforce.
Ensure social harmony and safety.
11. Sector-Specific Policies:-
Targeted Sectoral Policies-
Identify and promote key sectors with high growth potential.
Provide sector-specific incentives and support.
Facilitate industry clusters and special economic zones.
12. Technology and Innovation
Promote research and development (R&D) initiatives.
Provide grants and subsidies for technological advancement.
Encourage partnerships between foreign investors and local firms.
13. Environmental and Sustainability Policies:-
Sustainable Development-
Implement policies that encourage green investments.
Promote renewable energy projects.
Ensure compliance with international environmental standards.
14. Marketing and Promotion:-
Investor Promotion Agencies-
Establish dedicated agencies to promote and facilitate FDI.
Conduct international roadshows and investment summits.
Provide comprehensive information and support to potential investors.
15. Branding and Image Building:-
Develop a strong national brand as an investment destination.
Highlight success stories and case studies.
Engage in public relations and media campaigns.
Implementing these policies requires coordinated efforts between government, private sector, and civil society.
Regular assessment and adjustment of these policies are necessary to respond to global economic changes and investor needs.
By creating a conducive environment for foreign investors, countries can attract more FDI and foster sustainable economic growth.
The hardships faced by the majority in Nigeria, while political elites enjoy substantial pay, can be attributed to several interconnected factors.
These include systemic corruption, economic mismanagement, inequality, and lack of effective governance.
Here’s a detailed look at the underlying reasons:
1. Corruption
Prevalence of Corruption:
Corruption is deeply entrenched in Nigeria's political and administrative systems.
Misappropriation of public funds by politicians and government officials.
Bribery, kickbacks, and embezzlement are common, diverting resources meant for public services.
Impact on Development:
Corruption hampers economic development and leads to poor infrastructure, healthcare, and education.
International investors are deterred, reducing foreign direct investment (FDI) and economic growth.
2. Economic Mismanagement
Policy Failures:
Inconsistent and poorly implemented economic policies.
Mismanagement of Nigeria’s oil revenues, which constitute a significant portion of the national income.
Public Debt:
High levels of public debt with limited accountability on how borrowed funds are utilized.
Debt servicing takes up a significant part of the budget, reducing funds available for development projects.
3. Income Inequality
Disparities in Wealth Distribution:
A significant gap between the rich and the poor.
The political elite have access to numerous income streams, including salaries, allowances, and kickbacks, while the majority struggle with low wages and unemployment.
Social Inequality:
Poor access to quality education and healthcare for the majority.
Limited social mobility, with wealth and opportunities concentrated in the hands of a few.
4. Ineffective Governance
Poor Implementation of Policies:
Lack of continuity and effective implementation of development policies and projects.
Frequent changes in administration lead to policy inconsistencies.
Weak Institutions:
Weak institutions fail to hold the political elite accountable.
Judiciary and anti-corruption agencies are often compromised.
5. Political Patronage and Clientelism
Political Patronage:
Politicians use state resources to reward loyalists, ensuring their political survival.
Funds meant for public services are diverted to maintain political support.
Clientelism:
Distribution of resources is based on loyalty rather than need or merit.
This leads to inefficiency and waste, exacerbating hardships for the majority.
6. Poor Infrastructure and Public Services
Neglect of Public Services:
Inadequate investment in public services such as healthcare, education, and transportation.
Poor infrastructure development despite significant budget allocations.
Quality of Life:
The quality of life for the majority remains low due to poor public services and infrastructure.
High levels of poverty, unemployment, and insecurity.
7. Lack of Accountability and Transparency
Opaque Systems:
Lack of transparency in government spending and decision-making processes.
Difficulty in tracking public funds and holding officials accountable.
Citizen Disempowerment:
Limited avenues for citizens to demand accountability.
Fear of reprisals against whistleblowers and activists.
The hardships faced by the majority in Nigeria are a result of a complex interplay of corruption, economic mismanagement, income inequality, ineffective governance, political patronage, poor public services, and lack of accountability.
Addressing these issues requires comprehensive reforms to promote transparency, strengthen institutions, and ensure that public resources are used effectively for the benefit of all citizens.
By tackling these challenges, Nigeria can create a more equitable society where economic opportunities and quality of life improve for the majority, reducing the stark contrast between the political elite and the general populace.
Detailed Solutions for Addressing Hardships and Inequality in Nigeria.
1. Solutions for Political Elites
A. Implement Anti-Corruption Reforms:
Strengthen Anti-Corruption Agencies:
Ensure independence and adequate funding for agencies like the Economic and Financial Crimes Commission (EFCC) and the Independent Corrupt Practices Commission (ICPC).
Implement strict anti-corruption laws with severe penalties for offenders.
Asset Declaration and Monitoring:
Enforce mandatory and transparent asset declaration for all public officials.
Conduct regular audits and investigations to ensure compliance.
Whistleblower Protection:
Provide robust legal protection for whistleblowers.
Establish secure and anonymous reporting channels for corruption cases.
B. Promote Good Governance:
Transparency in Governance:
Mandate the publication of government budgets, spending, and procurement processes.
Use technology to create open databases accessible to the public for tracking government projects and funds.
Strengthen Institutions:
Enhance the capacity and independence of institutions like the judiciary, electoral bodies, and law enforcement agencies.
Promote merit-based appointments and reduce political interference in these institutions.
Electoral Reforms:
Ensure free, fair, and transparent elections.
Implement electronic voting systems to minimize electoral fraud and manipulation.
