1 hr. ago
Want to create a profitable online marketplace like OLX?
Use our OLX Clone Script to build your own buy-sell marketplace. Take advantage of secure payments, simple listings, advanced search, and complete customization. It facilitates the quick and simple launch of a profitable online classifieds platform with a variety of revenue options.
Black Friday just got more profitable! Grab up to 50% OFF on our OLX clone script and start your own revenue-generating marketplace today.
Free Demo: https://www.trioangle.com/...
Contact: salestrioangle.com
#OLX Clone Script #Buy and Sell Marketplace #Classified Script #online Classifieds Marketplace Script #Buy Sell Platform Clone App Development #online Marketplace
Use our OLX Clone Script to build your own buy-sell marketplace. Take advantage of secure payments, simple listings, advanced search, and complete customization. It facilitates the quick and simple launch of a profitable online classifieds platform with a variety of revenue options.
Black Friday just got more profitable! Grab up to 50% OFF on our OLX clone script and start your own revenue-generating marketplace today.
Free Demo: https://www.trioangle.com/...
Contact: salestrioangle.com
#OLX Clone Script #Buy and Sell Marketplace #Classified Script #online Classifieds Marketplace Script #Buy Sell Platform Clone App Development #online Marketplace
2 months ago
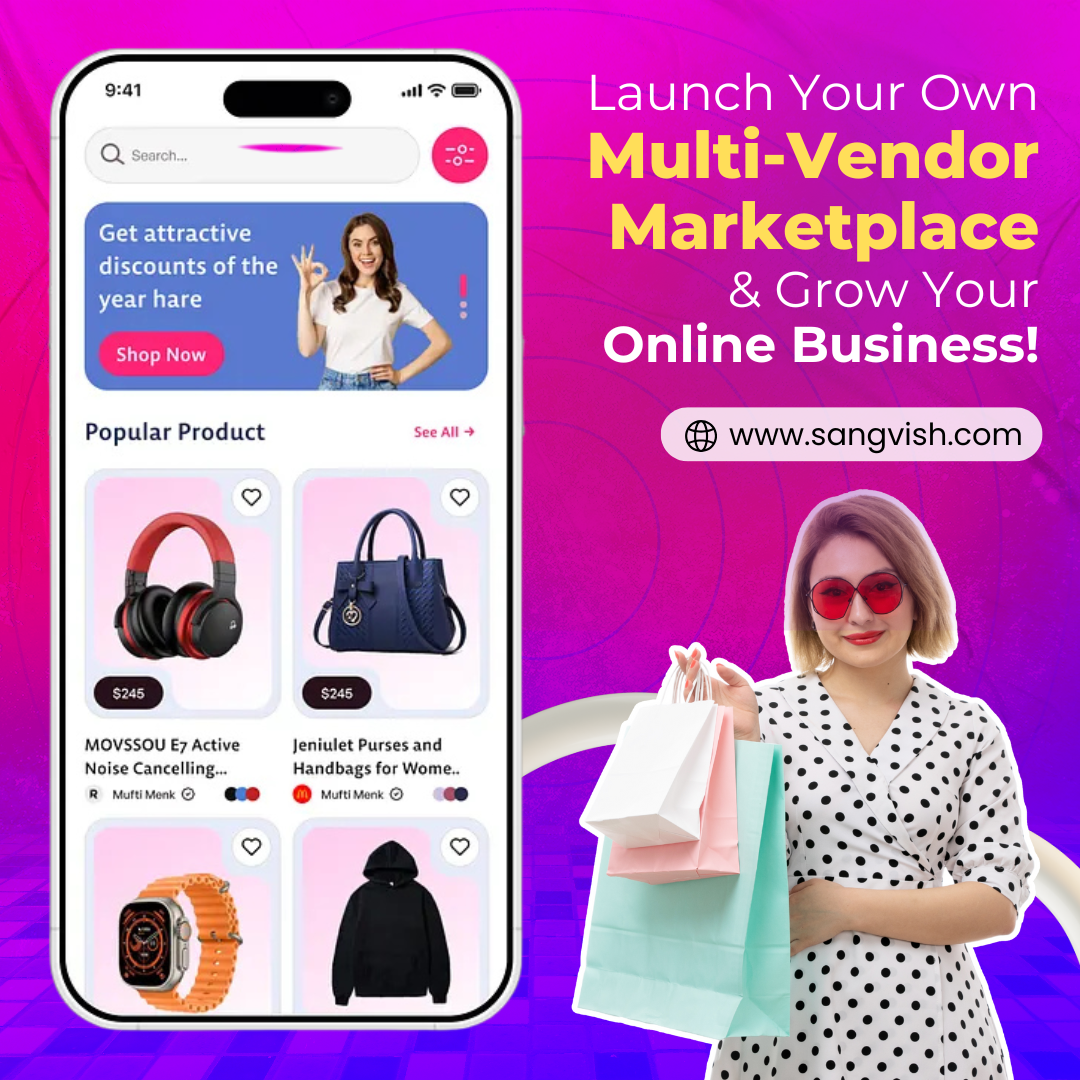
Looking to start a profitable eCommerce platform? Our ready-to-use Multi-Vendor Marketplace Script helps you:
✅ Empower multiple sellers
✅ Attract more buyers
✅ Manage your marketplace effortlessly
✅ Boost revenue & scale your business
📩 Get a Free Demo Today - https://sangvish.com/multi...
#MultiVendorMarketplace #EcommerceBusiness #OnlineMarketplace #MarketplaceScript #StartYourBusiness
✅ Empower multiple sellers
✅ Attract more buyers
✅ Manage your marketplace effortlessly
✅ Boost revenue & scale your business
📩 Get a Free Demo Today - https://sangvish.com/multi...
#MultiVendorMarketplace #EcommerceBusiness #OnlineMarketplace #MarketplaceScript #StartYourBusiness
2 months ago
Create a Unique Marketplace with Oyelabs’ Etsy Clone
Launch a curated platform for creators and artisans using the Etsy clone app from Oyelabs. Offer seller stores, custom listings, buyer-seller chat, wishlist & review systems, secure payments, and full admin control. Fully white-label with source code access.
https://oyelabs.com/etsy-c...
#EtsyClone #ArtisanMarketplace #HandmadeGoodsApp #CreativeCommerce #oyelabs #WhiteLabelMarketplace #SellerPlatform #CraftStartup
Launch a curated platform for creators and artisans using the Etsy clone app from Oyelabs. Offer seller stores, custom listings, buyer-seller chat, wishlist & review systems, secure payments, and full admin control. Fully white-label with source code access.
https://oyelabs.com/etsy-c...
#EtsyClone #ArtisanMarketplace #HandmadeGoodsApp #CreativeCommerce #oyelabs #WhiteLabelMarketplace #SellerPlatform #CraftStartup
Etsy Clone - Launch Social E-Commerce App in 7 Days
Etsy Clone, ready-to-launch 100% customizable, white label, feature-enriched multi-vendor marketplace platform comes with 2 months of free support by Oyelabs.
https://oyelabs.com/etsy-clone/
2 months ago
What is an AliExpress Clone? A Guide for Multi-Vendor Business
The eCommerce industry has witnessed immersive growth, fueled by new technology innovations and evolving user demands.
AliExpress Clone is one of the top on-demand platforms with a scalable architecture, unique layouts, and standard vendor management. It opens a new opportunity for startups to stand out in a competitive marketplace.
This blog provides a complete guide to building a multi-vendor app using an AliExpress clone script. We covered its essential features, development steps, and latest trends.
Dive in.
Aliexpress Clone: An Introduction
Don’t you know what an AliExpress clone is? Here’s a short overview of it. Let’s check in.
An AliExpress clone is a ready-made solution inspired by the original AliExpress business model, designed with its core functionalities intact. This connects every single user who wants to order products through an online medium. They can compare prices across multiple vendors and finally buy a product from a preferred store. It increases user convenience and satisfaction.
This eCommerce clone script streamlines the complete end-to-end purchasing process with advanced features, including user registration, multiple delivery addresses, shipment tracking, and secure payments.
Partner With Trioangle and Start Today!
Obviously, you are at the right place to start and implement your multi-vendor marketplace idea.
Trioangle's AliExpress Clone Script can help you turn your idea into a robust and revenue-generating eCommerce platform.
Connect with our experts to acknowledge business goals and craft solutions that meet your target audience's needs.
Subscribe now!
https://www.trioangle.com/...
#AliExpressClone #AliExpressCloneScript #AliExpressLikeApp #MultiVendorEcommerce #MarketplaceSoftware #EcommerceScript #ReadymadeEcommerce #B2BMarketplace #OnlineMarketplace
The eCommerce industry has witnessed immersive growth, fueled by new technology innovations and evolving user demands.
AliExpress Clone is one of the top on-demand platforms with a scalable architecture, unique layouts, and standard vendor management. It opens a new opportunity for startups to stand out in a competitive marketplace.
This blog provides a complete guide to building a multi-vendor app using an AliExpress clone script. We covered its essential features, development steps, and latest trends.
Dive in.
Aliexpress Clone: An Introduction
Don’t you know what an AliExpress clone is? Here’s a short overview of it. Let’s check in.
An AliExpress clone is a ready-made solution inspired by the original AliExpress business model, designed with its core functionalities intact. This connects every single user who wants to order products through an online medium. They can compare prices across multiple vendors and finally buy a product from a preferred store. It increases user convenience and satisfaction.
This eCommerce clone script streamlines the complete end-to-end purchasing process with advanced features, including user registration, multiple delivery addresses, shipment tracking, and secure payments.
Partner With Trioangle and Start Today!
Obviously, you are at the right place to start and implement your multi-vendor marketplace idea.
Trioangle's AliExpress Clone Script can help you turn your idea into a robust and revenue-generating eCommerce platform.
Connect with our experts to acknowledge business goals and craft solutions that meet your target audience's needs.
Subscribe now!
https://www.trioangle.com/...
#AliExpressClone #AliExpressCloneScript #AliExpressLikeApp #MultiVendorEcommerce #MarketplaceSoftware #EcommerceScript #ReadymadeEcommerce #B2BMarketplace #OnlineMarketplace
3 months ago
Grab the Startup Buzz: Launch Your Amazon Clone in Just 12 Days
Hello web development enthusiast,
The global e-commerce industry is growing steadily, expected to reach around $6 trillion by 2025. In particular, Amazon is a dominant platform in the marketplace, delivering a large products, excellent user interaction, and modern features that draw millions of buyers and sellers.
Jump in and learn how to properly design an Amazon clone website with a structured day-wise development plan.
Get started now.
What is the Best eCommerce Script?
An eCommerce script is a pre-built code program that allows businesses to swiftly develop and manage diverse stores. It offers basic functionality like as product listings, shopping carts, payment gateways, and order management, allowing merchants to sell products or services online more efficiently.
The key qualities that make it the best eCommerce script include customizability, mobile responsiveness, fast performance, multi-vendor support, reliable technical support, analytics, and reporting. It ensures a robust platform development experience and an engaging shopping journey.
Tying Up
Ultimately, we believe that this day-wise plan will help you successfully develop an Amazon clone website. With diverse solutions available, choose one of our best eCommerce script to build your powerful multi-vendor platform.
You're in the right place. Contact us today!
https://www.trioangle.com/...
#EcommercePlatform #TechForBusiness #AmazonCloneScript #USAeCommerce #EcommerceLondon #MiddleEastEcommerce #SAOnlineStore #OnlineMarketplace #MultiVendorMarketplace #DigitalRetailUSA #UAEStartupScene #MarketplaceTrends
Hello web development enthusiast,
The global e-commerce industry is growing steadily, expected to reach around $6 trillion by 2025. In particular, Amazon is a dominant platform in the marketplace, delivering a large products, excellent user interaction, and modern features that draw millions of buyers and sellers.
Jump in and learn how to properly design an Amazon clone website with a structured day-wise development plan.
Get started now.
What is the Best eCommerce Script?
An eCommerce script is a pre-built code program that allows businesses to swiftly develop and manage diverse stores. It offers basic functionality like as product listings, shopping carts, payment gateways, and order management, allowing merchants to sell products or services online more efficiently.
The key qualities that make it the best eCommerce script include customizability, mobile responsiveness, fast performance, multi-vendor support, reliable technical support, analytics, and reporting. It ensures a robust platform development experience and an engaging shopping journey.
Tying Up
Ultimately, we believe that this day-wise plan will help you successfully develop an Amazon clone website. With diverse solutions available, choose one of our best eCommerce script to build your powerful multi-vendor platform.
You're in the right place. Contact us today!
https://www.trioangle.com/...
#EcommercePlatform #TechForBusiness #AmazonCloneScript #USAeCommerce #EcommerceLondon #MiddleEastEcommerce #SAOnlineStore #OnlineMarketplace #MultiVendorMarketplace #DigitalRetailUSA #UAEStartupScene #MarketplaceTrends
3 months ago
Etsy Clone: Launch Your Profitable Online Selling App Today
Welcome, aspiring ecommerce entrepreneurs!.
The multi-vendor marketplace is booming vigorously, fueled by mobile penetration and innovative solutions. It provides immense opportunities for businesses to drive revenue and growth. An Etsy clone script is one of the most promising platforms for turning your vision into a thriving reality.
This blog guides you through the building steps and proven strategies for the Etsy Clone app. Get ready to discover here!.
What is the Etsy Clone Script?
An Etsy clone script is a built-in solution that duplicates the core features of the multi-vendor app Etsy. This is designed with dedicated features to help businesses create their own online selling app without starting development from scratch.
It allows buyers to search and purchase products from different sellers through effortless order placement and secure shipping. This white-label marketplace script works smoothly on both web and mobile platforms, offering a new shopping experience for buyers and sellers.
With this ready-made solution, you can deploy the app in a few days and quickly attract the modern community of users.
How the Etsy Clone Revolutionizes Your Business?
Now, let’ see the revolutionizing factors that make the Etsy Clone a game-changer of an eCommerce business. Dive in.
In a Nutshell,
We believe this blog provides you with detailed insights to build a successful Etsy clone app that delivers seamless buying experiences.
For more tips and updates, subscribe to my account and get upcoming guides on e-commerce marketplace app development.
Stay tuned!.
https://www.trioangle.com/...
#EtsyClone #EcommerceClone #MarketplaceScript #OnlineMarketplace #EcommerceBusiness #EtsyCloneUSA #EtsyCloneUK #EtsyCloneAustralia #EtsyCloneCanada
Welcome, aspiring ecommerce entrepreneurs!.
The multi-vendor marketplace is booming vigorously, fueled by mobile penetration and innovative solutions. It provides immense opportunities for businesses to drive revenue and growth. An Etsy clone script is one of the most promising platforms for turning your vision into a thriving reality.
This blog guides you through the building steps and proven strategies for the Etsy Clone app. Get ready to discover here!.
What is the Etsy Clone Script?
An Etsy clone script is a built-in solution that duplicates the core features of the multi-vendor app Etsy. This is designed with dedicated features to help businesses create their own online selling app without starting development from scratch.
It allows buyers to search and purchase products from different sellers through effortless order placement and secure shipping. This white-label marketplace script works smoothly on both web and mobile platforms, offering a new shopping experience for buyers and sellers.
With this ready-made solution, you can deploy the app in a few days and quickly attract the modern community of users.
How the Etsy Clone Revolutionizes Your Business?
Now, let’ see the revolutionizing factors that make the Etsy Clone a game-changer of an eCommerce business. Dive in.
In a Nutshell,
We believe this blog provides you with detailed insights to build a successful Etsy clone app that delivers seamless buying experiences.
For more tips and updates, subscribe to my account and get upcoming guides on e-commerce marketplace app development.
Stay tuned!.
https://www.trioangle.com/...
#EtsyClone #EcommerceClone #MarketplaceScript #OnlineMarketplace #EcommerceBusiness #EtsyCloneUSA #EtsyCloneUK #EtsyCloneAustralia #EtsyCloneCanada
4 months ago
Focus Africa-
Is cheap always better—or are we paying more in the long run for low-durability products?
No, cheap is not always better. While low-priced products offer a short-term financial gain, consumers and economies often pay a much higher price in the long run for their low durability. This is due to a cycle of frequent replacements and a host of hidden costs.
The True Cost of Cheap Goods-
The upfront price of an item is often just a small part of its total cost. The hidden costs of cheap, low-durability products include:
Frequent Replacement: Products that are not built to last break or wear out quickly. This forces consumers to repurchase the same item repeatedly. The combined cost of buying multiple cheap replacements over a few years often exceeds the initial price of a single, more durable, and higher-quality alternative. This cycle of consumption creates a financial drain on households.
Wasted Time and Effort: The time and effort spent on shopping for, purchasing, and disposing of low-durability products are significant. This includes the hassle of dealing with broken items, seeking repairs that may not be available, or waiting in queues to replace them.
Environmental Damage: The constant production and disposal of low-quality goods have a devastating environmental impact. These products are often made with cheap, non-sustainable materials and toxic chemicals, and are not designed for repair or recycling.
The resulting waste adds to landfills and pollutes local ecosystems, creating a burden on public waste management systems.
The Economic Principle of Planned Obsolescence-
This low-durability model is often driven by a concept known as planned obsolescence, where products are intentionally designed with a limited useful life.
The goal is to shorten the replacement cycle and guarantee repeat purchases, boosting sales and profits in the short term.
While this may seem to stimulate an economy, it is ultimately a flawed model that discourages innovation, creates consumer frustration, and wastes valuable resources.
This strategy works best in markets with limited competition and a large consumer base willing to accept lower quality for a lower price.
Is cheap always better—or are we paying more in the long run for low-durability products?
No, cheap is not always better. While low-priced products offer a short-term financial gain, consumers and economies often pay a much higher price in the long run for their low durability. This is due to a cycle of frequent replacements and a host of hidden costs.
The True Cost of Cheap Goods-
The upfront price of an item is often just a small part of its total cost. The hidden costs of cheap, low-durability products include:
Frequent Replacement: Products that are not built to last break or wear out quickly. This forces consumers to repurchase the same item repeatedly. The combined cost of buying multiple cheap replacements over a few years often exceeds the initial price of a single, more durable, and higher-quality alternative. This cycle of consumption creates a financial drain on households.
Wasted Time and Effort: The time and effort spent on shopping for, purchasing, and disposing of low-durability products are significant. This includes the hassle of dealing with broken items, seeking repairs that may not be available, or waiting in queues to replace them.
Environmental Damage: The constant production and disposal of low-quality goods have a devastating environmental impact. These products are often made with cheap, non-sustainable materials and toxic chemicals, and are not designed for repair or recycling.
The resulting waste adds to landfills and pollutes local ecosystems, creating a burden on public waste management systems.
The Economic Principle of Planned Obsolescence-
This low-durability model is often driven by a concept known as planned obsolescence, where products are intentionally designed with a limited useful life.
The goal is to shorten the replacement cycle and guarantee repeat purchases, boosting sales and profits in the short term.
While this may seem to stimulate an economy, it is ultimately a flawed model that discourages innovation, creates consumer frustration, and wastes valuable resources.
This strategy works best in markets with limited competition and a large consumer base willing to accept lower quality for a lower price.
4 months ago
Former Google exec says AI's going to lead to a 'short-term dystopia' because the idea it will create new jobs for the ones it's replacing is '100% crap'.
Something funny happened as I was watching Google X's former chief business officer Mo Gawdat, on the Google-owned platform YouTube, outline his exact take on the AI dystopia he thinks is coming. The host began to ask Gawdat about the idea AI will create new jobs, then the video halted while Google ads served me a 15-second clip showing someone using Microsoft CoPilot to do their job.
When Gawdat returns, he begins his answer by talking about the idea of the West transitioning into service or knowledge economies: people, as he puts it, who "type on a keyboard and use a mouse." Oh dear. Gawdat's economics lesson concludes that "all we produce in the West is words [...] and designs. All of these things can be produced by AI."
One thing is impossible to deny: the business world is very interested in the idea of replacing humans with AI and, where it can be done, will not hesitate to do so. There's also the fact that every big tech company is pushing AI into their products and our lives.
The AI industry has something of a stock line about its technology replacing existing careers: AI will simultaneously create new jobs we can't even imagine, and people will start working in those fields. But Gawdat doesn't buy that line, and in straightforward language calls the whole idea "100% crap" (thanks, Windows Central).
Gawdat left Google to form an AI startup, Emma.love, and cites this company as an example of what he's talking about: the app was apparently built with only two other developers, a job that Gawdat reckons would have taken "over 350 developers" without AI assistance.
"Artificial general intelligence is going to be better than humans at everything, including being a CEO," says Gawdat, referring to the idea that the industry will eventually produce an AI model capable of reasoning and more intelligent than humans. "There will be a time where most incompetent CEOs will be replaced.”
https://youtu.be/S9a1nLw70...
Gawdat's spin on this, however, is that society has to undergo a paradigm shift in how we think about our lives: "We were never made to wake up every morning and just occupy 20 hours of our day with work. We’re not made for that. We defined our purpose as work. That’s a capitalist lie."
Tell me more, comrade! Gawdat generally seems to hold a rather low view of executives and their priorities, pointing out that the AI future is subject to human "hunger for power, greed, and ego” because the tools themselves will be controlled by "stupid leaders." I'm not sure I'd characterise Elon Musk as stupid, but I doubt I'm alone in thinking I'd rather not have him in charge of re-arranging society.
"There is no doubt that lots of jobs will be lost," says Gawdat. "Are we prepared to tell our governments, this is an ideological shift similar to socialism, similar to Communism, and are we ready from a budget point of view? Instead of spending a trillion dollars a year on arms and explosives and autonomous weapons to suppress people because we can't feed them."
Gawdat runs through some beermat maths, offering an estimate that $2.4-2.7 dollars is spent on military hardware every year, a fraction of which could solve a problem like world hunger, or lift the global population out of extreme poverty. Then we get into the truly starry-eyed stuff like universal healthcare worldwide and the end of war, with Gawdat saying for AI these things would be "simple decisions."
Hmm. I'll have some of what he's smoking.
Gawdat's take on AI starts out more persuasive than many others I've seen, but when it gets onto the more fantastical ramifications the caveat is simply enormous. If the singularity happens and AI just takes over running the planet then, sure, all bets are off: who knows whether we'll end up with dystopia or utopia. But that day may never come and, until then, there will still be human beings somewhere pulling all the levers. And as history shows, time and again, humans can be horrendous at making simple decisions: and that's rarely good for the rest of us.
Something funny happened as I was watching Google X's former chief business officer Mo Gawdat, on the Google-owned platform YouTube, outline his exact take on the AI dystopia he thinks is coming. The host began to ask Gawdat about the idea AI will create new jobs, then the video halted while Google ads served me a 15-second clip showing someone using Microsoft CoPilot to do their job.
When Gawdat returns, he begins his answer by talking about the idea of the West transitioning into service or knowledge economies: people, as he puts it, who "type on a keyboard and use a mouse." Oh dear. Gawdat's economics lesson concludes that "all we produce in the West is words [...] and designs. All of these things can be produced by AI."
One thing is impossible to deny: the business world is very interested in the idea of replacing humans with AI and, where it can be done, will not hesitate to do so. There's also the fact that every big tech company is pushing AI into their products and our lives.
The AI industry has something of a stock line about its technology replacing existing careers: AI will simultaneously create new jobs we can't even imagine, and people will start working in those fields. But Gawdat doesn't buy that line, and in straightforward language calls the whole idea "100% crap" (thanks, Windows Central).
Gawdat left Google to form an AI startup, Emma.love, and cites this company as an example of what he's talking about: the app was apparently built with only two other developers, a job that Gawdat reckons would have taken "over 350 developers" without AI assistance.
"Artificial general intelligence is going to be better than humans at everything, including being a CEO," says Gawdat, referring to the idea that the industry will eventually produce an AI model capable of reasoning and more intelligent than humans. "There will be a time where most incompetent CEOs will be replaced.”
https://youtu.be/S9a1nLw70...
Gawdat's spin on this, however, is that society has to undergo a paradigm shift in how we think about our lives: "We were never made to wake up every morning and just occupy 20 hours of our day with work. We’re not made for that. We defined our purpose as work. That’s a capitalist lie."
