4 hours ago
Your #Architecture firm deserves to be seen. But with so many studios and designers competing #online , simply having a beautiful website isn’t enough. That’s where #seo for #architects makes all the difference.
I help architects and #InteriorDesigners grow visibility, attract high-quality #leads , and build long-term authority online through SEO strategies designed specifically for the architecture and #design industry.
https://pratsify.com/seo-f...
I help architects and #InteriorDesigners grow visibility, attract high-quality #leads , and build long-term authority online through SEO strategies designed specifically for the architecture and #design industry.
https://pratsify.com/seo-f...
1 month ago
Build a Ride-Hailing Platform with Fare Negotiation Using Oyelabs’ InDriver Clone
Empower riders with flexible fare bidding and transparency with Oyelabs’ InDriver clone app development. Features include real-time fare negotiation (bid rides), driver/rider mode switching, multi-gateway payments, secure document verification, and a robust admin panel for managing drivers, revenue & safety. Fully white-label and packed with scalable, source-code included architecture.
https://oyelabs.com/indriv...
#InDriverClone #BidRideApp #TaxiBookingSolution #FareNegotiation #RideHailingApp #oyelabs #OnDemandTaxi #CloneAppScript
Empower riders with flexible fare bidding and transparency with Oyelabs’ InDriver clone app development. Features include real-time fare negotiation (bid rides), driver/rider mode switching, multi-gateway payments, secure document verification, and a robust admin panel for managing drivers, revenue & safety. Fully white-label and packed with scalable, source-code included architecture.
https://oyelabs.com/indriv...
#InDriverClone #BidRideApp #TaxiBookingSolution #FareNegotiation #RideHailingApp #oyelabs #OnDemandTaxi #CloneAppScript
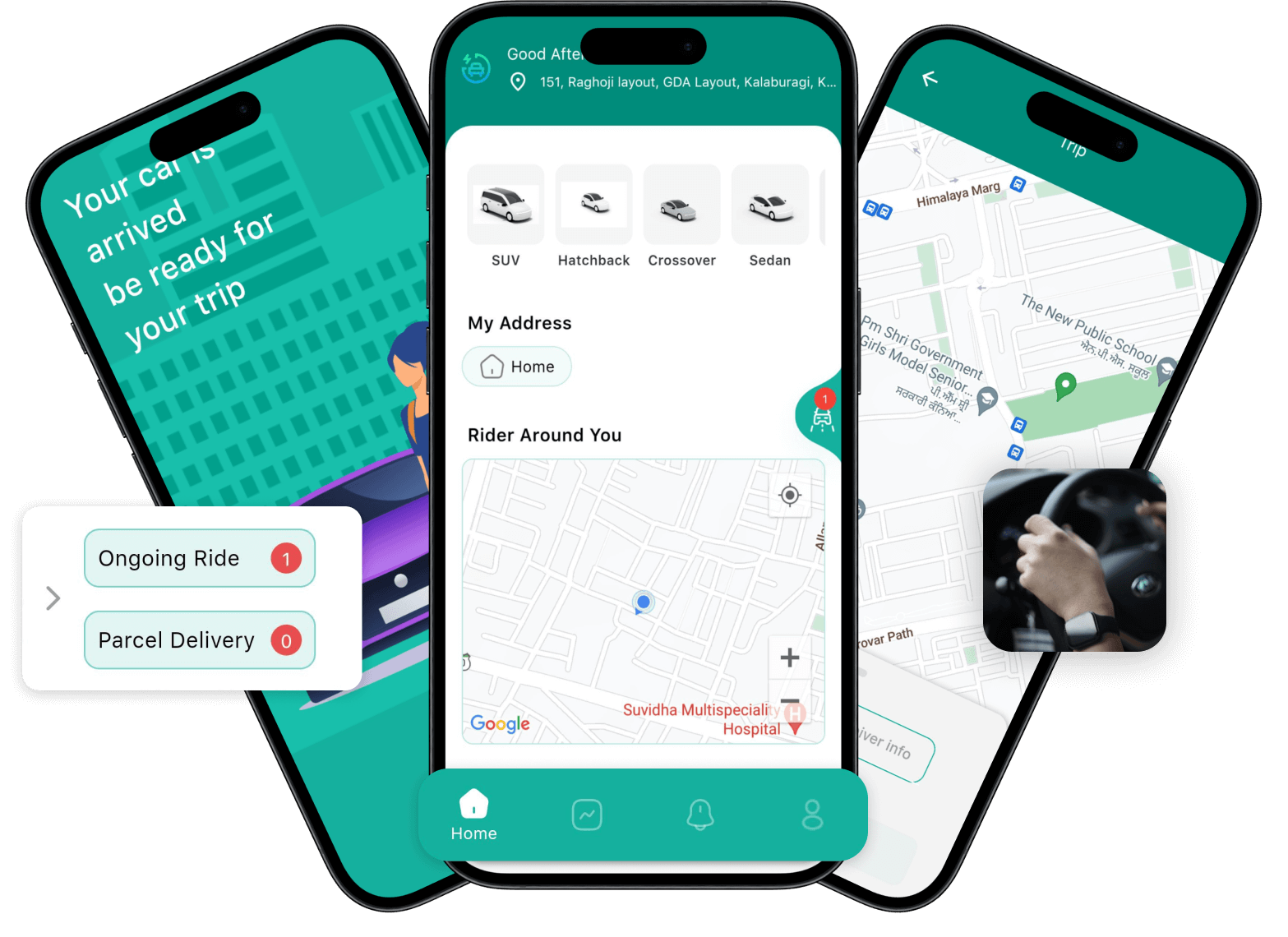
InDriver Clone App | Customizable Taxi Booking App Script
InDriver clone is a ready-to-launch taxi booking and delivery solution with the fare bidding feature to start your own business in just 3 days.
https://oyelabs.com/indriver-clone-app-development/
1 month ago
Build a Ride-Hailing Platform with Fare Negotiation Using Oyelabs’ InDriver Clone
Empower riders with flexible fare bidding and transparency with Oyelabs’ InDriver clone app development. Features include real-time fare negotiation (bid rides), driver/rider mode switching, multi-gateway payments, secure document verification, and a robust admin panel for managing drivers, revenue & safety. Fully white-label and packed with scalable, source-code included architecture.
https://oyelabs.com/indriv...
#InDriverClone #BidRideApp #TaxiBookingSolution #FareNegotiation #RideHailingApp #oyelabs #OnDemandTaxi #CloneAppScript
Empower riders with flexible fare bidding and transparency with Oyelabs’ InDriver clone app development. Features include real-time fare negotiation (bid rides), driver/rider mode switching, multi-gateway payments, secure document verification, and a robust admin panel for managing drivers, revenue & safety. Fully white-label and packed with scalable, source-code included architecture.
https://oyelabs.com/indriv...
#InDriverClone #BidRideApp #TaxiBookingSolution #FareNegotiation #RideHailingApp #oyelabs #OnDemandTaxi #CloneAppScript
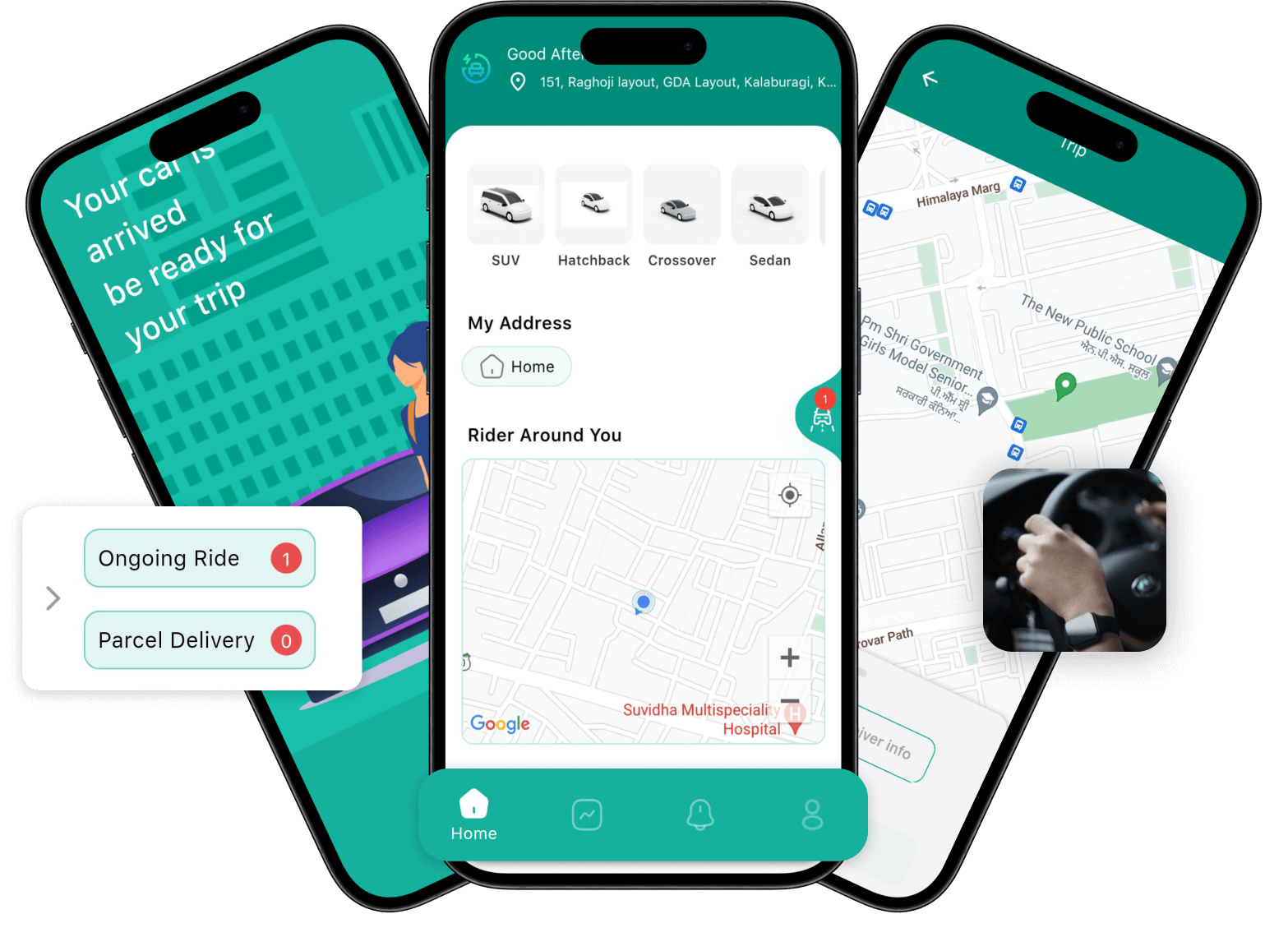
InDriver Clone App | Customizable Taxi Booking App Script
InDriver clone is a ready-to-launch taxi booking and delivery solution with the fare bidding feature to start your own business in just 3 days.
https://oyelabs.com/indriver-clone-app-development/
1 month ago
Build a Ride-Hailing Platform with Fare Negotiation Using Oyelabs’ InDriver Clone
Empower riders with flexible fare bidding and transparency with Oyelabs’ InDriver clone app development. Features include real-time fare negotiation (bid rides), driver/rider mode switching, multi-gateway payments, secure document verification, and a robust admin panel for managing drivers, revenue & safety. Fully white-label and packed with scalable, source-code included architecture.
https://oyelabs.com/indriv...
#InDriverClone #BidRideApp #TaxiBookingSolution #FareNegotiation #RideHailingApp #oyelabs #OnDemandTaxi #CloneAppScript
Empower riders with flexible fare bidding and transparency with Oyelabs’ InDriver clone app development. Features include real-time fare negotiation (bid rides), driver/rider mode switching, multi-gateway payments, secure document verification, and a robust admin panel for managing drivers, revenue & safety. Fully white-label and packed with scalable, source-code included architecture.
https://oyelabs.com/indriv...