2. Solutions for Government Officials
A. Effective Public Service Delivery:
Capacity Building:
Invest in training and development programs for public servants to enhance their skills and efficiency.
Foster a culture of professionalism and accountability in public service.
Performance-Based Incentives:
Implement performance-based evaluation systems for government officials.
Reward efficiency and effective service delivery, and penalize poor performance.
Citizen Engagement:
Establish mechanisms for regular feedback from citizens on government services.
Use feedback to improve service delivery and address public grievances.
B. Economic Management and Development:
Diversify the Economy:
Invest in non-oil sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, and technology to reduce dependence on oil revenues.
Promote small and medium enterprises (SMEs) through access to finance, training, and market opportunities.
Fiscal Responsibility:
Implement stringent fiscal policies to manage public debt and ensure sustainable economic growth.
Prioritize spending on critical sectors like education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
Job Creation Programs:
Develop and implement comprehensive job creation strategies targeting youth and vulnerable populations.
Support vocational training and entrepreneurship initiatives.
3. Solutions for the Populace
A. Civic Engagement and Empowerment:
Education and Awareness:
Conduct civic education campaigns to inform citizens about their rights and responsibilities.
Promote awareness about the importance of transparency, accountability, and good governance.
Active Participation:
Encourage active participation in electoral processes, including voting and running for office.
Support grassroots movements and community organizations advocating for accountability and social justice.
Demand Accountability:
Use social media and other platforms to hold government officials accountable.
Support investigative journalism and civil society organizations working on transparency and anti-corruption.
B. Economic and Social Empowerment:
Access to Quality Education:
Advocate for increased investment in education to ensure access to quality schooling for all children.
Promote vocational and technical education to equip citizens with practical skills.
Healthcare Access:
Support initiatives aimed at improving healthcare infrastructure and services.
Advocate for affordable and accessible healthcare for all citizens.
Entrepreneurship and Innovation:
Encourage and support entrepreneurial initiatives through access to finance, mentorship, and training.
Promote innovation and technology adoption to create new economic opportunities.
Conclusion
Addressing the hardships and inequality in Nigeria requires a multi-faceted approach involving political elites, government officials, and the populace.
By implementing anti-corruption reforms, promoting good governance, enhancing public service delivery, diversifying the economy, and empowering citizens, Nigeria can build a more equitable and prosperous society.
Collaborative efforts and a shared commitment to these solutions will be crucial in driving sustainable change and improving the quality of life for all Nigerians.
"This article is for anyone and you can add your own points and also ask questions to get answers from others."
Will You Become Lonely as You Age?
Research reveals how loneliness is experienced across the lifespan.
KEY POINTS-
One common denominator that impacts the experience of loneliness is age.
Loneliness is experienced differently at different stages in life.
Social support and having a social network impacts older adults differently.
Loneliness, the subjective feeling of a lack of meaningful social connections or a sense of belongingness, is a pervasive and distressing phenomenon affecting individuals across various age groups and populations. It remains a robust field of study given the number of people who experience it, either situationally or persistently. Because loneliness is a pervasive emotional experience, research has examined the way loneliness is experienced within certain populations such as older men,1 adolescents,2 and other specific groups. But one common denominator that often permeates such research is the impact of age.
Loneliness Across the Lifespan
Eileen K. Graham et al. (2024) examined whether people become lonelier as they age.3 Recognizing loneliness as a “pervasive experience” that negatively impacts both health and well-being, they sought to explore what types of factors impact the way the experience changes over the lifespan.
Analyzing data from 128,118 participants ranging in age from 13 to 103 years and from more than 20 countries, they found that the experience of loneliness follows a U-shaped curve, declining from the period of young adulthood to midlife, and then increasing during older adulthood. Although they noted that some general factors impacted levels of loneliness, such as marital status, gender, education, and physical function, few of them moderated the course of the loneliness experience. Graham et al. recognize that the dynamic nature of loneliness emphasizes the need for targeted interventions throughout adulthood.
Older Adults Are Becoming Less Lonely
Other research shows that older adults are less lonely today than their older peers. Bianca Suanet et al. (2024) studied historical changes in the loneliness trajectory of older adults.4 Using 1,068 age-matched longitudinal reports from the German city of Berlin, their results revealed that at 79 years old, subjects reported substantially lower levels of loneliness than subjects born 20 years earlier. However, they also found that age trajectories were the same when it came to differences in changes in the levels of experienced loneliness over time. They found the differences in rates of within-person changes were due to differences in education, gender, cognitive functioning, and beliefs about external control.
The Support of Social Networks
Suanet et al. note that in terms of public significance, their research fails to support the commonly cited view that there is a “loneliness epidemic” within Western societies because they found levels of loneliness are lower in older adults as compared to later-born peers. Among the explanations for the difference is the recognition that an increase in resources provides the opportunity to build a beneficial social network, which is an observation strongly relevant to all age groups today. As a practical observation, this may be true both in person and online for more recently born older adults, because social media connections have become one of the ways older adults can stay in touch, even if their mobility is restricted later in life.
Becoming aware of signs and symptoms of loneliness among family, friends, and peers of all ages can empower us to expand and strengthen networks of support to everyone within our sphere of influence, to encourage and care for each other.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
France and Armenia signed a contract for the supply of French self-propelled guns (SPG) CAESAR, which has wreaked havoc on Russian troops in the Ukraine War. The French big guns, along with the towed 155/52 Advanced Towed Artillery Guns (ATAGs) and mounted MArG 155/39, were procured from India to fortify against Azerbaijan.