Tell me more, comrade! Gawdat generally seems to hold a rather low view of executives and their priorities, pointing out that the AI future is subject to human "hunger for power, greed, and ego” because the tools themselves will be controlled by "stupid leaders." I'm not sure I'd characterise Elon Musk as stupid, but I doubt I'm alone in thinking I'd rather not have him in charge of re-arranging society.
"There is no doubt that lots of jobs will be lost," says Gawdat. "Are we prepared to tell our governments, this is an ideological shift similar to socialism, similar to Communism, and are we ready from a budget point of view? Instead of spending a trillion dollars a year on arms and explosives and autonomous weapons to suppress people because we can't feed them."
Gawdat runs through some beermat maths, offering an estimate that $2.4-2.7 dollars is spent on military hardware every year, a fraction of which could solve a problem like world hunger, or lift the global population out of extreme poverty. Then we get into the truly starry-eyed stuff like universal healthcare worldwide and the end of war, with Gawdat saying for AI these things would be "simple decisions."
Hmm. I'll have some of what he's smoking.
Gawdat's take on AI starts out more persuasive than many others I've seen, but when it gets onto the more fantastical ramifications the caveat is simply enormous. If the singularity happens and AI just takes over running the planet then, sure, all bets are off: who knows whether we'll end up with dystopia or utopia. But that day may never come and, until then, there will still be human beings somewhere pulling all the levers. And as history shows, time and again, humans can be horrendous at making simple decisions: and that's rarely good for the rest of us.
4 months ago
Focus Nigeria-
How can Nigeria stop the “brain drain” of doctors and nurses?
Stopping the "brain drain" of doctors and nurses from Nigeria requires a comprehensive, sustained, and multi-faceted approach that addresses the root causes of their migration.
It's not just about offering more money, but creating an enabling environment where healthcare professionals can thrive, feel valued, and provide quality care.
Here's a detailed strategy to combat the brain drain:
I. Improve Working Conditions and Environment:
Modernize Infrastructure and Equipment:
Adequate Funding: Significantly increase the healthcare budget allocation (currently far below the Abuja Declaration's 15% target) and ensure transparent and efficient utilization of funds.
Investment in Facilities: Renovate existing hospitals and clinics, and build new, well-equipped facilities, especially in underserved areas.
Modern Technology: Equip hospitals with up-to-date diagnostic tools, surgical equipment, and specialized machinery (e.g., MRI, CT scanners, radiotherapy machines). Ensure regular maintenance and availability of spare parts.
Reliable Utilities: Provide stable electricity (e.g., through solar power solutions and reliable backup generators) and clean water supply in all healthcare facilities.
Ensure Safety and Security:
Protection for Staff: Implement robust security measures within hospitals and clinics to protect healthcare workers from violence, harassment, and kidnapping, especially in high-risk areas.
Occupational Health & Safety: Establish and enforce comprehensive occupational health and safety policies that prioritize the physical and mental well-being of nurses and doctors.
Manage Workload and Staffing:
Adequate Staffing: Recruit more healthcare professionals to reduce the excessive workload on existing staff. This might require increasing training capacity within Nigeria.
Fair Scheduling: Implement equitable work schedules and shifts to prevent burnout and ensure a healthy work-life balance.
II. Enhance Remuneration and Welfare:
Competitive Salaries and Allowances:
Offer competitive salaries and allowances that are comparable to what healthcare professionals could earn in other sectors within Nigeria or in regional countries. While matching Western salaries might be challenging, making local pay significantly better than the current reality is crucial.
Timely Payments: Ensure prompt and consistent payment of salaries and benefits to avoid the frustration caused by arrears.
Attractive Benefits Package:
Health Insurance: Provide comprehensive health insurance for healthcare workers and their families.
Housing and Transportation: Offer subsidized housing, housing allowances, or transportation support, especially for those in rural or high-cost urban areas.
Retirement Benefits: Ensure robust and reliable pension and retirement benefit schemes.
Non-Financial Incentives:
Recognition and Appreciation: Create a culture of recognition and appreciation for healthcare workers' dedication and hard work.
Professional Support: Provide a supportive work environment that values their contributions and addresses their concerns.
III. Professional Development and Career Advancement:
Continuous Professional Development (CPD):
Fund and facilitate regular training programs, workshops, and seminars to keep doctors and nurses updated on the latest medical practices, technologies, and research.
Encourage and sponsor participation in international conferences and training programs where relevant.
Career Progression Opportunities:
Establish clear and transparent career progression pathways based on merit, performance, and further specialization.
Provide opportunities for specialization, postgraduate studies, and leadership roles within the Nigerian healthcare system.
Research Funding:
Allocate dedicated funds for medical research within Nigeria to encourage innovation and give professionals reasons to stay and contribute locally.
Mentorship Programs:
Establish mentorship programs where experienced doctors and nurses guide and support younger professionals.
IV. Strengthening Education and Training within Nigeria:
Increase Training Capacity:
Expand the capacity of medical and nursing schools to train more healthcare professionals, ensuring that the increase in quantity does not compromise quality.
Curriculum Review: Regularly review and update medical and nursing curricula to meet international standards and address Nigeria's specific health challenges.
"Train to Retain" Programs:
Consider policies that incentivize graduates (e.g., scholarships tied to service in Nigeria for a specific period, especially in underserved areas). This must be coupled with improved conditions to avoid simply delaying their eventual departure.
Rural-Focused Training: Develop programs that train healthcare professionals with a specific focus on rural health challenges and encourage them to serve in those areas.
V. Governance, Accountability, and Policy Coherence:
Effective Leadership and Management:
Appoint competent, ethical, and visionary leaders in healthcare institutions who prioritize staff welfare and quality of care.
Ensure efficient administrative management across all levels of the health system.
Robust Accountability:
Establish transparent mechanisms for addressing grievances, investigating misconduct, and ensuring accountability for poor management or corruption within the health sector.
Long-Term National Health Policy:
Develop and consistently implement a stable, long-term national health policy that is insulated from political fluctuations and prioritizes human resources for health. President Tinubu's new health policy is a step in this direction, but consistent implementation is key.
Engage Professional Bodies:
Foster better dialogue and collaboration with professional associations like the Nigerian Medical Association (NMA) and the National Association of Nigerian Nurses and Midwives (NANNM) to address their concerns and gain their buy-in for reforms.
Leverage Diaspora Engagement:
Create structured programs to engage Nigerian healthcare professionals in the diaspora (e.g., for short-term missions, training, mentorship, or tele-medicine consultations). This can help transfer knowledge and build connections without demanding permanent return initially.
Combating the brain drain is a marathon, not a sprint. It requires substantial financial investment, political will, a commitment to systemic change, and a fundamental shift in how healthcare professionals are valued and treated in Nigeria.
How can Nigeria stop the “brain drain” of doctors and nurses?
Stopping the "brain drain" of doctors and nurses from Nigeria requires a comprehensive, sustained, and multi-faceted approach that addresses the root causes of their migration.
It's not just about offering more money, but creating an enabling environment where healthcare professionals can thrive, feel valued, and provide quality care.
Here's a detailed strategy to combat the brain drain:
I. Improve Working Conditions and Environment:
Modernize Infrastructure and Equipment:
Adequate Funding: Significantly increase the healthcare budget allocation (currently far below the Abuja Declaration's 15% target) and ensure transparent and efficient utilization of funds.
Investment in Facilities: Renovate existing hospitals and clinics, and build new, well-equipped facilities, especially in underserved areas.
Modern Technology: Equip hospitals with up-to-date diagnostic tools, surgical equipment, and specialized machinery (e.g., MRI, CT scanners, radiotherapy machines). Ensure regular maintenance and availability of spare parts.
Reliable Utilities: Provide stable electricity (e.g., through solar power solutions and reliable backup generators) and clean water supply in all healthcare facilities.
Ensure Safety and Security:
Protection for Staff: Implement robust security measures within hospitals and clinics to protect healthcare workers from violence, harassment, and kidnapping, especially in high-risk areas.
Occupational Health & Safety: Establish and enforce comprehensive occupational health and safety policies that prioritize the physical and mental well-being of nurses and doctors.
Manage Workload and Staffing:
Adequate Staffing: Recruit more healthcare professionals to reduce the excessive workload on existing staff. This might require increasing training capacity within Nigeria.
Fair Scheduling: Implement equitable work schedules and shifts to prevent burnout and ensure a healthy work-life balance.
II. Enhance Remuneration and Welfare:
Competitive Salaries and Allowances:
Offer competitive salaries and allowances that are comparable to what healthcare professionals could earn in other sectors within Nigeria or in regional countries. While matching Western salaries might be challenging, making local pay significantly better than the current reality is crucial.
Timely Payments: Ensure prompt and consistent payment of salaries and benefits to avoid the frustration caused by arrears.
Attractive Benefits Package:
Health Insurance: Provide comprehensive health insurance for healthcare workers and their families.
Housing and Transportation: Offer subsidized housing, housing allowances, or transportation support, especially for those in rural or high-cost urban areas.
Retirement Benefits: Ensure robust and reliable pension and retirement benefit schemes.
Non-Financial Incentives:
Recognition and Appreciation: Create a culture of recognition and appreciation for healthcare workers' dedication and hard work.
Professional Support: Provide a supportive work environment that values their contributions and addresses their concerns.
III. Professional Development and Career Advancement:
Continuous Professional Development (CPD):
Fund and facilitate regular training programs, workshops, and seminars to keep doctors and nurses updated on the latest medical practices, technologies, and research.
Encourage and sponsor participation in international conferences and training programs where relevant.
Career Progression Opportunities:
Establish clear and transparent career progression pathways based on merit, performance, and further specialization.
Provide opportunities for specialization, postgraduate studies, and leadership roles within the Nigerian healthcare system.
Research Funding:
Allocate dedicated funds for medical research within Nigeria to encourage innovation and give professionals reasons to stay and contribute locally.
Mentorship Programs:
Establish mentorship programs where experienced doctors and nurses guide and support younger professionals.
IV. Strengthening Education and Training within Nigeria:
Increase Training Capacity:
Expand the capacity of medical and nursing schools to train more healthcare professionals, ensuring that the increase in quantity does not compromise quality.
Curriculum Review: Regularly review and update medical and nursing curricula to meet international standards and address Nigeria's specific health challenges.
"Train to Retain" Programs:
Consider policies that incentivize graduates (e.g., scholarships tied to service in Nigeria for a specific period, especially in underserved areas). This must be coupled with improved conditions to avoid simply delaying their eventual departure.
Rural-Focused Training: Develop programs that train healthcare professionals with a specific focus on rural health challenges and encourage them to serve in those areas.
V. Governance, Accountability, and Policy Coherence:
Effective Leadership and Management:
Appoint competent, ethical, and visionary leaders in healthcare institutions who prioritize staff welfare and quality of care.
Ensure efficient administrative management across all levels of the health system.
Robust Accountability:
Establish transparent mechanisms for addressing grievances, investigating misconduct, and ensuring accountability for poor management or corruption within the health sector.
Long-Term National Health Policy:
Develop and consistently implement a stable, long-term national health policy that is insulated from political fluctuations and prioritizes human resources for health. President Tinubu's new health policy is a step in this direction, but consistent implementation is key.
Engage Professional Bodies:
Foster better dialogue and collaboration with professional associations like the Nigerian Medical Association (NMA) and the National Association of Nigerian Nurses and Midwives (NANNM) to address their concerns and gain their buy-in for reforms.
Leverage Diaspora Engagement:
Create structured programs to engage Nigerian healthcare professionals in the diaspora (e.g., for short-term missions, training, mentorship, or tele-medicine consultations). This can help transfer knowledge and build connections without demanding permanent return initially.
Combating the brain drain is a marathon, not a sprint. It requires substantial financial investment, political will, a commitment to systemic change, and a fundamental shift in how healthcare professionals are valued and treated in Nigeria.
4 months ago
What percentage of our national budget or consumer goods is spent on imports, and what’s the hidden cost?
There isn't a single, universally applicable percentage for the amount of a national budget or consumer spending dedicated to imports, as this varies drastically by country and is influenced by a nation's size, economic structure, and trade policies. For example, some data from the U.S. suggests that around 10-11% of personal consumer spending can be traced to imported goods, but this figure includes a complex mix of finished products and imported components used in domestic manufacturing.
The hidden costs of this over-reliance on imports are substantial and go far beyond the price tag of a single product.
The Hidden Costs of Over-Importation
The true cost of a reliance on imports isn't just the money spent, but the long-term damage to a country's economic and strategic health.
Decline of Local Industries: The most significant hidden cost is the erosion of domestic manufacturing. Cheap imports often make it impossible for local producers to compete on price, leading to factory closures, job losses, and the loss of critical skills and expertise. This stunts a nation's ability to innovate and diversify its economy, trapping it in a cycle of dependency.
Increased Economic Vulnerability: An over-reliance on imports makes a country's supply chains fragile and susceptible to external shocks. A global pandemic, geopolitical conflict, or trade dispute could disrupt the flow of essential goods, such as food, medical supplies, or technology components, with severe consequences for the economy and national security.
Currency Depreciation and Inflation: A trade deficit, where a country imports more than it exports, puts downward pressure on its currency. To pay for more imports, the country needs to sell more of its own currency to buy foreign currency. This increases the supply of the local currency and drives down its value. A weaker currency then makes all imports, including raw materials for local producers, more expensive, leading to imported inflation that hurts consumers' purchasing power.
Reduced National Sovereignty: Long-term economic dependence on a few key trading partners can be used as a form of leverage. A dependent nation may be pressured to align its foreign policy with its suppliers' interests to avoid trade sanctions or embargos. This compromises a country's ability to act independently on the global stage.
There isn't a single, universally applicable percentage for the amount of a national budget or consumer spending dedicated to imports, as this varies drastically by country and is influenced by a nation's size, economic structure, and trade policies. For example, some data from the U.S. suggests that around 10-11% of personal consumer spending can be traced to imported goods, but this figure includes a complex mix of finished products and imported components used in domestic manufacturing.
The hidden costs of this over-reliance on imports are substantial and go far beyond the price tag of a single product.
The Hidden Costs of Over-Importation
The true cost of a reliance on imports isn't just the money spent, but the long-term damage to a country's economic and strategic health.
Decline of Local Industries: The most significant hidden cost is the erosion of domestic manufacturing. Cheap imports often make it impossible for local producers to compete on price, leading to factory closures, job losses, and the loss of critical skills and expertise. This stunts a nation's ability to innovate and diversify its economy, trapping it in a cycle of dependency.
Increased Economic Vulnerability: An over-reliance on imports makes a country's supply chains fragile and susceptible to external shocks. A global pandemic, geopolitical conflict, or trade dispute could disrupt the flow of essential goods, such as food, medical supplies, or technology components, with severe consequences for the economy and national security.
Currency Depreciation and Inflation: A trade deficit, where a country imports more than it exports, puts downward pressure on its currency. To pay for more imports, the country needs to sell more of its own currency to buy foreign currency. This increases the supply of the local currency and drives down its value. A weaker currency then makes all imports, including raw materials for local producers, more expensive, leading to imported inflation that hurts consumers' purchasing power.
Reduced National Sovereignty: Long-term economic dependence on a few key trading partners can be used as a form of leverage. A dependent nation may be pressured to align its foreign policy with its suppliers' interests to avoid trade sanctions or embargos. This compromises a country's ability to act independently on the global stage.
4 months ago
How to Implement AI‑Powered Product Recommendations in an Amazon clone app
What if your app could predict what users want, before they even type in a search? That’s the power of AI recommendations. Do you want to know how to implement AI-powered product recommendations in your Amazon clone? Here are some steps. Let's dive in.
What is AI-Powered Recommendation?
An artificially intelligent system that makes real-time product recommendations to consumers based on their interests, behaviour, and previous purchases is known as an AI-powered recommendation system in e-commerce. AI customises the shopping experience to boost sales, engagement, and customer satisfaction rather than displaying the same product list to every user.
Types of recommendation strategies:
1. Collaborative Filtering
Collaborative Filtering is a recommendation strategy that recommends products based on user activity and preferences rather than product information in an Amazon-like app.
User-based collaborative filtering detects folks who share similar interests. If a user likes a product, it will be recommended to another person who shares their interests.
Item-based collaborative filtering: This type of filtering shows recommendations based on similarities. For example, it recommends a phone case to the people who purchased New phones.
2. Content-based Filtering:
Content-based filtering recommends products based on the traits or features that the customer has previously purchased. For example, if you frequently buy or see bags, the algorithm would suggest alternatives or products with comparable characteristics such as brand, style, price range, or material.
3. Hybrid Filtering:
Hybrid filtering blends collaborative filtering, which proposes products based on the preferences of other users, with content-based filtering, which recommends items similar to those a user has previously liked. This strategy takes advantage of both methods' strengths while correcting their faults, yielding more accurate and personalised recommendations.
4. Trending and popular items:
In an Amazon clone website, Trending or Popular Items recommendations highlight things that are currently best-sellers, most viewed, or highly rated throughout the platform or within a category. Helping consumers find popular, in-demand items while increasing interaction and revenue.
5. Personalized rankings:
Personalized rankings reorder the search results or other lists of items based on users' preferences and behaviour. Instead of showing the same products to every user, it improves the user experience and increases the platform engagement.
Implementing AI-powered recommendations in an Amazon clone app:
Implement AI-powered suggestions in your Amazon clone. You should concentrate on collecting data, selecting the best AI solution, and optimising recommendations.
1. Data Collection and analysis:
Collect vast data: Gather the users' purchase history, product preferences, browsing habits, and product interactions such as clicks, add to cart, and reviews. Collecting these diverse data points provides a detailed picture of each customer's interests and habits.
2. Choosing the Right AI Solution:
Utilise data points: Analyse individual consumer preferences, detect bigger trends across users, and create dynamic customer profiles that evolve as new data is received.
Ensure data privacy: When developing AI-powered product suggestions, you must protect the privacy and security of user data. Encryption, secure servers, and access controls can all help to protect user data from unauthorised access. This is especially important when dealing with sensitive information such as purchasing history, behaviour, or personal details.
Consider Your Needs: Before deciding on an AI recommendation, you should first understand your business goals, budget, and technical resources.
Investigate diverse AI models: There are several recommendation models, each with a unique function. There are three types of filtering: collaborative, content-based, and hybrid.
Look for user-friendly options: If you're not ready to start from scratch with an Amazon clone website, look for choices that are easy to use. Many e-commerce platforms have built-in AI recommendation algorithms or third-party applications.
3. Implementing and optimizing recommendations:
Integrate cross-platform: Ensure that your recommendations are consistent and personalised across all platforms, including the website, email marketing, mobile app, and even customer support chat. This will improve the user experience and maintain personalisation seamlessly.
Use various formats: Use several recommendation styles, such as pop-ups and inline sections, to keep shoppers' attention at different phases of their purchasing journey.
A/B testing and optimisation: Continuously monitor the performance of the recommendations and make improvements depending on data and user input.
Focus on user experience: Make sure that recommendations are not only appropriate but also easy to navigate, quick to load, and visually integrated on mobile sites.
Prioritise Explainability: Be open about how recommendations are made, and give users control over their preferences.
Begin small, then scale: Start with a pilot or test group to validate performance and get feedback. Use this feedback to develop and expand your recommendation system throughout the platform.
Benefits of AI-powered recommendations:
1. Improved conversion performance:
The AI algorithm examines clients' browsing histories and purchasing habits to help them get what they want without using their hands. This will boost your Amazon clone conversion rate.
2. Enhanced user experience:
This AI-powered customised suggestion saves users time and effort by guiding them to the proper products. The end outcome is customer satisfaction and a good purchasing experience.
3. Increased average order value:
AI-powered suggestions in your Amazon clone app encourage customers to buy complementary, upsell, and cross-sell items, which raises the overall order value.
4. Insights based on data:
Artificial intelligence (AI) recommendation systems gather and analyse consumer data to learn about preferences and purchasing habits. Businesses can use this to enhance their marketing, select better products to sell, and more effectively manage their inventory.
5. Improved customer retention:
When users consistently receive relevant product recommendations, they are more likely to return to the platform. This strengthens brand presence and generates recurring sales.
6. Enhanced marketing strategies:
AI-powered recommendations customize marketing strategies based on each customer’s individual preferences and behaviors. This personalized approach results in more relevant and engaging marketing campaigns that resonate better with customers, ultimately increasing their interest and likelihood to respond positively.
7. Reduced cart abandonment:
AI-powered recommendations lower cart abandonment by using personalized recommendations, timely reminders, and providing discounts or free shipping. These strategies help users complete their purchases and increase the overall sales rates in your Amazon clone website.
8. Real-time discovery:
This enables AI to make real-time product recommendations to users based on their interests, assisting consumers in finding things they may not have previously found. It is most helpful in vast product catalogues where customers may find manual searching daunting. AI speeds up, simplifies, and enhances the pleasure of shopping by providing timely and pertinent recommendations.
Summing up:
I hope this blog helps you understand the importance of Artificial Intelligence in product recommendations for your Amazon clone app.
It covers the implementation of AI-powered recommendation systems, different types of recommendation strategies, and their benefits.
Now is the perfect time to launch AI-powered recommendations in your Amazon clone app.
https://www.trioangle.com/...
#EcommercePlatform #TechForBusiness #AmazonCloneScript #USAeCommerce #EcommerceLondon #MiddleEastEcommerce #SAOnlineStore # OnlineMarketplace
#MultiVendorMarketplace #DigitalRetailUSA #UAEStartupScene #MarketplaceTrends
What if your app could predict what users want, before they even type in a search? That’s the power of AI recommendations. Do you want to know how to implement AI-powered product recommendations in your Amazon clone? Here are some steps. Let's dive in.
What is AI-Powered Recommendation?
An artificially intelligent system that makes real-time product recommendations to consumers based on their interests, behaviour, and previous purchases is known as an AI-powered recommendation system in e-commerce. AI customises the shopping experience to boost sales, engagement, and customer satisfaction rather than displaying the same product list to every user.
Types of recommendation strategies:
1. Collaborative Filtering
Collaborative Filtering is a recommendation strategy that recommends products based on user activity and preferences rather than product information in an Amazon-like app.
User-based collaborative filtering detects folks who share similar interests. If a user likes a product, it will be recommended to another person who shares their interests.
Item-based collaborative filtering: This type of filtering shows recommendations based on similarities. For example, it recommends a phone case to the people who purchased New phones.
2. Content-based Filtering:
Content-based filtering recommends products based on the traits or features that the customer has previously purchased. For example, if you frequently buy or see bags, the algorithm would suggest alternatives or products with comparable characteristics such as brand, style, price range, or material.
3. Hybrid Filtering:
Hybrid filtering blends collaborative filtering, which proposes products based on the preferences of other users, with content-based filtering, which recommends items similar to those a user has previously liked. This strategy takes advantage of both methods' strengths while correcting their faults, yielding more accurate and personalised recommendations.
4. Trending and popular items:
In an Amazon clone website, Trending or Popular Items recommendations highlight things that are currently best-sellers, most viewed, or highly rated throughout the platform or within a category. Helping consumers find popular, in-demand items while increasing interaction and revenue.
5. Personalized rankings:
Personalized rankings reorder the search results or other lists of items based on users' preferences and behaviour. Instead of showing the same products to every user, it improves the user experience and increases the platform engagement.
Implementing AI-powered recommendations in an Amazon clone app:
Implement AI-powered suggestions in your Amazon clone. You should concentrate on collecting data, selecting the best AI solution, and optimising recommendations.
1. Data Collection and analysis:
Collect vast data: Gather the users' purchase history, product preferences, browsing habits, and product interactions such as clicks, add to cart, and reviews. Collecting these diverse data points provides a detailed picture of each customer's interests and habits.
2. Choosing the Right AI Solution:
Utilise data points: Analyse individual consumer preferences, detect bigger trends across users, and create dynamic customer profiles that evolve as new data is received.
Ensure data privacy: When developing AI-powered product suggestions, you must protect the privacy and security of user data. Encryption, secure servers, and access controls can all help to protect user data from unauthorised access. This is especially important when dealing with sensitive information such as purchasing history, behaviour, or personal details.
Consider Your Needs: Before deciding on an AI recommendation, you should first understand your business goals, budget, and technical resources.