#InDriverClone #BidRideApp #TaxiBookingSolution #FareNegotiation #RideHailingApp #oyelabs #OnDemandTaxi #CloneAppScript
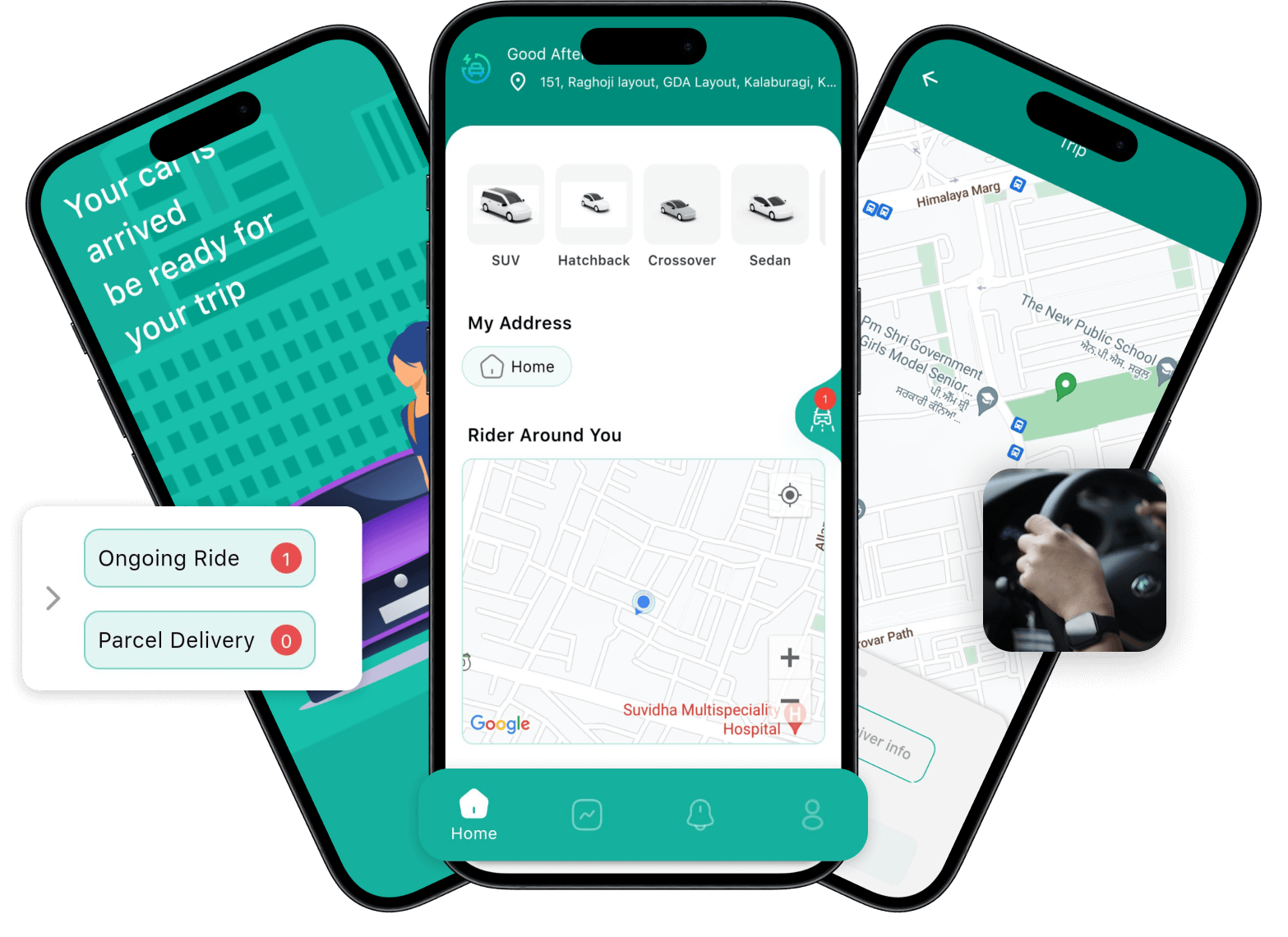
InDriver Clone App | Customizable Taxi Booking App Script
InDriver clone is a ready-to-launch taxi booking and delivery solution with the fare bidding feature to start your own business in just 3 days.
https://oyelabs.com/indriver-clone-app-development/
2 months ago
Koinkart Develop a Crypto Sniper Bot with high-speed solution
Expand your trading opportunities with Koinkart. Our Crypto Sniper Bot Development service delivers a high-speed solution that helps traders capture profits with split-second accuracy. Built for traders who want smarter entries and exits without missing opportunities.
We list out the features offered for our clients:
• Automated instant order execution
• Real-time market scanning and alerts
• Smart risk controls and take-profit settings
• User-friendly dashboard with performance tracking
• Secure architecture and regular updates
📲 Get Demo or Quote Now!
🌐 Website: https://www.koinkart.org/b...
📞 WhatsApp: +91 93842 63771
Expand your trading opportunities with Koinkart. Our Crypto Sniper Bot Development service delivers a high-speed solution that helps traders capture profits with split-second accuracy. Built for traders who want smarter entries and exits without missing opportunities.
We list out the features offered for our clients:
• Automated instant order execution
• Real-time market scanning and alerts
• Smart risk controls and take-profit settings
• User-friendly dashboard with performance tracking
• Secure architecture and regular updates
📲 Get Demo or Quote Now!
🌐 Website: https://www.koinkart.org/b...
📞 WhatsApp: +91 93842 63771
2 months ago
What is an AliExpress Clone? A Guide for Multi-Vendor Business
The eCommerce industry has witnessed immersive growth, fueled by new technology innovations and evolving user demands.
AliExpress Clone is one of the top on-demand platforms with a scalable architecture, unique layouts, and standard vendor management. It opens a new opportunity for startups to stand out in a competitive marketplace.
This blog provides a complete guide to building a multi-vendor app using an AliExpress clone script. We covered its essential features, development steps, and latest trends.
Dive in.
Aliexpress Clone: An Introduction
Don’t you know what an AliExpress clone is? Here’s a short overview of it. Let’s check in.
An AliExpress clone is a ready-made solution inspired by the original AliExpress business model, designed with its core functionalities intact. This connects every single user who wants to order products through an online medium. They can compare prices across multiple vendors and finally buy a product from a preferred store. It increases user convenience and satisfaction.
This eCommerce clone script streamlines the complete end-to-end purchasing process with advanced features, including user registration, multiple delivery addresses, shipment tracking, and secure payments.
Partner With Trioangle and Start Today!
Obviously, you are at the right place to start and implement your multi-vendor marketplace idea.
Trioangle's AliExpress Clone Script can help you turn your idea into a robust and revenue-generating eCommerce platform.
Connect with our experts to acknowledge business goals and craft solutions that meet your target audience's needs.
Subscribe now!
https://www.trioangle.com/...
#AliExpressClone #AliExpressCloneScript #AliExpressLikeApp #MultiVendorEcommerce #MarketplaceSoftware #EcommerceScript #ReadymadeEcommerce #B2BMarketplace #OnlineMarketplace
The eCommerce industry has witnessed immersive growth, fueled by new technology innovations and evolving user demands.
AliExpress Clone is one of the top on-demand platforms with a scalable architecture, unique layouts, and standard vendor management. It opens a new opportunity for startups to stand out in a competitive marketplace.
This blog provides a complete guide to building a multi-vendor app using an AliExpress clone script. We covered its essential features, development steps, and latest trends.
Dive in.
Aliexpress Clone: An Introduction
Don’t you know what an AliExpress clone is? Here’s a short overview of it. Let’s check in.
An AliExpress clone is a ready-made solution inspired by the original AliExpress business model, designed with its core functionalities intact. This connects every single user who wants to order products through an online medium. They can compare prices across multiple vendors and finally buy a product from a preferred store. It increases user convenience and satisfaction.
This eCommerce clone script streamlines the complete end-to-end purchasing process with advanced features, including user registration, multiple delivery addresses, shipment tracking, and secure payments.
Partner With Trioangle and Start Today!
Obviously, you are at the right place to start and implement your multi-vendor marketplace idea.
Trioangle's AliExpress Clone Script can help you turn your idea into a robust and revenue-generating eCommerce platform.
Connect with our experts to acknowledge business goals and craft solutions that meet your target audience's needs.
Subscribe now!
https://www.trioangle.com/...
#AliExpressClone #AliExpressCloneScript #AliExpressLikeApp #MultiVendorEcommerce #MarketplaceSoftware #EcommerceScript #ReadymadeEcommerce #B2BMarketplace #OnlineMarketplace
2 months ago
With most people searching #online for #architects , #housedesigners , and #design firms, having a #website alone isn’t enough. You need to appear at the top of Google when potential clients are searching for services like yours.
At PratsDigital, I specialize in helping architects grow online with proven #seo #strategies designed specifically for the architecture and design industry.
https://pratsdigital.in/se...
At PratsDigital, I specialize in helping architects grow online with proven #seo #strategies designed specifically for the architecture and design industry.
https://pratsdigital.in/se...
3 months ago
Koinkart Upgraded Binance Clone Script Software with Superior Features
Koinkart introduces the upgraded Binance clone script, packed with superior features to launch a professional crypto exchange effortlessly. Our advanced solution ensures high performance, robust security, and a seamless trading experience for users of all levels.
Enhanced Security: Multi-layer authentication, encrypted wallets, and real-time fraud detection
Fast Deployment: Fully functional exchange ready in weeks
User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive design with multi-language and multi-currency support
Advanced Trading Tools: Spot, margin, and futures trading with real-time charts
Scalable Architecture: Grow your exchange without limits
📲 Get Demo or Quote Now!
🌐 Website: https://www.koinkart.org/b...
📞 WhatsApp: +91 93842 63771
Koinkart introduces the upgraded Binance clone script, packed with superior features to launch a professional crypto exchange effortlessly. Our advanced solution ensures high performance, robust security, and a seamless trading experience for users of all levels.
Enhanced Security: Multi-layer authentication, encrypted wallets, and real-time fraud detection
Fast Deployment: Fully functional exchange ready in weeks
User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive design with multi-language and multi-currency support
Advanced Trading Tools: Spot, margin, and futures trading with real-time charts
Scalable Architecture: Grow your exchange without limits
📲 Get Demo or Quote Now!
🌐 Website: https://www.koinkart.org/b...
📞 WhatsApp: +91 93842 63771
3 months ago
Koinkart Upgraded Binance Clone Script Software with Superior Features
Koinkart introduces the upgraded Binance clone script, packed with superior features to launch a professional crypto exchange effortlessly. Our advanced solution ensures high performance, robust security, and a seamless trading experience for users of all levels.
Enhanced Security: Multi-layer authentication, encrypted wallets, and real-time fraud detection
Fast Deployment: Fully functional exchange ready in weeks
User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive design with multi-language and multi-currency support
Advanced Trading Tools: Spot, margin, and futures trading with real-time charts
Scalable Architecture: Grow your exchange without limits
📲 Get Demo or Quote Now!
🌐 Website: https://www.koinkart.org/b...
📞 WhatsApp: +91 93842 63771
Koinkart introduces the upgraded Binance clone script, packed with superior features to launch a professional crypto exchange effortlessly. Our advanced solution ensures high performance, robust security, and a seamless trading experience for users of all levels.
Enhanced Security: Multi-layer authentication, encrypted wallets, and real-time fraud detection
Fast Deployment: Fully functional exchange ready in weeks
User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive design with multi-language and multi-currency support
Advanced Trading Tools: Spot, margin, and futures trading with real-time charts
Scalable Architecture: Grow your exchange without limits
📲 Get Demo or Quote Now!
🌐 Website: https://www.koinkart.org/b...
📞 WhatsApp: +91 93842 63771
3 months ago
"What they don't teach you" on religion- For the general public: Why is religious literacy crucial for peaceful coexistence and informed civic engagement in a diverse world?
The question of "What they don't teach you" about religion, particularly for the general public, directly hits upon why religious literacy is not just a niche academic interest but an absolutely crucial skill for peaceful coexistence and informed civic engagement in our diverse, interconnected world.
Here's why:
1. Fostering Peaceful Coexistence: Bridging Divides and Reducing Conflict
Deconstructing Stereotypes and Prejudice:
What's Often Taught (or Inferred): Simplistic, often media-driven caricatures of religious groups (e.g., all Muslims are extremists, all Christians are judgmental, all atheists are immoral).
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The vast internal diversity within every major religion (different sects, denominations, interpretations, cultural expressions), the existence of peaceful and compassionate majority adherents, and the historical and political factors that often fuel extremism more than theology itself.
Why it's Crucial: Without this, the general public falls prey to misinformation and prejudice. Religious literacy allows individuals to look beyond headlines, challenge harmful stereotypes, and recognize the humanity in those with different beliefs. This directly reduces the likelihood of "othering," discrimination, and religiously-motivated violence or tension.
Understanding the Roots of Global Conflict:
What's Often Taught: Geopolitical conflicts are presented primarily through political, economic, or nationalistic lenses.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The deep and often complex ways religious identity, historical grievances, theological interpretations, and religious leadership intertwine with political and economic factors to drive or exacerbate conflicts globally (e.g., in the Middle East, South Asia, parts of Africa).
Why it's Crucial: To genuinely understand and respond to global crises, the public needs to grasp the religious dimensions at play. Ignoring them leads to ineffective policies, misjudged interventions, and a perpetuation of conflict due to a lack of fundamental understanding of the actors' motivations and worldviews.
Promoting Effective Interfaith Dialogue:
What's Often Taught: Little about other religions beyond basic facts, leading to a perception that different faiths are fundamentally incompatible.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The common ethical concerns, shared human experiences, and often similar underlying quests for meaning that exist across diverse religious and secular traditions. Also, how to engage in respectful dialogue without proselytizing or being dismissive.
Why it's Crucial: In pluralistic societies, friction is inevitable without dialogue. Religious literacy provides the tools to engage across belief systems, find common ground on shared values (e.g., justice, compassion, care for the environment), and work together on community issues, fostering social cohesion.
2. Informed Civic Engagement: Navigating a Complex Society
Understanding Domestic Politics and Policy Debates:
What's Often Taught: Political issues are framed as purely secular matters of policy and economics.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The powerful role of religious lobbying groups, the influence of faith-based organizations on social policy (e.g., healthcare, education, social welfare), and how religious values inform voters' choices and politicians' positions on a vast array of issues (e.g., abortion, LGBTQ+ rights, environmental regulations, foreign aid).
Why it's Crucial: A religiously illiterate public cannot fully grasp the motivations behind certain political movements or legislative efforts. They may misinterpret policy debates or be unable to critically evaluate the arguments presented, hindering their ability to vote and participate effectively in a democracy.
Navigating Rights and Responsibilities in a Pluralistic Society:
What's Often Taught: Basic concepts of freedom of speech and religion.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The complexities of religious freedom (e.g., balancing individual religious rights with public good, "reasonable accommodation" vs. discrimination), the historical evolution of church-state separation, and the diverse ways different societies approach religion in the public square.
Why it's Crucial: The general public needs to understand why certain religious groups act or advocate in particular ways, and how their rights intersect with the rights of others. This is essential for preventing clashes over public space, school curricula, workplace policies, and ultimately, for upholding a truly inclusive and equitable society.
Critical Media Literacy:
What's Often Taught: How to identify basic bias in news.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): How religious narratives are often oversimplified, sensationalized, or misinterpreted in media coverage; how to discern between genuine religious expression and the political manipulation of religious identity.
Why it's Crucial: In an age of widespread misinformation, religious literacy empowers individuals to critically evaluate news stories, recognize loaded language, and demand more nuanced reporting on religious issues, protecting them from being swayed by harmful narratives.
Appreciating Cultural Heritage and Diversity:
What's Often Taught: Culture is often presented broadly, without diving into its foundational elements.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The immense influence of religion on art, architecture, music, literature, holidays, and social customs around the world.
Why it's Crucial: Understanding this enriches cultural appreciation, whether visiting a historic site, reading a classic novel, or participating in a festival. It allows the public to appreciate the depth and beauty of human creativity and tradition, fostering a richer civic life and more respectful interactions with diverse communities.