French Defense Minister Sebastien Lecornu broke the news on X.
“We continue to strengthen our defense relations with Armenia. I had a warm and productive conversation with my colleague, Suren Papikyan. The signing of a contract for the purchase of CAESAR guns is a new important milestone,” he wrote.
He did not say how many systems Armenia would acquire. France has a large Armenian diaspora and is traditionally one of Yerevan’s strongest allies in Europe.
The Caesar is a self-propelled gun mounted on a Renault Sherpa 10 truck chassis with an armored cab. The Ukraine war showed the vulnerability of artillery guns to drones. The French artillery engineers devised a simple solution—they took the big gun and mounted it on a truck. The self-wheeled guns are low-cost and have high mobility, increasing their survival odds in the face of drones.
Systems like the Caesar can pull into position, fire multiple rounds, and race off in a few minutes – a tactic known in military parlance as “shoot and scoot.”
In Ukraine, the omniscience of drones requires gun operators to hide their positions well and shift positions immediately after firing to avoid retaliatory strikes. Ukraine war has seen an increased leaning of the world’s forces towards wheeled and self-propelled howitzers instead of towed ones.
The French have claimed that leaks from Russian soldiers on Telegram indicate that Caesar is well-feared. According to spokesman Guillem Monsonis, Russian military bloggers on Telegram in April 2024 described Caesar’s range, accuracy, and mobility, saying the system killed numerous Russian artillerymen with counter-battery fire.
Caesar’s USP is its agility, which doesn’t give Russian forces enough reaction time to locate and target the Ukrainian crews, an artilleryman told French broadcaster TF1 last year.
Russia joined the trend towards wheeled howitzers in 2023, citing greater maneuverability. Another advantage is the lower cost of wheels over tracks.
The French shift in strategy towards Armenia came in 2023 as Yerevan sought to diversify its arms imports after Russia failed to provide the country with ordered weapons worth around US $400 million (it has not yet returned the money). The failed arms deal was an additional trigger in the worsening Russia-Armenia relations, which made Armenia seek to diversify the sources of its arms imports, looking at the West and India.
France and Armenia have shared strong diplomatic ties, as the former is home to a large Armenian diaspora. In 2001, Paris was among the first Western capitals to recognize the Armenian genocide, two decades before the United States did. Till 2023, France had backed Armenia only politically in the conflict.
Indian Guns For Armenia
As reported by the EurAsian Times earlier, in March 2024, Armenia placed an order for the ATAGS from India. These guns are considered to be the best in their category and can be deployed at high altitudes.
This procurement report has come even as the Indian Army is yet to finalize the contract for these guns that will be deployed along its border with China, an official confirmed.
The guns have been the result of collaboration between the Defense Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), Bharat Forge Limited, and Tata Advanced Systems Limited. Armenia had ordered an MArG 155 wheeled self-propelled howitzer from Kalyani Forge India. In 2023, Armenia ordered six of these ATAGS. Now, it wants to procure 84 more ATAGS under US $155 million.
These ATAGS are designed for high mobility and rapid deployment. They have advanced communication systems and automatic command and control systems.
The ATAGS will replace the obsolete Soviet-vintage D-30 towed 122mm howitzers and 2A65 Msta-B 152 mm towed howitzers. Its high-altitude operability makes it ideal for Armenian forces. Armenia will be the first export customer of the ATAGS.
The Indian Army has already field-tested these guns in Pokhran, Balasore, and Sikkim, with temperatures ranging between -15 degrees Celsius and 50 degrees Celsius. The 155/52 mm caliber towed gun is an all-weather and terrain system.
These howitzers can strike targets up to 50 kilometers, making them the best guns in their class. They can fire a burst of 5 rounds in 60 seconds and at a sustained rate of up to 60 rounds in 60 minutes.
Armenia has almost doubled its defense investments over the last year. In 2022, the spending was around US$700 million to US$800 million; now, in 2024, it will be US $1.4 billion or US $1.5 billion. The defense contracts with India alone account for a billion dollars.
Armenia has equipped itself with Indian-made Pinaka MBRLS (considered at par with American HIMARS) and an anti-drone system. The Pinaka was delivered to Armenia via Iran in 2023.
Pinaka Mk-1 is a free-flight artillery rocket area bombardment system with a range of 38 kilometers, quick reaction time, and a high rate of fire. A single Pinaka system fires a salvo of 12 rockets from a multi-barrel launcher in 44 seconds, while a battery can fire 72 rockets.
Armenia has also purchased an Indian-built surface-to-air missile (SAM) Akash. Akash is a short-range SAM system manufactured by Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) to protect vulnerable areas and points from air attacks. The Akash Weapon System (AWS) can simultaneously engage Multiple Targets in Group Mode or Autonomous Mode.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
In a notable development on the frontlines, Ukrainian forces have successfully captured Russia’s unconventional ‘turtle tank,’ along with its crew.
The incident, which marks the first known capture of this peculiar armored vehicle, was documented in a video initially shared on Telegram on June 17. The footage quickly went viral on social media platform X (formerly Twitter).
The video reveals that the tank, characterized by a large superstructure made of sheet metal and nets, was immobilized before being seized by Ukrainian soldiers.
Ukrainian troops can be seen climbing into the superstructure, where they encountered and captured the tank’s crew.
The footage shows two Russian crew members being apprehended. Following the capture, the Ukrainian soldiers drove the tank, now adorned with the Ukrainian flag, to their positions.