Investigate diverse AI models: There are several recommendation models, each with a unique function. There are three types of filtering: collaborative, content-based, and hybrid.
Look for user-friendly options: If you're not ready to start from scratch with an Amazon clone website, look for choices that are easy to use. Many e-commerce platforms have built-in AI recommendation algorithms or third-party applications.
3. Implementing and optimizing recommendations:
Integrate cross-platform: Ensure that your recommendations are consistent and personalised across all platforms, including the website, email marketing, mobile app, and even customer support chat. This will improve the user experience and maintain personalisation seamlessly.
Use various formats: Use several recommendation styles, such as pop-ups and inline sections, to keep shoppers' attention at different phases of their purchasing journey.
A/B testing and optimisation: Continuously monitor the performance of the recommendations and make improvements depending on data and user input.
Focus on user experience: Make sure that recommendations are not only appropriate but also easy to navigate, quick to load, and visually integrated on mobile sites.
Prioritise Explainability: Be open about how recommendations are made, and give users control over their preferences.
Begin small, then scale: Start with a pilot or test group to validate performance and get feedback. Use this feedback to develop and expand your recommendation system throughout the platform.
Benefits of AI-powered recommendations:
1. Improved conversion performance:
The AI algorithm examines clients' browsing histories and purchasing habits to help them get what they want without using their hands. This will boost your Amazon clone conversion rate.
2. Enhanced user experience:
This AI-powered customised suggestion saves users time and effort by guiding them to the proper products. The end outcome is customer satisfaction and a good purchasing experience.
3. Increased average order value:
AI-powered suggestions in your Amazon clone app encourage customers to buy complementary, upsell, and cross-sell items, which raises the overall order value.
4. Insights based on data:
Artificial intelligence (AI) recommendation systems gather and analyse consumer data to learn about preferences and purchasing habits. Businesses can use this to enhance their marketing, select better products to sell, and more effectively manage their inventory.
5. Improved customer retention:
When users consistently receive relevant product recommendations, they are more likely to return to the platform. This strengthens brand presence and generates recurring sales.
6. Enhanced marketing strategies:
AI-powered recommendations customize marketing strategies based on each customer’s individual preferences and behaviors. This personalized approach results in more relevant and engaging marketing campaigns that resonate better with customers, ultimately increasing their interest and likelihood to respond positively.
7. Reduced cart abandonment:
AI-powered recommendations lower cart abandonment by using personalized recommendations, timely reminders, and providing discounts or free shipping. These strategies help users complete their purchases and increase the overall sales rates in your Amazon clone website.
8. Real-time discovery:
This enables AI to make real-time product recommendations to users based on their interests, assisting consumers in finding things they may not have previously found. It is most helpful in vast product catalogues where customers may find manual searching daunting. AI speeds up, simplifies, and enhances the pleasure of shopping by providing timely and pertinent recommendations.
Summing up:
I hope this blog helps you understand the importance of Artificial Intelligence in product recommendations for your Amazon clone app.
It covers the implementation of AI-powered recommendation systems, different types of recommendation strategies, and their benefits.
Now is the perfect time to launch AI-powered recommendations in your Amazon clone app.
https://www.trioangle.com/...
#EcommercePlatform #TechForBusiness #AmazonCloneScript #USAeCommerce #EcommerceLondon #MiddleEastEcommerce #SAOnlineStore # OnlineMarketplace
#MultiVendorMarketplace #DigitalRetailUSA #UAEStartupScene #MarketplaceTrends
4 months ago
How do trade imbalances caused by over-importation affect our currency, inflation, and economic stability?
Trade imbalances from over-importation can have a significant negative impact on a country's currency, inflation, and economic stability. A persistent trade deficit, where imports far exceed exports, often leads to a weaker currency, higher inflation, and a more fragile economy.
Currency and Exchange Rates
A country's currency value is a reflection of international demand for its goods and services. When a nation imports more than it exports, it needs to sell its own currency to buy foreign currency to pay for those imports. This creates a high supply of the domestic currency on the global market and a high demand for foreign currency. According to the principles of supply and demand, this drives down the value of the domestic currency.
Depreciation: A weaker currency means it takes more of the local currency to buy the same amount of a foreign currency (e.g., the US dollar). This makes all imports, from raw materials to finished consumer goods, more expensive.
Inflation
The depreciation of a country's currency directly contributes to inflation. As imports become more expensive, the cost of goods and services for businesses and consumers rises. This is known as imported inflation.
Rising Costs: Businesses that rely on imported raw materials or machinery will see their production costs increase. They often pass these costs on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
Cost of Living: For consumers, the price of imported goods like electronics, cars, and even food staples will rise. This reduces their purchasing power and increases the overall cost of living.
Economic Stability
A persistent trade imbalance can undermine a country's long-term economic stability.
Foreign Debt: To finance a trade deficit, a country often has to borrow from abroad. This increases its foreign debt and makes the economy more vulnerable to shifts in global financial markets. If foreign investors suddenly lose confidence, they could pull their capital out, potentially triggering a financial crisis.
Loss of Industrial Base: The flow of cheap imports can destroy local industries, leading to factory closures and job losses. This makes the economy less diversified and more reliant on a narrow range of sectors, often primary commodities. This over-reliance leaves the country highly susceptible to fluctuations in global commodity prices.
Reduced Sovereignty: A heavy economic dependence on foreign countries for essential goods can weaken a nation's ability to make independent policy decisions. It may be pressured to align its political and foreign policy with its main trading partners to maintain access to critical imports.
Trade imbalances from over-importation can have a significant negative impact on a country's currency, inflation, and economic stability. A persistent trade deficit, where imports far exceed exports, often leads to a weaker currency, higher inflation, and a more fragile economy.
Currency and Exchange Rates
A country's currency value is a reflection of international demand for its goods and services. When a nation imports more than it exports, it needs to sell its own currency to buy foreign currency to pay for those imports. This creates a high supply of the domestic currency on the global market and a high demand for foreign currency. According to the principles of supply and demand, this drives down the value of the domestic currency.
Depreciation: A weaker currency means it takes more of the local currency to buy the same amount of a foreign currency (e.g., the US dollar). This makes all imports, from raw materials to finished consumer goods, more expensive.
Inflation
The depreciation of a country's currency directly contributes to inflation. As imports become more expensive, the cost of goods and services for businesses and consumers rises. This is known as imported inflation.
Rising Costs: Businesses that rely on imported raw materials or machinery will see their production costs increase. They often pass these costs on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
Cost of Living: For consumers, the price of imported goods like electronics, cars, and even food staples will rise. This reduces their purchasing power and increases the overall cost of living.
Economic Stability
A persistent trade imbalance can undermine a country's long-term economic stability.
Foreign Debt: To finance a trade deficit, a country often has to borrow from abroad. This increases its foreign debt and makes the economy more vulnerable to shifts in global financial markets. If foreign investors suddenly lose confidence, they could pull their capital out, potentially triggering a financial crisis.
Loss of Industrial Base: The flow of cheap imports can destroy local industries, leading to factory closures and job losses. This makes the economy less diversified and more reliant on a narrow range of sectors, often primary commodities. This over-reliance leaves the country highly susceptible to fluctuations in global commodity prices.
Reduced Sovereignty: A heavy economic dependence on foreign countries for essential goods can weaken a nation's ability to make independent policy decisions. It may be pressured to align its political and foreign policy with its main trading partners to maintain access to critical imports.
4 months ago
What incentives or policies could protect and grow local manufacturing in the face of cheap imports?
To protect and grow local manufacturing against cheap imports, governments can implement a mix of protectionist policies and incentives for domestic industries. These strategies aim to either make imports less competitive or boost the capabilities and competitiveness of local businesses.
Protectionist Policies
These policies directly address the challenge of low-priced imports by raising their cost or limiting their quantity.
Tariffs: A tariff is a tax on imported goods. By increasing the price of imports, tariffs make locally produced goods more attractive to consumers. Governments can use specific tariffs (a fixed fee per unit) or ad valorem tariffs (a percentage of the item's value).
Import Quotas: This is a non-tax barrier that sets a strict limit on the volume of a specific good that can be imported over a given period. Quotas reduce the supply of foreign goods, which drives up their price and creates a market for domestic producers to fill the gap.
Anti-Dumping Duties: "Dumping" occurs when a foreign company sells its products in an export market at a price below its production cost to gain market share. Governments can impose special tariffs, known as anti-dumping duties, on these goods to level the playing field and prevent predatory pricing that could destroy local industries.
Local Content Requirements: This policy mandates that a certain percentage of a product's components or labor must be sourced locally. This measure is often used in sectors like automotive manufacturing or electronics to build a domestic supply chain and foster related industries.
Incentives and Support for Local Industry
Beyond restricting imports, governments can also take proactive steps to make local businesses more competitive.
Subsidies and Financial Support: Governments can provide financial assistance to local manufacturers through cash grants, low-interest loans, or tax breaks. These subsidies help reduce the cost of production, making local products more affordable and competitive without directly raising consumer prices.
Investment in Infrastructure and Technology: Improving a nation's infrastructure, such as power grids, transportation networks, and ports, can significantly lower the operational costs for local businesses. Governments can also fund research and development or offer tax credits for businesses that invest in new technology to improve efficiency and productivity.
Export Promotion: Policies that support local firms in selling their products abroad can help them achieve economies of scale. This includes government-sponsored trade missions, export subsidies, and assistance with marketing and logistics. A larger market allows companies to grow, become more efficient, and better withstand foreign competition at home.
"Buy Local" Campaigns: These are public awareness campaigns that encourage consumers and government agencies to prioritize purchasing locally made goods. For example, a "Buy Local" program for government procurement can guarantee a steady market for domestic producers, providing a stable foundation for growth.
To protect and grow local manufacturing against cheap imports, governments can implement a mix of protectionist policies and incentives for domestic industries. These strategies aim to either make imports less competitive or boost the capabilities and competitiveness of local businesses.
Protectionist Policies
These policies directly address the challenge of low-priced imports by raising their cost or limiting their quantity.
Tariffs: A tariff is a tax on imported goods. By increasing the price of imports, tariffs make locally produced goods more attractive to consumers. Governments can use specific tariffs (a fixed fee per unit) or ad valorem tariffs (a percentage of the item's value).
Import Quotas: This is a non-tax barrier that sets a strict limit on the volume of a specific good that can be imported over a given period. Quotas reduce the supply of foreign goods, which drives up their price and creates a market for domestic producers to fill the gap.
Anti-Dumping Duties: "Dumping" occurs when a foreign company sells its products in an export market at a price below its production cost to gain market share. Governments can impose special tariffs, known as anti-dumping duties, on these goods to level the playing field and prevent predatory pricing that could destroy local industries.
Local Content Requirements: This policy mandates that a certain percentage of a product's components or labor must be sourced locally. This measure is often used in sectors like automotive manufacturing or electronics to build a domestic supply chain and foster related industries.
Incentives and Support for Local Industry
Beyond restricting imports, governments can also take proactive steps to make local businesses more competitive.
Subsidies and Financial Support: Governments can provide financial assistance to local manufacturers through cash grants, low-interest loans, or tax breaks. These subsidies help reduce the cost of production, making local products more affordable and competitive without directly raising consumer prices.
Investment in Infrastructure and Technology: Improving a nation's infrastructure, such as power grids, transportation networks, and ports, can significantly lower the operational costs for local businesses. Governments can also fund research and development or offer tax credits for businesses that invest in new technology to improve efficiency and productivity.
Export Promotion: Policies that support local firms in selling their products abroad can help them achieve economies of scale. This includes government-sponsored trade missions, export subsidies, and assistance with marketing and logistics. A larger market allows companies to grow, become more efficient, and better withstand foreign competition at home.
"Buy Local" Campaigns: These are public awareness campaigns that encourage consumers and government agencies to prioritize purchasing locally made goods. For example, a "Buy Local" program for government procurement can guarantee a steady market for domestic producers, providing a stable foundation for growth.
4 months ago
“Sky Is NOT The Limit”: Su-57, S-500, R-37M In Spotlight As IAF Thrilled By Super Success Of S-400 & BrahMos (Part2)
Let us look at the two Russia-origin systems.
S-400 Missile System “Sudarshan Chakra”
The S-400 is a Russian mobile SAM system developed in the 1990s by Russia’s NPO Almaz as an upgrade to the S-300 family of missiles.
The S-400 joined the Russian armed forces in 2007. The system is complemented by its successor, the S-500. The S-400 system has four radars and four sets of missiles covering different ranges and vertical bubbles.
The maximum target detection range is 600 kilometres, and targets can be engaged as far as 400 kilometres. The five S-400 batteries contracted by India in 2018 cost $5.43 billion, including reserve missiles.
All the sub-units are data-linked and controlled by a central command and control system with sufficient redundancy. The system is capable of layered defence and integrates with other Indian air defences.
One system can control 72 launchers, with a maximum of 384 missiles. All missiles are equipped with directed explosion warheads, which increases the probability of complete destruction of aerial targets.
The system is designed to destroy aircraft, cruise, and ballistic missiles, and can also be used against ground targets. It can engage targets up to 17,000 km/h or Mach 14. It can intercept low-flying cruise missiles at a range of about 40 km due to the line-of-sight requirement. The anti-ballistic missile (ABM) capabilities of the S-400 system are near the maximum allowed under the (now void) Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty. The number of simultaneously engaged targets by the full system is 36.
The system ground mobility speed is close to 60 km/h on roads and 25 km/h cross-country. It takes 5 minutes to be operational and fire when ordered while driving. Otherwise, the system response time is just 10 seconds. The time between major overhauls is 10,000 hours. The Service life is at least 20 years.
In Russia, the system was made operational around Moscow in 2007. Russia reportedly deployed S-400 in Syria. The system has been widely used in the ongoing conflict in Ukraine, and it is claimed to have shot down many aircraft.
Meanwhile, Ukraine has reportedly used Western weapons, mainly U.S.-made ATACMS missiles, to hit S-400 units on the ground.
Belarus has unspecified numbers of S-400 units. Deliveries to China, of the six batteries ordered, began in January 2018. Four batteries consisting of 36 fire units and 192 or more missiles were delivered to Turkey.
Algeria is another operator. Some other countries, like Iran, Egypt, Iraq, and Serbia, have also shown interest. South Korea is developing the KM-SAM, a medium-range SAM system based on technology from S-400 missiles, with assistance from NPO Almaz.
Three of the five batteries have arrived in India. India took deliveries despite the American threat of CAATSA (Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act).
The remaining two are expected in 2025/26. The recent conflict has revealed the rough location of two systems, one each in Punjab and Gujarat. As per open sources, the third is somewhere in the east. The systems have been tested in various Indian military exercises.
BrahMos
The BrahMos is a long-range ramjet supersonic cruise missile that can be launched from land, submarines, ships, and fighter aircraft. It is a joint venture between the Indian Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and the Russian Federation’s NPO Mashinostroyeniya, which together have formed BrahMos Aerospace.
The missile is based on Russian P-800 Oniks. The name BrahMos is a portmanteau formed from the names of two rivers, the Brahmaputra of India and the Moskva of Russia. India holds 50.5 percent share of the joint venture. 75 percent of the missile is manufactured in India and there are plans to increase this to 85 percent.
Large numbers of land-launched, ship-launched as well as air-launched versions have been inducted and are in service with the Indian armed forces.
The missile guidance has been developed by BrahMos Aerospace. In 2016, after India became a member of the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR), India and Russia gradually increased the range of the missile to 800 km. The latest deliveries to the Indian Navy are of this type.
The cruise missile has anti-ship and land-attack roles, and has been in service since June 2007. The other operator is the Philippine Marine Corps. The unit cost is around $ 3.5 million.
The extended range variant costs around $4.85 million. Many futuristic variants are evolving. The BrahMos-A is a modified air-launched variant of the missile with a reduced size and weight (2.55 tons). It has a range of 500 km when launched from Su-30 MKI, and it can carry only one BrahMos missile.
50 IAF SU-30MKI were modified to carry the BrahMos-A missile. Smaller-sized variants like BrahMos-NG could be carried on more types of aircraft, even on LCA. Additionally, the BrahMos-NG will have an AESA radar rather than the current mechanically scanned one.
The Sukhoi Su-30MKI will carry three NG missiles, while other IAF fighters will carry one. The BrahMos-NG will be ready by the end of 2025. BrahMos-II will be a hypersonic cruise missile. A UCAV variant is planned.
This solid propellant missile can carry a 200–300 kg warhead that could be nuclear or conventional semi-armour-piercing. Max operational ranges are up to 8-900 kilometres. Export variants are currently restricted to 290 kilometres.
The BrahMos is generally considered the world’s fastest supersonic cruise missile. Currently, the missile speed is Mach 3. Later variants will be hypersonic (M 5+). The missile is very accurate with a CEP of less than one metre.
BrahMos was first test-fired on 12 June 2001 from the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur, in a vertical launch configuration. The September 2010 test of BrahMos created a world record for being the first cruise missile to be tested at supersonic speeds in a steep-dive mode.
BrahMos was tested with an Indian seeker for the first time in March 2018, and was tested with an India-developed propulsion system, airframe, and power supply in September 2019. On 30 September 2020, India successfully test-fired an extended-range BrahMos, offering a range of around 350 km, at speeds up to Mach 2.8.
The submarine-launched variant of BrahMos was test-fired successfully for the first time from a submerged pontoon on 20 March 2013. Even BrahMos Block III land-attack variants are operational. There are plans to have missiles with a range of 1500 km or more.
BrahMos is operationally deployed in large numbers by the three services. Additional missile orders have been recently placed for extended-range variants.
The Philippines has placed a substantial order for their services, and deliveries began in 2024. Russia, too, has plans to buy many missiles. Brazil has shown interest in the missile system. Vietnam and Indonesia have already signed deals.
Sky Is Not The Limit
Resolute political will, choice of targets, weapon matching and accuracy, actionable intelligence, strong Indian air defences, and great IAF professionals. and hitting strategic targets in depth were the clear clinchers.
Aerospace has become the primary means of prosecuting war. India-Russia relations are time-tested. Nearly 60 percent of IAF aircraft are of Russian origin.
Russian platforms and weapons with the Indian armed forces have performed exceedingly well for many decades, since the MiG-21s of the 1960s. The S-400 and Su-30MKI-BrahMos combination have excelled in Op Sindoor.
Could S-500 (600 km) be the next acquisition? Will India select the Su-57 fifth-generation aircraft and Make in India? Can Russia help accelerate the Indian nuclear submarine program? Should India acquire the “AWACS Killer” Russian R-37M AAM and collaborate on developing futuristic long-range aerial missiles?
Should there be more work together on the Su-30MKI upgrade? Can the two enter into a joint venture for Kamikaze drones required by both sides in large numbers, and India can help scale up production?
The Sky is NO more the limit!
Let us look at the two Russia-origin systems.
S-400 Missile System “Sudarshan Chakra”
The S-400 is a Russian mobile SAM system developed in the 1990s by Russia’s NPO Almaz as an upgrade to the S-300 family of missiles.
The S-400 joined the Russian armed forces in 2007. The system is complemented by its successor, the S-500. The S-400 system has four radars and four sets of missiles covering different ranges and vertical bubbles.
The maximum target detection range is 600 kilometres, and targets can be engaged as far as 400 kilometres. The five S-400 batteries contracted by India in 2018 cost $5.43 billion, including reserve missiles.
All the sub-units are data-linked and controlled by a central command and control system with sufficient redundancy. The system is capable of layered defence and integrates with other Indian air defences.
One system can control 72 launchers, with a maximum of 384 missiles. All missiles are equipped with directed explosion warheads, which increases the probability of complete destruction of aerial targets.
The system is designed to destroy aircraft, cruise, and ballistic missiles, and can also be used against ground targets. It can engage targets up to 17,000 km/h or Mach 14. It can intercept low-flying cruise missiles at a range of about 40 km due to the line-of-sight requirement. The anti-ballistic missile (ABM) capabilities of the S-400 system are near the maximum allowed under the (now void) Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty. The number of simultaneously engaged targets by the full system is 36.
The system ground mobility speed is close to 60 km/h on roads and 25 km/h cross-country. It takes 5 minutes to be operational and fire when ordered while driving. Otherwise, the system response time is just 10 seconds. The time between major overhauls is 10,000 hours. The Service life is at least 20 years.
In Russia, the system was made operational around Moscow in 2007. Russia reportedly deployed S-400 in Syria. The system has been widely used in the ongoing conflict in Ukraine, and it is claimed to have shot down many aircraft.
Meanwhile, Ukraine has reportedly used Western weapons, mainly U.S.-made ATACMS missiles, to hit S-400 units on the ground.
Belarus has unspecified numbers of S-400 units. Deliveries to China, of the six batteries ordered, began in January 2018. Four batteries consisting of 36 fire units and 192 or more missiles were delivered to Turkey.
Algeria is another operator. Some other countries, like Iran, Egypt, Iraq, and Serbia, have also shown interest. South Korea is developing the KM-SAM, a medium-range SAM system based on technology from S-400 missiles, with assistance from NPO Almaz.
Three of the five batteries have arrived in India. India took deliveries despite the American threat of CAATSA (Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act).
The remaining two are expected in 2025/26. The recent conflict has revealed the rough location of two systems, one each in Punjab and Gujarat. As per open sources, the third is somewhere in the east. The systems have been tested in various Indian military exercises.
BrahMos
The BrahMos is a long-range ramjet supersonic cruise missile that can be launched from land, submarines, ships, and fighter aircraft. It is a joint venture between the Indian Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and the Russian Federation’s NPO Mashinostroyeniya, which together have formed BrahMos Aerospace.
The missile is based on Russian P-800 Oniks. The name BrahMos is a portmanteau formed from the names of two rivers, the Brahmaputra of India and the Moskva of Russia. India holds 50.5 percent share of the joint venture. 75 percent of the missile is manufactured in India and there are plans to increase this to 85 percent.
Large numbers of land-launched, ship-launched as well as air-launched versions have been inducted and are in service with the Indian armed forces.
The missile guidance has been developed by BrahMos Aerospace. In 2016, after India became a member of the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR), India and Russia gradually increased the range of the missile to 800 km. The latest deliveries to the Indian Navy are of this type.
The cruise missile has anti-ship and land-attack roles, and has been in service since June 2007. The other operator is the Philippine Marine Corps. The unit cost is around $ 3.5 million.
The extended range variant costs around $4.85 million. Many futuristic variants are evolving. The BrahMos-A is a modified air-launched variant of the missile with a reduced size and weight (2.55 tons). It has a range of 500 km when launched from Su-30 MKI, and it can carry only one BrahMos missile.
50 IAF SU-30MKI were modified to carry the BrahMos-A missile. Smaller-sized variants like BrahMos-NG could be carried on more types of aircraft, even on LCA. Additionally, the BrahMos-NG will have an AESA radar rather than the current mechanically scanned one.
The Sukhoi Su-30MKI will carry three NG missiles, while other IAF fighters will carry one. The BrahMos-NG will be ready by the end of 2025. BrahMos-II will be a hypersonic cruise missile. A UCAV variant is planned.
This solid propellant missile can carry a 200–300 kg warhead that could be nuclear or conventional semi-armour-piercing. Max operational ranges are up to 8-900 kilometres. Export variants are currently restricted to 290 kilometres.
The BrahMos is generally considered the world’s fastest supersonic cruise missile. Currently, the missile speed is Mach 3. Later variants will be hypersonic (M 5+). The missile is very accurate with a CEP of less than one metre.
BrahMos was first test-fired on 12 June 2001 from the Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur, in a vertical launch configuration. The September 2010 test of BrahMos created a world record for being the first cruise missile to be tested at supersonic speeds in a steep-dive mode.
BrahMos was tested with an Indian seeker for the first time in March 2018, and was tested with an India-developed propulsion system, airframe, and power supply in September 2019. On 30 September 2020, India successfully test-fired an extended-range BrahMos, offering a range of around 350 km, at speeds up to Mach 2.8.
The submarine-launched variant of BrahMos was test-fired successfully for the first time from a submerged pontoon on 20 March 2013. Even BrahMos Block III land-attack variants are operational. There are plans to have missiles with a range of 1500 km or more.