In conclusion, for the general public, religious literacy moves beyond mere curiosity; it is a practical necessity for navigating the complexities of modern life. It equips individuals with the understanding, empathy, and critical thinking skills needed to contribute to a society that is not only tolerant but genuinely capable of peaceful coexistence and robust, informed democratic engagement in a truly diverse world.
The question of "What they don't teach you" about religion, particularly for the general public, directly hits upon why religious literacy is not just a niche academic interest but an absolutely crucial skill for peaceful coexistence and informed civic engagement in our diverse, interconnected world.
Here's why:
1. Fostering Peaceful Coexistence: Bridging Divides and Reducing Conflict
Deconstructing Stereotypes and Prejudice:
What's Often Taught (or Inferred): Simplistic, often media-driven caricatures of religious groups (e.g., all Muslims are extremists, all Christians are judgmental, all atheists are immoral).
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The vast internal diversity within every major religion (different sects, denominations, interpretations, cultural expressions), the existence of peaceful and compassionate majority adherents, and the historical and political factors that often fuel extremism more than theology itself.
Why it's Crucial: Without this, the general public falls prey to misinformation and prejudice. Religious literacy allows individuals to look beyond headlines, challenge harmful stereotypes, and recognize the humanity in those with different beliefs. This directly reduces the likelihood of "othering," discrimination, and religiously-motivated violence or tension.
Understanding the Roots of Global Conflict:
What's Often Taught: Geopolitical conflicts are presented primarily through political, economic, or nationalistic lenses.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The deep and often complex ways religious identity, historical grievances, theological interpretations, and religious leadership intertwine with political and economic factors to drive or exacerbate conflicts globally (e.g., in the Middle East, South Asia, parts of Africa).
Why it's Crucial: To genuinely understand and respond to global crises, the public needs to grasp the religious dimensions at play. Ignoring them leads to ineffective policies, misjudged interventions, and a perpetuation of conflict due to a lack of fundamental understanding of the actors' motivations and worldviews.
Promoting Effective Interfaith Dialogue:
What's Often Taught: Little about other religions beyond basic facts, leading to a perception that different faiths are fundamentally incompatible.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The common ethical concerns, shared human experiences, and often similar underlying quests for meaning that exist across diverse religious and secular traditions. Also, how to engage in respectful dialogue without proselytizing or being dismissive.
Why it's Crucial: In pluralistic societies, friction is inevitable without dialogue. Religious literacy provides the tools to engage across belief systems, find common ground on shared values (e.g., justice, compassion, care for the environment), and work together on community issues, fostering social cohesion.
2. Informed Civic Engagement: Navigating a Complex Society
Understanding Domestic Politics and Policy Debates:
What's Often Taught: Political issues are framed as purely secular matters of policy and economics.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The powerful role of religious lobbying groups, the influence of faith-based organizations on social policy (e.g., healthcare, education, social welfare), and how religious values inform voters' choices and politicians' positions on a vast array of issues (e.g., abortion, LGBTQ+ rights, environmental regulations, foreign aid).
Why it's Crucial: A religiously illiterate public cannot fully grasp the motivations behind certain political movements or legislative efforts. They may misinterpret policy debates or be unable to critically evaluate the arguments presented, hindering their ability to vote and participate effectively in a democracy.
Navigating Rights and Responsibilities in a Pluralistic Society:
What's Often Taught: Basic concepts of freedom of speech and religion.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The complexities of religious freedom (e.g., balancing individual religious rights with public good, "reasonable accommodation" vs. discrimination), the historical evolution of church-state separation, and the diverse ways different societies approach religion in the public square.
Why it's Crucial: The general public needs to understand why certain religious groups act or advocate in particular ways, and how their rights intersect with the rights of others. This is essential for preventing clashes over public space, school curricula, workplace policies, and ultimately, for upholding a truly inclusive and equitable society.
Critical Media Literacy:
What's Often Taught: How to identify basic bias in news.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): How religious narratives are often oversimplified, sensationalized, or misinterpreted in media coverage; how to discern between genuine religious expression and the political manipulation of religious identity.
Why it's Crucial: In an age of widespread misinformation, religious literacy empowers individuals to critically evaluate news stories, recognize loaded language, and demand more nuanced reporting on religious issues, protecting them from being swayed by harmful narratives.
Appreciating Cultural Heritage and Diversity:
What's Often Taught: Culture is often presented broadly, without diving into its foundational elements.
What's Untaught (and Crucial): The immense influence of religion on art, architecture, music, literature, holidays, and social customs around the world.
Why it's Crucial: Understanding this enriches cultural appreciation, whether visiting a historic site, reading a classic novel, or participating in a festival. It allows the public to appreciate the depth and beauty of human creativity and tradition, fostering a richer civic life and more respectful interactions with diverse communities.
In conclusion, for the general public, religious literacy moves beyond mere curiosity; it is a practical necessity for navigating the complexities of modern life. It equips individuals with the understanding, empathy, and critical thinking skills needed to contribute to a society that is not only tolerant but genuinely capable of peaceful coexistence and robust, informed democratic engagement in a truly diverse world.
3 months ago
U.S. Fights Su-57 Fighter Threat With F-16’s New Paint Scheme; Is USAF Acknowledging The Might Of Felons?
A Top Aces’ F-16A fighter jet has been spotted in an eye-catching new adversary paint scheme. The fighter aircraft, formerly with the Israeli Air Force, was seen supporting a Russian Su-57 Felon-inspired paint scheme.
Dubbed the “Felon Paint Job,” the aircraft was spotted in Arizona. It flew from Mesa Gateway Airport, where Top Aces performs maintenance on its F-16s, to Luke AFB, Arizona, as ACES 51.
After reaching Luke AFB, Arizona, the fighter jet took part in a local mission under the callsign ACES 1.
Though the fighter jet, formerly known as Netz 284, was also photographed while being wheeled out of the paint barn at Mesa, its return to Luke AFB, Arizona, offered a better look.
The F-16, tail number N871TA and bort number “284” Red, features a low-visibility, splinter-style grey camouflage pattern similar to that used by Russia’s fifth-generation stealth fighter.
The two-tone scheme includes angular transitions across the airframe, mimicking the faceted radar-evading design philosophy of the T-50/Su-57, the Aviationist reported.
The “Felon Paint Job” was complete with Soviet-style red stars on its tail and wings. The tail fin also carried Cyrillic script that read “Опыт Важен” (which translates to “Experience Matters”).
Notably, despite the “Felon Paint Job,” the fighter jet still retains the kill marking it earned in September 1981, when Netz 284 shot down a Syrian MiG-23.
Last year, another F-16 fighter jet from the Top Aces fleet was spotted sporting a “Flanker Blue” color scheme, inspired by the one used by some F-16s of the U.S. Air Force’s 64th Aggressor Squadron at Nellis Air Force Base, Nevada.
It remains to be seen what other paint schemes the Top Aces F-16 fleet will support in the coming days.
F-16’s Journey: From Israeli Air Force To Top Aces
The F-16A Netz 284 was one of the fighter jets that were retired from the Israeli Air Force at the end of 2016 and delivered to the US in 2021.
The aircraft was part of the 29 F-16 Netz (Hawk) fighter jets, which retired from the Israeli Air Force in 2016 after 36 years in service, and were subsequently bought by Top Aces for adversary training.
In 2021, the Israeli Ministry of Defense acknowledged the unprecedented sale of 29 F-16 Netz (Hawk) aircraft to Top Aces.
“Following negotiations led by SIBAT, the MoD has signed an unprecedented agreement to supply 29 F-16 aircraft to TOP ACES. These will be employed as staged adversary aircraft in U.S. Air Force training,” the Israeli Ministry of Defense posted on social media site X in 2021.
The first four of these F-16s were received at Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport in February 2021.
The four F-16s, with their wings, tail, and tailerons removed, were loaded on a Ukrainian Antonov An-124 at Tel Aviv-Ben Gurion airport on January 27 and, after a stop in Keflavik, Iceland, they arrived a day later at Phoenix-Mesa Gateway airport.
With these F-16s, Top Aces became the first company to provide a 4th-generation aircraft for staged adversary aircraft training. Till today, these F-16s remain the world’s only privately owned F-16s.
The F-16s were subsequently upgraded to a standard that is known as F-16 AAF (Advanced Aggressor Fighter).
These upgrades included the proprietary Advanced Aggressor Mission System (AAMS), which allows the F-16s to accurately replicate near-peer adversary fighters, enhancing training realism for U.S. pilots, AESA radars, infrared search and track (IRST), helmet-mounted cueing systems, datalinks, and electronic countermeasures to replicate near-peer threats.
The Top Aces’ F-16 fleet has also been equipped with IRST pods.
The “Felon Paint Job” for the F-16 suggests that in the coming days, the US Air Force pilots want to train against the threat posed by advanced fifth-generation Russian aircraft, the Su-57 Felon.
The Su-57 Felon Threat
After struggling with slow deliveries, it seems that Russia is finally making progress with expanding Su-57 production lines.
While the Komsomolsk-on-Amur Aviation Plant is the primary production facility, new facilities have been opened to support this.
Officials have put into operation new development facilities related to the fuel system and started construction of a hangar for avionics testing at the Komsomolsk-on-Amur factory in eastern Russia, the state-owned aerospace conglomerate United Aircraft Corporation announced in August last year.
Russia only has a small number of Su-57 aircraft and they have played a limited role in the war in Ukraine, confined mainly to long-range strikes from within Russian territory.
The contract for the production of 76 planes by the end of 2027 was signed by the Defense Ministry at the Army Forum in June 2019, with Komsomolsk-on-Amur specified as the leading production site.
However, the plant was quickly deemed too small, forcing officials to spend time expanding production space, which entailed changing and adding new equipment.
The Su-57, designed to compete with NATO’s fifth-generation fighters, such as the US F-22 Raptor and F-35 Lightning II, boasts cutting-edge stealth technology, supermaneuverability, and advanced avionics. The VKS received three batches of aircraft over the last year, with the last delivery recorded in December 2024.
Furthermore, in February this year, Yuri Kondratyev, Director of the Komsomolsk-on-Amur Aircraft Production Association (KnAAPO), said that a new version of the aircraft will be delivered to the VKS in 2025.
He did not specify any particular improvements, although there is speculation that the new version might feature the more advanced AL-51F1 or product 30 engines, which could improve the fighter’s performance.
Russian aerospace engineers are also continuously improving the Su-57 avionics and armaments.
Earlier this year, UAC chief Vadim Badekha said that as production expands, the aircraft will be integrated with newer features.
“The Su-57 platform has been created for a minimum of 40-50 years. It has an open architecture and can use a broad range of technologies with minimal changes to the basic solutions. Su-57 integration with unmanned aerial vehicles will be the central element of future combat systems. In the coming years, new features will be introduced into the serial Su-57 in the framework of the modernization program,” he said.
Additionally, last week, Chief of the Main Staff and First Deputy Commander in Chief of the Russian Aerospace Forces Lieutenant General Alexander Maksimtsev said that the Su-57 fifth-generation fighter has been equipped with hypersonic weapons.
“In accordance with the state defense order, the Aerospace Forces annually receive advanced and modernized weapon systems. The pace of deliveries of fifth-generation Su-57 aircraft is increasing, along with modern aviation strike systems and hypersonic weapons,” the commander reported in an interview.
There is speculation that the hypersonic weapon referred to is an air-launched derivative of the Zircon hypersonic cruise missile. Integrating the Zircon hypersonic cruise missile with the Su-57 will make it a much more lethal platform.
The F-16’s “Felon paint job” suggests that the USAF pilots are finally gearing up to train against the Russian Air Force’s most advanced fighter jet.
A Top Aces’ F-16A fighter jet has been spotted in an eye-catching new adversary paint scheme. The fighter aircraft, formerly with the Israeli Air Force, was seen supporting a Russian Su-57 Felon-inspired paint scheme.
Dubbed the “Felon Paint Job,” the aircraft was spotted in Arizona. It flew from Mesa Gateway Airport, where Top Aces performs maintenance on its F-16s, to Luke AFB, Arizona, as ACES 51.
After reaching Luke AFB, Arizona, the fighter jet took part in a local mission under the callsign ACES 1.
Though the fighter jet, formerly known as Netz 284, was also photographed while being wheeled out of the paint barn at Mesa, its return to Luke AFB, Arizona, offered a better look.
The F-16, tail number N871TA and bort number “284” Red, features a low-visibility, splinter-style grey camouflage pattern similar to that used by Russia’s fifth-generation stealth fighter.
The two-tone scheme includes angular transitions across the airframe, mimicking the faceted radar-evading design philosophy of the T-50/Su-57, the Aviationist reported.
The “Felon Paint Job” was complete with Soviet-style red stars on its tail and wings. The tail fin also carried Cyrillic script that read “Опыт Важен” (which translates to “Experience Matters”).
Notably, despite the “Felon Paint Job,” the fighter jet still retains the kill marking it earned in September 1981, when Netz 284 shot down a Syrian MiG-23.
Last year, another F-16 fighter jet from the Top Aces fleet was spotted sporting a “Flanker Blue” color scheme, inspired by the one used by some F-16s of the U.S. Air Force’s 64th Aggressor Squadron at Nellis Air Force Base, Nevada.
It remains to be seen what other paint schemes the Top Aces F-16 fleet will support in the coming days.
F-16’s Journey: From Israeli Air Force To Top Aces
The F-16A Netz 284 was one of the fighter jets that were retired from the Israeli Air Force at the end of 2016 and delivered to the US in 2021.
The aircraft was part of the 29 F-16 Netz (Hawk) fighter jets, which retired from the Israeli Air Force in 2016 after 36 years in service, and were subsequently bought by Top Aces for adversary training.
In 2021, the Israeli Ministry of Defense acknowledged the unprecedented sale of 29 F-16 Netz (Hawk) aircraft to Top Aces.