Information circulating online attributed the capture to the 22nd Separate Mechanized Brigade of the Armed Forces of Ukraine. Along with the video, an image has surfaced showing Ukrainian soldiers posing in front of the captured tank.
The Russian tank’s unique metal superstructure is designed to mitigate threats from enemy drones, particularly the Ukrainian FPV (first-person-view) drones. However, this adaptation significantly compromises the tank’s ability to use its main gun effectively.
While the turtle-like shell offers some protection against lighter drone attacks and shrapnel, it remains highly vulnerable to heavier weapons and anti-tank rounds, which can easily penetrate the metal shell and inflict severe damage.
Despite its limited effectiveness, the capture of the ‘turtle tank’ has sparked widespread attention and amusement among pro-Ukrainian social media users.
One user mockingly suggested that the tank, referred to as “Russian nanotechnology,” should be sent to NATO headquarters for research purposes.
The Ministry of Defense of Ukraine shared a photo of a captured tank, captioning it, “A trophy ‘turtle’ tank now in service with the UA army.”
The capture of the ‘turtle tank’ has boosted the morale of Ukrainian forces and underscored the continuous innovations and countermeasures taking place in modern warfare.
Russia’s ‘Turtle Tank’
The introduction of Russia’s ‘turtle tanks’ follows the earlier use of increasingly elaborate cage-like anti-drone armor, known as “cope cages.”
In late 2021, in an attempt to shield its tanks from attacks, Russia began welding metal cages over the turrets of its tanks. These cages, however, showed limited effectiveness, with some Western analysts mockingly referring to them as “emotional support armor.”
These makeshift defenses have become common on armored vehicles from both sides of the conflict and have even appeared outside Ukraine, potentially on submarines.
Russia has intensified these retrofits by using metal sheeting to completely enclose some tanks, earning them the nickname “turtle tanks.”
These vehicles are also equipped with electronic warfare stations to disrupt the control signals of FPV drones, and mine trawls to clear paths. The rise of these turtle tanks on the battlefield in recent months suggests attention to certain tactical challenges.
Analyst Rob Lee from the Foreign Policy Research Institute in Philadelphia commented, “I know people are laughing at this, but I don’t think it is a crazy adaptation. The Russians are adapting to the particular conditions of the battlefield in which Ukraine has a lot of FPVs but not enough ATGMs, anti-tank mines, and artillery.”
“So, sacrificing observation and the ability to rotate the turret on one tank per platoon that can jam many FPVs frequencies at once makes sense. The priority is to get infantry assault groups across open fields to buildings or defensive positions,” he added.
Evidence indicates that these turtle tanks, with their armored shells, are being deployed to spearhead assaults on well-defended Ukrainian positions, including through minefields.
The first observed example was equipped with a mine plow. However, the additional armor does not guarantee protection, as the Ukrainian military has successfully targeted these vehicles on multiple occasions.
Despite their intended protective benefits, ‘turtle tanks’ have significant drawbacks. The vertical posts can hinder the turret from rotating, and the bulkiness can limit visibility and mobility. Also, the design seems to leave a gap at the front, which a skilled FPV drone operator can exploit.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
The timing, to put it mildly, is slightly odd.
Any of us watching the start of the Euro 2024 football tournament this weekend may well have noticed the logo of the Chinese electric vehicle manufacturer BYD plastered everywhere in its role both as one of its main sponsors and as the “mobility partner” for matches staged across German cities.
In the same week, the European Union slapped punitive tariffs on imports of Chinese EVs. On the one hand Europe is welcoming the Chinese brands, and on the other it is telling them to get lost.
These mixed messages are typical of the EU’s hopelessly mismanaged response to electric vehicles. Its war on cheap Chinese imports is going to misfire spectacularly – and all it will do is end up destroying its once-mighty auto industry.
It has certainly been a tough few days for the Chinese electric vehicle giants planning to bring their brands to Europe. On Wednesday, the EU announced that it would impose extra tariffs on imports of up to 38pc, on top of the existing 10pc levies, putting almost 50pc in taxes on any cars Chinese brands bring into the bloc.
It follows a decision by US President Joe Biden to impose tariffs of 100pc.
At a stroke, the price advantage that the likes of BYD, Geely and Nio planned to use to force the market open and to start building a presence on the Continent has been wiped out. Chinese EVs will end up being a lot more expensive and the EU will rake in huge levies on each sale.
It is not hard to understand why the decision was made. Officials in Brussels are terrified that the Chinese EV manufacturers will wipe out the European auto industry, which still employs an estimated 13.8 million people, or 6pc of the total workforce, and generates €150bn (£130bn) of annual exports.
We can argue about whether the Chinese cars are subsidised by the state or are simply manufactured more efficiently by companies that have brilliantly mastered the technology in a very short space of time (the truth is probably somewhere between the two).
And yet leaving that aside, one point is certain: it will stall their advance. It is hard to compete when you face a 50pc tax on each car you sell.
The trouble is the policy is going to backfire spectacularly on the EU and of course on the UK if we are foolish enough to impose similar levies. There are three reasons for that.
First, anyone who thinks the Chinese will simply shrug their shoulders is simply kidding themselves. It will inevitably mean retaliation. There are already reports that China will respond with tariffs on large-engine imports from the EU, specifically targeting the high-end, luxury vehicles that sell best in that country.
Given that the EU exports €18bn of vehicles to China every year, and has even more money tied up in local joint-venture operations, that is going to be very painful for European manufacturers.