BrahMos is operationally deployed in large numbers by the three services. Additional missile orders have been recently placed for extended-range variants.
The Philippines has placed a substantial order for their services, and deliveries began in 2024. Russia, too, has plans to buy many missiles. Brazil has shown interest in the missile system. Vietnam and Indonesia have already signed deals.
Sky Is Not The Limit
Resolute political will, choice of targets, weapon matching and accuracy, actionable intelligence, strong Indian air defences, and great IAF professionals. and hitting strategic targets in depth were the clear clinchers.
Aerospace has become the primary means of prosecuting war. India-Russia relations are time-tested. Nearly 60 percent of IAF aircraft are of Russian origin.
Russian platforms and weapons with the Indian armed forces have performed exceedingly well for many decades, since the MiG-21s of the 1960s. The S-400 and Su-30MKI-BrahMos combination have excelled in Op Sindoor.
Could S-500 (600 km) be the next acquisition? Will India select the Su-57 fifth-generation aircraft and Make in India? Can Russia help accelerate the Indian nuclear submarine program? Should India acquire the “AWACS Killer” Russian R-37M AAM and collaborate on developing futuristic long-range aerial missiles?
Should there be more work together on the Su-30MKI upgrade? Can the two enter into a joint venture for Kamikaze drones required by both sides in large numbers, and India can help scale up production?
The Sky is NO more the limit!
4 months ago
China’s Darwin Port Control: Trump’s ‘New Appointee’ Fuels Australia’s Plan To End Landbridge‘s 99-Year Lease?
Is the appointment of Stephen Andrew Feinberg, an American businessman and investor, as the 36th United States deputy secretary of defense by President Donald Trump, the prime reason for Australia considering terminating the Chinese-owned company Landbridge‘s 99-year lease for the strategically important Darwin port?
“Not exactly” could be the answer, though Feinberg’s private equity group Cerberus (he is the founder and co-CEO, but had to resign from the post for joining the Pentagon) is reported to be one of the bidders, along with the Japanese logistics company Toll Group, to buy back the lease from Landbridge.
If done, it will be on the pattern of Hong Kong-based CK Hutchison’s proposed sale of Panama Canal ports to Swiss-Italian Mediterranean Shipping Co and BlackRock, following pressure from the Trump Administration over alleged Chinese influence at the vital waterway.
There is also the possibility of Australia not leasing the port to any other country after taking it back from the Landbridge, based on recent statements by Australian politicians. The country will manage the port itself.
Landbridge’s lease has been a controversial issue in Australian politics ever since it was signed on November 15, 2015.
In fact, the debate surrounding the port predates the Trump Presidency. The lease was opposed by even President Barack Obama. But the then Liberal government led by Prime Minister Malcolm Turnbull gave the go-ahead for the lease. The Labor Party, then in opposition, had opposed the move.
Now in power, Labor has not changed its position, with Prime Minister Anthony Albanes, who got reelected in May this year, asserting during his election-campaign, “ “Obviously we live in an uncertain world at the moment, the idea that you would have the major port in northern Australia owned by any foreign interest is not in Australia’s national interest”.
The Liberals, now in opposition, have also changed their position. They are now against the lease. Thus, there is now a more or less political consensus in Australia against the Darwin port remaining in Chinese hands.
It may be noted that Darwin Port, located in Australia’s Northern Territories (NT), was leased for $506 million by the Landbridge, which is controlled by Chinese billionaire Ye Cheng, who was a member of the national committee of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference, a political advisory body, from 2013 to 2018.
The Labor Party, then, had alleged that Landbridge had “extensive connections” to the Chinese Communist Party and People’s Liberation Army, warning that the lease “compromised Australia’s long-term strategic security”.
However, it is also noteworthy that Australia’s Defence Department had in 2015 reviewed the strategic and operational risks of the deal, including cyberattacks, intellectual property theft, infrastructure degradation, and port shutdowns, and okayed it. Likewise, the Australian Security Intelligence Organisation (ASIO) was equally satisfied with the level of due diligence conducted before the lease was approved.
Reconsideration Of The Lease
So, why is security a factor now in the demands behind the reconsideration of the lease?
It is because the geopolitical considerations in 2015 of the Australian security elites have changed. The optimistic perception of China in Australia in 2014 seems to be no longer there today, thanks to Beijing’s increasing assertiveness in the Indo-Pacific region in recent years.
After all, so runs the argument, every civilian Chinese farm, state-owned or not, and the Landbridge being no exception, has to comply with the ruling Communist Party’s mandates on matters relating to national security. Businesses do constitute a geopolitical cudgel for Beijing.
And that being the case, Darwin’s strategic location is significant as it is Australia’s northernmost maritime facility, situated on the edge of Southeast Asia and the South China Sea.
Maritime forces stationed there can always enjoy a central position just outside the southerly arc of Asia’s first island chain, which runs from Japan through Taiwan, the Philippines, and the Indonesian archipelago before terminating at the Strait of Malacca.
The Sunda and Lombok straits, key alternatives to the Malacca Strait, are within Darwin’s reach. Amid China’s growing assertiveness in the South China Sea, U.S. Marine forces, allies of Australia, have direct access from Darwin, with approximately 2,500 Marines from the I Marine Expeditionary Force rotating through the port annually.
Among other functions, these Marines are also said to be honing tactics for “access denial” while helping beleaguered allies and partners like the Philippines and Taiwan.
In other words, with Darwin occupying such a strategic position, it is argued that Australia and its allies cannot afford to leave the port in Chinese hands.
As James Holmes of the U.S. Naval War College fears, Chinese observers at the port could gather intelligence on the Australian Defense Force and allied comings and goings while abetting net assessment of allied capabilities, tactics, techniques, and procedures.
“In so doing, they help acquaint the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) with potential foes, the first step toward defeating them. Nor is it far-fetched to imagine Chinese port operators slow-rolling—or, more likely, actively hampering—allied military movements and resupply in wartime”.
All these apprehensions, when fitted in the overall framework of China outpacing the developed Western countries in general and the United States in particular in investing in “the port infrastructure around the world”, have further sharpened the geopolitical focus on Darwin.
Incidentally, as per the latest available data, China operates or has ownership in at least one port on every continent except Antarctica. Of the 129 projects, 115 are active, whereas the remaining 14 port projects have become inactive due to cancellation or suspension over environmental concerns, souring of political relations, financial problems, and security issues raised domestically and internationally.
It is said that China has ownership of 91 active port projects across the globe, where military use is a possibility, providing it with a foothold on every continent except Antarctica.
These projects are part of its Maritime Silk Road (MSR). If the American military analysts are to be believed, China’s position of control and influence over the majority of port infrastructure globally poses a significant economic and military security threat to the United States and its allies.
It is feared that China could always use its power to interfere with operations that rely on port access—including military and economic operations that are vital to American interests and those of its allies and partners.
In fact, according to a study, out of the 70 commercial port projects that China has in the “Global South,” which includes Australia, an estimated 55 projects have the potential for naval use as well.
In addition to commercial and military use, China is believed to be using port infrastructure for spying and intelligence gathering. Apparently, a U.S. Congressional probe in 2024 showed communications equipment in Chinese-made cranes at U.S. ports, suggesting vulnerabilities to supply chains, trade data, and other sensitive information.
It is also said that China has secured a commanding position through Logink (also known as the National Transportation and Logistics Public Information Platform), a Chinese state-owned digital logistics platform.
At least 24 ports worldwide reportedly have adopted the Logink system, which could allow China to access significant amounts of confidential information related to transportation, pricing, and management of goods (including military equipment), threatening its rivals’ security.
Given all this, the United States would obviously like Prime Minister Anthony Albanese to keep up his election promise of taking back Darwin from the Chinese hands. But then, it is easier said than done.
Albanese had avoided giving a definite answer when questioned on this during his six-day trip to China, one of Australia’s “strategic partners”, last month.
In any case, China is speaking out vehemently opposing the termination of the lease, terming the move as “ethically questionable.”
Chinese Premier Li Qiang has called for his country’s companies to be treated properly, saying, “We hope that the Australian side can provide a fair, open, and non-discriminatory business environment for Chinese enterprises in Australia”.
But the point is that gone are the days when China was seen in Australia as a benign trade partner. China’s lease of the port is no longer an issue limited to trade; it has become the battleground over Beijing’s overall geopolitical ambitions, something Australia’s ally, the United States, is trying to keep limited.
Is the appointment of Stephen Andrew Feinberg, an American businessman and investor, as the 36th United States deputy secretary of defense by President Donald Trump, the prime reason for Australia considering terminating the Chinese-owned company Landbridge‘s 99-year lease for the strategically important Darwin port?
“Not exactly” could be the answer, though Feinberg’s private equity group Cerberus (he is the founder and co-CEO, but had to resign from the post for joining the Pentagon) is reported to be one of the bidders, along with the Japanese logistics company Toll Group, to buy back the lease from Landbridge.
If done, it will be on the pattern of Hong Kong-based CK Hutchison’s proposed sale of Panama Canal ports to Swiss-Italian Mediterranean Shipping Co and BlackRock, following pressure from the Trump Administration over alleged Chinese influence at the vital waterway.
There is also the possibility of Australia not leasing the port to any other country after taking it back from the Landbridge, based on recent statements by Australian politicians. The country will manage the port itself.
Landbridge’s lease has been a controversial issue in Australian politics ever since it was signed on November 15, 2015.
In fact, the debate surrounding the port predates the Trump Presidency. The lease was opposed by even President Barack Obama. But the then Liberal government led by Prime Minister Malcolm Turnbull gave the go-ahead for the lease. The Labor Party, then in opposition, had opposed the move.
Now in power, Labor has not changed its position, with Prime Minister Anthony Albanes, who got reelected in May this year, asserting during his election-campaign, “ “Obviously we live in an uncertain world at the moment, the idea that you would have the major port in northern Australia owned by any foreign interest is not in Australia’s national interest”.
The Liberals, now in opposition, have also changed their position. They are now against the lease. Thus, there is now a more or less political consensus in Australia against the Darwin port remaining in Chinese hands.
It may be noted that Darwin Port, located in Australia’s Northern Territories (NT), was leased for $506 million by the Landbridge, which is controlled by Chinese billionaire Ye Cheng, who was a member of the national committee of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference, a political advisory body, from 2013 to 2018.
The Labor Party, then, had alleged that Landbridge had “extensive connections” to the Chinese Communist Party and People’s Liberation Army, warning that the lease “compromised Australia’s long-term strategic security”.
However, it is also noteworthy that Australia’s Defence Department had in 2015 reviewed the strategic and operational risks of the deal, including cyberattacks, intellectual property theft, infrastructure degradation, and port shutdowns, and okayed it. Likewise, the Australian Security Intelligence Organisation (ASIO) was equally satisfied with the level of due diligence conducted before the lease was approved.
Reconsideration Of The Lease
So, why is security a factor now in the demands behind the reconsideration of the lease?
It is because the geopolitical considerations in 2015 of the Australian security elites have changed. The optimistic perception of China in Australia in 2014 seems to be no longer there today, thanks to Beijing’s increasing assertiveness in the Indo-Pacific region in recent years.
After all, so runs the argument, every civilian Chinese farm, state-owned or not, and the Landbridge being no exception, has to comply with the ruling Communist Party’s mandates on matters relating to national security. Businesses do constitute a geopolitical cudgel for Beijing.
And that being the case, Darwin’s strategic location is significant as it is Australia’s northernmost maritime facility, situated on the edge of Southeast Asia and the South China Sea.
Maritime forces stationed there can always enjoy a central position just outside the southerly arc of Asia’s first island chain, which runs from Japan through Taiwan, the Philippines, and the Indonesian archipelago before terminating at the Strait of Malacca.
The Sunda and Lombok straits, key alternatives to the Malacca Strait, are within Darwin’s reach. Amid China’s growing assertiveness in the South China Sea, U.S. Marine forces, allies of Australia, have direct access from Darwin, with approximately 2,500 Marines from the I Marine Expeditionary Force rotating through the port annually.
Among other functions, these Marines are also said to be honing tactics for “access denial” while helping beleaguered allies and partners like the Philippines and Taiwan.
In other words, with Darwin occupying such a strategic position, it is argued that Australia and its allies cannot afford to leave the port in Chinese hands.
As James Holmes of the U.S. Naval War College fears, Chinese observers at the port could gather intelligence on the Australian Defense Force and allied comings and goings while abetting net assessment of allied capabilities, tactics, techniques, and procedures.
“In so doing, they help acquaint the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) with potential foes, the first step toward defeating them. Nor is it far-fetched to imagine Chinese port operators slow-rolling—or, more likely, actively hampering—allied military movements and resupply in wartime”.
All these apprehensions, when fitted in the overall framework of China outpacing the developed Western countries in general and the United States in particular in investing in “the port infrastructure around the world”, have further sharpened the geopolitical focus on Darwin.
Incidentally, as per the latest available data, China operates or has ownership in at least one port on every continent except Antarctica. Of the 129 projects, 115 are active, whereas the remaining 14 port projects have become inactive due to cancellation or suspension over environmental concerns, souring of political relations, financial problems, and security issues raised domestically and internationally.
It is said that China has ownership of 91 active port projects across the globe, where military use is a possibility, providing it with a foothold on every continent except Antarctica.
These projects are part of its Maritime Silk Road (MSR). If the American military analysts are to be believed, China’s position of control and influence over the majority of port infrastructure globally poses a significant economic and military security threat to the United States and its allies.
It is feared that China could always use its power to interfere with operations that rely on port access—including military and economic operations that are vital to American interests and those of its allies and partners.
In fact, according to a study, out of the 70 commercial port projects that China has in the “Global South,” which includes Australia, an estimated 55 projects have the potential for naval use as well.
In addition to commercial and military use, China is believed to be using port infrastructure for spying and intelligence gathering. Apparently, a U.S. Congressional probe in 2024 showed communications equipment in Chinese-made cranes at U.S. ports, suggesting vulnerabilities to supply chains, trade data, and other sensitive information.
It is also said that China has secured a commanding position through Logink (also known as the National Transportation and Logistics Public Information Platform), a Chinese state-owned digital logistics platform.
At least 24 ports worldwide reportedly have adopted the Logink system, which could allow China to access significant amounts of confidential information related to transportation, pricing, and management of goods (including military equipment), threatening its rivals’ security.
Given all this, the United States would obviously like Prime Minister Anthony Albanese to keep up his election promise of taking back Darwin from the Chinese hands. But then, it is easier said than done.
Albanese had avoided giving a definite answer when questioned on this during his six-day trip to China, one of Australia’s “strategic partners”, last month.
In any case, China is speaking out vehemently opposing the termination of the lease, terming the move as “ethically questionable.”
Chinese Premier Li Qiang has called for his country’s companies to be treated properly, saying, “We hope that the Australian side can provide a fair, open, and non-discriminatory business environment for Chinese enterprises in Australia”.
But the point is that gone are the days when China was seen in Australia as a benign trade partner. China’s lease of the port is no longer an issue limited to trade; it has become the battleground over Beijing’s overall geopolitical ambitions, something Australia’s ally, the United States, is trying to keep limited.
4 months ago
After Combat Debut Of JAS-39 Gripens, Thailand To Add More SAAB Fighter Jets To Boost Its Air Force.
Thailand has finally approved the acquisition of four SAAB Gripen-E/F fighter jets as it modernizes its aging air force amid rising security threats, as seen in the recent border conflict with Cambodia.
What began as skirmishes between the two countries in July 2025 quickly escalated into full-scale firefights, with artillery and gunfire rattling border villages for nearly a week. The conflict lasted for about five days before the two warring sides decided to accept an “immediate and unconditional ceasefire” on July 28.
The Royal Thai Air Force (RTAF) currently operates the Gripen-C/D and the older American F-16 Fighting Falcons. Both aircraft were deployed in combat and used to launch strikes on Cambodian artillery positions.
This marked the combat debut for the Gripens anywhere in the world, 37 years after their first flight.
The conflict, rooted in a century-long border dispute, has raised concerns about further escalation. However, the purchase of Gripen-E/F was decided well in advance of this latest conflict and is not directly influenced by the hostilities with Cambodia.
The Royal Thai Air Force (RTAF) officially announced its decision to buy a dozen Saab Gripen-E fighter jets over the American Lockheed Martin F-16 Block 70/72 aircraft in June. The Gripen-E outperformed the American F-16 Block 70/72 by offering technological and financial advantages that made its offer far more appealing and beneficial to Thailand.
The deal is a part of a long-term plan to acquire all 12 Gripen E/F aircraft by 2035 and integrate them operationally. The newly purchased Gripen-E variant will replace the archaic F-16 A/B and will be integrated into the RTAF alongside the existing SAAB Gripen jets.
Saab describes Gripen-E as “Designed to defeat any adversary. Made for forward-thinking air forces, Gripen E incorporates cutting-edge technologies, the latest systems, sensors, weapons, and pods to ensure combat advantage, delivering air superiority in highly contested environments. Silent networking and total sensor fusion across a tactical air unit to blind and confuse the enemy. One aircraft is active, the others go passive.”
The Swedish manufacturer promises that the aircraft allows the first missile launch opportunity and the first kill. Saab claims its design represents a breakthrough, allowing it to swiftly integrate new hardware and update software applications to adapt to evolving mission requirements. Further, the fighter jet incorporates more prominent air intakes and is powered by the enhanced General Electric F414-GE-39E engine.
It is designed for quick field deployment, especially at remote bases, and can be effectively maintained by a few people.
While Thailand was impressed by the cutting-edge features of the Gripen, it was the large scope of the Swedish deal, particularly the technology transfer, that mainly bore fruit. Lockheed Martin, the manufacturer of the F-16, was a lot more conservative in offering a deal to Thailand, as previously explained in detail by the EurAsian Times.
With a fighter fleet including upgraded F-16s, F-5s, and Gripens, Thailand has been steadily modernising its capabilities with multi-role platforms. That dominance became apparent during the border clashes. Cambodia, with no dedicated fighter jets in its inventory, had little ability to deter or respond to Thailand’s precision air strikes.
This may come as an added impetus to the acquisition.
However, Thailand is not the only country in the Southeast Asian region to go on fighter jet shopping in recent times. Several others, including Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Vietnam, are exploring options and looking to sign new deals.
New And Advanced Fighter Jets In SEA
In addition to Thailand, Indonesia has been in the headlines for its intention to acquire new and more advanced combat aircraft.
The Indonesian government recently signed a contract to acquire 48 KAAN fighter jets from Turkey. The agreement covers extensive collaboration in manufacturing, technology transfer, engineering, and includes the establishment of a local aerospace infrastructure.
Indonesia is also co-developing the KF-21 4.5th generation aircraft, along with South Korea, and has a deal for 42 Rafale fighter jets with French Dassault Aviation. It could acquire an additional batch of Rafales from France, as indicated by the letter of intent (LoI) signed by the government recently.
Another Southeast Asian country, Malaysia, is building up its air power amid rising security threats in the South China Sea. On June 17, Royal Malaysian Air Force (RMAF) Chief General Tan Sri Asghar Khan Goriman Khan confirmed that Washington had approved the third-party transfer of up to 33 F/A-18C/D Hornets currently in service with the Kuwaiti Air Force (KAF). In addition to this, the RMAF is also acquiring the South Korean FA-50.
Malaysia launched the MRCA (Multi-Role Combat Aircraft) program to acquire advanced fighter jets that could replace its aging fleet and help enhance Malaysia’s air power with a modern, multi-role fighter jet. This program has remained in limbo for several years. Some unconfirmed reports earlier suggested that Malaysia was interested in Russia’s Su-57 but those rumours have now fizzled out.
The most significant fighter jet acquisition in the region is the purchase of the US F-16 by the Philippines. The United States approved the sale of F-16 fighter jets worth US$5.58 billion to the Philippines in April as Manila builds capability to deter an increasingly aggressive China in the South China Sea. The Philippines Air Force (PAF), like its Thai counterpart, had earlier been examining two combat aircraft on offer, the Lockheed Martin F-16 Block 70/72 and the Saab Gripen-E.
The upgrade of the PAF would be essential for enhancing the Philippines’ ability to project power beyond its territorial waters. In addition to a new multi-role fighter, the country is also considering purchasing a dozen additional FA-50 fighters from South Korea to increase its numbers and boost readiness.
Meanwhile, Vietnam has reportedly been discussing a potential purchase of two dozen F-16s from the United States, in what is being interpreted as a break in the country’s strategic alignment with Russia.
The move is aimed at deterring China, which claims almost the entire South China Sea, has several territorial disputes in the region, and has been steadily expanding its military influence in the region.
Though unconfirmed, the reports suggest that Vietnam has been on the lookout for an alternative to its retired MiG-21, the Soviet-designed supersonic jet fighter and interceptor aircraft. There is no information on which F-16 is being negotiated and whether it would be a new aircraft or a used one.
The war-torn country of Myanmar has also made a significant acquisition. In January 2025, the Myanmar Air Force took delivery of its six Su-30 SMEs from Russia.
The six Russian jets were acquired under a 2018 contract valued at US$400 million. The acquisition has been financed through a Russian loan, and the final two fighter jets were commissioned on December 15, 2024, at Meiktila Air Base in Mandalay.
These Su-30 jets will serve as Myanmar’s primary aircraft for safeguarding territorial integrity and countering terror threats, and are stationed at Naypyidaw Air Base, enabling coverage of the entire country.
The Myanmar Junta is strengthening its air capabilities to deal with the rebels. On December 15 alone, the military commissioned six Russian-made Mi-17 helicopters, six Chinese-made FTC-2000G fighter jets, one K-8W fighter jet, and one Y-8 support aircraft, as earlier reported by the EurAsian Times.
Though attention has largely been focused on the turbulence and military build-up in Asia, the above-listed acquisitions suggest that Southeast Asia is evolving and going through a catharsis of its own as new security threats emerge and existing threats become bigger and more pronounced
Thailand has finally approved the acquisition of four SAAB Gripen-E/F fighter jets as it modernizes its aging air force amid rising security threats, as seen in the recent border conflict with Cambodia.
What began as skirmishes between the two countries in July 2025 quickly escalated into full-scale firefights, with artillery and gunfire rattling border villages for nearly a week. The conflict lasted for about five days before the two warring sides decided to accept an “immediate and unconditional ceasefire” on July 28.
The Royal Thai Air Force (RTAF) currently operates the Gripen-C/D and the older American F-16 Fighting Falcons. Both aircraft were deployed in combat and used to launch strikes on Cambodian artillery positions.
This marked the combat debut for the Gripens anywhere in the world, 37 years after their first flight.
The conflict, rooted in a century-long border dispute, has raised concerns about further escalation. However, the purchase of Gripen-E/F was decided well in advance of this latest conflict and is not directly influenced by the hostilities with Cambodia.
The Royal Thai Air Force (RTAF) officially announced its decision to buy a dozen Saab Gripen-E fighter jets over the American Lockheed Martin F-16 Block 70/72 aircraft in June. The Gripen-E outperformed the American F-16 Block 70/72 by offering technological and financial advantages that made its offer far more appealing and beneficial to Thailand.
The deal is a part of a long-term plan to acquire all 12 Gripen E/F aircraft by 2035 and integrate them operationally. The newly purchased Gripen-E variant will replace the archaic F-16 A/B and will be integrated into the RTAF alongside the existing SAAB Gripen jets.
Saab describes Gripen-E as “Designed to defeat any adversary. Made for forward-thinking air forces, Gripen E incorporates cutting-edge technologies, the latest systems, sensors, weapons, and pods to ensure combat advantage, delivering air superiority in highly contested environments. Silent networking and total sensor fusion across a tactical air unit to blind and confuse the enemy. One aircraft is active, the others go passive.”
The Swedish manufacturer promises that the aircraft allows the first missile launch opportunity and the first kill. Saab claims its design represents a breakthrough, allowing it to swiftly integrate new hardware and update software applications to adapt to evolving mission requirements. Further, the fighter jet incorporates more prominent air intakes and is powered by the enhanced General Electric F414-GE-39E engine.
It is designed for quick field deployment, especially at remote bases, and can be effectively maintained by a few people.