“Following negotiations led by SIBAT, the MoD has signed an unprecedented agreement to supply 29 F-16 aircraft to TOP ACES. These will be employed as staged adversary aircraft in U.S. Air Force training,” the Israeli Ministry of Defense posted on social media site X in 2021.
The first four of these F-16s were received at Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport in February 2021.
The four F-16s, with their wings, tail, and tailerons removed, were loaded on a Ukrainian Antonov An-124 at Tel Aviv-Ben Gurion airport on January 27 and, after a stop in Keflavik, Iceland, they arrived a day later at Phoenix-Mesa Gateway airport.
With these F-16s, Top Aces became the first company to provide a 4th-generation aircraft for staged adversary aircraft training. Till today, these F-16s remain the world’s only privately owned F-16s.
The F-16s were subsequently upgraded to a standard that is known as F-16 AAF (Advanced Aggressor Fighter).
These upgrades included the proprietary Advanced Aggressor Mission System (AAMS), which allows the F-16s to accurately replicate near-peer adversary fighters, enhancing training realism for U.S. pilots, AESA radars, infrared search and track (IRST), helmet-mounted cueing systems, datalinks, and electronic countermeasures to replicate near-peer threats.
The Top Aces’ F-16 fleet has also been equipped with IRST pods.
The “Felon Paint Job” for the F-16 suggests that in the coming days, the US Air Force pilots want to train against the threat posed by advanced fifth-generation Russian aircraft, the Su-57 Felon.
The Su-57 Felon Threat
After struggling with slow deliveries, it seems that Russia is finally making progress with expanding Su-57 production lines.
While the Komsomolsk-on-Amur Aviation Plant is the primary production facility, new facilities have been opened to support this.
Officials have put into operation new development facilities related to the fuel system and started construction of a hangar for avionics testing at the Komsomolsk-on-Amur factory in eastern Russia, the state-owned aerospace conglomerate United Aircraft Corporation announced in August last year.
Russia only has a small number of Su-57 aircraft and they have played a limited role in the war in Ukraine, confined mainly to long-range strikes from within Russian territory.
The contract for the production of 76 planes by the end of 2027 was signed by the Defense Ministry at the Army Forum in June 2019, with Komsomolsk-on-Amur specified as the leading production site.
However, the plant was quickly deemed too small, forcing officials to spend time expanding production space, which entailed changing and adding new equipment.
The Su-57, designed to compete with NATO’s fifth-generation fighters, such as the US F-22 Raptor and F-35 Lightning II, boasts cutting-edge stealth technology, supermaneuverability, and advanced avionics. The VKS received three batches of aircraft over the last year, with the last delivery recorded in December 2024.
Furthermore, in February this year, Yuri Kondratyev, Director of the Komsomolsk-on-Amur Aircraft Production Association (KnAAPO), said that a new version of the aircraft will be delivered to the VKS in 2025.
He did not specify any particular improvements, although there is speculation that the new version might feature the more advanced AL-51F1 or product 30 engines, which could improve the fighter’s performance.
Russian aerospace engineers are also continuously improving the Su-57 avionics and armaments.
Earlier this year, UAC chief Vadim Badekha said that as production expands, the aircraft will be integrated with newer features.
“The Su-57 platform has been created for a minimum of 40-50 years. It has an open architecture and can use a broad range of technologies with minimal changes to the basic solutions. Su-57 integration with unmanned aerial vehicles will be the central element of future combat systems. In the coming years, new features will be introduced into the serial Su-57 in the framework of the modernization program,” he said.
Additionally, last week, Chief of the Main Staff and First Deputy Commander in Chief of the Russian Aerospace Forces Lieutenant General Alexander Maksimtsev said that the Su-57 fifth-generation fighter has been equipped with hypersonic weapons.
“In accordance with the state defense order, the Aerospace Forces annually receive advanced and modernized weapon systems. The pace of deliveries of fifth-generation Su-57 aircraft is increasing, along with modern aviation strike systems and hypersonic weapons,” the commander reported in an interview.
There is speculation that the hypersonic weapon referred to is an air-launched derivative of the Zircon hypersonic cruise missile. Integrating the Zircon hypersonic cruise missile with the Su-57 will make it a much more lethal platform.
The F-16’s “Felon paint job” suggests that the USAF pilots are finally gearing up to train against the Russian Air Force’s most advanced fighter jet.
3 months ago
Taxi App Development Solution
Nowadays, traditional taxi services are being replaced with tech-enabled ride-hailing systems.
Car Rental App
Create a taxi app that allows consumers to select a diverse range of vehicles and book their rental on an hourly, daily, or weekly basis.
Fleet Management App
A fleet management app can help you streamline diverse fleet operations. It meets all of your particular service requirements.
Corporate Taxi App
Provide a dedicated corporate taxi app for employee transportation with scheduled rides, expense tracking, and billing management for businesses of any size.
Wrapping Up
Trioangle offers a robust taxi app development solution with advanced features, easy navigation, intuitive design, and scalable architecture. It's aimed to fulfil modern mobility demands while streamlining operations.
https://www.trioangle.com/...
#TaxiAppUSA #CabAppUK #RideHailingAfrica #GulfTaxiApp #TaxiAppDevelopment #UberLik
Nowadays, traditional taxi services are being replaced with tech-enabled ride-hailing systems.
Car Rental App
Create a taxi app that allows consumers to select a diverse range of vehicles and book their rental on an hourly, daily, or weekly basis.
Fleet Management App
A fleet management app can help you streamline diverse fleet operations. It meets all of your particular service requirements.
Corporate Taxi App
Provide a dedicated corporate taxi app for employee transportation with scheduled rides, expense tracking, and billing management for businesses of any size.
Wrapping Up
Trioangle offers a robust taxi app development solution with advanced features, easy navigation, intuitive design, and scalable architecture. It's aimed to fulfil modern mobility demands while streamlining operations.
https://www.trioangle.com/...
#TaxiAppUSA #CabAppUK #RideHailingAfrica #GulfTaxiApp #TaxiAppDevelopment #UberLik
5 months ago
Chinese Web Around U.S. Military Bases Worries Americans; Is Ukraine’s ‘Shock’ Attack On Russia A Wake-Up Call For Trump?
The surprise Ukrainian drone attack on Russia, facilitated by the smuggling of drones inside trucks, has rattled the world at large. American analysts and lawmakers are now concerned that Chinese cargo ships that dock at U.S. ports could potentially carry out a similar stunt against the United States.
The Security Service of Ukraine, or SBU, launched the drone attacks on multiple Russian military bases on June 1 under ‘Operation Spiderweb.’ The operation involved 117 First Person View (FPV) drones that were smuggled into Russia, concealed in wooden containers with remotely operated roofs mounted on trucks.
These trucks, driven by individuals reportedly unaware of the cargo they were carrying, were positioned near the target air bases to ensure precision strikes.
Russia couldn’t have fathomed that an infiltration like that was taking place right under its nose. The strikes, meticulously planned over 18 months, humiliated Russia’s military by exposing the gaps in its intelligence architecture and the vulnerabilities in its air defenses.
Caught unaware, the Russian military sustained losses of billions of dollars. In the aftermath of the incident, several pro-Russian military bloggers said it was Russia’s Pearl Harbor, a reference to the surprise Japanese attack on the US Pearl Harbor port during World War II, that destroyed multiple US warships and aircraft.
The attack, perhaps the most significant demonstration of asymmetric warfare in recent times, will have far-reaching global repercussions. US analysts are concerned that China could replicate a similar move against America, utilizing its cargo ships that have unrestricted access to US ports, as highlighted by Newsweek in a recent report.
The report noted that lawmakers and security experts have expressed concerns over China’s state-owned shipping behemoth, COSCO Shipping, operating across US ports, despite being classified as a Chinese military enterprise by the Pentagon in January 2025.
US analysts have voiced concern that these cargo ships could be used to deploy drones, possibly hidden inside ships, to launch a preemptive strike on US ports in the event of a conflict.
COSCO is the largest state-owned shipping firm in China and a significant force in international marine logistics, with a considerable presence in important US ports, including Oakland, Long Beach, and Los Angeles, among others.
In January 2025, the House Committee on Homeland Security expressed concern about COSCO’s access to major US ports and the alleged presence of suspected Chinese Communist Party (CCP) political officers on board its ships, suggesting direct CCP influence. It warned of threats like espionage, cyber intrusion, or even sabotage by the Chinese.
The Trump administration has imposed port fees on COSCO to challenge China’s hegemony in the world’s shipbuilding industry. Additionally, the recently imposed US tariffs, including a 145% tariff on Chinese goods, have led to a sharp decline in COSCO’s shipments to American ports.
For example, the Port of Los Angeles saw a 35% plunge in cargo volume in May 2025, with COSCO and other carriers canceling transits.
Notably, a temporary US-China tariff truce last month spurred a surge in bookings, but COSCO continues to face operational challenges due to fees and reduced demand.
Despite COSCO’s reduced presence in the US, US analysts remain suspicious. Retired Navy Commander Thomas Shugart and a fellow at the Center for a New American Security said: “It is becoming borderline-insane that we routinely allow ships owned and operated by DoD-designated Chinese military companies to sit in our ports with thousands of containers onboard and under their control.”
While a Chinese attack is unlikely without an existing state of war, the presence of COSCO vessels near critical infrastructure, like the Norfolk Naval Station, raises concerns about espionage or sabotage.
It is pertinent to note that even the Ukrainian operation took 18 months of planning and intelligence gathering to achieve the desired result.
Moreover, there have been suggestive reports about China spying on US military facilities by purchasing land nearby and even infiltrating the US port infrastructure in the past, which makes the threat of a Ukraine drone-like attack more plausible to some in the US.
Chinese Spying Concerns Loom Large
Chinese ships docking at US ports have been a matter of discourse in the US for quite some time. Last year, a US Congressional investigation discovered that a Chinese business installed intelligence-gathering equipment on cranes used at US seaports, potentially enabling Beijing to spy on Americans or damage vital infrastructure.
ZPMC, a state-owned engineering company based in Shanghai, exerted pressure on American port authorities to grant remote access to its cranes, specifically those situated on the West Coast, i.e., the contiguous states of California, Oregon, and Washington.
The report, produced after a year-long research, warned that “This access could potentially be extended to other [People’s Republic of China] government entities, posing a significant risk due to the PRC’s national security laws that mandate cooperation with state intelligence agencies.”
Citing contract paperwork and testimonies from port operators, the investigation stated that “these unknown modems were believed to have been installed under the auspices of collecting usage data for the equipment.” These modems allegedly employed a covert approach to gathering data and circumventing firewalls, which could potentially disrupt port operations, even though they were unnecessary for the cranes to operate.
At the time, these findings caused alarm because about 80% of the cargo cranes in American ports are owned by ZPMC.
Transporting goods through US marine ports, which generate trillions of dollars in economic activity every year, requires ship-to-shore cranes. However, because these cranes can often be controlled remotely, anyone with access to the networks may be able to collect intelligence from ports or damage equipment.
In a hypothetical scenario, the intelligence collected through the cranes could be used to launch an ‘Operation Spiderweb’ type of operation where Chinese cargos double up as carriers of drones that go off by flicking a button on a remote.
Earlier, the White House disclosed plans to “phase out Chinese-made port equipment and fully return crane making to the United States to deal with 200 Chinese-made cranes at U.S. ports and facilities”. However, the progress of that effort under the Trump administration remains unknown.
Another prevailing concern in the United States has been the ownership of farm and commercial land near US military facilities by Chinese people and corporations.
A previous report revealed that Chinese companies purchased several farmlands close to strategic US military installations, including some of the most strategically important military installations, such as MacDill Air Force Base in Tampa, Florida; Marine Corps Base Camp Pendleton in San Diego, California; Fort Liberty (formerly Fort Bragg) in Fayetteville, North Carolina; and Fort Cavazos (formerly Fort Hood) in Killeen, Texas.
Sources suggest that under the guise of farming, Chinese landowners could potentially set up surveillance equipment or use drones to monitor military sites. According to the January 2024 data from the US Department of Agriculture, China claims 349,442 acres out of roughly 40 million acres of foreign-owned farmland, or 0.87 percent.
It does not help that Chinese nationals have sneaked into military bases and other sensitive US sites more than 100 times in recent years, as the Wall Street Journal reported in 2023. This raises a very alarming issue regarding Chinese ownership of land near military sites.
Additionally, the US National Association of Realtors (NAR) stated in a report last year that the Chinese have remained the top foreign buyers of US residential property for the 11th consecutive year.
Experts caution that, just as Ukraine’s drones targeted Russian airfields, Chinese-owned property may be used for tracking devices, reconnaissance sites, or drones to observe US military activities.
The strategic placement of these lands near bases like Fort Liberty, which hosts critical airborne and special operations units, amplifies concerns about a surprise threat akin to Pearl Harbor’s unexpected attack.
Although no US federal law mandates a ban, individual states have been passing laws to curtail Chinese ownership of land near US military bases.
The surprise Ukrainian drone attack on Russia, facilitated by the smuggling of drones inside trucks, has rattled the world at large. American analysts and lawmakers are now concerned that Chinese cargo ships that dock at U.S. ports could potentially carry out a similar stunt against the United States.
The Security Service of Ukraine, or SBU, launched the drone attacks on multiple Russian military bases on June 1 under ‘Operation Spiderweb.’ The operation involved 117 First Person View (FPV) drones that were smuggled into Russia, concealed in wooden containers with remotely operated roofs mounted on trucks.
These trucks, driven by individuals reportedly unaware of the cargo they were carrying, were positioned near the target air bases to ensure precision strikes.
Russia couldn’t have fathomed that an infiltration like that was taking place right under its nose. The strikes, meticulously planned over 18 months, humiliated Russia’s military by exposing the gaps in its intelligence architecture and the vulnerabilities in its air defenses.
Caught unaware, the Russian military sustained losses of billions of dollars. In the aftermath of the incident, several pro-Russian military bloggers said it was Russia’s Pearl Harbor, a reference to the surprise Japanese attack on the US Pearl Harbor port during World War II, that destroyed multiple US warships and aircraft.