Tariffs may well be targeted at other EU goods as well. It is not as if China does not have a robust trade policy or that it is ever slow to defend its industries. In the wake of the announcement, €4.5bn was wiped off the value of the major German auto manufacturers as investors braced themselves for the inevitable response.
With grim inevitability, the EU’s giants will end up paying a high price and will end up locked out of what will soon be the world’s largest market. It is hard to see that as a great victory for anyone.
Next, the European manufacturers will inevitably grow flabby behind tariff walls. We have a long history of trade wars, tariffs and protectionism to teach us that the result is always the same. The protected industry does not have to compete anymore, it doesn’t bother to innovate and it simply puts up prices to milk easy profits out of customers who no longer have the choice of going elsewhere.
EVs are still a new technology, and there need to be huge improvements in driving range, battery life, vehicle weight and most of all price if they are to become the standard way of getting around.
That is only going to happen with ferocious competition between lots of different companies. Once a cosy cartel is established, they will just stagnate. The result? Even if they are protected at home, the European manufacturers will be steadily less competitive on the global market where they can’t hide behind tariff walls.
Finally, it is a tax that will be paid by European consumers. Some of us heard a rumour that governments across Europe were encouraging us all to switch to electric vehicles to help curb carbon emissions and hit our net zero targets. Now it turns out that they are also imposing massive levies on them.
All the mandates and quotas will still be in place, but the cars will be far more expensive, draining spending power out of the economy and taxing the transition to green energies. It would be hard to think of a more comically mismanaged policy, or one that is likely to do more damage.
In reality, even by the standards of incompetent officials in Brussels, it is a mess. The EU should have made sure it was competitive in EVs before imposing quotas and targets on the industry.
It should have made sure its own industry was ahead in technology and had worked out how to scale up production to deliver the low-cost cars that could take on the world.
It is too late to fix any of that now with tariffs. All it will end up doing is making a bad situation a whole lot worse. The EU will end up destroying one of its biggest and most strategic industries – and it will only have itself to blame.
Scholz hopes to avoid EU punitive tariffs on China's electric cars.....
German Chancellor Olaf Scholz is hoping that that punitive tariffs the EU has threatened to slap on Chinese electric vehicles can still be prevented in negotiations with Beijing.
Scholz said he had been "firmly promised" that the EU's talks with Beijing would take place with this goal in mind, and that it was "the right way to go."
He said the dispute could be resolved by the end of the month if all goes well.
The European Commission, the EU's executive arm, threatened on Wednesday to impose import tariffs on Chinese electric vehicles of up to 38.1%, after an investigation found evidence of illegal support from subsidies.
The higher import duties will only be applied if the EU and China cannot find a solution to the issue, and would come into force from July 4.
According to the commission, Chinese electric cars are normally around 20% cheaper than models built in the EU.
The German automotive industry has come out against the higher tariffs. It fears that the government in China, a key market, could impose retaliatory duties on electric cars imported from Europe.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
The US has sent more than $50 billion worth of military aid to Ukraine, said the State Department.
The assistance has included advanced US weapons like HIMARS missiles and Abrams tanks.
The US has also sent weapons of Russian origin, including the T-72 tank and Mi-17 helicopter.
The US has spent $51.2 billion in military assistance for Ukraine since Russia invaded in 2022, according to a recent fact sheet published by the State Department. This total rises to $54 billion when the years since Russia's initial invasion of Ukraine in 2014 are included.
The range and quantity of weapons is far-reaching. Ukraine has received over four million shells, 400,000,000 small arms rounds, and grenades, as well as hundreds of advanced missile systems, tanks, armored vehicles, artillery pieces, river patrol boats, and electronic warfare technologies.
The US has even sent Ukraine weapons of Russian origin including 45 T-72s (versus 31 US Abrams tanks), Mi-17 helicopters and 122mm GRAD rockets.
Check out the range of military hardware the US has supplied Ukraine, according to the comprehensive list compiled by the US State Department.
Tanks
The US delivered 31 M1 Abrams tanks to Ukraine in the fall of last year.
More surprisingly, Ukraine has received 45 tanks of Russian origin from the US, 14 more than the US's own Abrams. These T-72B tanks are cheaper and less advanced than the US-made Abrams.
The Abrams were a major addition to Ukraine's arsenal of mostly aging Soviet armor and augmented previous deliveries of the German-made Leopard tanks and British Challengers.
Robert Greenway, a Hudson Institute expert who served in the Army with the Abrams, previously told Business Insider that the Abrams "can do other things, but it's built to kill tanks."
"The A1 may be old in the sense that it's been in our inventory for quite some time, but it's far superior to anything that the Russians have," he said.
Soviet-designed choppers
Ukraine has also been sent 20 Mi-17 helicopters. Like the T-72B tanks, these aircraft are Russian in origin.
Ukraine has also received many unmanned aerial systems (UAS), such as the Cyber Lux K8 and the Phoenix Ghost drones.
Artillery rounds by the million
Ukraine has received a colossal number of artillery shells from the US, including More than 3,000,000 155mm, 800,000 105mm, and 400,000 152mm artillery rounds.
It has also supplied tens of thousands of precision-guided 155mm artillery rounds.
However, these prodigious supplies didn't satisfy Ukraine's armed forces' appetite for munitions. Over the winter months, it faced a severe shortage of artillery shells, partly due to a US military aid package being stalled in Congress.
Ukraine's defense minister, Rustem Umerov, wrote in a February letter to EU counterparts that the shortages had left Ukraine unable to fire more than 2,000 artillery shells a day, roughly one-third of Russia's capacity.