While Thailand was impressed by the cutting-edge features of the Gripen, it was the large scope of the Swedish deal, particularly the technology transfer, that mainly bore fruit. Lockheed Martin, the manufacturer of the F-16, was a lot more conservative in offering a deal to Thailand, as previously explained in detail by the EurAsian Times.
With a fighter fleet including upgraded F-16s, F-5s, and Gripens, Thailand has been steadily modernising its capabilities with multi-role platforms. That dominance became apparent during the border clashes. Cambodia, with no dedicated fighter jets in its inventory, had little ability to deter or respond to Thailand’s precision air strikes.
This may come as an added impetus to the acquisition.
However, Thailand is not the only country in the Southeast Asian region to go on fighter jet shopping in recent times. Several others, including Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Vietnam, are exploring options and looking to sign new deals.
New And Advanced Fighter Jets In SEA
In addition to Thailand, Indonesia has been in the headlines for its intention to acquire new and more advanced combat aircraft.
The Indonesian government recently signed a contract to acquire 48 KAAN fighter jets from Turkey. The agreement covers extensive collaboration in manufacturing, technology transfer, engineering, and includes the establishment of a local aerospace infrastructure.
Indonesia is also co-developing the KF-21 4.5th generation aircraft, along with South Korea, and has a deal for 42 Rafale fighter jets with French Dassault Aviation. It could acquire an additional batch of Rafales from France, as indicated by the letter of intent (LoI) signed by the government recently.
Another Southeast Asian country, Malaysia, is building up its air power amid rising security threats in the South China Sea. On June 17, Royal Malaysian Air Force (RMAF) Chief General Tan Sri Asghar Khan Goriman Khan confirmed that Washington had approved the third-party transfer of up to 33 F/A-18C/D Hornets currently in service with the Kuwaiti Air Force (KAF). In addition to this, the RMAF is also acquiring the South Korean FA-50.
Malaysia launched the MRCA (Multi-Role Combat Aircraft) program to acquire advanced fighter jets that could replace its aging fleet and help enhance Malaysia’s air power with a modern, multi-role fighter jet. This program has remained in limbo for several years. Some unconfirmed reports earlier suggested that Malaysia was interested in Russia’s Su-57 but those rumours have now fizzled out.
The most significant fighter jet acquisition in the region is the purchase of the US F-16 by the Philippines. The United States approved the sale of F-16 fighter jets worth US$5.58 billion to the Philippines in April as Manila builds capability to deter an increasingly aggressive China in the South China Sea. The Philippines Air Force (PAF), like its Thai counterpart, had earlier been examining two combat aircraft on offer, the Lockheed Martin F-16 Block 70/72 and the Saab Gripen-E.
The upgrade of the PAF would be essential for enhancing the Philippines’ ability to project power beyond its territorial waters. In addition to a new multi-role fighter, the country is also considering purchasing a dozen additional FA-50 fighters from South Korea to increase its numbers and boost readiness.
Meanwhile, Vietnam has reportedly been discussing a potential purchase of two dozen F-16s from the United States, in what is being interpreted as a break in the country’s strategic alignment with Russia.
The move is aimed at deterring China, which claims almost the entire South China Sea, has several territorial disputes in the region, and has been steadily expanding its military influence in the region.
Though unconfirmed, the reports suggest that Vietnam has been on the lookout for an alternative to its retired MiG-21, the Soviet-designed supersonic jet fighter and interceptor aircraft. There is no information on which F-16 is being negotiated and whether it would be a new aircraft or a used one.
The war-torn country of Myanmar has also made a significant acquisition. In January 2025, the Myanmar Air Force took delivery of its six Su-30 SMEs from Russia.
The six Russian jets were acquired under a 2018 contract valued at US$400 million. The acquisition has been financed through a Russian loan, and the final two fighter jets were commissioned on December 15, 2024, at Meiktila Air Base in Mandalay.
These Su-30 jets will serve as Myanmar’s primary aircraft for safeguarding territorial integrity and countering terror threats, and are stationed at Naypyidaw Air Base, enabling coverage of the entire country.
The Myanmar Junta is strengthening its air capabilities to deal with the rebels. On December 15 alone, the military commissioned six Russian-made Mi-17 helicopters, six Chinese-made FTC-2000G fighter jets, one K-8W fighter jet, and one Y-8 support aircraft, as earlier reported by the EurAsian Times.
Though attention has largely been focused on the turbulence and military build-up in Asia, the above-listed acquisitions suggest that Southeast Asia is evolving and going through a catharsis of its own as new security threats emerge and existing threats become bigger and more pronounced
4 months ago
From BrahMos To Maritime Drills: India-Philippines Military Partnership Redefines Indo-Pacific Security.
The strategic partnership announced between India and the Philippines during the successful visit of President Ferdinand Marcos Jr. to India this month is significant and unique in several ways, with far-reaching implications.
The Philippines is geographically the farthest ASEAN member from India and has traditionally had limited engagement with New Delhi.
Its severe challenge from China over the Scarborough Shoal and nearby islets in the South China Sea (or West Philippine Sea) has reshaped its strategic outlook. Despite winning the 2016 arbitral award that rejected China’s so-called traditional rights over the “nine-dash line,” the then-Philippine administration chose not to press its advantage and instead sought to accommodate Beijing.
This approach brought few tangible benefits.
Upon assuming office, President Marcos reversed this policy of accommodation at all costs, taking a firm stand against Chinese assertiveness, a lonely position within ASEAN.
The Philippines has borne the brunt of aggressive actions by Chinese coast guard vessels, including ramming incidents and injuries to its seamen.
This shift aligns closely with India’s evolving stance: over the last three years, Indian statements have moved beyond general support for freedom of navigation and UNCLOS implementation to openly endorsing the arbitral award.
This convergence forms the foundation of the new strategic partnership, rooted in shared security concerns rather than primarily economic ties. Bilateral trade remains modest, and unlike with other ASEAN members, the partnership with the Philippines is driven by genuine strategic considerations.
Notably, the Philippines has emerged as a major buyer of Indian defence equipment, particularly the BrahMos missile system.
In a determined manner, it overtook earlier interest shown by Vietnam and Indonesia, both existing strategic partners of India, and has begun deploying BrahMos batteries.
Although no new weapons deals were announced during the visit, it is clear that Manila seeks to strengthen its coast guard, coastal defence, and related capabilities, and sees India’s competitive defence pricing as an advantage.
The Philippines has acknowledged the BrahMos system’s operational effectiveness during Op Sindoor. The Philippines has relatively few strategic partnerships: this is only its fifth, after those with Japan, Australia, Vietnam, and South Korea.
Traditionally, its strategic lens has been regional, but it now recognizes the Indo-Pacific framework, in which India plays a central role.
Since China’s assertive posture in the South China Sea became evident two decades ago, ASEAN unity in challenging Beijing has steadily weakened.
In 2012, at the ASEAN Foreign Ministers’ Meeting, all but Cambodia criticized China. By 2017, when the Philippines last hosted the ASEAN Summit, only Manila and Hanoi remained openly critical.
Today, even Vietnam has shifted towards compromise, leaving the Philippines as perhaps the only ASEAN state willing to confront China directly. This isolation has led it to adopt an “ASEAN Plus” approach, engaging robustly with Japan, the U.S., and Australia to strengthen its defence and strategic posture.
The reopening of U.S. bases in the Philippines, including one in the northern islands, underscores its role in any potential Taiwan crisis. Japan is also supplying substantial defence equipment under its new Official Security Assistance policy.
With the Philippines already aligned closely with the Quad countries, a strategic partnership with India is a natural progression.
The Philippines will chair ASEAN in 2026. During its chairmanship, India is expected to hold the second ASEAN–India Maritime Exercise (AIME). The first, in May 2023, included a harbour phase at Changi Naval Base in Singapore and a sea phase in the South China Sea.
These exercises enhance interoperability between Indian and ASEAN navies and demonstrate their ability to operate jointly to promote regional security. It remains to be seen whether the next exercise will be held closer to Philippine waters.
Indian naval and coast guard presence in the Philippines has grown steadily, with visits averaging twice a year. During President Marcos’s visit, Indian ships had just completed a joint exercise with the Philippine Navy, including three warships and a hydrography vessel.
The newly signed strategic partnership document, detailed and resembling a joint statement, marks the 75th anniversary of India–Philippines diplomatic relations and sets out the Plan of Action 2025–2029 to guide cooperation.
On the strategic front, India and the Philippines have had a Defence Cooperation Agreement since 2006, supported by mechanisms such as the Joint Defence Cooperation Committee and the Joint Defence Industry and Logistics Committee.
These bodies are working to deepen defence industrial collaboration, technology research, and training. Efforts are underway to institutionalize military training across the tri-services. The two sides will also hold the India–Philippines Maritime Dialogue annually, following its inaugural session in December 2024.
The partnership includes enhanced maritime domain awareness, shipbuilding cooperation, maritime connectivity, coastal surveillance, humanitarian assistance and disaster relief, co-development and production of defence equipment to achieve self-reliance, and joint investments in defence R&D and supply chains.
The AIME, Philippine maritime cooperation activities, and the MILAN naval exercise are all identified as platforms for collaboration.
Both countries are committed to counter-terrorism through more frequent dialogues, information-sharing, and best-practice exchanges, with zero tolerance for terrorism.
The Philippines values India’s naval capacities, a fact underscored by President Marcos’s public thanks for India’s 2024 rescue of Philippine seafarers after a Houthi rebel attack in the Red Sea. For Manila, which sees itself as the “Sentinel of the Pacific,” and for India, positioned at the heart of the Indian Ocean, this partnership broadens their shared strategic horizons.
Key outcomes of the visit include:
Terms of Reference for tri-service staff talks between the two armed forces.
A Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty in criminal matters.
A Statement of Intent for cooperation between the Indian and Philippine space agencies.
Terms of Reference for enhanced coast guard cooperation.
An invitation for the Philippines to participate in the Information Fusion Centre for the Indian Ocean Region in Gurugram.
Philippine interest in collaborating under one of the pillars of India’s Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI), complementing the ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific (AOIP) provides further opportunities ahead.
With converging strategic perceptions, a record of successful defence cooperation, and a shared commitment to a free and open Indo-Pacific, the India–Philippines partnership has entered a new and more ambitious phase.
The strategic partnership announced between India and the Philippines during the successful visit of President Ferdinand Marcos Jr. to India this month is significant and unique in several ways, with far-reaching implications.
The Philippines is geographically the farthest ASEAN member from India and has traditionally had limited engagement with New Delhi.
Its severe challenge from China over the Scarborough Shoal and nearby islets in the South China Sea (or West Philippine Sea) has reshaped its strategic outlook. Despite winning the 2016 arbitral award that rejected China’s so-called traditional rights over the “nine-dash line,” the then-Philippine administration chose not to press its advantage and instead sought to accommodate Beijing.
This approach brought few tangible benefits.
Upon assuming office, President Marcos reversed this policy of accommodation at all costs, taking a firm stand against Chinese assertiveness, a lonely position within ASEAN.
The Philippines has borne the brunt of aggressive actions by Chinese coast guard vessels, including ramming incidents and injuries to its seamen.
This shift aligns closely with India’s evolving stance: over the last three years, Indian statements have moved beyond general support for freedom of navigation and UNCLOS implementation to openly endorsing the arbitral award.
This convergence forms the foundation of the new strategic partnership, rooted in shared security concerns rather than primarily economic ties. Bilateral trade remains modest, and unlike with other ASEAN members, the partnership with the Philippines is driven by genuine strategic considerations.
Notably, the Philippines has emerged as a major buyer of Indian defence equipment, particularly the BrahMos missile system.
In a determined manner, it overtook earlier interest shown by Vietnam and Indonesia, both existing strategic partners of India, and has begun deploying BrahMos batteries.
Although no new weapons deals were announced during the visit, it is clear that Manila seeks to strengthen its coast guard, coastal defence, and related capabilities, and sees India’s competitive defence pricing as an advantage.
The Philippines has acknowledged the BrahMos system’s operational effectiveness during Op Sindoor. The Philippines has relatively few strategic partnerships: this is only its fifth, after those with Japan, Australia, Vietnam, and South Korea.
Traditionally, its strategic lens has been regional, but it now recognizes the Indo-Pacific framework, in which India plays a central role.
Since China’s assertive posture in the South China Sea became evident two decades ago, ASEAN unity in challenging Beijing has steadily weakened.
In 2012, at the ASEAN Foreign Ministers’ Meeting, all but Cambodia criticized China. By 2017, when the Philippines last hosted the ASEAN Summit, only Manila and Hanoi remained openly critical.
Today, even Vietnam has shifted towards compromise, leaving the Philippines as perhaps the only ASEAN state willing to confront China directly. This isolation has led it to adopt an “ASEAN Plus” approach, engaging robustly with Japan, the U.S., and Australia to strengthen its defence and strategic posture.
The reopening of U.S. bases in the Philippines, including one in the northern islands, underscores its role in any potential Taiwan crisis. Japan is also supplying substantial defence equipment under its new Official Security Assistance policy.
With the Philippines already aligned closely with the Quad countries, a strategic partnership with India is a natural progression.
The Philippines will chair ASEAN in 2026. During its chairmanship, India is expected to hold the second ASEAN–India Maritime Exercise (AIME). The first, in May 2023, included a harbour phase at Changi Naval Base in Singapore and a sea phase in the South China Sea.
These exercises enhance interoperability between Indian and ASEAN navies and demonstrate their ability to operate jointly to promote regional security. It remains to be seen whether the next exercise will be held closer to Philippine waters.
Indian naval and coast guard presence in the Philippines has grown steadily, with visits averaging twice a year. During President Marcos’s visit, Indian ships had just completed a joint exercise with the Philippine Navy, including three warships and a hydrography vessel.
The newly signed strategic partnership document, detailed and resembling a joint statement, marks the 75th anniversary of India–Philippines diplomatic relations and sets out the Plan of Action 2025–2029 to guide cooperation.
On the strategic front, India and the Philippines have had a Defence Cooperation Agreement since 2006, supported by mechanisms such as the Joint Defence Cooperation Committee and the Joint Defence Industry and Logistics Committee.
These bodies are working to deepen defence industrial collaboration, technology research, and training. Efforts are underway to institutionalize military training across the tri-services. The two sides will also hold the India–Philippines Maritime Dialogue annually, following its inaugural session in December 2024.
The partnership includes enhanced maritime domain awareness, shipbuilding cooperation, maritime connectivity, coastal surveillance, humanitarian assistance and disaster relief, co-development and production of defence equipment to achieve self-reliance, and joint investments in defence R&D and supply chains.
The AIME, Philippine maritime cooperation activities, and the MILAN naval exercise are all identified as platforms for collaboration.
Both countries are committed to counter-terrorism through more frequent dialogues, information-sharing, and best-practice exchanges, with zero tolerance for terrorism.
The Philippines values India’s naval capacities, a fact underscored by President Marcos’s public thanks for India’s 2024 rescue of Philippine seafarers after a Houthi rebel attack in the Red Sea. For Manila, which sees itself as the “Sentinel of the Pacific,” and for India, positioned at the heart of the Indian Ocean, this partnership broadens their shared strategic horizons.
Key outcomes of the visit include:
Terms of Reference for tri-service staff talks between the two armed forces.
A Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty in criminal matters.
A Statement of Intent for cooperation between the Indian and Philippine space agencies.
Terms of Reference for enhanced coast guard cooperation.
An invitation for the Philippines to participate in the Information Fusion Centre for the Indian Ocean Region in Gurugram.
Philippine interest in collaborating under one of the pillars of India’s Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI), complementing the ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific (AOIP) provides further opportunities ahead.
With converging strategic perceptions, a record of successful defence cooperation, and a shared commitment to a free and open Indo-Pacific, the India–Philippines partnership has entered a new and more ambitious phase.
4 months ago
The crypto market is growing fast. People are buying, selling, and trading digital coins every day, and platforms like Coinbase have become a go-to for millions.
But if you’ve ever thought about starting your own exchange, you’ll know it’s not simple. Building one from the ground up takes months of coding, large budgets, and a skilled tech team.
A Coinbase Clone Script changes all that. It’s a ready-made solution with the features you need to run a crypto exchange. You can customise it to suit your brand, launch it quickly, and start earning sooner.
Website:https://www.thecryptoape.c...
Email : infothecryptoape.com
But if you’ve ever thought about starting your own exchange, you’ll know it’s not simple. Building one from the ground up takes months of coding, large budgets, and a skilled tech team.
A Coinbase Clone Script changes all that. It’s a ready-made solution with the features you need to run a crypto exchange. You can customise it to suit your brand, launch it quickly, and start earning sooner.
Website:https://www.thecryptoape.c...
Email : infothecryptoape.com
4 months ago
Introducing CANNAPAIN – the new age of pain relief with the wisdom of Ayurveda + therapeutic cannabis
Designed to ease chronic pain, inflammation, and stress holistically.
Use This Discount Code To Get a 15% Offer DISCOUNT CODE: AYUSHO15
Call Us: +91 95664 46688
Mail Us: infoayushohealth.com
Buy now: https://ayushohealth.com/s...
Play Store: https://play.google.com/st...
App Store: https://apps.apple.com/mu/... #CannaCare #AyurvedicPainRelief #CannabisWellness #AyushoExclusive #CANNAPAIN10CAPS #CANNAPAIN #AyushoHealth
Designed to ease chronic pain, inflammation, and stress holistically.
Use This Discount Code To Get a 15% Offer DISCOUNT CODE: AYUSHO15
Call Us: +91 95664 46688
Mail Us: infoayushohealth.com
Buy now: https://ayushohealth.com/s...
Play Store: https://play.google.com/st...
App Store: https://apps.apple.com/mu/... #CannaCare #AyurvedicPainRelief #CannabisWellness #AyushoExclusive #CANNAPAIN10CAPS #CANNAPAIN #AyushoHealth
6 months ago
Serbia's populist President Aleksandar Vucic travelled to the Ukrainian city of Odesa for a regional summit on Wednesday, the first time the Moscow-friendly leader has visited the country during his 12 years in power.
Vucic travelled to Ukraine for one day to take part in the Ukraine-Southeastern Europe Summit in the Black Sea port of Odesa, which this week faced a major Russian drone and missile attack.
Senior politicians from 12 Southeastern European nations also took part in the summit, which was hosted by Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskiy.
At the summit, Vucic, who has previously met Zelenskiy at least three times, said Serbia could help Kyiv in the renewal of Ukraine's war-torn regions.
Vucic who balances relations between Russia and the West, said he abstained from signing the joint declaration at the summit, reflecting Serbia's bid to maintain good ties with both Kyiv and Moscow.
"By protecting our (Serbia's) interests I am partially protecting both Russian and Ukrainian interests alike ... as we are protecting interests of international ... law," he said in remarks to Serbian journalists.
The joint declaration supports Ukraine’s efforts to find a diplomatic path to a just and lasting peace, and includes a call to the international community to intensify its support for Kyiv and refrain from offering material or other assistance to Russia’s war effort.
Serbia wants to join the European Union, but Russia, a traditional Slavic and Orthodox Christian ally, remains its biggest gas supplier, and the country's sole oil refinery is majority-owned by Gazprom and Gazprom Neft.
Although Belgrade has refused to join Western sanctions on Russia over its invasion of Ukraine, it has condemned Moscow's policies in the United Nations and expressed support for Ukraine's territorial integrity.
Belgrade recognises Ukraine in its entirety, including territories seized by Russia since 2014, while Kyiv refused to recognise the 2008 independence of Kosovo, Serbia's predominantly Albanian former southern province.
In late May, the SVR, the Russian foreign intelligence service, accused Belgrade of "a stab in the back", alleging Serbia's defence manufacturers were selling ammunition and weapons to Ukraine via intermediaries.
According to a classified Pentagon document leaked online, Serbia in 2023 agreed to supply arms to Kyiv, despite the country's professed military neutrality. Moscow has criticised Belgrade several times over the issue. Serbia has denied it ever supplied arms to Ukraine but has said it has sold to other buyers worldwide.
The only Serbian president to visit Ukraine since the Balkan country became independent in 2006 was Boris Tadic in 2011. Ukraine's previous president, Petro Poroshenko, visited Serbia in 2018.
Vucic travelled to Ukraine for one day to take part in the Ukraine-Southeastern Europe Summit in the Black Sea port of Odesa, which this week faced a major Russian drone and missile attack.
Senior politicians from 12 Southeastern European nations also took part in the summit, which was hosted by Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskiy.
At the summit, Vucic, who has previously met Zelenskiy at least three times, said Serbia could help Kyiv in the renewal of Ukraine's war-torn regions.
Vucic who balances relations between Russia and the West, said he abstained from signing the joint declaration at the summit, reflecting Serbia's bid to maintain good ties with both Kyiv and Moscow.
"By protecting our (Serbia's) interests I am partially protecting both Russian and Ukrainian interests alike ... as we are protecting interests of international ... law," he said in remarks to Serbian journalists.
The joint declaration supports Ukraine’s efforts to find a diplomatic path to a just and lasting peace, and includes a call to the international community to intensify its support for Kyiv and refrain from offering material or other assistance to Russia’s war effort.
Serbia wants to join the European Union, but Russia, a traditional Slavic and Orthodox Christian ally, remains its biggest gas supplier, and the country's sole oil refinery is majority-owned by Gazprom and Gazprom Neft.
Although Belgrade has refused to join Western sanctions on Russia over its invasion of Ukraine, it has condemned Moscow's policies in the United Nations and expressed support for Ukraine's territorial integrity.
Belgrade recognises Ukraine in its entirety, including territories seized by Russia since 2014, while Kyiv refused to recognise the 2008 independence of Kosovo, Serbia's predominantly Albanian former southern province.
In late May, the SVR, the Russian foreign intelligence service, accused Belgrade of "a stab in the back", alleging Serbia's defence manufacturers were selling ammunition and weapons to Ukraine via intermediaries.
According to a classified Pentagon document leaked online, Serbia in 2023 agreed to supply arms to Kyiv, despite the country's professed military neutrality. Moscow has criticised Belgrade several times over the issue. Serbia has denied it ever supplied arms to Ukraine but has said it has sold to other buyers worldwide.
The only Serbian president to visit Ukraine since the Balkan country became independent in 2006 was Boris Tadic in 2011. Ukraine's previous president, Petro Poroshenko, visited Serbia in 2018.
6 months ago
US President Donald Trump told Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu to end the war in Gaza and stop talk of an attack on Iran, according to a source familiar with the conversation.
The two leaders spoke on the phone on Monday. Trump later said the call went “very well, very smooth.”
The call for Israel to change course comes as Washington pushes for a nuclear deal with Iran and engages in indirect talks with Hamas over a ceasefire in Gaza.
Netanyahu convened his top ministers Tuesday night after there was “some progress” in negotiations toward a ceasefire deal, according to his office. The purpose of the meeting was to give updates on the negotiations and discuss next steps.
Earlier in the day, Israeli Foreign Minister Gideon Sa’ar said there had been recent progress in ceasefire talks that also aim to bring back hostages held in Gaza.
“Israel is serious in its will to secure a hostage deal. There has recently been certain progress,” Sa’ar told a news conference in Jerusalem, adding that “in light of past experience, I don’t want to overstate it at this point.”
On Thursday, Hamas said it remains open to the ceasefire deal proposed by US envoy Steve Witkoff, but said it requires stronger guarantees against Israeli attacks.
In a televised speech on Thursday, Khalil Al-Hayya, a high-ranking official in the militant group, said Hamas has not rejected Witkoff’s proposal but has submitted amendments with stronger security guarantees.
Hamas wants any deal to include a permanent end to the war in Gaza and a withdrawal of Israeli forces.
Growing rift
Trump and Netanyahu appear increasingly at odds over the war in Gaza as the conflict passes the 20-month mark. Netanyahu has made clear that his war goals include the complete disarmament and removal of Hamas, while Trump has pushed for an end to the war.
It’s one of several major issues in the region where a growing rift is emerging between the US and Israel. In recent weeks, the Trump administration bypassed Israel on a trip to the Middle East, reached a ceasefire deal with the Iran-backed Houthis in Yemen that failed to halt their ballistic missile attacks at Israel, and lifted sanctions on Syria – even as Israel warns against legitimizing a regime run by former jihadists.