The attack, perhaps the most significant demonstration of asymmetric warfare in recent times, will have far-reaching global repercussions. US analysts are concerned that China could replicate a similar move against America, utilizing its cargo ships that have unrestricted access to US ports, as highlighted by Newsweek in a recent report.
The report noted that lawmakers and security experts have expressed concerns over China’s state-owned shipping behemoth, COSCO Shipping, operating across US ports, despite being classified as a Chinese military enterprise by the Pentagon in January 2025.
US analysts have voiced concern that these cargo ships could be used to deploy drones, possibly hidden inside ships, to launch a preemptive strike on US ports in the event of a conflict.
COSCO is the largest state-owned shipping firm in China and a significant force in international marine logistics, with a considerable presence in important US ports, including Oakland, Long Beach, and Los Angeles, among others.
In January 2025, the House Committee on Homeland Security expressed concern about COSCO’s access to major US ports and the alleged presence of suspected Chinese Communist Party (CCP) political officers on board its ships, suggesting direct CCP influence. It warned of threats like espionage, cyber intrusion, or even sabotage by the Chinese.
The Trump administration has imposed port fees on COSCO to challenge China’s hegemony in the world’s shipbuilding industry. Additionally, the recently imposed US tariffs, including a 145% tariff on Chinese goods, have led to a sharp decline in COSCO’s shipments to American ports.
For example, the Port of Los Angeles saw a 35% plunge in cargo volume in May 2025, with COSCO and other carriers canceling transits.
Notably, a temporary US-China tariff truce last month spurred a surge in bookings, but COSCO continues to face operational challenges due to fees and reduced demand.
Despite COSCO’s reduced presence in the US, US analysts remain suspicious. Retired Navy Commander Thomas Shugart and a fellow at the Center for a New American Security said: “It is becoming borderline-insane that we routinely allow ships owned and operated by DoD-designated Chinese military companies to sit in our ports with thousands of containers onboard and under their control.”
While a Chinese attack is unlikely without an existing state of war, the presence of COSCO vessels near critical infrastructure, like the Norfolk Naval Station, raises concerns about espionage or sabotage.
It is pertinent to note that even the Ukrainian operation took 18 months of planning and intelligence gathering to achieve the desired result.
Moreover, there have been suggestive reports about China spying on US military facilities by purchasing land nearby and even infiltrating the US port infrastructure in the past, which makes the threat of a Ukraine drone-like attack more plausible to some in the US.
Chinese Spying Concerns Loom Large
Chinese ships docking at US ports have been a matter of discourse in the US for quite some time. Last year, a US Congressional investigation discovered that a Chinese business installed intelligence-gathering equipment on cranes used at US seaports, potentially enabling Beijing to spy on Americans or damage vital infrastructure.
ZPMC, a state-owned engineering company based in Shanghai, exerted pressure on American port authorities to grant remote access to its cranes, specifically those situated on the West Coast, i.e., the contiguous states of California, Oregon, and Washington.
The report, produced after a year-long research, warned that “This access could potentially be extended to other [People’s Republic of China] government entities, posing a significant risk due to the PRC’s national security laws that mandate cooperation with state intelligence agencies.”
Citing contract paperwork and testimonies from port operators, the investigation stated that “these unknown modems were believed to have been installed under the auspices of collecting usage data for the equipment.” These modems allegedly employed a covert approach to gathering data and circumventing firewalls, which could potentially disrupt port operations, even though they were unnecessary for the cranes to operate.
At the time, these findings caused alarm because about 80% of the cargo cranes in American ports are owned by ZPMC.
Transporting goods through US marine ports, which generate trillions of dollars in economic activity every year, requires ship-to-shore cranes. However, because these cranes can often be controlled remotely, anyone with access to the networks may be able to collect intelligence from ports or damage equipment.
In a hypothetical scenario, the intelligence collected through the cranes could be used to launch an ‘Operation Spiderweb’ type of operation where Chinese cargos double up as carriers of drones that go off by flicking a button on a remote.
Earlier, the White House disclosed plans to “phase out Chinese-made port equipment and fully return crane making to the United States to deal with 200 Chinese-made cranes at U.S. ports and facilities”. However, the progress of that effort under the Trump administration remains unknown.
Another prevailing concern in the United States has been the ownership of farm and commercial land near US military facilities by Chinese people and corporations.
A previous report revealed that Chinese companies purchased several farmlands close to strategic US military installations, including some of the most strategically important military installations, such as MacDill Air Force Base in Tampa, Florida; Marine Corps Base Camp Pendleton in San Diego, California; Fort Liberty (formerly Fort Bragg) in Fayetteville, North Carolina; and Fort Cavazos (formerly Fort Hood) in Killeen, Texas.
Sources suggest that under the guise of farming, Chinese landowners could potentially set up surveillance equipment or use drones to monitor military sites. According to the January 2024 data from the US Department of Agriculture, China claims 349,442 acres out of roughly 40 million acres of foreign-owned farmland, or 0.87 percent.
It does not help that Chinese nationals have sneaked into military bases and other sensitive US sites more than 100 times in recent years, as the Wall Street Journal reported in 2023. This raises a very alarming issue regarding Chinese ownership of land near military sites.
Additionally, the US National Association of Realtors (NAR) stated in a report last year that the Chinese have remained the top foreign buyers of US residential property for the 11th consecutive year.
Experts caution that, just as Ukraine’s drones targeted Russian airfields, Chinese-owned property may be used for tracking devices, reconnaissance sites, or drones to observe US military activities.
The strategic placement of these lands near bases like Fort Liberty, which hosts critical airborne and special operations units, amplifies concerns about a surprise threat akin to Pearl Harbor’s unexpected attack.
Although no US federal law mandates a ban, individual states have been passing laws to curtail Chinese ownership of land near US military bases.
5 months ago
India-Pak War: China’s Military Satellites Helped Pakistan To Attack India; Delhi Works To Bridge The ‘Big Gap’ With Beijing (Part 1)
It is no news that China supported Pakistan with military hardware during the recent military confrontation with India. However, less discussed has been the support the constellation of Chinese satellites provided in terms of Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) to Islamabad, and how New Delhi countered it by mobilizing all its military and civilian assets in space.
The Indian military is taking incremental steps to build its own constellation of 52 satellites over the next five years, aiming to enhance its capability to spy from space. However, the ambitious plan hit a speed bump as the attempt to position the NVS-02 satellite in its intended orbit was not achieved due to a failure in the satellite’s onboard thrusters.
Launched on January 29, 2025, aboard the GSLV-Mk 2 rocket, this mission marked ISRO’s 100th launch from the Sriharikota spaceport.
The satellite is a crucial component of India’s Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC) system, which aims to provide accurate positioning services across India and extend up to 1500 km beyond its borders.
“We pulled all the resources (civilian and military space assets) and gave them to the armed forces. We were virtually looking at each other all the time. We had gaps, but we were much better,” a source familiar with the matter told the EurAsian Times about the space-based reconnaissance during the Indo-Pak war. The source admitted that India has gaps, and its space capabilities in comparison to China are currently inadequate.
In fact, the purported “kill chain” achieved by Pakistan with the help of Chinese space assets has been cited as the reason behind the alleged downing of India’s fighter jets. The official conceded that China is far ahead when it comes to space assets.
“They have 4-5 times more assets than us. The Chinese have 7 geo-stationary satellites. They are able to see all the time. But the resolution is lower. They are critical for their maritime security,” the official added.
China’s space architecture includes multiple layers of infrastructure, ranging from low-Earth orbit satellites to ground control stations, all of which are interconnected to form a resilient network.
The Chinese can see all the time, but their satellites have limitations of bandwidth, duty cycle, and orbit configuration. However, despite its space assets, China was unable to help Pakistan pinpoint key Indian assets, such as the S-400 Long Range Surface-to-Air Missile System.
According to comprehensive databases, such as the one published by Keep Track, China is associated with approximately 5,330 satellites in orbit. The United States leads with about 11,655 satellites, and Russia follows with around 7,187 satellites.
Here, satellites include objects launched for commercial, scientific, military, and joint international purposes—even if they involve non-government actors—and sometimes even defunct spacecraft that are still tracked in orbit. In comparison, India has 218 satellites.
It is challenging to pinpoint precise details about the military reconnaissance satellites China operates; however, open-source information suggests that China has approximately 30 to 40 active reconnaissance satellites.
Most of these are from the Yaogan series, specifically designed to provide imaging and other forms of signals intelligence for China’s military. As many satellites have dual use and certain assets are kept secret by the Chinese government, the total number of military satellites could be higher.
The Yaogan series— including the launch of Yaogan-41 indicates a continuing expansion in capability and numbers for China.
Yaogan-41 Ensures No One Escapes China’s Spy Satellites
The remote sensing satellite Yaogan-41 was launched into geostationary orbit (GEO) on December 15, 2023. The satellite is expected to allow continuous surveillance of the Pacific and Indian Oceans, as well as Taiwan and Mainland China.
According to the Chinese government, Yaogan-41 is a civilian high-altitude optical remote-sensing satellite intended for crop yield estimation, environmental management, weather forecasting, and disaster prevention.
However, Western analysts observe that alongside other Chinese surveillance satellites, Yaogan-41 purportedly gives China an unprecedented ability to identify and track objects as small as cars throughout the entire Indo-Pacific region, putting the US and other countries’ naval and air forces in the region at risk.
The majority of surveillance satellites operate in Low Earth Orbit, as it is easier and cheaper to put satellites into LEO. Also, satellites in LEO produce sharper resolution as it is closer to Earth. However, the major drawback of LEO satellites is a lack of continuity, which is important for surveillance.
A satellite in LEO takes less than two hours to orbit the Earth. So, it can only oversee a given spot on Earth for a few minutes. Also, due to orbital mechanics, it may take hours or days for that satellite to revisit the same spot again. However, a constellation of satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) can help reduce the revisit time.
On the other hand, satellites in GEO orbit are at the same rate as the Earth. This means that they view the Earth as if it is stationary. Only GEO provides a satellite, like Yaogan-41, with a continuous view of the same place. An added advantage is that a GEO satellite from its altitude of 36,000 km can see almost half of Earth’s surface.
The Yaogan satellites also play a crucial role in supporting China’s missile forces, providing the data needed for accurate targeting of long-range ballistic and cruise missiles.
There are several geosynchronous satellites, but they are primarily dedicated to weather forecasting and utilize low-resolution remote sensing systems for tracking large cloud formations and storms. Only China and India operate high-resolution optical GEO satellites; however, India’s system features a multi-spectral payload, unlike its Chinese counterparts, which carry a visible light optical imager.
India’s Baby Steps To Space
India had woken up to the strategic importance of space assets in warfare during the Kargil War when the US’s denial of GPS left its soldiers high and dry as they were trying to push the Pakistani insurgents from their entrenched positions. However, work has been going at a snail’s pace.
“It has been only in the last couple of years that India has awakened to the military implications of space, and the Indian armed forces have started claiming ownership of it. IAF has realized the utilisation of Kautilaya (an indigenously developed Electronic Intelligence system),” the official added.
India established the Defense Space Agency in 2019, which is slated to evolve into a fully fledged Space Command. The IAF has envisioned India having over 100 military satellites, both large and small, within the next seven to eight years, with active participation from the private sector.
To keep pace with global developments, the IAF is gradually expanding its mission scope from offensive and defensive counter-air operations to operations in the space domain. As part of this transition, the existing Integrated Air Command and Control System (IACCS) will evolve into the Integrated Air and Space Command and Control System (IASCCS).
The government, on its part, has been shortening the launch time for military satellites. The DRDO’s project Kautilya added to India’s space surveillance capability.
The 436-kg satellite, placed in a 749-km orbit, helps the Indian armed forces pinpoint the location of enemy radars by detecting the electromagnetic signals they emit. In the making for about eight years, it carries instrumentation capable of detecting, locating, and characterising electromagnetic signals, specifically of military radars.
India’s premier intelligence-gathering satellite, EMISAT, has taken a good look at the positions of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army (PLA) in occupied Tibet.
India also has an ELINT satellite, launched in 2019, which underscored its usefulness by passing over the PLA position in Tibet near Arunachal Pradesh. The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has launched 29 satellites, including EMISAT, from the US, Lithuania, Spain, and Switzerland. This was the first time the Indian space agency launched these satellites in three different orbits.
The launch of the electronic spy satellite was a significant achievement for India; China has already been using ELINT satellites in triplets, as a single satellite will not be enough to pinpoint a target.
At least three of them are required to receive electronic transmissions from a target on the ground and locate it through triangulation. A typical ELINT satellite constellation consists of three satellites in orbit, flying in a triangular formation with an orbit inclination of 63.4 degrees.
The recent launch failure to place NVS-02 in its designated orbit is a setback for India’s NAVIC navigation system. China’s Beidou Navigation Satellite System is central to China’s space architecture.
It is no news that China supported Pakistan with military hardware during the recent military confrontation with India. However, less discussed has been the support the constellation of Chinese satellites provided in terms of Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) to Islamabad, and how New Delhi countered it by mobilizing all its military and civilian assets in space.
The Indian military is taking incremental steps to build its own constellation of 52 satellites over the next five years, aiming to enhance its capability to spy from space. However, the ambitious plan hit a speed bump as the attempt to position the NVS-02 satellite in its intended orbit was not achieved due to a failure in the satellite’s onboard thrusters.
Launched on January 29, 2025, aboard the GSLV-Mk 2 rocket, this mission marked ISRO’s 100th launch from the Sriharikota spaceport.
The satellite is a crucial component of India’s Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC) system, which aims to provide accurate positioning services across India and extend up to 1500 km beyond its borders.
“We pulled all the resources (civilian and military space assets) and gave them to the armed forces. We were virtually looking at each other all the time. We had gaps, but we were much better,” a source familiar with the matter told the EurAsian Times about the space-based reconnaissance during the Indo-Pak war. The source admitted that India has gaps, and its space capabilities in comparison to China are currently inadequate.