In May, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy said for the first time since Russia's invasion, Ukraine's forces had reported no shortages of artillery shells.
Patriots
Since February 2022, the US has provided Ukraine with one MIM-104 Patriot air defense system and munitions for the battery. The $1-billion Patriot is a ground-based, mobile surface-to-air missile battery that can down crewed and uncrewed aircraft, cruise missiles, and short-range and tactical ballistic missiles.
According to Frederik Mertens, a Hague Center for Strategic Studies analyst, their performance in Ukraine has been "an unmitigated success."
After months of pleas from Ukrainian officials, President Joe Biden approved the transfer of a second battery from the US last week, unnamed senior military and administration officials told The New York Times.
Ukraine has received one other Patriot battery jointly provided by Germany and the Netherlands. Germany has also pledged three more Patriots and is considering pledging a fourth, per Bloomberg.
President Volodymyr Zelenskyy told NATO that Ukraine needs at least seven in April, Reuters reported.
Surface-to-air missiles
Ukraine has received 12 National Advanced Surface-to-Air Missile Systems (NASAMS).
According to one developer, Kongsberg Defence and Aerospace, NASAMS are short-to-medium-range ground-based air defense systems that target UAVs and cruise missiles, perform counter-fire operations, and provide coastal defense.
Though not on the list published by the US State Department, America has also supplied Ukraine with a mixture of shorter and, more recently, longer-range MGM-140 Army Tactical Missile Systems (or ATACMS).
The longer-range ATACMS could prove crucial for Ukraine, as they can travel about 190 miles and hit higher-value targets in places like Crimea, which has been occupied by Russia since 2014.
According to the US Department of Defense, Ukraine has also received Avenger air defense systems and the HAWK (an acronym for "Homing All the Way Killer"), a medium-range surface-to-air missile.
Ukraine has also received equipment to help integrate Western launchers, missiles, and radars with Ukrainian systems, often older Soviet models.
This suggests a link to the Pentagon's FrankenSAM project, a hybrid air defense system that combines Soviet launchers with US missiles.
Ukraine published photos of the finished products in May after months of experimenting with US engineers. Ukraine's existing inventory of Soviet-era Buk systems has been developed to fire old RIM-7 Sea Sparrow missiles supplied by Washington.
HIMARS and howitzers
Ukraine has received 12 National Advanced Surface-to-Air Missiles, more than 40 High Mobility Artillery Rocket Systems (or HIMARS), and the accompanying ammunition. The HIMARS can fire rockets up to 50 miles and be hailed as a lifeline for Ukraine in the early months of the war.
However, recent reports suggested that US-supplied HIMARS rocket launchers had been rendered "completely ineffective" as a result of Russian electronic jamming systems.
Ukraine also received 72 105mm Howitzers.
The howitzer requires five people to operate it and can launch 100-pound, 155-millimeter shells 18 miles without rocket assistance.
They are among the best big guns in the Ukrainian armory. "The reason is its precision," one Ukrainian gunner told Radio Free Europe.
Russian rockets
Ukraine has been sent thousands of rockets, including 60,000 122mm GRAD rockets for the Russian launchers still used by Ukraine's army.
The highly-rated Bradley fighting vehicle
Ukraine has received 300 Bradley infantry fighting vehicles capable of transporting troops on the battlefield, providing fire support, and conducting reconnaissance missions.
These vehicles, which are quick and highly maneuverable, are operated by a three-person crew consisting of a driver, the commander, and a gunner and can carry up to half a dozen fully equipped soldiers.
Ukraine's soldiers highly rate the Bradley.
Last week, a war video released by Ukraine appeared to show a US-supplied M2 Bradley infantry fighting vehicle in a head-on clash with a Russian armored personnel carrier.
Ukrainian troops have reported that Russian soldiers are "afraid" of facing US-supplied Bradley fighting vehicles.
Javelins missiles have helped destroy Russian armor
The US has supplied over 10,000 Javelin anti-armor systems. Ukraine has successfully used the weapons to strike Russian tanks and vehicles.
Maritime weapons
Ukraine has received two Harpoon coastal defense systems, anti-ship missiles from the US, and over 80 coastal and riverine patrol boats.
Body armor
More than 100,000 body armor and helmets have been sent to Ukraine from the US. Various Medical supplies, including first aid kits, bandages, monitors, and other equipment, as well as field equipment, cold weather gear, generators, and spare parts, have also reached the front line.
More serious protective equipment like chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear protective gear, along with bomb disposal equipment and protective gear, have been received by Ukraine.
They've also had night vision devices, surveillance and thermal imagery systems, optics, and rangefinders.
Satellites and electronic warfare equipment
Russia has a sophisticated electronic warfare program and has improved at disabling high-tech missiles provided to Ukraine by its Western allies, such as HIMARS.
Ukraine has received various types of Electronic warfare (EW) and counter-EW equipment from the US, four SATCOM antennas, SATCOM terminals and services, and secure communications systems.
The US has also sent 21 air surveillance radars to support Ukraine's existing air defense.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
The European Commission is this week expected to disclose the tariffs it plans to slap on Chinese electric vehicles (EVs) over what it says are excessive subsidies – a move likely to prompt stern words and possible retaliation from Beijing.
Less than a month after Washington quadrupled duties for Chinese EVs to 100 percent, Brussels followed suit – announcing extra tariffs of up to 38 percent.