Meanwhile, Trump said his administration is “trying to make a deal so that there’s no destruction and death” in Iran. The sixth round of talks between the US and Iran is slated to start in the coming days.
During their call, Trump asked Netanyahu to stop talking about an attack on Iran, the source familiar with the conversation said, and halt the leaks and reports about plans and preparations for an Israeli attack on Iran’s nuclear facilities.
Netanyahu has repeatedly pushed for a military option to stop Iran’s nuclear program. In the conversation with Trump, Netanyahu told Trump that Iran is just trying to buy time and isn’t serious about negotiations, the source said. CNN reported last month that Israel was preparing for a possible strike on Iran’s nuclear facilities.
The Trump administration has also been trying to expand the Abraham Accords, the landmark series of agreements from Trump’s first term that saw Israel normalize relations with the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain and Morocco.
But Saudi Arabia – whose agreement to such a deal would be the ultimate prize – has repeatedly made clear that it will not normalize relations with Israel without concrete steps towards recognition of a Palestinian state and a plan to implement the two-state solution.
US Ambassador to Israel Mike Huckabee said this week that a two-state solution is no longer a goal of US policy, as it had been for decades of both Republican and Democrat administrations.
“Unless there are some significant things that happen that change the culture, there’s no room for it,” Huckabee told Bloomberg News in an interview in Jerusalem. He said it won’t happen “in our lifetime.” Huckabee has previously advocated for Israeli settlements in the occupied West Bank and once said that “there’s really no such thing as a Palestinian.”
Earlier in the war, Trump laid out vague plans for a “Gaza Riviera” that envisioned US control of the coastal enclave and the displacement of large parts of the Palestinian population living there.
The two leaders spoke on the phone on Monday. Trump later said the call went “very well, very smooth.”
The call for Israel to change course comes as Washington pushes for a nuclear deal with Iran and engages in indirect talks with Hamas over a ceasefire in Gaza.
Netanyahu convened his top ministers Tuesday night after there was “some progress” in negotiations toward a ceasefire deal, according to his office. The purpose of the meeting was to give updates on the negotiations and discuss next steps.
Earlier in the day, Israeli Foreign Minister Gideon Sa’ar said there had been recent progress in ceasefire talks that also aim to bring back hostages held in Gaza.
“Israel is serious in its will to secure a hostage deal. There has recently been certain progress,” Sa’ar told a news conference in Jerusalem, adding that “in light of past experience, I don’t want to overstate it at this point.”
On Thursday, Hamas said it remains open to the ceasefire deal proposed by US envoy Steve Witkoff, but said it requires stronger guarantees against Israeli attacks.
In a televised speech on Thursday, Khalil Al-Hayya, a high-ranking official in the militant group, said Hamas has not rejected Witkoff’s proposal but has submitted amendments with stronger security guarantees.
Hamas wants any deal to include a permanent end to the war in Gaza and a withdrawal of Israeli forces.
Growing rift
Trump and Netanyahu appear increasingly at odds over the war in Gaza as the conflict passes the 20-month mark. Netanyahu has made clear that his war goals include the complete disarmament and removal of Hamas, while Trump has pushed for an end to the war.
It’s one of several major issues in the region where a growing rift is emerging between the US and Israel. In recent weeks, the Trump administration bypassed Israel on a trip to the Middle East, reached a ceasefire deal with the Iran-backed Houthis in Yemen that failed to halt their ballistic missile attacks at Israel, and lifted sanctions on Syria – even as Israel warns against legitimizing a regime run by former jihadists.
Meanwhile, Trump said his administration is “trying to make a deal so that there’s no destruction and death” in Iran. The sixth round of talks between the US and Iran is slated to start in the coming days.
During their call, Trump asked Netanyahu to stop talking about an attack on Iran, the source familiar with the conversation said, and halt the leaks and reports about plans and preparations for an Israeli attack on Iran’s nuclear facilities.
Netanyahu has repeatedly pushed for a military option to stop Iran’s nuclear program. In the conversation with Trump, Netanyahu told Trump that Iran is just trying to buy time and isn’t serious about negotiations, the source said. CNN reported last month that Israel was preparing for a possible strike on Iran’s nuclear facilities.
The Trump administration has also been trying to expand the Abraham Accords, the landmark series of agreements from Trump’s first term that saw Israel normalize relations with the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain and Morocco.
But Saudi Arabia – whose agreement to such a deal would be the ultimate prize – has repeatedly made clear that it will not normalize relations with Israel without concrete steps towards recognition of a Palestinian state and a plan to implement the two-state solution.
US Ambassador to Israel Mike Huckabee said this week that a two-state solution is no longer a goal of US policy, as it had been for decades of both Republican and Democrat administrations.
“Unless there are some significant things that happen that change the culture, there’s no room for it,” Huckabee told Bloomberg News in an interview in Jerusalem. He said it won’t happen “in our lifetime.” Huckabee has previously advocated for Israeli settlements in the occupied West Bank and once said that “there’s really no such thing as a Palestinian.”
Earlier in the war, Trump laid out vague plans for a “Gaza Riviera” that envisioned US control of the coastal enclave and the displacement of large parts of the Palestinian population living there.
6 months ago
China can shrug off U.S. tech controls, thanks to open-source design and chip packaging techniques, says Huawei’s founder.
Huawei, the Chinese tech giant, has borne the brunt of U.S. restrictions since 2019, when Washington barred it from acquiring advanced components. Export controls passed in 2022 further constrained Huawei’s ability to get advanced chips.
But despite U.S. pressure, Huawei is returning to the forefront of China’s tech sector, with new successes in smartphones, AI processors, and EVs. Observers, in and out of China, see Huawei as proof that the country can succeed even if cut off from advanced technologies produced in the West.
Yet Huawei’s founder is cautioning against reading too much into the tech giant’s progress. Ren Zhengfei, in a Tuesday interview with People’s Daily, the Chinese Communist Party’s official newspaper, said that the U.S. was overstating Huawei’s successes. He suggested the company’s chips were still a generation behind those of the U.S.
“Huawei is not that great. We have to work hard to reach [the U.S.’s] evaluation,” he said.
Nevertheless, Ren batted away concerns that U.S. export controls will constrain the growth of both Huawei and the Chinese tech sector.
The Biden administration argued that chip export control measures would slow China’s tech development and maintain the U.S.’s edge in industries like AI. U.S. rules now bar Chinese companies from buying the most advanced chips, as well as the equipment and software needed to design and manufacture them.
Yet Ren countered that chip packaging and stacking techniques could help Chinese semiconductor firms keep up with the most advanced chips. (Stacking involves bundling multiple chips into a package to get higher performance.)
Ren also argued that an increasingly open-source environment will benefit the country in the future.
Chinese tech companies are reportedly embracing RISC-V, an open-source platform that can be used for chip design.
Several of China’s leading tech companies, like e-commerce giant Alibaba and startup DeepSeek, have also made their AI open-source, allowing other developers to download, run, and tweak the models themselves. That has encouraged more widespread adoption, including outside China.
Export controls to the fore
Ren’s comments come as export controls start to dominate U.S.-China trade conversations.
Trade officials from both countries are meeting in London for a second day of trade talks. The U.S. has accused China of slow-rolling its shipments of rare earths, critical minerals used in an array of sophisticated products, including smartphones and cars.
China holds a dominant position in the production of rare earths. Beijing restricted exports of these metals in April, requiring companies to apply for a license to export rare earths out of the country. These regulations are snarling supply chains for some manufacturers, particularly in the auto industry.
It’s an odd reversal of positions for the U.S., which increasingly uses export controls to leverage its edge in strategic technologies. Chinese officials have long complained about U.S. tech export restrictions, arguing–among other things–that they undermine globalization and threaten China’s development.
U.S. Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick is taking part in the London talks, which could be an indication that some U.S. restrictions could be up for negotiation.
Huawei, the Chinese tech giant, has borne the brunt of U.S. restrictions since 2019, when Washington barred it from acquiring advanced components. Export controls passed in 2022 further constrained Huawei’s ability to get advanced chips.
But despite U.S. pressure, Huawei is returning to the forefront of China’s tech sector, with new successes in smartphones, AI processors, and EVs. Observers, in and out of China, see Huawei as proof that the country can succeed even if cut off from advanced technologies produced in the West.
Yet Huawei’s founder is cautioning against reading too much into the tech giant’s progress. Ren Zhengfei, in a Tuesday interview with People’s Daily, the Chinese Communist Party’s official newspaper, said that the U.S. was overstating Huawei’s successes. He suggested the company’s chips were still a generation behind those of the U.S.
“Huawei is not that great. We have to work hard to reach [the U.S.’s] evaluation,” he said.
Nevertheless, Ren batted away concerns that U.S. export controls will constrain the growth of both Huawei and the Chinese tech sector.
The Biden administration argued that chip export control measures would slow China’s tech development and maintain the U.S.’s edge in industries like AI. U.S. rules now bar Chinese companies from buying the most advanced chips, as well as the equipment and software needed to design and manufacture them.
Yet Ren countered that chip packaging and stacking techniques could help Chinese semiconductor firms keep up with the most advanced chips. (Stacking involves bundling multiple chips into a package to get higher performance.)
Ren also argued that an increasingly open-source environment will benefit the country in the future.
Chinese tech companies are reportedly embracing RISC-V, an open-source platform that can be used for chip design.
Several of China’s leading tech companies, like e-commerce giant Alibaba and startup DeepSeek, have also made their AI open-source, allowing other developers to download, run, and tweak the models themselves. That has encouraged more widespread adoption, including outside China.
Export controls to the fore
Ren’s comments come as export controls start to dominate U.S.-China trade conversations.
Trade officials from both countries are meeting in London for a second day of trade talks. The U.S. has accused China of slow-rolling its shipments of rare earths, critical minerals used in an array of sophisticated products, including smartphones and cars.
China holds a dominant position in the production of rare earths. Beijing restricted exports of these metals in April, requiring companies to apply for a license to export rare earths out of the country. These regulations are snarling supply chains for some manufacturers, particularly in the auto industry.
It’s an odd reversal of positions for the U.S., which increasingly uses export controls to leverage its edge in strategic technologies. Chinese officials have long complained about U.S. tech export restrictions, arguing–among other things–that they undermine globalization and threaten China’s development.
U.S. Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick is taking part in the London talks, which could be an indication that some U.S. restrictions could be up for negotiation.
6 months ago
NATO member Poland has put on hold plans to buy 32 Black Hawk helicopters.
It suggested that Russia's invasion of Ukraine shows they're not the right weapon to focus on.
It's not abandoned helicopters, but they have proven vulnerable in Ukraine.
NATO member Poland has postponed its purchase of 32 S-70i Black Hawk helicopters, with military officials there suggesting the way Russia is fighting in Ukraine shows they're not the right equipment for it to focus on.
General Wieslaw Kukula, the Polish armed forces chief of staff, said at a Friday press conference that "we have decided to change the priorities of the helicopter programs" in order to "better adapt to the challenges of future warfare," Reuters reported.
Poland's deputy defense minister, Pawel Bejda, said on X that his country's military, pilots, and experts were analyzing the geopolitical situation, as well as "the war in Ukraine" and what Russia is buying and equipping its military with.
Poland shares a land border with Ukraine.
Grzegorz Polak, a spokesman for Poland's Armament Agency, which buys equipment for its military, told Reuters that its priorities needed "some correction" and that it might be necessary to buy other equipment instead of the helicopters, "such as drones, or tanks, or some kind of communication."
He also told Polish outlet Defence24 that the armed force's priorities have changed amid evolving threats.
Poland, like other European countries, has warned that Russia could attack elsewhere on the continent.
Its prime minister, Donald Tusk, warned in March that Russia's big military investments suggest it's readying for a conflict with someone bigger than Ukraine in the next three to four years.
Poland is already the highest spender on defense in NATO, as a proportion of its GDP, and has been a major ally of Ukraine throughout the invasion.
Helicopters over Ukraine
Helicopters have played a role in Russia's invasion, with both sides using them to counter drones, offer air support, and launch attacks.
It suggested that Russia's invasion of Ukraine shows they're not the right weapon to focus on.
It's not abandoned helicopters, but they have proven vulnerable in Ukraine.
NATO member Poland has postponed its purchase of 32 S-70i Black Hawk helicopters, with military officials there suggesting the way Russia is fighting in Ukraine shows they're not the right equipment for it to focus on.
General Wieslaw Kukula, the Polish armed forces chief of staff, said at a Friday press conference that "we have decided to change the priorities of the helicopter programs" in order to "better adapt to the challenges of future warfare," Reuters reported.
Poland's deputy defense minister, Pawel Bejda, said on X that his country's military, pilots, and experts were analyzing the geopolitical situation, as well as "the war in Ukraine" and what Russia is buying and equipping its military with.
Poland shares a land border with Ukraine.
Grzegorz Polak, a spokesman for Poland's Armament Agency, which buys equipment for its military, told Reuters that its priorities needed "some correction" and that it might be necessary to buy other equipment instead of the helicopters, "such as drones, or tanks, or some kind of communication."
He also told Polish outlet Defence24 that the armed force's priorities have changed amid evolving threats.
Poland, like other European countries, has warned that Russia could attack elsewhere on the continent.
Its prime minister, Donald Tusk, warned in March that Russia's big military investments suggest it's readying for a conflict with someone bigger than Ukraine in the next three to four years.
Poland is already the highest spender on defense in NATO, as a proportion of its GDP, and has been a major ally of Ukraine throughout the invasion.
Helicopters over Ukraine
Helicopters have played a role in Russia's invasion, with both sides using them to counter drones, offer air support, and launch attacks.
6 months ago
“Arriving In Months”: China’s 5th-Gen Stealth Fighter Ready For Pakistan; To Be Armed With PL-17 Missiles: Media
Pakistan is reportedly all set to induct the Chinese-origin FC-31 fifth-generation stealth fighter to bolster its air power, weeks after the Pakistani Air Force (PAF) engaged in a brief but intense clash with the Indian Air Force.
A senior unidentified Pakistani official told Janes that China will soon begin supplying the Pakistan Air Force (PAF) with its Shenyang FC-31 “Gyrfalcon” multirole stealth fighter aircraft.
The aircraft “will begin arriving within months,” and confirmed that PAF pilots are currently in China training to fly the aircraft, the official stated.
The FC-31 is believed to be the export variant of the J-35A, a fifth-generation stealth aircraft unveiled by China at the Zhuhai Air Show in November 2024.
The official did not reveal when the deal for the aircraft was signed or the specific number of aircraft that Pakistan is acquiring.
According to the publication, another Pakistani government insider informed it in May 2025 that the purchased FC-31 would be fitted with China’s PL-17 air-to-air missile (AAM), which has a range of 400 kilometers.
Islamabad first announced its intention to acquire an unspecified number of stealth fighter jets from China in January 2024. At the time, the then chief of the Pakistan Air Force, Air Chief Marshal Zaheer Ahmed Baber Sidhu, stated that the “foundation for acquiring the J-31 stealth fighter aircraft has already been laid,” and it’s set to become part of the PAF’s fleet shortly.”
Later, in December 2024, another set of reports stated that Islamabad is acquiring approximately 40 J-35A fighters, which are expected to be delivered within 24 months.
None of these reports and claims could be independently verified by the EurAsian Times, and the acquisition has not officially been confirmed by either the Pakistani or Chinese government.
Pakistan is the largest operator of Chinese military equipment outside the country. The PAF earlier inducted the Chinese J-10CE in 2022, an aircraft that was deployed in the conflict with India in May 2025.
The PAF claimed that it downed multiple IAF fighters, including three Rafales, using the deadly combination of J-10CE and PL-15E long-range missiles.
Sources in Pakistan have emphasised that the “success” of the J-10CE has reinforced Pakistan’s faith in Chinese aerospace technology and paved the way for more advanced acquisitions, like that of the FC-31.
Last month, some reports indicated that China was fast-tracking the delivery of the J-35A to Pakistan, following the finalisation of logistics and financing details by Pakistan’s Foreign Minister Ishaq Dar during his visit to China immediately after Operation Sindoor.
Notably, the FC-31 will be the first major Chinese military platform that Pakistan will induct after the military clash with India between May 7 and 10. Though it was planned well in advance and does not have a direct link to the conflict, the timing of the potential induction is significant, as a clearer picture of Pakistani military losses is now emerging.
According to reports by Indian media, the IAF destroyed six fighter jets, two high-value surveillance aircraft, one C-130 transport aircraft, over 30 missiles, and several unmanned aerial vehicles during the four-day conflict that ended in a ceasefire in the evening of May 10. The report cited technical analysis of operational data to back its claims.
If these claims are true, the PAF might need to add some serious air power to build capability against the Indian Air Force.
The induction of the Chinese fifth-generation aircraft is believed to be a pivotal moment for the PAF due to the aircraft’s cutting-edge technology and low-observable characteristics.
More notably, the aircraft will be equipped with the PL-17, which boasts a 400-kilometer range, a significant upgrade over the PL-15E that was “allegedly” used by the PAF to down Indian fighter jets.
The FC-31, developed by China’s Shenyang Aircraft Corporation (SAC) under the Aviation Industry Corporation of China (AVIC), is a single-seat, twin-engine, medium-sized fifth-generation fighter that features advanced stealth capabilities, including a low-observable design with forward-swept intake ramps, Diverterless Supersonic Inlet (DSI) bumps, and composite materials to evade L-band and Ku-band radars.
It is powered by WS-19 engines, which provide the aircraft with a thrust of 12 tons. The aircraft features two internal weapon bays, each with a capacity for two medium-range air-to-air missiles, and external hardpoints for various bombs and missiles, including air-to-ground and air-to-surface munitions.
Designed for air superiority, close air support, air interdiction, and precision strikes, the aircraft features an active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar and advanced sensor fusion for enhanced situational awareness.
The induction of this aircraft could tilt the regional balance in Pakistan’s favour, which explains China’s alacrity in exporting the aircraft to Islamabad.
Capability Gap In The Making
The acquisition is seen as a move to counter India’s air force, which currently relies on 4.5-generation fighters like the Rafale and Su-30MKI.
India is currently developing its own fifth-generation Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program, with the prototype expected to roll out by 2028.
However, if Pakistan starts inducting the FC-31 in the next few months, a glaring capability gap would persist for years until the AMCA is ready for induction.
A ten-year development plan laid down by India, five prototypes, and extensive flight testing are on the cards. However, India’s indigenous aircraft programs are notorious for delays, creating uncertainty and suspicion.
Some experts believe that the acquisition of a Chinese fifth-generation stealth aircraft by Pakistan would pose a threat to India.
A stealth fighter can significantly alter the regional balance. Stealth fighters have a much smaller radar cross section (RCS) than non-stealth fighters. Since fighter detection and tracking are radar-based, the reduced RCS degrades the adversary’s air defense capability.
Indian Air Force veteran and military expert, Squadron Leader Vijainder K. Thakur (retd), earlier argued: “Air defense systems’ performance degrades when operating against stealth fighters because of their lower detection range. While the extent of degradation depends on the effectiveness of stealth shaping, it always occurs.”
“China is known to have developed air-to-air and air-to-ground missiles that will allow the J-35A fighters to launch their weapons before they can be effectively tracked on IAF radars,” he added.
The situation becomes much worse for India, as its other adversary, China, already operates more than 200 J-20 fifth-generation stealth fighters and is now flying two different prototypes of sixth-generation jets, namely the J-36 and J-50.
By the time India operationalises the AMCA, China would have significantly increased its fleet of J-20s and possibly inducted a sixth-generation aircraft. Meanwhile, Pakistan would be operating about 30-40 FC-31. In addition to that, Islamabad is also reportedly participating in the Turkish KAAN fifth-generation aircraft program.
This has already divided the Indian strategic community, with one section asserting that there is a need to buy a fifth-generation aircraft, such as the Su-57, as an interim solution. Several experts have pointed out that the Russian offer could be considered, as it would entail both local production and assistance with the AMCA.
“If India wants to maintain the AMCA program in the long run, it needs an interim fighter, and the Su-57 may be the better choice,” Indian Air Force veteran, Air Marshal Anil Chopra (retd) argued. “It may be worthwhile to quickly build a large inventory of 4.5-generation fighters like LCA Mk2 and Rafale and acquire long-range Air-to-surface missiles (BrahMos II) and longer-range AAMs like Astra III or Russian R-37M.”
However, some former IAF leaders remain skeptical. Former IAF chief RKS Bhadauria recently suggested that India should not import any aircraft and instead focus on the AMCA.
“Now, the government has put its faith in AMCA, and now we need to do everything as a nation to expedite AMCA,” Bhadauria said. “That cause of concern in terms of what Pakistan is going to get from China in the interim — be it J-20 or J-35 — let them get these. That will be studied. What is important is in the interim, how do you handle these threats, and there are ways and means of tackling this threat that they will have.”
For now, it is safe to say that Pakistan is once again beating India to the induction of an advanced next-generation aircraft, a trend that has been visible since the mid-1950s, when the two countries began building their air power.
Pakistan is reportedly all set to induct the Chinese-origin FC-31 fifth-generation stealth fighter to bolster its air power, weeks after the Pakistani Air Force (PAF) engaged in a brief but intense clash with the Indian Air Force.
A senior unidentified Pakistani official told Janes that China will soon begin supplying the Pakistan Air Force (PAF) with its Shenyang FC-31 “Gyrfalcon” multirole stealth fighter aircraft.
The aircraft “will begin arriving within months,” and confirmed that PAF pilots are currently in China training to fly the aircraft, the official stated.
The FC-31 is believed to be the export variant of the J-35A, a fifth-generation stealth aircraft unveiled by China at the Zhuhai Air Show in November 2024.
The official did not reveal when the deal for the aircraft was signed or the specific number of aircraft that Pakistan is acquiring.
According to the publication, another Pakistani government insider informed it in May 2025 that the purchased FC-31 would be fitted with China’s PL-17 air-to-air missile (AAM), which has a range of 400 kilometers.
Islamabad first announced its intention to acquire an unspecified number of stealth fighter jets from China in January 2024. At the time, the then chief of the Pakistan Air Force, Air Chief Marshal Zaheer Ahmed Baber Sidhu, stated that the “foundation for acquiring the J-31 stealth fighter aircraft has already been laid,” and it’s set to become part of the PAF’s fleet shortly.”
Later, in December 2024, another set of reports stated that Islamabad is acquiring approximately 40 J-35A fighters, which are expected to be delivered within 24 months.
None of these reports and claims could be independently verified by the EurAsian Times, and the acquisition has not officially been confirmed by either the Pakistani or Chinese government.
Pakistan is the largest operator of Chinese military equipment outside the country. The PAF earlier inducted the Chinese J-10CE in 2022, an aircraft that was deployed in the conflict with India in May 2025.
The PAF claimed that it downed multiple IAF fighters, including three Rafales, using the deadly combination of J-10CE and PL-15E long-range missiles.
Sources in Pakistan have emphasised that the “success” of the J-10CE has reinforced Pakistan’s faith in Chinese aerospace technology and paved the way for more advanced acquisitions, like that of the FC-31.
Last month, some reports indicated that China was fast-tracking the delivery of the J-35A to Pakistan, following the finalisation of logistics and financing details by Pakistan’s Foreign Minister Ishaq Dar during his visit to China immediately after Operation Sindoor.
Notably, the FC-31 will be the first major Chinese military platform that Pakistan will induct after the military clash with India between May 7 and 10. Though it was planned well in advance and does not have a direct link to the conflict, the timing of the potential induction is significant, as a clearer picture of Pakistani military losses is now emerging.
According to reports by Indian media, the IAF destroyed six fighter jets, two high-value surveillance aircraft, one C-130 transport aircraft, over 30 missiles, and several unmanned aerial vehicles during the four-day conflict that ended in a ceasefire in the evening of May 10. The report cited technical analysis of operational data to back its claims.
If these claims are true, the PAF might need to add some serious air power to build capability against the Indian Air Force.
The induction of the Chinese fifth-generation aircraft is believed to be a pivotal moment for the PAF due to the aircraft’s cutting-edge technology and low-observable characteristics.
More notably, the aircraft will be equipped with the PL-17, which boasts a 400-kilometer range, a significant upgrade over the PL-15E that was “allegedly” used by the PAF to down Indian fighter jets.