In fact, the purported “kill chain” achieved by Pakistan with the help of Chinese space assets has been cited as the reason behind the alleged downing of India’s fighter jets. The official conceded that China is far ahead when it comes to space assets.
“They have 4-5 times more assets than us. The Chinese have 7 geo-stationary satellites. They are able to see all the time. But the resolution is lower. They are critical for their maritime security,” the official added.
China’s space architecture includes multiple layers of infrastructure, ranging from low-Earth orbit satellites to ground control stations, all of which are interconnected to form a resilient network.
The Chinese can see all the time, but their satellites have limitations of bandwidth, duty cycle, and orbit configuration. However, despite its space assets, China was unable to help Pakistan pinpoint key Indian assets, such as the S-400 Long Range Surface-to-Air Missile System.
According to comprehensive databases, such as the one published by Keep Track, China is associated with approximately 5,330 satellites in orbit. The United States leads with about 11,655 satellites, and Russia follows with around 7,187 satellites.
Here, satellites include objects launched for commercial, scientific, military, and joint international purposes—even if they involve non-government actors—and sometimes even defunct spacecraft that are still tracked in orbit. In comparison, India has 218 satellites.
It is challenging to pinpoint precise details about the military reconnaissance satellites China operates; however, open-source information suggests that China has approximately 30 to 40 active reconnaissance satellites.
Most of these are from the Yaogan series, specifically designed to provide imaging and other forms of signals intelligence for China’s military. As many satellites have dual use and certain assets are kept secret by the Chinese government, the total number of military satellites could be higher.
The Yaogan series— including the launch of Yaogan-41 indicates a continuing expansion in capability and numbers for China.
Yaogan-41 Ensures No One Escapes China’s Spy Satellites
The remote sensing satellite Yaogan-41 was launched into geostationary orbit (GEO) on December 15, 2023. The satellite is expected to allow continuous surveillance of the Pacific and Indian Oceans, as well as Taiwan and Mainland China.
According to the Chinese government, Yaogan-41 is a civilian high-altitude optical remote-sensing satellite intended for crop yield estimation, environmental management, weather forecasting, and disaster prevention.
However, Western analysts observe that alongside other Chinese surveillance satellites, Yaogan-41 purportedly gives China an unprecedented ability to identify and track objects as small as cars throughout the entire Indo-Pacific region, putting the US and other countries’ naval and air forces in the region at risk.
The majority of surveillance satellites operate in Low Earth Orbit, as it is easier and cheaper to put satellites into LEO. Also, satellites in LEO produce sharper resolution as it is closer to Earth. However, the major drawback of LEO satellites is a lack of continuity, which is important for surveillance.
A satellite in LEO takes less than two hours to orbit the Earth. So, it can only oversee a given spot on Earth for a few minutes. Also, due to orbital mechanics, it may take hours or days for that satellite to revisit the same spot again. However, a constellation of satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) can help reduce the revisit time.
On the other hand, satellites in GEO orbit are at the same rate as the Earth. This means that they view the Earth as if it is stationary. Only GEO provides a satellite, like Yaogan-41, with a continuous view of the same place. An added advantage is that a GEO satellite from its altitude of 36,000 km can see almost half of Earth’s surface.
The Yaogan satellites also play a crucial role in supporting China’s missile forces, providing the data needed for accurate targeting of long-range ballistic and cruise missiles.
There are several geosynchronous satellites, but they are primarily dedicated to weather forecasting and utilize low-resolution remote sensing systems for tracking large cloud formations and storms. Only China and India operate high-resolution optical GEO satellites; however, India’s system features a multi-spectral payload, unlike its Chinese counterparts, which carry a visible light optical imager.
India’s Baby Steps To Space
India had woken up to the strategic importance of space assets in warfare during the Kargil War when the US’s denial of GPS left its soldiers high and dry as they were trying to push the Pakistani insurgents from their entrenched positions. However, work has been going at a snail’s pace.
“It has been only in the last couple of years that India has awakened to the military implications of space, and the Indian armed forces have started claiming ownership of it. IAF has realized the utilisation of Kautilaya (an indigenously developed Electronic Intelligence system),” the official added.
India established the Defense Space Agency in 2019, which is slated to evolve into a fully fledged Space Command. The IAF has envisioned India having over 100 military satellites, both large and small, within the next seven to eight years, with active participation from the private sector.
To keep pace with global developments, the IAF is gradually expanding its mission scope from offensive and defensive counter-air operations to operations in the space domain. As part of this transition, the existing Integrated Air Command and Control System (IACCS) will evolve into the Integrated Air and Space Command and Control System (IASCCS).
The government, on its part, has been shortening the launch time for military satellites. The DRDO’s project Kautilya added to India’s space surveillance capability.
The 436-kg satellite, placed in a 749-km orbit, helps the Indian armed forces pinpoint the location of enemy radars by detecting the electromagnetic signals they emit. In the making for about eight years, it carries instrumentation capable of detecting, locating, and characterising electromagnetic signals, specifically of military radars.
India’s premier intelligence-gathering satellite, EMISAT, has taken a good look at the positions of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army (PLA) in occupied Tibet.
India also has an ELINT satellite, launched in 2019, which underscored its usefulness by passing over the PLA position in Tibet near Arunachal Pradesh. The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has launched 29 satellites, including EMISAT, from the US, Lithuania, Spain, and Switzerland. This was the first time the Indian space agency launched these satellites in three different orbits.
The launch of the electronic spy satellite was a significant achievement for India; China has already been using ELINT satellites in triplets, as a single satellite will not be enough to pinpoint a target.
At least three of them are required to receive electronic transmissions from a target on the ground and locate it through triangulation. A typical ELINT satellite constellation consists of three satellites in orbit, flying in a triangular formation with an orbit inclination of 63.4 degrees.
The recent launch failure to place NVS-02 in its designated orbit is a setback for India’s NAVIC navigation system. China’s Beidou Navigation Satellite System is central to China’s space architecture.
5 months ago
AEW&CS Aircraft: Russia Chops, U.S. Slashes & Pakistan Loses ‘Eye In The Sky’; Is Era Of ‘Flying Radars’ Ending?
For decades, AEW&CS aircraft have been a cornerstone of air operations, offering unmatched situational awareness and coordination. However, with the United States and Russia reportedly chopping their AEW&CS programs, has their relevance become questionable?
As the replacement for the decades-old E-3 Sentry AWACS aircraft, the US Air Force (USAF) decided to purchase the E-7 Airborne Early Warning and Control System (AEW&CS) to serve as the new battle management platform, offering airborne moving target indication (AMTI). However, its future has now become uncertain.
Earlier this month, an Air and Space Forces report stated that the USAF’s plan to acquire 26 Boeing E-7 Wedgetail aircraft is under review and faces potential cuts as part of the fiscal 2026 budget process under the current Trump administration.
Citing informed sources, the report claimed that those who advocate for slashing the planned purchase argue that space-based assets could accomplish the same job.
Before this, the UK reduced its order of E-7 Wedgetail aircraft from five to three as a cost-saving measure. The decision to cancel the purchase was made despite the Royal Air Force (RAF) E-3D Sentry fleet being retired in 2021, leaving the UK without a dedicated, crewed, fixed-wing airborne early warning aircraft.
Similarly, reports surfaced recently that Russia’s A-100 AEW&CS development program had been canceled. The A-100 was anticipated to replace the A-50, which is currently in service with the Russian Aerospace Forces (VKS). However, with no recent update on the aircraft, there is growing concern that the program may have been effectively canceled or put on hold indefinitely.
The cancellation of A-100 has been widely discussed on social media. The prevailing narrative attributes the cancellation to Western sanctions, which allegedly hindered Russia’s ability to procure components for the advanced system.
However, some experts believe that a potential cancellation might have been decided upon due to combat losses of A-50, and the feasibility of cheaper, more flexible alternatives to traditional AWACS platforms.
Russia has lost two A-50 in the grinding Ukraine War, in January and February 2024, respectively. They may have lost another during Ukraine’s stunning drone attack on Russian military bases on 1st June.
While AEW&CS platforms are equipped with defensive countermeasures, the recent losses indicate that these systems do not guarantee survivability.
This was also observed in the latest India-Pakistan conflict, where an Indian S-400 air defense system reportedly downed a Pakistan Air Force’s Saab Erieye-2000 flying radar. Pakistan lost another Saab Erieye-2000 in an Indian missile strike on Pakistan’s Bholari Air Base, as confirmed by PAF’s ex-Air Marshal.
Indian Air Force veteran and popular military expert, Squadron Leader Vijainder K. Thakur, says, “The increasing cost, complexity, and vulnerability of traditional AEW&CS systems raise serious questions about their long-term viability.”
Thakur attributed the vulnerability of AEW&CS aircraft to modern air defense missiles as a factor that potentially contributes to their progressive redundancy.
“An airborne radar with a 300 km surveillance range is highly advantageous if enemy missile systems have a 60–70 km reach. However, that advantage erodes—and the risk to the platform increases significantly—when missile ranges exceed 150 km, especially if their launchers are mobile and untrackable. While AEW&CS platforms are equipped with defensive countermeasures, the recent losses indicate that these systems do not guarantee survivability”. He emphasised that this threat will only grow as air defense missile ranges continue to increase.
Thakur said that Russia’s transition to a different aerial warning and control architecture, where high-endurance fighter aircraft outfitted with long-range radars and missiles serve as dispersed nodes of an AEW&CS network, is arguably the strongest argument for scrapping the A-100 program.
AEW&CS Still Relevant In Combat?
Typically, an AEW&CS aircraft is considered crucial as it provides real-time surveillance, command, and control over large areas. Its powerful radars can detect warplanes, missiles, and even drones at long ranges, providing critical situational awareness that ground-based radars may struggle to match.
They coordinate air operations, guide fighters, and integrate data from multiple sources, including satellites, other aircraft, and ground-based sensors, serving as airborne command centers. This role is vital in complex, dynamic battlefields where rapid decision-making holds the key.
AEW&CS enable early warning of incoming threats, including low-flying aircraft or cruise missiles, which are harder to detect from the ground. They essentially extend the range of air defense networks and enhance offensive operations by guiding assets efficiently.
AEW&CS are critical in contested regions where air superiority and early warning may prove to be decisive against a near-peer adversary. For example, NATO has extensively used its AEW&CS fleet for monitoring Russian air activity near Ukraine since the war began more than three years ago.
The utility of an AEW&CS is best explained by the USAF. The service maintains that the E-7 AEW&CS is crucial for all modern-day offensive and defensive missions. Speaking at the House Appropriations subcommittee on defense May 6, Air Force Chief of Staff Gen. David W. Allvin said, “We have to do more than just sense.”
He was explaining why space-based assets, as suggested by some at the Pentagon, cannot replace a cutting-edge AEW&CS aircraft.
“We have to sense, make sense, and act. And right now, the E-7 is the platform that delivers what the E-3 can with greater capability. But I think we just need to ensure that we’re adequately covering all parts of that as we do that migration, before we just go from one domain to another specifically.”
Despite its efforts to develop a future space-based moving-target indication capability, US officials believe that the Space Force will not be able to take on the E-7’s operations anytime soon.
“Space offers a lot of advantages, particularly in a contested environment, but it isn’t necessarily optimized for the full spectrum of operations that your military is going to be asked to do,” said Chief of Space Operations Gen. B. Chance Saltzman during the hearing. “No one system is going to be perfectly optimized to take care of the full spectrum of ops. And so that’s where I think you need a mix of systems.”
While it is true that AEW&CS are large, slow-moving platforms, which makes them vulnerable to long-range missiles, they could be granted enhanced protection with the help of escorts to enhance survivability.
The newer, more advanced AEW&CS systems are being upgraded with advanced sensors and counter-jamming tech to stay effective. Additionally, they could be integrated with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and multi-spectral sensors to track smaller, faster targets, thereby defeating the burgeoning threat posed by drones.
Some experts argue that advanced fighter jets can be equipped with specialized reconnaissance pods on external pylons and other advanced sensors, enabling them to function as airborne surveillance and control platforms. They can provide theater-wide situational awareness through real-time sensor fusion when networked with other advanced fighters, creating a distributed and resilient alternative to traditional airborne early warning systems.
A networked group of fighters can act as a “sensor web,” pooling data to cover large areas, potentially mimicking some AWACS functions like early warning and target tracking.
Although fighter jets, particularly stealth fighters, are less susceptible on their own, it is essential to remember that a networked approach relies on multiple platforms, and the loss of even a handful could significantly reduce the network’s effectiveness.
AEW&CS uses sophisticated multi-spectral sensors and artificial intelligence (AI) to identify low-observable (stealth) aircraft, drones, and hypersonic missiles. Although fighters are getting better at this, their smaller radars and limited sensor suites are less effective against such threats when compared to the’ specialized systems of the AEW&CS.
AEW&CS remain critical for wide-area surveillance and coordinating complex air operations, especially in contested environments. The most likely future model is a hybrid one that combines AEW&CS, drones, satellites, and networked fighters.
So, while governments can cut down on purchases due to fiscal constraints, it might not mean that these AEW&CS are a thing of the past.
For decades, AEW&CS aircraft have been a cornerstone of air operations, offering unmatched situational awareness and coordination. However, with the United States and Russia reportedly chopping their AEW&CS programs, has their relevance become questionable?
As the replacement for the decades-old E-3 Sentry AWACS aircraft, the US Air Force (USAF) decided to purchase the E-7 Airborne Early Warning and Control System (AEW&CS) to serve as the new battle management platform, offering airborne moving target indication (AMTI). However, its future has now become uncertain.
Earlier this month, an Air and Space Forces report stated that the USAF’s plan to acquire 26 Boeing E-7 Wedgetail aircraft is under review and faces potential cuts as part of the fiscal 2026 budget process under the current Trump administration.
Citing informed sources, the report claimed that those who advocate for slashing the planned purchase argue that space-based assets could accomplish the same job.
Before this, the UK reduced its order of E-7 Wedgetail aircraft from five to three as a cost-saving measure. The decision to cancel the purchase was made despite the Royal Air Force (RAF) E-3D Sentry fleet being retired in 2021, leaving the UK without a dedicated, crewed, fixed-wing airborne early warning aircraft.