The reason? To counter China’s official policy of boosting its EV sector. Beijing has poured the equivalent of €25 billion in subsidies into domestic firms and research and development – giving homegrown companies the edge over their rivals based in the EU and US.
The European Commission on Tuesday said in a statement that the battery electric vehicles (BEV) value chain in China had benefitted from unfair help that was causing "economic injury" to BEV producers in the EU.
It ordered a provisional hike of tariffs on Chinese manufacturers: 17.4 percent for the world's largest electric car maker, BYD, 20 percent for manufacturer Geely and 38.1 percent for SAIC Motor.
Other electric car producers in China would face an average duty of 21 percent, the commission added. Definitive measures were to be officially launched in November.
Showing 'weakness'
In China, the move was immediately criticised.
"It's projecting weakness to China," Bill Russo, the CEO of Shanghai-based consultancy Automobility, told RFI.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Ukraine claimed to have hit Russian S-400 and S-300 systems in Crimea in an overnight strike on June 10. The statement came after a series of explosions were reported in the peninsula at night.
One S-400 air-defense missile unit was reportedly hit near Dzhankoi, and two more S-300 anti-aircraft missile units were attacked near Chornomorske and Yevpatoria. Russia’s S-400 Triumf air defense system, which is globally recognized for its unmatched capability, has an estimated price tag of around $1.2 billion.
On 15 October 2016, during the BRICS Summit, India and Russia signed an Inter-governmental Agreement (IGA) for the supply of five S-400 regiments to India. The US$5.43 billion deal (₹40,000 crore) was formally signed on 5 October 2018, ignoring the threat of US sanctions.
Commencing 2020, Russia was supposed to deliver the five squadrons by early 2024, but the supplies suffered delays due to the ongoing Russia-Ukraine war and payment complexities. Three systems have been delivered and have been operationally deployed by the Indian Air Force (IAF), covering the threat from across the two borders. Russia will now deliver the remaining two S-400 air defense systems to India by August 2026.
Russia, China, Turkey, and Belarus already operate the S-400, and many more have shown interest. Even the American security establishment has acknowledged the effectiveness and lethality of this very potent air defense system. Any loss of the system in combat conditions requires a revisit to check operational effectiveness and defense capability.
Ukrainian Attack Against S-400
Four S-400 launchers were destroyed in mid-April along with other equipment in an attack on a Russian military airfield in Crimea, Ukraine’s military intelligence (HUR) reported.
Ukraine reportedly also struck and significantly damaged a ferry crossing in Kerch with U.S.-provided long-range ATACMS missiles overnight on May 30. Moscow actively uses the ferry crossing to supply Russian troops in Crimea. The peninsula and ferries are defended by Russian Pantsir, Tor, and S-400 Triumph air defense systems.
Ukrainian strikes destroyed MiG-31 and Su-57 fighter jets, forcing Russia to recalibrate its strategy. Ukrainian drone strikes have also hit targets, even in Moscow. Clearly, Russia has not been able to defend a few important operational assets.
MGM-140 ATACMS
The Lockheed Martin MGM-140 Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) is an American tactical ballistic missile that has been in service since 1991 and was recently supplied to Ukraine.
This 1,670 kg weapon, solid propellant, Mach 3 missile has a range of 300 kilometers, and a launch system costs nearly $1.4 million. It uses GPS-aided inertial navigation guidance. The precision attack missiles can be fired from the tracked M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS) and the wheeled M142 High Mobility Artillery Rocket System (HIMARS).
In October 2023, a year and eight months after the Russian invasion, the United States delivered ATACMS to Ukraine. The use of these missiles threatened the entire Russian land corridor in southern Ukraine.
It further placed within reach the vast majority of the airbases operated by Russia inside Ukraine (north of Crimea) and complicated Russia’s use of attack helicopters against Ukrainian targets. On 17 April 2024, six explosions were reported at the Dzhankoi airbase in Crimea. Some of these missiles deployed cluster munitions.
On April 20, 2024, the U.S. House of Representatives approved an additional $61 billion in foreign aid to Ukraine, which included the delivery of the longer-range version (300 km) of ATACMS. Shorter range variants have a 165 km range.
In June 2020, the US Army tested a new multi-mode seeker—an upgrade for the Precision Strike Missile. The missile will enter service in 2024. Current operators of the ATACMS variants are the USA, Bahrain, Greece, South Korea, Romania, Poland, Turkey, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, and Ukraine.
S-400 Triumf Air Defence System
The S-400 Missile System is a Russian mobile long-range surface-to-air/anti-ballistic missile system that entered service in August 2007. Its missiles and battery cost around $1.2 billion.
It has four radars and four missiles that cover a range of 40 to 400 kilometers, thus covering a huge AD bubble. The system is the successor to the S-300, and the next version is the S-500. The S-400 Triumf and Pantsir missile systems can be integrated into a two-layer defense system.
The S-400 administrative complex can coordinate eight battalions. The mobile command and control center has a panoramic radar detection system with a 340 km range and is well protected against jamming.
Eight battalions of surface-to-air missile (SAM) combat systems parked up to 40 kilometers apart are fully integrated and can track targets independently. A single system can manage 72 launchers, with a maximum of 384 missiles. The battalion’s multi-functional radar can track 20 targets. A transporter-erector-launcher on a trailer can have 12 launchers.
The kill zone for a ballistic missile target (RCS < 0.4 square meters) is 200 km. For a target with an RCS of 4 square meters, it is 340 km.