The FC-31, developed by China’s Shenyang Aircraft Corporation (SAC) under the Aviation Industry Corporation of China (AVIC), is a single-seat, twin-engine, medium-sized fifth-generation fighter that features advanced stealth capabilities, including a low-observable design with forward-swept intake ramps, Diverterless Supersonic Inlet (DSI) bumps, and composite materials to evade L-band and Ku-band radars.
It is powered by WS-19 engines, which provide the aircraft with a thrust of 12 tons. The aircraft features two internal weapon bays, each with a capacity for two medium-range air-to-air missiles, and external hardpoints for various bombs and missiles, including air-to-ground and air-to-surface munitions.
Designed for air superiority, close air support, air interdiction, and precision strikes, the aircraft features an active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar and advanced sensor fusion for enhanced situational awareness.
The induction of this aircraft could tilt the regional balance in Pakistan’s favour, which explains China’s alacrity in exporting the aircraft to Islamabad.
Capability Gap In The Making
The acquisition is seen as a move to counter India’s air force, which currently relies on 4.5-generation fighters like the Rafale and Su-30MKI.
India is currently developing its own fifth-generation Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program, with the prototype expected to roll out by 2028.
However, if Pakistan starts inducting the FC-31 in the next few months, a glaring capability gap would persist for years until the AMCA is ready for induction.
A ten-year development plan laid down by India, five prototypes, and extensive flight testing are on the cards. However, India’s indigenous aircraft programs are notorious for delays, creating uncertainty and suspicion.
Some experts believe that the acquisition of a Chinese fifth-generation stealth aircraft by Pakistan would pose a threat to India.
A stealth fighter can significantly alter the regional balance. Stealth fighters have a much smaller radar cross section (RCS) than non-stealth fighters. Since fighter detection and tracking are radar-based, the reduced RCS degrades the adversary’s air defense capability.
Indian Air Force veteran and military expert, Squadron Leader Vijainder K. Thakur (retd), earlier argued: “Air defense systems’ performance degrades when operating against stealth fighters because of their lower detection range. While the extent of degradation depends on the effectiveness of stealth shaping, it always occurs.”
“China is known to have developed air-to-air and air-to-ground missiles that will allow the J-35A fighters to launch their weapons before they can be effectively tracked on IAF radars,” he added.
The situation becomes much worse for India, as its other adversary, China, already operates more than 200 J-20 fifth-generation stealth fighters and is now flying two different prototypes of sixth-generation jets, namely the J-36 and J-50.
By the time India operationalises the AMCA, China would have significantly increased its fleet of J-20s and possibly inducted a sixth-generation aircraft. Meanwhile, Pakistan would be operating about 30-40 FC-31. In addition to that, Islamabad is also reportedly participating in the Turkish KAAN fifth-generation aircraft program.
This has already divided the Indian strategic community, with one section asserting that there is a need to buy a fifth-generation aircraft, such as the Su-57, as an interim solution. Several experts have pointed out that the Russian offer could be considered, as it would entail both local production and assistance with the AMCA.
“If India wants to maintain the AMCA program in the long run, it needs an interim fighter, and the Su-57 may be the better choice,” Indian Air Force veteran, Air Marshal Anil Chopra (retd) argued. “It may be worthwhile to quickly build a large inventory of 4.5-generation fighters like LCA Mk2 and Rafale and acquire long-range Air-to-surface missiles (BrahMos II) and longer-range AAMs like Astra III or Russian R-37M.”
However, some former IAF leaders remain skeptical. Former IAF chief RKS Bhadauria recently suggested that India should not import any aircraft and instead focus on the AMCA.
“Now, the government has put its faith in AMCA, and now we need to do everything as a nation to expedite AMCA,” Bhadauria said. “That cause of concern in terms of what Pakistan is going to get from China in the interim — be it J-20 or J-35 — let them get these. That will be studied. What is important is in the interim, how do you handle these threats, and there are ways and means of tackling this threat that they will have.”
For now, it is safe to say that Pakistan is once again beating India to the induction of an advanced next-generation aircraft, a trend that has been visible since the mid-1950s, when the two countries began building their air power.
6 months ago
China is drawing up plans to order hundreds of Airbus planes as Xi Jinping seeks to build closer ties with Europe.
Beijing is in talks with the European aerospace giant to order up to 500 jets against the backdrop of the trade war with the US.
If completed, the order could be announced at a summit in the Chinese capital next month where Xi will host Friedrich Merz, the new German chancellor, and Emmanuel Macron, the president of France, as first reported by Bloomberg.
Ursula von der Leyen, the president of the European Commission, and Antonio Costa, the EU Council chief, are also expected to attend in a sign of the bloc’s increased willingness to forge a closer relationship with China.
It comes amid heightened trade tensions between China and the US, with Beijing recently banning its airlines from buying jets from Boeing. That followed Donald Trump’s decision to impose aggressive tariffs on China.
The potential 500-plane deal between China and Airbus would pile further pressure on Boeing, which has battled to rebuild its reputation after one of its doors blew out last year.
The proposed agreement would be one of the largest single orders of commercial aircraft ever. The current record is held by Indian airline IndiGo, which ordered 500 Airbus planes in 2023.
It would likely be China’s largest order ever too, overtaking the $37bn (£27bn) spent on 300 Airbus jets three years ago.
The deal highlights China’s lingering dependence on imported planes despite its attempts to build up its own aerospace industry.
The C919, a rival to the 737 developed by local plane maker Comac, has won only a handful of export deals.
Boeing has what it calls a completion and delivery centre in China but no actual production line there.
That is in contrast to Airbus, which operates two final assembly lines for narrow-body jets in the city of Tianjin, 70 miles from Beijing.
China has long sought to limit its trade with Boeing, notably becoming the first country in the world to ground its 737 Max planes in the wake of two deadly crashes involving the jets in 2019.
It was also one of the last to allow the plane to re-enter service, which led some Chinese airlines to abandon orders.
Beijing is in talks with the European aerospace giant to order up to 500 jets against the backdrop of the trade war with the US.
If completed, the order could be announced at a summit in the Chinese capital next month where Xi will host Friedrich Merz, the new German chancellor, and Emmanuel Macron, the president of France, as first reported by Bloomberg.
Ursula von der Leyen, the president of the European Commission, and Antonio Costa, the EU Council chief, are also expected to attend in a sign of the bloc’s increased willingness to forge a closer relationship with China.
It comes amid heightened trade tensions between China and the US, with Beijing recently banning its airlines from buying jets from Boeing. That followed Donald Trump’s decision to impose aggressive tariffs on China.
The potential 500-plane deal between China and Airbus would pile further pressure on Boeing, which has battled to rebuild its reputation after one of its doors blew out last year.
The proposed agreement would be one of the largest single orders of commercial aircraft ever. The current record is held by Indian airline IndiGo, which ordered 500 Airbus planes in 2023.
It would likely be China’s largest order ever too, overtaking the $37bn (£27bn) spent on 300 Airbus jets three years ago.
The deal highlights China’s lingering dependence on imported planes despite its attempts to build up its own aerospace industry.
The C919, a rival to the 737 developed by local plane maker Comac, has won only a handful of export deals.
Boeing has what it calls a completion and delivery centre in China but no actual production line there.
That is in contrast to Airbus, which operates two final assembly lines for narrow-body jets in the city of Tianjin, 70 miles from Beijing.
China has long sought to limit its trade with Boeing, notably becoming the first country in the world to ground its 737 Max planes in the wake of two deadly crashes involving the jets in 2019.
It was also one of the last to allow the plane to re-enter service, which led some Chinese airlines to abandon orders.
6 months ago
Chinese Web Around U.S. Military Bases Worries Americans; Is Ukraine’s ‘Shock’ Attack On Russia A Wake-Up Call For Trump?
The surprise Ukrainian drone attack on Russia, facilitated by the smuggling of drones inside trucks, has rattled the world at large. American analysts and lawmakers are now concerned that Chinese cargo ships that dock at U.S. ports could potentially carry out a similar stunt against the United States.
The Security Service of Ukraine, or SBU, launched the drone attacks on multiple Russian military bases on June 1 under ‘Operation Spiderweb.’ The operation involved 117 First Person View (FPV) drones that were smuggled into Russia, concealed in wooden containers with remotely operated roofs mounted on trucks.
These trucks, driven by individuals reportedly unaware of the cargo they were carrying, were positioned near the target air bases to ensure precision strikes.
Russia couldn’t have fathomed that an infiltration like that was taking place right under its nose. The strikes, meticulously planned over 18 months, humiliated Russia’s military by exposing the gaps in its intelligence architecture and the vulnerabilities in its air defenses.
Caught unaware, the Russian military sustained losses of billions of dollars. In the aftermath of the incident, several pro-Russian military bloggers said it was Russia’s Pearl Harbor, a reference to the surprise Japanese attack on the US Pearl Harbor port during World War II, that destroyed multiple US warships and aircraft.
The attack, perhaps the most significant demonstration of asymmetric warfare in recent times, will have far-reaching global repercussions. US analysts are concerned that China could replicate a similar move against America, utilizing its cargo ships that have unrestricted access to US ports, as highlighted by Newsweek in a recent report.
The report noted that lawmakers and security experts have expressed concerns over China’s state-owned shipping behemoth, COSCO Shipping, operating across US ports, despite being classified as a Chinese military enterprise by the Pentagon in January 2025.
US analysts have voiced concern that these cargo ships could be used to deploy drones, possibly hidden inside ships, to launch a preemptive strike on US ports in the event of a conflict.
COSCO is the largest state-owned shipping firm in China and a significant force in international marine logistics, with a considerable presence in important US ports, including Oakland, Long Beach, and Los Angeles, among others.
In January 2025, the House Committee on Homeland Security expressed concern about COSCO’s access to major US ports and the alleged presence of suspected Chinese Communist Party (CCP) political officers on board its ships, suggesting direct CCP influence. It warned of threats like espionage, cyber intrusion, or even sabotage by the Chinese.
The Trump administration has imposed port fees on COSCO to challenge China’s hegemony in the world’s shipbuilding industry. Additionally, the recently imposed US tariffs, including a 145% tariff on Chinese goods, have led to a sharp decline in COSCO’s shipments to American ports.
For example, the Port of Los Angeles saw a 35% plunge in cargo volume in May 2025, with COSCO and other carriers canceling transits.
Notably, a temporary US-China tariff truce last month spurred a surge in bookings, but COSCO continues to face operational challenges due to fees and reduced demand.
Despite COSCO’s reduced presence in the US, US analysts remain suspicious. Retired Navy Commander Thomas Shugart and a fellow at the Center for a New American Security said: “It is becoming borderline-insane that we routinely allow ships owned and operated by DoD-designated Chinese military companies to sit in our ports with thousands of containers onboard and under their control.”
While a Chinese attack is unlikely without an existing state of war, the presence of COSCO vessels near critical infrastructure, like the Norfolk Naval Station, raises concerns about espionage or sabotage.
It is pertinent to note that even the Ukrainian operation took 18 months of planning and intelligence gathering to achieve the desired result.
Moreover, there have been suggestive reports about China spying on US military facilities by purchasing land nearby and even infiltrating the US port infrastructure in the past, which makes the threat of a Ukraine drone-like attack more plausible to some in the US.
Chinese Spying Concerns Loom Large
Chinese ships docking at US ports have been a matter of discourse in the US for quite some time. Last year, a US Congressional investigation discovered that a Chinese business installed intelligence-gathering equipment on cranes used at US seaports, potentially enabling Beijing to spy on Americans or damage vital infrastructure.
ZPMC, a state-owned engineering company based in Shanghai, exerted pressure on American port authorities to grant remote access to its cranes, specifically those situated on the West Coast, i.e., the contiguous states of California, Oregon, and Washington.
The report, produced after a year-long research, warned that “This access could potentially be extended to other [People’s Republic of China] government entities, posing a significant risk due to the PRC’s national security laws that mandate cooperation with state intelligence agencies.”
Citing contract paperwork and testimonies from port operators, the investigation stated that “these unknown modems were believed to have been installed under the auspices of collecting usage data for the equipment.” These modems allegedly employed a covert approach to gathering data and circumventing firewalls, which could potentially disrupt port operations, even though they were unnecessary for the cranes to operate.
At the time, these findings caused alarm because about 80% of the cargo cranes in American ports are owned by ZPMC.
Transporting goods through US marine ports, which generate trillions of dollars in economic activity every year, requires ship-to-shore cranes. However, because these cranes can often be controlled remotely, anyone with access to the networks may be able to collect intelligence from ports or damage equipment.
In a hypothetical scenario, the intelligence collected through the cranes could be used to launch an ‘Operation Spiderweb’ type of operation where Chinese cargos double up as carriers of drones that go off by flicking a button on a remote.
Earlier, the White House disclosed plans to “phase out Chinese-made port equipment and fully return crane making to the United States to deal with 200 Chinese-made cranes at U.S. ports and facilities”. However, the progress of that effort under the Trump administration remains unknown.
Another prevailing concern in the United States has been the ownership of farm and commercial land near US military facilities by Chinese people and corporations.
A previous report revealed that Chinese companies purchased several farmlands close to strategic US military installations, including some of the most strategically important military installations, such as MacDill Air Force Base in Tampa, Florida; Marine Corps Base Camp Pendleton in San Diego, California; Fort Liberty (formerly Fort Bragg) in Fayetteville, North Carolina; and Fort Cavazos (formerly Fort Hood) in Killeen, Texas.
Sources suggest that under the guise of farming, Chinese landowners could potentially set up surveillance equipment or use drones to monitor military sites. According to the January 2024 data from the US Department of Agriculture, China claims 349,442 acres out of roughly 40 million acres of foreign-owned farmland, or 0.87 percent.
It does not help that Chinese nationals have sneaked into military bases and other sensitive US sites more than 100 times in recent years, as the Wall Street Journal reported in 2023. This raises a very alarming issue regarding Chinese ownership of land near military sites.
Additionally, the US National Association of Realtors (NAR) stated in a report last year that the Chinese have remained the top foreign buyers of US residential property for the 11th consecutive year.
Experts caution that, just as Ukraine’s drones targeted Russian airfields, Chinese-owned property may be used for tracking devices, reconnaissance sites, or drones to observe US military activities.
The strategic placement of these lands near bases like Fort Liberty, which hosts critical airborne and special operations units, amplifies concerns about a surprise threat akin to Pearl Harbor’s unexpected attack.
Although no US federal law mandates a ban, individual states have been passing laws to curtail Chinese ownership of land near US military bases.
The surprise Ukrainian drone attack on Russia, facilitated by the smuggling of drones inside trucks, has rattled the world at large. American analysts and lawmakers are now concerned that Chinese cargo ships that dock at U.S. ports could potentially carry out a similar stunt against the United States.
The Security Service of Ukraine, or SBU, launched the drone attacks on multiple Russian military bases on June 1 under ‘Operation Spiderweb.’ The operation involved 117 First Person View (FPV) drones that were smuggled into Russia, concealed in wooden containers with remotely operated roofs mounted on trucks.
These trucks, driven by individuals reportedly unaware of the cargo they were carrying, were positioned near the target air bases to ensure precision strikes.
Russia couldn’t have fathomed that an infiltration like that was taking place right under its nose. The strikes, meticulously planned over 18 months, humiliated Russia’s military by exposing the gaps in its intelligence architecture and the vulnerabilities in its air defenses.
Caught unaware, the Russian military sustained losses of billions of dollars. In the aftermath of the incident, several pro-Russian military bloggers said it was Russia’s Pearl Harbor, a reference to the surprise Japanese attack on the US Pearl Harbor port during World War II, that destroyed multiple US warships and aircraft.
The attack, perhaps the most significant demonstration of asymmetric warfare in recent times, will have far-reaching global repercussions. US analysts are concerned that China could replicate a similar move against America, utilizing its cargo ships that have unrestricted access to US ports, as highlighted by Newsweek in a recent report.
The report noted that lawmakers and security experts have expressed concerns over China’s state-owned shipping behemoth, COSCO Shipping, operating across US ports, despite being classified as a Chinese military enterprise by the Pentagon in January 2025.
US analysts have voiced concern that these cargo ships could be used to deploy drones, possibly hidden inside ships, to launch a preemptive strike on US ports in the event of a conflict.
COSCO is the largest state-owned shipping firm in China and a significant force in international marine logistics, with a considerable presence in important US ports, including Oakland, Long Beach, and Los Angeles, among others.
In January 2025, the House Committee on Homeland Security expressed concern about COSCO’s access to major US ports and the alleged presence of suspected Chinese Communist Party (CCP) political officers on board its ships, suggesting direct CCP influence. It warned of threats like espionage, cyber intrusion, or even sabotage by the Chinese.
The Trump administration has imposed port fees on COSCO to challenge China’s hegemony in the world’s shipbuilding industry. Additionally, the recently imposed US tariffs, including a 145% tariff on Chinese goods, have led to a sharp decline in COSCO’s shipments to American ports.
For example, the Port of Los Angeles saw a 35% plunge in cargo volume in May 2025, with COSCO and other carriers canceling transits.
Notably, a temporary US-China tariff truce last month spurred a surge in bookings, but COSCO continues to face operational challenges due to fees and reduced demand.
Despite COSCO’s reduced presence in the US, US analysts remain suspicious. Retired Navy Commander Thomas Shugart and a fellow at the Center for a New American Security said: “It is becoming borderline-insane that we routinely allow ships owned and operated by DoD-designated Chinese military companies to sit in our ports with thousands of containers onboard and under their control.”
While a Chinese attack is unlikely without an existing state of war, the presence of COSCO vessels near critical infrastructure, like the Norfolk Naval Station, raises concerns about espionage or sabotage.
It is pertinent to note that even the Ukrainian operation took 18 months of planning and intelligence gathering to achieve the desired result.
Moreover, there have been suggestive reports about China spying on US military facilities by purchasing land nearby and even infiltrating the US port infrastructure in the past, which makes the threat of a Ukraine drone-like attack more plausible to some in the US.
Chinese Spying Concerns Loom Large
Chinese ships docking at US ports have been a matter of discourse in the US for quite some time. Last year, a US Congressional investigation discovered that a Chinese business installed intelligence-gathering equipment on cranes used at US seaports, potentially enabling Beijing to spy on Americans or damage vital infrastructure.
ZPMC, a state-owned engineering company based in Shanghai, exerted pressure on American port authorities to grant remote access to its cranes, specifically those situated on the West Coast, i.e., the contiguous states of California, Oregon, and Washington.
The report, produced after a year-long research, warned that “This access could potentially be extended to other [People’s Republic of China] government entities, posing a significant risk due to the PRC’s national security laws that mandate cooperation with state intelligence agencies.”
Citing contract paperwork and testimonies from port operators, the investigation stated that “these unknown modems were believed to have been installed under the auspices of collecting usage data for the equipment.” These modems allegedly employed a covert approach to gathering data and circumventing firewalls, which could potentially disrupt port operations, even though they were unnecessary for the cranes to operate.
At the time, these findings caused alarm because about 80% of the cargo cranes in American ports are owned by ZPMC.
Transporting goods through US marine ports, which generate trillions of dollars in economic activity every year, requires ship-to-shore cranes. However, because these cranes can often be controlled remotely, anyone with access to the networks may be able to collect intelligence from ports or damage equipment.
In a hypothetical scenario, the intelligence collected through the cranes could be used to launch an ‘Operation Spiderweb’ type of operation where Chinese cargos double up as carriers of drones that go off by flicking a button on a remote.
Earlier, the White House disclosed plans to “phase out Chinese-made port equipment and fully return crane making to the United States to deal with 200 Chinese-made cranes at U.S. ports and facilities”. However, the progress of that effort under the Trump administration remains unknown.
Another prevailing concern in the United States has been the ownership of farm and commercial land near US military facilities by Chinese people and corporations.
A previous report revealed that Chinese companies purchased several farmlands close to strategic US military installations, including some of the most strategically important military installations, such as MacDill Air Force Base in Tampa, Florida; Marine Corps Base Camp Pendleton in San Diego, California; Fort Liberty (formerly Fort Bragg) in Fayetteville, North Carolina; and Fort Cavazos (formerly Fort Hood) in Killeen, Texas.
Sources suggest that under the guise of farming, Chinese landowners could potentially set up surveillance equipment or use drones to monitor military sites. According to the January 2024 data from the US Department of Agriculture, China claims 349,442 acres out of roughly 40 million acres of foreign-owned farmland, or 0.87 percent.
It does not help that Chinese nationals have sneaked into military bases and other sensitive US sites more than 100 times in recent years, as the Wall Street Journal reported in 2023. This raises a very alarming issue regarding Chinese ownership of land near military sites.
Additionally, the US National Association of Realtors (NAR) stated in a report last year that the Chinese have remained the top foreign buyers of US residential property for the 11th consecutive year.
Experts caution that, just as Ukraine’s drones targeted Russian airfields, Chinese-owned property may be used for tracking devices, reconnaissance sites, or drones to observe US military activities.
The strategic placement of these lands near bases like Fort Liberty, which hosts critical airborne and special operations units, amplifies concerns about a surprise threat akin to Pearl Harbor’s unexpected attack.
Although no US federal law mandates a ban, individual states have been passing laws to curtail Chinese ownership of land near US military bases.
6 months ago
3 Months After Tragic FA-50 Crash, The Philippines Signs Deal For 12 More Fighter Jets, Doubling Its Fleet
Amid rising security challenges in the South China Sea and Beijing’s increasing muscle flexing, the Philippines has decided to double its fleet of South Korean FA-50 fighter jets, signing a contract for 12 additional aircraft, following its initial purchase of 12 jets in 2014.
Notably, the deal was signed despite the Philippines grounding its entire FA-50 fleet earlier this year following the crash of an aircraft during a mission against communist rebels in March, in which two pilots were killed.
With ongoing tensions in the South China Sea (known as the West Philippines Sea in Manila), the Philippines intends to acquire 12 more light aircraft from South Korea at a cost of P40 billion (US$690 million), significantly enhancing its air capability.
However, questions were raised on the capability of the aircraft after the March crash. Now, these questions have been put to rest with the announcement of an additional order for 12 more aircraft.
“The Philippines has signed a contract for 12 more FA-50 fighter jets,” its South Korean manufacturer said on June 4.
Korea Aerospace Industries (KAI) valued the deal with the Department of National Defense at $700 million, with delivery of the jets to be completed by 2030. The Philippines, which has yet to confirm the pact, previously purchased a dozen of the light warplanes in 2014.
In a statement, the South Korean firm said the fighter jets would feature enhanced capabilities including “aerial refueling for extended range, (Active Electronically Scanned Array) radar, and advanced air-to-air and air-to-ground weapons systems”.
One of the Philippines’ original fleet of FA-50s went missing on March 4 while on a mission to provide air support for troops fighting guerrillas in a mountainous area of the southern island of Mindanao.
Rescuers found the wreckage of the plane and the bodies of two crewmen a day later.
After temporarily grounding the fleet, the Philippine Air Force ruled out any mechanical problems with the aircraft.
Air Force spokeswoman Maria Consuelo Castillo told a press conference in April that a confluence of factors had contributed to the crash, including mountainous terrain and visibility issues.
Castillo said in March that the purchase of additional FA-50s was under consideration by the defence department.
The Philippines has extensively used its FA-50 fleet in the fight against the Islamic State in 2017, called the “Marawi Siege,” and it was dubbed a “game changer” by the PAF officials. Currently, the fighter jets are also used in operations against the Communist rebels.
The Philippines is also using the jets in patrolling missions in the contested South China Sea.
In February this year, the Philippines’ FA-50 fighter jet fleet also took part in drills over the West Philippine Sea with the US B-1 “Lancer” bombers.
The exercise included maneuvering the aircraft within the Philippines’ exclusive economic zone (EEZ). The exercise aimed to strengthen interoperability between the two air forces, enhance air domain awareness, and improve agile combat employment capabilities.
The FA-50, a modern light combat aircraft, represents the PAF’s first line of defense in maintaining air superiority over the contested areas.
The latest FA-50 purchase comes at a time when the Philippines has virtually been pushed to the wall in the South China Sea. China has been conducting aggressive maneuvers against Filipino forces in disputed territories, occasionally assaulting and expelling them from waters that China considers its “territorial waters.”