Similarly, reports surfaced recently that Russia’s A-100 AEW&CS development program had been canceled. The A-100 was anticipated to replace the A-50, which is currently in service with the Russian Aerospace Forces (VKS). However, with no recent update on the aircraft, there is growing concern that the program may have been effectively canceled or put on hold indefinitely.
The cancellation of A-100 has been widely discussed on social media. The prevailing narrative attributes the cancellation to Western sanctions, which allegedly hindered Russia’s ability to procure components for the advanced system.
However, some experts believe that a potential cancellation might have been decided upon due to combat losses of A-50, and the feasibility of cheaper, more flexible alternatives to traditional AWACS platforms.
Russia has lost two A-50 in the grinding Ukraine War, in January and February 2024, respectively. They may have lost another during Ukraine’s stunning drone attack on Russian military bases on 1st June.
While AEW&CS platforms are equipped with defensive countermeasures, the recent losses indicate that these systems do not guarantee survivability.
This was also observed in the latest India-Pakistan conflict, where an Indian S-400 air defense system reportedly downed a Pakistan Air Force’s Saab Erieye-2000 flying radar. Pakistan lost another Saab Erieye-2000 in an Indian missile strike on Pakistan’s Bholari Air Base, as confirmed by PAF’s ex-Air Marshal.
Indian Air Force veteran and popular military expert, Squadron Leader Vijainder K. Thakur, says, “The increasing cost, complexity, and vulnerability of traditional AEW&CS systems raise serious questions about their long-term viability.”
Thakur attributed the vulnerability of AEW&CS aircraft to modern air defense missiles as a factor that potentially contributes to their progressive redundancy.
“An airborne radar with a 300 km surveillance range is highly advantageous if enemy missile systems have a 60–70 km reach. However, that advantage erodes—and the risk to the platform increases significantly—when missile ranges exceed 150 km, especially if their launchers are mobile and untrackable. While AEW&CS platforms are equipped with defensive countermeasures, the recent losses indicate that these systems do not guarantee survivability”. He emphasised that this threat will only grow as air defense missile ranges continue to increase.
Thakur said that Russia’s transition to a different aerial warning and control architecture, where high-endurance fighter aircraft outfitted with long-range radars and missiles serve as dispersed nodes of an AEW&CS network, is arguably the strongest argument for scrapping the A-100 program.
AEW&CS Still Relevant In Combat?
Typically, an AEW&CS aircraft is considered crucial as it provides real-time surveillance, command, and control over large areas. Its powerful radars can detect warplanes, missiles, and even drones at long ranges, providing critical situational awareness that ground-based radars may struggle to match.
They coordinate air operations, guide fighters, and integrate data from multiple sources, including satellites, other aircraft, and ground-based sensors, serving as airborne command centers. This role is vital in complex, dynamic battlefields where rapid decision-making holds the key.
AEW&CS enable early warning of incoming threats, including low-flying aircraft or cruise missiles, which are harder to detect from the ground. They essentially extend the range of air defense networks and enhance offensive operations by guiding assets efficiently.
AEW&CS are critical in contested regions where air superiority and early warning may prove to be decisive against a near-peer adversary. For example, NATO has extensively used its AEW&CS fleet for monitoring Russian air activity near Ukraine since the war began more than three years ago.
The utility of an AEW&CS is best explained by the USAF. The service maintains that the E-7 AEW&CS is crucial for all modern-day offensive and defensive missions. Speaking at the House Appropriations subcommittee on defense May 6, Air Force Chief of Staff Gen. David W. Allvin said, “We have to do more than just sense.”
He was explaining why space-based assets, as suggested by some at the Pentagon, cannot replace a cutting-edge AEW&CS aircraft.
“We have to sense, make sense, and act. And right now, the E-7 is the platform that delivers what the E-3 can with greater capability. But I think we just need to ensure that we’re adequately covering all parts of that as we do that migration, before we just go from one domain to another specifically.”
Despite its efforts to develop a future space-based moving-target indication capability, US officials believe that the Space Force will not be able to take on the E-7’s operations anytime soon.
“Space offers a lot of advantages, particularly in a contested environment, but it isn’t necessarily optimized for the full spectrum of operations that your military is going to be asked to do,” said Chief of Space Operations Gen. B. Chance Saltzman during the hearing. “No one system is going to be perfectly optimized to take care of the full spectrum of ops. And so that’s where I think you need a mix of systems.”
While it is true that AEW&CS are large, slow-moving platforms, which makes them vulnerable to long-range missiles, they could be granted enhanced protection with the help of escorts to enhance survivability.
The newer, more advanced AEW&CS systems are being upgraded with advanced sensors and counter-jamming tech to stay effective. Additionally, they could be integrated with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and multi-spectral sensors to track smaller, faster targets, thereby defeating the burgeoning threat posed by drones.
Some experts argue that advanced fighter jets can be equipped with specialized reconnaissance pods on external pylons and other advanced sensors, enabling them to function as airborne surveillance and control platforms. They can provide theater-wide situational awareness through real-time sensor fusion when networked with other advanced fighters, creating a distributed and resilient alternative to traditional airborne early warning systems.
A networked group of fighters can act as a “sensor web,” pooling data to cover large areas, potentially mimicking some AWACS functions like early warning and target tracking.
Although fighter jets, particularly stealth fighters, are less susceptible on their own, it is essential to remember that a networked approach relies on multiple platforms, and the loss of even a handful could significantly reduce the network’s effectiveness.
AEW&CS uses sophisticated multi-spectral sensors and artificial intelligence (AI) to identify low-observable (stealth) aircraft, drones, and hypersonic missiles. Although fighters are getting better at this, their smaller radars and limited sensor suites are less effective against such threats when compared to the’ specialized systems of the AEW&CS.
AEW&CS remain critical for wide-area surveillance and coordinating complex air operations, especially in contested environments. The most likely future model is a hybrid one that combines AEW&CS, drones, satellites, and networked fighters.
So, while governments can cut down on purchases due to fiscal constraints, it might not mean that these AEW&CS are a thing of the past.
5 months ago
(E)
Ukraine’s Ferocious UAV Attack “Rocks & Shocks” Russia; Here’s Why It Should Alarm U.S., Europe & India. (Part 1)
In the shadowy theater of modern warfare, a new, chilling act has just unfolded, leaving the world to ponder its terrifying implications.
Imagine, if you dare, a scenario where the very bastions of a nation’s aerial might – its strategic air bases – are simultaneously struck by a swarm of unseen, silent assassins.
This isn’t the script of a dystopian thriller; it’s a stark reality that recently played out in Russia, where an audacious drone attack reportedly crippled dozens of many strategic bombers.
The whispers on the wind suggest these robotic harbingers of destruction were smuggled in, hidden in plain sight, within ordinary containers. This single, audacious act has ripped open a Pandora’s Box of vulnerabilities, raising a chilling question: If it can happen to Russia, who’s next?
The strategic implications are seismic, and the tremors are being felt worldwide.
We’re talking about a paradigm shift in asymmetric warfare, where the lines between state actors and rogue elements blur, and where the most advanced military hardware can be rendered obsolete by off-the-shelf technology.
This isn’t just about damaged aircraft; it’s about shattered illusions of invincibility, about the terrifying ease with which a sophisticated nation’s defenses can be bypassed. The message is clear: the future of warfare is here, and it’s buzzing with a potentially devastating anonymity.
Let’s not mince words: this Russian air base attack is a crimson-letter warning to every major power, a visceral demonstration of how a seemingly low-tech, high-impact assault can achieve strategic objectives.
It exposes a gaping chasm in traditional defense paradigms, a vulnerability that demands immediate, radical re-evaluation. The very notion of secure borders and impregnable airspaces has been challenged, not by intercontinental ballistic missiles, but by something far more insidious – a container-borne threat, silently deployed, striking at the heart of military might.
The question isn’t if a similar attack could happen in India, the United States, or the European Union; it’s when, and with what devastating consequences.
The globalized world, with its interconnected supply chains and porous borders, is a fertile ground for such clandestine operations. The same commercial arteries that nourish our economies can become conduits for destruction. The allure of such an attack is undeniable for those seeking to destabilize, to inflict economic and military pain without the traditional risks of open confrontation.
So, let’s pull back the curtain on the potential nightmare scenarios and, more importantly, illuminate the urgent measures that must be taken to prevent such a catastrophic event from unfolding on their own soil.
United States: The Fortress Under Siege From Within
The United States, with its immense military footprint and highly advanced technological capabilities, might seem impenetrable. However, the Russian incident highlights that even the most formidable fortresses have hidden weaknesses, particularly when the threat originates from within.
An attack on a major air force base like Nellis, Edwards, or Barksdale, targeting B-2 stealth bombers or F-35 fighters, would send shockwaves through the global security architecture.
The economic fallout from even a temporary grounding of a significant portion of its air fleet, coupled with the psychological blow to national morale, would be immense.
Reimagining Homeland Security: From Borders to Basements: The current focus on border security, while important, needs to expand to encompass the domestic threat posed by easily accessible drone technology.
This means scrutinizing supply chains for critical components, especially those that can be procured through seemingly innocuous e-commerce platforms. The Department of Homeland Security must collaborate more intensely with federal and local law enforcement to identify and dismantle domestic extremist groups or individuals who might harbor the intent and capability to weaponize drones.
AI-Powered Surveillance and Predictive Analytics: The sheer volume of data involved in tracking potential threats necessitates the use of cutting-edge technology.
The US should invest heavily in AI-powered surveillance systems capable of identifying anomalies in logistics, recognizing suspicious drone flight patterns, and even predicting potential attack vectors based on open-source intelligence and dark web monitoring.
This isn’t about mass surveillance of citizens, but about intelligent threat detection.
Rapid Response & Interdiction Units: Specialized tactical units, equipped with advanced counter-drone technology and trained in urban warfare scenarios, need to be established or enhanced.
These units should be capable of rapidly deploying to intercept and neutralize drone threats, whether in transit or on final approach to a target. Their training must include scenarios involving high-density urban environments and the complexities of civilian infrastructure.
Cyber-Hardening of Drone Systems: Given the increasing sophistication of drones, even commercial ones, cyberattacks on their control systems or navigation software become a potential vulnerability.
The US military and relevant civilian agencies must invest in developing offensive cyber capabilities to disable or hijack hostile drones mid-flight, turning their own technology against them. This also includes securing domestic drone manufacturers and supply chains from hostile state or non-state actors.
India: The Subcontinental Crucible of Vulnerability and Resilience
India, a nation of immense strategic importance, is uniquely susceptible to such an attack. Its vast and often challenging geography, coupled with a dense population and complex logistical networks, presents a multifaceted security challenge.
Imagine a rogue drone swarm, unleashed from within, targeting critical air force bases like Hindon, Gwalior, or Jodhpur. The economic and psychological impact of even a partial crippling of India’s air power would be immense, disrupting regional stability and potentially inviting further aggression.
Intelligence Deep Dive and Proactive Disruption: India’s intelligence agencies (RAW, IB) must adopt a proactive stance, rather than a reactive one.
This means aggressively penetrating and disrupting nascent drone procurement networks within and around its borders. Special emphasis needs to be placed on tracking the movement of sensitive electronic components, high-capacity batteries, and guidance systems that could be repurposed for hostile drone operations.
This isn’t just about intercepting communications; it’s about human intelligence, about turning sources, about understanding the dark web’s burgeoning marketplace for weaponized drone technology.
Fortifying the Perimeter & Beyond: While physical security at air bases is paramount – think reinforced hangars, anti-drone netting, and layered air defenses – the true vulnerability lies outside the immediate perimeter.
The Russian attack highlights the risks associated with internal deployment. This necessitates enhanced surveillance of industrial estates, warehouses, and transportation hubs within a significant radius of critical military installations.
Thermal imaging, ground-penetrating radar, and even sniffer dogs trained to detect explosives and electronics in cargo containers should become standard protocols.
Counter-Drone Systems: A Multi-Layered Shield: India needs to rapidly deploy a comprehensive suite of counter-drone technologies. This includes jammers that disrupt control signals, spoofers that deceive GPS navigation, and kinetic systems like drone-catching nets or even laser-based weapons for larger, more sophisticated drones.
The key is a multi-layered approach, capable of neutralizing threats at varying ranges and altitudes. Furthermore, developing indigenous counter-drone technology should be a national priority, reducing reliance on external suppliers and fostering innovation.
Community Vigilance and Awareness Campaigns: In a country as vast and diverse as India, the eyes and ears of the populace can be a powerful deterrent. Public awareness campaigns, akin to disaster preparedness drills, could educate citizens on identifying suspicious drone activity, unusual container movements, or clandestine workshop setups. Encouraging anonymous reporting through easily accessible channels would be vital.
European Union: A Patchwork of Preparedness
The European Union, a mosaic of nations with diverse security infrastructures, faces a unique set of challenges. Its open borders, while facilitating trade and travel, can also be exploited by those seeking to smuggle illicit materials.
An attack on an air base in Germany, France, or the UK, perhaps targeting a fleet of Eurofighter Typhoons or Rafales, would not only cripple national defense but also undermine the very notion of collective security within the EU. The ripple effect across interdependent economies would be catastrophic.
Harmonized Intelligence Sharing and Joint Task Forces: The fragmented nature of European intelligence agencies is a significant weakness.
The EU needs to establish more robust and seamless intelligence-sharing mechanisms, creating a unified threat assessment picture. Joint task forces, comprising personnel from various member states, should be specifically dedicated to counter-drone intelligence and operations, pooling resources and expertise.
In the shadowy theater of modern warfare, a new, chilling act has just unfolded, leaving the world to ponder its terrifying implications.
Imagine, if you dare, a scenario where the very bastions of a nation’s aerial might – its strategic air bases – are simultaneously struck by a swarm of unseen, silent assassins.
This isn’t the script of a dystopian thriller; it’s a stark reality that recently played out in Russia, where an audacious drone attack reportedly crippled dozens of many strategic bombers.