It is 400 kilometers for a strategic bomber-sized target. Due to their low-altitude flight paths, the S-400 can intercept cruise missiles at a range of about 40 km. The missiles use semi-active or active radar homing.
A full unit can engage 36 targets simultaneously, and two missiles can engage a single target. The reaction time in case of target detection on the move is 5 minutes to launch. The service life is 20 years, and the time between major overhauls is 10,000 hours.
S-400s have protected Moscow since 2007. The Baltic Fleet in Kaliningrad received S-400 SAM systems in 2012. Russia’s Northern Fleet’s Coastal Forces had deployed S-400s. Six S-400 units had been activated for the air defense of Russia’s Novosibirsk Oblast in South-East Russia. 56 battalions were operational by 2020. In November 2015, S-400s were deployed to Syria at the Khmeimim Air Base, and later, a second S-400 unit was activated near Masyaf.
In late December 2021, the Israeli Air Force flew military jets, including F-35I, over areas protected by S-400 and Pantsir SAM in Syria and bombed Iran-backed Hezbollah militia based in Latakia. But both sides chose not to attack each other due to a mutual understanding.
Ukraine has claimed targeting Russian S-400 units since mid-2023. Finally, in April-June 2024, Ukraine launched ATACMS missiles and HIMARS rockets at a Russian military airfield in Crimea and Belgorod and destroyed a few S-400 launchers, a variety of radars, and a Fundament-M air surveillance system.
Russia has 57 batteries/battalions comprising 456 Transporter erector launchers deployed with at least 25 regiments. 28 Battalions are in the Western Sector facing Ukraine and NATO.
S-400s are deployed in Belarus. Algeria has had them since 2012. China has six systems starting in 2018. As of 2020, Turkey had 4 batteries consisting of 36 fire units and 192 missiles. Turkey has tested the S-400 against drones and F-16 fighter jets at low altitudes and reportedly had some observations.
India received the first of the five units ordered in December 2021. The third squadron was formed in February 2023. Others who have shown interest include Iran, Egypt, Iraq, and Qatar. Deals have still to fructify.
S-400 Operational Engagements
The S-400 is projected to be one of the best AD systems in the world. China bought the S-400 to take on the US threat in the Indo-Pacific and to cover its intended Taiwan invasion.
They have all been closely watching the Ukraine war and the capability of the system to defend itself and other prospective targets. For a long time, even the US has been praising the S-400 system.
In fact, they decided not to sell the F-35 to Turkey because they had acquired the S-400 system, which has the means to record crucial aircraft electronic and other parameters. With a successful ATACMS attack in which it destroyed elements of the S-400 system, more analysis is required.
The S-400 was attacked in Mospyne in the Donetsk region, which lies less than 50 kilometers from the frontline. Some reports suggest that the S-400 system was deployed in the area just a day before the attack. Videos indicate that the S-400s did try to engage the attacking missiles.
The S-400’s main long-range detection radar, the 92N6 (Grave Stone) radar, was struck. Destroying Russian AD Systems is important to carry out more surface attacks and to provide greater freedom of operations for inducting F-16s and other fighter aircraft.
Ukraine has used the ATACMS with cluster warheads that can cover the area with munitions. If radar elements are hit, it can literally disable the whole system. If they hit missiles, then they can explode and cause further damage.
S-400 Operational Dynamics & Implications For India
Any air defense system, including the famous Israeli Iron Dome, has operational dynamics and limitations when it comes to defense against low RCS ballistic or cruise missiles, rockets, or drones.
While they have been designed to defend high-value targets, they themselves will be targeted first as part of the enemy’s Suppression of Enemy’s Air Defences (SEAD). Any AD system has its own vulnerabilities.
Despite being mobile, the S-400 requires around 5 minutes to launch a missile after detection when it has to stop. Modern satellite-based and airborne ISR platforms and ELINT systems can track location. S-400 is a large system, albeit well spread out, it will be difficult to hide. Also, many times the batteries are used at static locations.
The radar antennas, command post vehicles, and missiles on launchers are quite vulnerable to rocket, missile, or large drone swarm attacks. While the S-400 has redundancies, some damage will occur, and its effectiveness will be reduced. The level of degradation of the S-400 in the recent attacks is still not known.
Often, the media backing each side tries to overplay the effects. Weapon systems manufacturers also have media on their payrolls. A platform’s success in operations gives it great advertisement mileage and, in turn, sales. Even the success of AD’s response to the Houthi and Iranian attacks on Israel was overplayed a little.
When India or China bought the S-400, it was based on known technical parameters and system tests under trial conditions. Actual combat has many variables, and trials cannot create all of these, however realistic they may be. This was the best and most comprehensible system available for the price. The fact that the US had put sanctions on the purchase of the system also confirmed its capability.
Notwithstanding the above, no knee-jerk actions are required. We should not fall into the social media and information warfare trap. Some of it may be to keep Ukrainian morale up. India and China will have a close look at the system vulnerabilities and capabilities.
Russia may also offer upgrades. India would have to exploit the system’s mobility, well-spread-out layout, and redundancies. The systems would have to be camouflaged well. The full system will not be destroyed; at best, there will be some degradation.
India acquired the systems to defend against attacks from China and Pakistan. Both will certainly target it using missile and rocket attacks, as well as drones.
India would do the same to their AD systems. We must remember that the S-400 will be a great deterrent for adversaries AEW&C, FRA, and fighters to come closer. That itself will be a significant bang for the buck. Wait and watch, and get facts first is the correct approach.