Currently, the FA-50 is the only combat-capable aircraft in the PAF’s inventory. In fact, the service had earlier considered deploying the FA-50 to escort its patrol aircraft over the South China Sea last year. The FA-50 is based on the T-50, a trainer aircraft capable of supersonic flight that was modified from the F-16 to train pilots for the KF-16 and F-15K.
The FA-50 is predominantly designed for air defense, strike, and jet training missions.
Expanding Military Shopping List Of The Philippines
Manila is rapidly modernizing its armed forces to deter China and enhance its combat capability. The Philippines Department of National Defense (DND) earlier stated that it plans to buy 40 multi-role fighter jets, among other sophisticated weapon systems. Two aircraft have been offered to the country: the Saab Gripen-E and Lockheed Martin’s F-16 Block 70/72.
Notably, the latest FA-50 acquisition comes amid warnings from military analysts that the PAF is arguably the country’s least robust military component, highlighting the need for at least a dozen squadrons of multirole jets to protect the archipelago’s airspace effectively.
Earlier, the Philippines’ DND also confirmed that a P6.5 billion (US$110 million) deal for six Embraer Super Tucano light attack aircraft for the PAF’s 15th Strike Wing was signed in December 2024. The purchase is meant to reinforce the PAF fleet in the wake of the gap left by the decommissioning of the last two remaining Rockwell OV-10 Bronco light attack aircraft and two AH-1S Cobra attack helicopters.
In addition, the DND has announced the P1 billion (US$17 million) purchase of an aeromedical Bell 412 EPX helicopter for the Philippine Army’s use in emergency medical missions.
The country has also planned upgrades for various cyber systems of the Armed Forces of the Philippines, as well as enhancements for the PAF’s ground-based air defense system and the introduction of new missiles.
In addition to the above-mentioned systems, the Philippines is reportedly considering the purchase of nine BrahMos missile batteries for its Army.
If finalized, this would be Manila’s second order of the BrahMos missile. In 2022, the Philippines signed a US$375 million deal with India for three batteries of the shore-based, anti-ship variant of the BrahMos missile for its naval forces.
Last year, Manila said it wanted to acquire the US Typhon mid-range missile system to bolster external defense capabilities.
Cornered by the PLA forces in the South China Sea, Manila is committed to spending at least 1.894 trillion pesos (approximately US$33.74 billion) to modernize and enhance its military capabilities by acquiring new systems, upgrading existing ones, and improving military infrastructure.
The deal for 12 additional FA-50 fighter jets will add crucial capabilities to the PAF.
Amid rising security challenges in the South China Sea and Beijing’s increasing muscle flexing, the Philippines has decided to double its fleet of South Korean FA-50 fighter jets, signing a contract for 12 additional aircraft, following its initial purchase of 12 jets in 2014.
Notably, the deal was signed despite the Philippines grounding its entire FA-50 fleet earlier this year following the crash of an aircraft during a mission against communist rebels in March, in which two pilots were killed.
With ongoing tensions in the South China Sea (known as the West Philippines Sea in Manila), the Philippines intends to acquire 12 more light aircraft from South Korea at a cost of P40 billion (US$690 million), significantly enhancing its air capability.
However, questions were raised on the capability of the aircraft after the March crash. Now, these questions have been put to rest with the announcement of an additional order for 12 more aircraft.
“The Philippines has signed a contract for 12 more FA-50 fighter jets,” its South Korean manufacturer said on June 4.
Korea Aerospace Industries (KAI) valued the deal with the Department of National Defense at $700 million, with delivery of the jets to be completed by 2030. The Philippines, which has yet to confirm the pact, previously purchased a dozen of the light warplanes in 2014.
In a statement, the South Korean firm said the fighter jets would feature enhanced capabilities including “aerial refueling for extended range, (Active Electronically Scanned Array) radar, and advanced air-to-air and air-to-ground weapons systems”.
One of the Philippines’ original fleet of FA-50s went missing on March 4 while on a mission to provide air support for troops fighting guerrillas in a mountainous area of the southern island of Mindanao.
Rescuers found the wreckage of the plane and the bodies of two crewmen a day later.
After temporarily grounding the fleet, the Philippine Air Force ruled out any mechanical problems with the aircraft.
Air Force spokeswoman Maria Consuelo Castillo told a press conference in April that a confluence of factors had contributed to the crash, including mountainous terrain and visibility issues.
Castillo said in March that the purchase of additional FA-50s was under consideration by the defence department.
The Philippines has extensively used its FA-50 fleet in the fight against the Islamic State in 2017, called the “Marawi Siege,” and it was dubbed a “game changer” by the PAF officials. Currently, the fighter jets are also used in operations against the Communist rebels.
The Philippines is also using the jets in patrolling missions in the contested South China Sea.
In February this year, the Philippines’ FA-50 fighter jet fleet also took part in drills over the West Philippine Sea with the US B-1 “Lancer” bombers.
The exercise included maneuvering the aircraft within the Philippines’ exclusive economic zone (EEZ). The exercise aimed to strengthen interoperability between the two air forces, enhance air domain awareness, and improve agile combat employment capabilities.
The FA-50, a modern light combat aircraft, represents the PAF’s first line of defense in maintaining air superiority over the contested areas.
The latest FA-50 purchase comes at a time when the Philippines has virtually been pushed to the wall in the South China Sea. China has been conducting aggressive maneuvers against Filipino forces in disputed territories, occasionally assaulting and expelling them from waters that China considers its “territorial waters.”
Currently, the FA-50 is the only combat-capable aircraft in the PAF’s inventory. In fact, the service had earlier considered deploying the FA-50 to escort its patrol aircraft over the South China Sea last year. The FA-50 is based on the T-50, a trainer aircraft capable of supersonic flight that was modified from the F-16 to train pilots for the KF-16 and F-15K.
The FA-50 is predominantly designed for air defense, strike, and jet training missions.
Expanding Military Shopping List Of The Philippines
Manila is rapidly modernizing its armed forces to deter China and enhance its combat capability. The Philippines Department of National Defense (DND) earlier stated that it plans to buy 40 multi-role fighter jets, among other sophisticated weapon systems. Two aircraft have been offered to the country: the Saab Gripen-E and Lockheed Martin’s F-16 Block 70/72.
Notably, the latest FA-50 acquisition comes amid warnings from military analysts that the PAF is arguably the country’s least robust military component, highlighting the need for at least a dozen squadrons of multirole jets to protect the archipelago’s airspace effectively.
Earlier, the Philippines’ DND also confirmed that a P6.5 billion (US$110 million) deal for six Embraer Super Tucano light attack aircraft for the PAF’s 15th Strike Wing was signed in December 2024. The purchase is meant to reinforce the PAF fleet in the wake of the gap left by the decommissioning of the last two remaining Rockwell OV-10 Bronco light attack aircraft and two AH-1S Cobra attack helicopters.
In addition, the DND has announced the P1 billion (US$17 million) purchase of an aeromedical Bell 412 EPX helicopter for the Philippine Army’s use in emergency medical missions.
The country has also planned upgrades for various cyber systems of the Armed Forces of the Philippines, as well as enhancements for the PAF’s ground-based air defense system and the introduction of new missiles.
In addition to the above-mentioned systems, the Philippines is reportedly considering the purchase of nine BrahMos missile batteries for its Army.
If finalized, this would be Manila’s second order of the BrahMos missile. In 2022, the Philippines signed a US$375 million deal with India for three batteries of the shore-based, anti-ship variant of the BrahMos missile for its naval forces.
Last year, Manila said it wanted to acquire the US Typhon mid-range missile system to bolster external defense capabilities.
Cornered by the PLA forces in the South China Sea, Manila is committed to spending at least 1.894 trillion pesos (approximately US$33.74 billion) to modernize and enhance its military capabilities by acquiring new systems, upgrading existing ones, and improving military infrastructure.
The deal for 12 additional FA-50 fighter jets will add crucial capabilities to the PAF.
6 months ago
Thailand Selects Gripen Fighter Jets Over F-16 Fighting Falcons For Its Air Force; Official Win For Swedish SAAB
Thailand on Wednesday announced plans to buy four Gripen fighter jets in a $500 million deal, choosing the Swedish-made planes over American F-16s as it renews its air combat fleet.
The Gripen E/F models, made by Nordic industrial giant Saab, will replace the Royal Thai Air Force’s older F-16 A/B jets bought in the 1980s.
The announcement is the first phase of a 10-year plan to buy 12 fighter aircraft as Thailand updates its air power.
“This is an important project to strengthen our force to protect our sovereignty,” Air Force Chief Punpakdee Pattanakul told reporters.
The procurement order will be submitted to the Thai cabinet for approval around mid-July and is expected to be finalized by the end of August.
A procurement committee recommended buying the Gripen rather than the F-16 last August after a 10-month process of deliberation. The kingdom already operates 11 older Gripens, as well as dozens of F-16s.
The decision to favour the Swedish fighter over the American one is unlikely to help Thailand’s efforts to reach a tariff deal with US President Donald Trump’s administration.
Thailand is hoping to negotiate a reduction or relief from Trump’s threatened 36 percent levy, announced as part of the president’s sweeping global “reciprocal” tariffs.
Earlier, as EurAsian Times reported, the Royal Thai Air Force selected Gripen-E jets to replace its aging fleet of F-16A/B/B.
The RTAF announced the acquisition in a Facebook post on August 27 last year. The service stated that it wants to acquire Gripen-E/F, which is built by SAAB. The decision was reached after a careful evaluation conducted over ten months.
The RTAF concluded that the Gripen-E/F fighter jet has a capability range that meets the Air Force’s principled and strategic needs. The aircraft can be further developed, resulting in increased multidimensional operational capabilities. The text was machine-translated.
The RTAF had been evaluating the two fighters—the Swedish Saab Gripen-E and the Lockheed Martin F-16 Block 70/72 —that were offered to it.
Earlier, in July 2024, an RTAF spokesperson said that the RTAF favored the Swedish jets after conducting a thorough evaluation that demonstrated the Gripen better met its needs.
“The procurement is in process [but is] dependent on the government,” the spokesperson said. However, the final decision was left to the Thai government.
Thailand on Wednesday announced plans to buy four Gripen fighter jets in a $500 million deal, choosing the Swedish-made planes over American F-16s as it renews its air combat fleet.
The Gripen E/F models, made by Nordic industrial giant Saab, will replace the Royal Thai Air Force’s older F-16 A/B jets bought in the 1980s.
The announcement is the first phase of a 10-year plan to buy 12 fighter aircraft as Thailand updates its air power.
“This is an important project to strengthen our force to protect our sovereignty,” Air Force Chief Punpakdee Pattanakul told reporters.
The procurement order will be submitted to the Thai cabinet for approval around mid-July and is expected to be finalized by the end of August.
A procurement committee recommended buying the Gripen rather than the F-16 last August after a 10-month process of deliberation. The kingdom already operates 11 older Gripens, as well as dozens of F-16s.
The decision to favour the Swedish fighter over the American one is unlikely to help Thailand’s efforts to reach a tariff deal with US President Donald Trump’s administration.
Thailand is hoping to negotiate a reduction or relief from Trump’s threatened 36 percent levy, announced as part of the president’s sweeping global “reciprocal” tariffs.
Earlier, as EurAsian Times reported, the Royal Thai Air Force selected Gripen-E jets to replace its aging fleet of F-16A/B/B.
The RTAF announced the acquisition in a Facebook post on August 27 last year. The service stated that it wants to acquire Gripen-E/F, which is built by SAAB. The decision was reached after a careful evaluation conducted over ten months.
The RTAF concluded that the Gripen-E/F fighter jet has a capability range that meets the Air Force’s principled and strategic needs. The aircraft can be further developed, resulting in increased multidimensional operational capabilities. The text was machine-translated.
The RTAF had been evaluating the two fighters—the Swedish Saab Gripen-E and the Lockheed Martin F-16 Block 70/72 —that were offered to it.
Earlier, in July 2024, an RTAF spokesperson said that the RTAF favored the Swedish jets after conducting a thorough evaluation that demonstrated the Gripen better met its needs.
“The procurement is in process [but is] dependent on the government,” the spokesperson said. However, the final decision was left to the Thai government.
6 months ago
The Pentagon plans to move its oversight of Greenland from U.S. European Command to U.S. Northern Command, a switch that would bring the Denmark-aligned island closer to alignment with the United States.
The change, first reported by Politico, comes as President Trump has repeatedly expressed an interest in taking control of the autonomous territory, where the U.S. military houses a base. Trump on the campaign trail and after taking office has said the U.S. taking control Greenland is a national security issue.
Shifting the responsibility for U.S. security interests in Greenland to Northcom, the military command that oversees America’s homeland defense, would largely be symbolic but underscores Trump’s focus on the territory.
The move could come as soon as this week, a Defense Department official and two people familiar with the planning told Politico.
The Pentagon did not return a request for comment from The Hill.
Reports first emerged last month that the Trump administration was mulling the move as Greenland is part of the North American continent, even as it is associated with Europe politically and culturally given it is a semiautonomous territory of Denmark.
Trump in his first term floated the notion of buying Greenland, but in his second term has doubled down on the idea. He has declined to rule out using military force in taking the island.
“I don’t rule it out. I don’t say I’m going to do it, but I don’t rule out anything,” Trump said in a May 4 interview with NBC’s “Meet the Press.”
“We need Greenland very badly,” he added. “Greenland is a very small amount of people, which we’ll take care of and we’ll cherish them and all of that. But we need that for international security.”
The change, first reported by Politico, comes as President Trump has repeatedly expressed an interest in taking control of the autonomous territory, where the U.S. military houses a base. Trump on the campaign trail and after taking office has said the U.S. taking control Greenland is a national security issue.
Shifting the responsibility for U.S. security interests in Greenland to Northcom, the military command that oversees America’s homeland defense, would largely be symbolic but underscores Trump’s focus on the territory.
The move could come as soon as this week, a Defense Department official and two people familiar with the planning told Politico.
The Pentagon did not return a request for comment from The Hill.
Reports first emerged last month that the Trump administration was mulling the move as Greenland is part of the North American continent, even as it is associated with Europe politically and culturally given it is a semiautonomous territory of Denmark.
Trump in his first term floated the notion of buying Greenland, but in his second term has doubled down on the idea. He has declined to rule out using military force in taking the island.
“I don’t rule it out. I don’t say I’m going to do it, but I don’t rule out anything,” Trump said in a May 4 interview with NBC’s “Meet the Press.”
“We need Greenland very badly,” he added. “Greenland is a very small amount of people, which we’ll take care of and we’ll cherish them and all of that. But we need that for international security.”
6 months ago
Prediction: Lockheed Martin Stock Could Explode as Donald Trump Touts F-55 Fighter Jet and a Bigger F-22
Key Points
The Pentagon awarded Lockheed archrival Boeing a surprise win in March: a $20 billion F-47 fighter jet contract.
Now, President Trump is suggesting Lockheed Martin could get two contracts of its own, to build F-55 and F-22 Super stealth fighters.
The Greed is Good and War Mongers are on stock prediction-
Whether or not the contracts materialize, relative to its peers, Lockheed Martin stock already looks attractive.
10 stocks we like better than Lockheed Martin ›
The Lockheed Martin (NYSE: LMT) F-22 Raptor stealth fighter is arguably the most expensive fighter jet ever built, costing an estimated $400 billion per unit. That's part of the reason it's no longer being built, by the way. (The F-22 program was canceled more than a decade ago, although the plane remains in service.)
Now, President Donald Trump wants to have the Air Force buy a new fighter jet that could cost even more. Two of them, in fact.
Upgrading the F-22, and the F-35, too
As Reuters reported earlier this month, the president recently raised the possibility of having Lockheed build a new stealth fighter, based on Lockheed's F-35 stealth fighter but with two engines instead of just one, to be called the F-55. A second idea floated by the president is to let Lockheed restart production of its long-canceled F-22 program in an upgraded form, to be known as the F-22 Super.
No price was named for either aircraft, although price is definitely on the president's mind. Speaking at a meeting of business leaders and aerospace executives in Doha, Qatar, Trump explained, "We're going to do an F-55 and -- I think, if we get the right price, we have to get the right price -- that'll be two engines and a super upgrade on the F-35, and then we're going to do the F-22 [Super] ... a very modern version of the F-22 fighter jet."
Furthermore, he stated, "We're going to be going with it pretty quickly."
Throwing a life preserver to Lockheed
Not everyone's on board with the idea. As defense-focused news site 19fortyfive.com quickly pointed out, creating a twin-engine version of the stealthy F-35 may not even be "feasible." On the other hand, the website noted that the Air Force has already agreed to pay RTX (NYSE: RTX) more than $1 billion to upgrade sensors on the F-22 fleet, turning it into what Lockheed CEO Jim Taiclet has called a "fifth-generation plus" fighter able to sense and strike targets farther out than currently possible.
So Lockheed Martin is likely to like the president's proposals (both of them). The more so seeing as it's been only a couple of months since the Air Force handed Lockheed a rather shocking defeat, when it awarded the $20 billion contract to build a sixth-generation stealth fighter, the F-47, to rival Boeing (NYSE: BA).
With only one such sixth-generation warbird so far announced, that loss holds the potential to put Lockheed a generation behind Boeing in its competency building stealthy fighter jets. This could create a whole new dynamic in which Boeing, not Lockheed, has the advantage in winning future fighter jet contracts.
But if Lockheed gets to build a "fifth-generation plus" fighter (or two), the technology gap might not loom quite so large, and Lockheed might remain within striking distance of its rival.
Boeing versus Lockheed Martin versus Northrop Grumman
In fact, that might be the plan. Trump, of course, has a well-known penchant for shaking up chessboards in order to create new and more advantageous negotiating positions (albeit with the unfortunate side effect of sometimes knocking over pieces).
That's not easy to do in the defense industry, which, after going through repeated rounds of consolidation after the Cold War, now comprises really just five big "defense primes" capable of executing the Pentagon's biggest defense contracts. Awarding F-47 to Boeing, then perhaps handing F-55 and F-22 Super contracts to Lockheed, could be the president's way of ensuring these aerospace companies remain both solvent, with enough revenue coming in to stay in business, and able to keep competing with each other, such that no one company gets so dominant that it can dictate prices to its primary customer, the U.S. government.
If this is the president's plan, it could also help the Pentagon when it comes time to negotiate pricing on a new F/A-XX stealth fighter jet that the Navy wants to buy, and that both Boeing and Northrop Grumman (NYSE: NOC) are angling to build. (And if this is the president's plan, it may also give investors a hint at who will win F/A-XX. Should that one go to Northrop, the Pentagon would have three aerospace defense prime contractors, all bidding against each other on future stealth fighter contracts.)
Which defense stock to buy?
Whoever ends up winning these fighter jet contracts, from an investor's perspective, I see one of these three stocks as clearly superior to the others: Lockheed Martin.
Lockheed (20 times earnings) costs slightly more than Northrop Grumman (19) when valued on generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) earnings, but sports a much better price-to-free-cash-flow valuation, 22 to Northrop's 38, as confirmed by data from S&P Global Market Intelligence. (Unprofitable and cash-burning Boeing doesn't even make it to the starting line in this race.) Lockheed also boasts a projected long-term earnings growth rate of 13%, twice as fast as Northrop. Why, Lockheed even has the best dividend yield of the bunch at 2.8%.
Regardless of whether the president's mooted new fighter jets actually materialize as defense contracts for Lockheed, the stock is already the one with the most value to offer investors.
Key Points
The Pentagon awarded Lockheed archrival Boeing a surprise win in March: a $20 billion F-47 fighter jet contract.
Now, President Trump is suggesting Lockheed Martin could get two contracts of its own, to build F-55 and F-22 Super stealth fighters.
The Greed is Good and War Mongers are on stock prediction-
Whether or not the contracts materialize, relative to its peers, Lockheed Martin stock already looks attractive.
10 stocks we like better than Lockheed Martin ›
The Lockheed Martin (NYSE: LMT) F-22 Raptor stealth fighter is arguably the most expensive fighter jet ever built, costing an estimated $400 billion per unit. That's part of the reason it's no longer being built, by the way. (The F-22 program was canceled more than a decade ago, although the plane remains in service.)
Now, President Donald Trump wants to have the Air Force buy a new fighter jet that could cost even more. Two of them, in fact.
Upgrading the F-22, and the F-35, too
As Reuters reported earlier this month, the president recently raised the possibility of having Lockheed build a new stealth fighter, based on Lockheed's F-35 stealth fighter but with two engines instead of just one, to be called the F-55. A second idea floated by the president is to let Lockheed restart production of its long-canceled F-22 program in an upgraded form, to be known as the F-22 Super.
No price was named for either aircraft, although price is definitely on the president's mind. Speaking at a meeting of business leaders and aerospace executives in Doha, Qatar, Trump explained, "We're going to do an F-55 and -- I think, if we get the right price, we have to get the right price -- that'll be two engines and a super upgrade on the F-35, and then we're going to do the F-22 [Super] ... a very modern version of the F-22 fighter jet."
Furthermore, he stated, "We're going to be going with it pretty quickly."
Throwing a life preserver to Lockheed
Not everyone's on board with the idea. As defense-focused news site 19fortyfive.com quickly pointed out, creating a twin-engine version of the stealthy F-35 may not even be "feasible." On the other hand, the website noted that the Air Force has already agreed to pay RTX (NYSE: RTX) more than $1 billion to upgrade sensors on the F-22 fleet, turning it into what Lockheed CEO Jim Taiclet has called a "fifth-generation plus" fighter able to sense and strike targets farther out than currently possible.
So Lockheed Martin is likely to like the president's proposals (both of them). The more so seeing as it's been only a couple of months since the Air Force handed Lockheed a rather shocking defeat, when it awarded the $20 billion contract to build a sixth-generation stealth fighter, the F-47, to rival Boeing (NYSE: BA).
With only one such sixth-generation warbird so far announced, that loss holds the potential to put Lockheed a generation behind Boeing in its competency building stealthy fighter jets. This could create a whole new dynamic in which Boeing, not Lockheed, has the advantage in winning future fighter jet contracts.
But if Lockheed gets to build a "fifth-generation plus" fighter (or two), the technology gap might not loom quite so large, and Lockheed might remain within striking distance of its rival.
Boeing versus Lockheed Martin versus Northrop Grumman
In fact, that might be the plan. Trump, of course, has a well-known penchant for shaking up chessboards in order to create new and more advantageous negotiating positions (albeit with the unfortunate side effect of sometimes knocking over pieces).
That's not easy to do in the defense industry, which, after going through repeated rounds of consolidation after the Cold War, now comprises really just five big "defense primes" capable of executing the Pentagon's biggest defense contracts. Awarding F-47 to Boeing, then perhaps handing F-55 and F-22 Super contracts to Lockheed, could be the president's way of ensuring these aerospace companies remain both solvent, with enough revenue coming in to stay in business, and able to keep competing with each other, such that no one company gets so dominant that it can dictate prices to its primary customer, the U.S. government.
If this is the president's plan, it could also help the Pentagon when it comes time to negotiate pricing on a new F/A-XX stealth fighter jet that the Navy wants to buy, and that both Boeing and Northrop Grumman (NYSE: NOC) are angling to build. (And if this is the president's plan, it may also give investors a hint at who will win F/A-XX. Should that one go to Northrop, the Pentagon would have three aerospace defense prime contractors, all bidding against each other on future stealth fighter contracts.)
Which defense stock to buy?
Whoever ends up winning these fighter jet contracts, from an investor's perspective, I see one of these three stocks as clearly superior to the others: Lockheed Martin.
Lockheed (20 times earnings) costs slightly more than Northrop Grumman (19) when valued on generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) earnings, but sports a much better price-to-free-cash-flow valuation, 22 to Northrop's 38, as confirmed by data from S&P Global Market Intelligence. (Unprofitable and cash-burning Boeing doesn't even make it to the starting line in this race.) Lockheed also boasts a projected long-term earnings growth rate of 13%, twice as fast as Northrop. Why, Lockheed even has the best dividend yield of the bunch at 2.8%.
Regardless of whether the president's mooted new fighter jets actually materialize as defense contracts for Lockheed, the stock is already the one with the most value to offer investors.