The whispers on the wind suggest these robotic harbingers of destruction were smuggled in, hidden in plain sight, within ordinary containers. This single, audacious act has ripped open a Pandora’s Box of vulnerabilities, raising a chilling question: If it can happen to Russia, who’s next?
The strategic implications are seismic, and the tremors are being felt worldwide.
We’re talking about a paradigm shift in asymmetric warfare, where the lines between state actors and rogue elements blur, and where the most advanced military hardware can be rendered obsolete by off-the-shelf technology.
This isn’t just about damaged aircraft; it’s about shattered illusions of invincibility, about the terrifying ease with which a sophisticated nation’s defenses can be bypassed. The message is clear: the future of warfare is here, and it’s buzzing with a potentially devastating anonymity.
Let’s not mince words: this Russian air base attack is a crimson-letter warning to every major power, a visceral demonstration of how a seemingly low-tech, high-impact assault can achieve strategic objectives.
It exposes a gaping chasm in traditional defense paradigms, a vulnerability that demands immediate, radical re-evaluation. The very notion of secure borders and impregnable airspaces has been challenged, not by intercontinental ballistic missiles, but by something far more insidious – a container-borne threat, silently deployed, striking at the heart of military might.
The question isn’t if a similar attack could happen in India, the United States, or the European Union; it’s when, and with what devastating consequences.
The globalized world, with its interconnected supply chains and porous borders, is a fertile ground for such clandestine operations. The same commercial arteries that nourish our economies can become conduits for destruction. The allure of such an attack is undeniable for those seeking to destabilize, to inflict economic and military pain without the traditional risks of open confrontation.
So, let’s pull back the curtain on the potential nightmare scenarios and, more importantly, illuminate the urgent measures that must be taken to prevent such a catastrophic event from unfolding on their own soil.
United States: The Fortress Under Siege From Within
The United States, with its immense military footprint and highly advanced technological capabilities, might seem impenetrable. However, the Russian incident highlights that even the most formidable fortresses have hidden weaknesses, particularly when the threat originates from within.
An attack on a major air force base like Nellis, Edwards, or Barksdale, targeting B-2 stealth bombers or F-35 fighters, would send shockwaves through the global security architecture.
The economic fallout from even a temporary grounding of a significant portion of its air fleet, coupled with the psychological blow to national morale, would be immense.
Reimagining Homeland Security: From Borders to Basements: The current focus on border security, while important, needs to expand to encompass the domestic threat posed by easily accessible drone technology.
This means scrutinizing supply chains for critical components, especially those that can be procured through seemingly innocuous e-commerce platforms. The Department of Homeland Security must collaborate more intensely with federal and local law enforcement to identify and dismantle domestic extremist groups or individuals who might harbor the intent and capability to weaponize drones.
AI-Powered Surveillance and Predictive Analytics: The sheer volume of data involved in tracking potential threats necessitates the use of cutting-edge technology.
The US should invest heavily in AI-powered surveillance systems capable of identifying anomalies in logistics, recognizing suspicious drone flight patterns, and even predicting potential attack vectors based on open-source intelligence and dark web monitoring.
This isn’t about mass surveillance of citizens, but about intelligent threat detection.
Rapid Response & Interdiction Units: Specialized tactical units, equipped with advanced counter-drone technology and trained in urban warfare scenarios, need to be established or enhanced.
These units should be capable of rapidly deploying to intercept and neutralize drone threats, whether in transit or on final approach to a target. Their training must include scenarios involving high-density urban environments and the complexities of civilian infrastructure.
Cyber-Hardening of Drone Systems: Given the increasing sophistication of drones, even commercial ones, cyberattacks on their control systems or navigation software become a potential vulnerability.
The US military and relevant civilian agencies must invest in developing offensive cyber capabilities to disable or hijack hostile drones mid-flight, turning their own technology against them. This also includes securing domestic drone manufacturers and supply chains from hostile state or non-state actors.
India: The Subcontinental Crucible of Vulnerability and Resilience
India, a nation of immense strategic importance, is uniquely susceptible to such an attack. Its vast and often challenging geography, coupled with a dense population and complex logistical networks, presents a multifaceted security challenge.
Imagine a rogue drone swarm, unleashed from within, targeting critical air force bases like Hindon, Gwalior, or Jodhpur. The economic and psychological impact of even a partial crippling of India’s air power would be immense, disrupting regional stability and potentially inviting further aggression.
Intelligence Deep Dive and Proactive Disruption: India’s intelligence agencies (RAW, IB) must adopt a proactive stance, rather than a reactive one.
This means aggressively penetrating and disrupting nascent drone procurement networks within and around its borders. Special emphasis needs to be placed on tracking the movement of sensitive electronic components, high-capacity batteries, and guidance systems that could be repurposed for hostile drone operations.
This isn’t just about intercepting communications; it’s about human intelligence, about turning sources, about understanding the dark web’s burgeoning marketplace for weaponized drone technology.
Fortifying the Perimeter & Beyond: While physical security at air bases is paramount – think reinforced hangars, anti-drone netting, and layered air defenses – the true vulnerability lies outside the immediate perimeter.
The Russian attack highlights the risks associated with internal deployment. This necessitates enhanced surveillance of industrial estates, warehouses, and transportation hubs within a significant radius of critical military installations.
Thermal imaging, ground-penetrating radar, and even sniffer dogs trained to detect explosives and electronics in cargo containers should become standard protocols.
Counter-Drone Systems: A Multi-Layered Shield: India needs to rapidly deploy a comprehensive suite of counter-drone technologies. This includes jammers that disrupt control signals, spoofers that deceive GPS navigation, and kinetic systems like drone-catching nets or even laser-based weapons for larger, more sophisticated drones.
The key is a multi-layered approach, capable of neutralizing threats at varying ranges and altitudes. Furthermore, developing indigenous counter-drone technology should be a national priority, reducing reliance on external suppliers and fostering innovation.
Community Vigilance and Awareness Campaigns: In a country as vast and diverse as India, the eyes and ears of the populace can be a powerful deterrent. Public awareness campaigns, akin to disaster preparedness drills, could educate citizens on identifying suspicious drone activity, unusual container movements, or clandestine workshop setups. Encouraging anonymous reporting through easily accessible channels would be vital.
European Union: A Patchwork of Preparedness
The European Union, a mosaic of nations with diverse security infrastructures, faces a unique set of challenges. Its open borders, while facilitating trade and travel, can also be exploited by those seeking to smuggle illicit materials.
An attack on an air base in Germany, France, or the UK, perhaps targeting a fleet of Eurofighter Typhoons or Rafales, would not only cripple national defense but also undermine the very notion of collective security within the EU. The ripple effect across interdependent economies would be catastrophic.
Harmonized Intelligence Sharing and Joint Task Forces: The fragmented nature of European intelligence agencies is a significant weakness.
The EU needs to establish more robust and seamless intelligence-sharing mechanisms, creating a unified threat assessment picture. Joint task forces, comprising personnel from various member states, should be specifically dedicated to counter-drone intelligence and operations, pooling resources and expertise.
8 months ago
China plans to issue guidance to encourage the use of open-source RISC-V chips nationwide for the first time, two sources briefed on the matter said, as Beijing accelerates efforts to curb the country's dependence on Western-owned technology.
The policy guidance on boosting the use of RISC-V chips could be released as soon as this month, although the final date could change, the sources said.
It is being drafted jointly by eight government bodies, including the Cyberspace Administration of China, China's Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the Ministry of Science and Technology, and the China National Intellectual Property Administration, they added.
The sources declined to be named as the policy discussions were still under way. The four ministries did not respond to requests for comment.
RISC-V is a open-source technology that is used to design a range of less-sophisticated chips, from those in smartphones to CPUs for artificial intelligence servers.
It competes globally with proprietary and more commonly used chip architecture technology including x86, dominated by U.S. firms Intel and Advanced Micro Devices, and Arm, developed by SoftBank Group-owned Arm Holdings.
The policy guidance on boosting the use of RISC-V chips could be released as soon as this month, although the final date could change, the sources said.
It is being drafted jointly by eight government bodies, including the Cyberspace Administration of China, China's Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the Ministry of Science and Technology, and the China National Intellectual Property Administration, they added.
The sources declined to be named as the policy discussions were still under way. The four ministries did not respond to requests for comment.
RISC-V is a open-source technology that is used to design a range of less-sophisticated chips, from those in smartphones to CPUs for artificial intelligence servers.
It competes globally with proprietary and more commonly used chip architecture technology including x86, dominated by U.S. firms Intel and Advanced Micro Devices, and Arm, developed by SoftBank Group-owned Arm Holdings.
11 months ago
The world is at the brink of a third nuclear age, the head of the United Kingdom’s armed forces.
“The world has changed,” Admiral Sir Tony Radakin said in a lecture at the UK’s Royal United Services Institute. “Global power is shifting, and a third nuclear age is upon us.”
This age, he warned, is “altogether more complex” than those that came before it. The first of these ages was the Cold War, while the second was defined by disarmament efforts.
This third nuclear age, which, according to Radakin, the world is “at the dawn of,” is “defined by multiple and concurrent dilemmas, proliferating nuclear and disruptive technologies, and the almost total absence of the security architectures that went before.”
Russia’s war in Ukraine and multiple conflicts in the Middle East have upended global stability. Radakin believes that there is only a “remote chance” that Russia will attack or invade NATO, as it knows that the “response would be overwhelming, whether conventional or nuclear.”
“The world has changed,” Admiral Sir Tony Radakin said in a lecture at the UK’s Royal United Services Institute. “Global power is shifting, and a third nuclear age is upon us.”
This age, he warned, is “altogether more complex” than those that came before it. The first of these ages was the Cold War, while the second was defined by disarmament efforts.
This third nuclear age, which, according to Radakin, the world is “at the dawn of,” is “defined by multiple and concurrent dilemmas, proliferating nuclear and disruptive technologies, and the almost total absence of the security architectures that went before.”
Russia’s war in Ukraine and multiple conflicts in the Middle East have upended global stability. Radakin believes that there is only a “remote chance” that Russia will attack or invade NATO, as it knows that the “response would be overwhelming, whether conventional or nuclear.”
1 yr. ago
Chinese President Xi Jinping called for the Brics nations to lead the "urgent" reform of the international financial architecture to better reflect the global economy.
He told the bloc's annual summit it should also drive reform of global governance and cooperate further in innovation and green development.
The meeting in the Russian city of Kazan is the first since it added five new members earlier this year and Xi confirmed the bloc will soon invite more "partner countries" to join.
"Under the current circumstances, the urgency of reforming the international financial architecture is prominent," Xi said, according to state news agency Xinhua.
"The Brics countries should play a leading role, deepen financial cooperation, promote the interconnection of financial infrastructure, maintain high-level financial security, expand and strengthen the New Development Bank, and promote the international financial system to better reflect changes in the world economic landscape."
He told the bloc's annual summit it should also drive reform of global governance and cooperate further in innovation and green development.
The meeting in the Russian city of Kazan is the first since it added five new members earlier this year and Xi confirmed the bloc will soon invite more "partner countries" to join.
"Under the current circumstances, the urgency of reforming the international financial architecture is prominent," Xi said, according to state news agency Xinhua.
"The Brics countries should play a leading role, deepen financial cooperation, promote the interconnection of financial infrastructure, maintain high-level financial security, expand and strengthen the New Development Bank, and promote the international financial system to better reflect changes in the world economic landscape."
1 yr. ago
How do traditional customs influence modern practices in different cultures?
By Hugo Keji
Traditional customs significantly influence modern practices in various cultures, often blending the old with the new to create unique contemporary expressions.
Here are some ways traditional customs shape modern practices in different cultural contexts:
1. Festivals and Celebrations
India: Traditional festivals like Diwali and Holi continue to be widely celebrated, but with modern twists such as eco-friendly fireworks and digital greetings.
China: The Chinese New Year remains a major celebration with traditional elements like dragon dances and red envelopes, now often featuring digital transfers and virtual red envelopes.
2. Cuisine
Italy: Traditional recipes and cooking methods are preserved in modern Italian cuisine, with classic dishes like pasta and pizza being served in contemporary settings and often reinterpreted with new ingredients.
Japan: Traditional food items like sushi and ramen have been adapted for modern tastes, with fusion variations and innovative presentation techniques becoming popular worldwide.
3. Fashion
Africa: Traditional fabrics and patterns, such as kente cloth and Ankara prints, are incorporated into modern fashion, blending heritage with contemporary styles.
India: Traditional garments like sarees and kurta pajamas are often worn during festivals and formal occasions, sometimes updated with modern cuts and fabrics.
4. Architecture
China: Modern Chinese architecture often incorporates elements from traditional designs, such as curved roofs and Feng Shui principles, into contemporary buildings.
Middle East: Traditional Islamic architecture, with its geometric patterns and courtyards, influences modern designs in both residential and commercial buildings.
5. Medicine
India: Traditional Ayurvedic practices influence modern wellness and health practices, with yoga and meditation becoming mainstream worldwide.
China: Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) practices, including acupuncture and herbal treatments, are integrated into modern health and wellness routines.
6. Education
Finland: The Finnish education system incorporates traditional values of equality and cooperation, which are reflected in modern educational practices such as collaborative learning and emphasis on student well-being.
Japan: Traditional values of discipline and respect are maintained in modern educational settings, influencing classroom behavior and student-teacher relationships.
7. Art and Literature
Mexico: Traditional folk art and motifs influence modern Mexican art, with contemporary artists drawing inspiration from indigenous symbols and techniques.
Russia: Russian literature often reflects traditional themes and folklore, influencing contemporary writers who blend these elements with modern narratives.
8. Social Practices
Spain: The tradition of the siesta continues to influence modern work-life balance, with some businesses adopting flexible hours to allow for afternoon breaks.
Sweden: The concept of "fika," a traditional coffee break, remains a cherished social practice in modern Swedish culture, emphasizing the importance of taking time to relax and socialize.
9. Rituals and Ceremonies
Africa: Traditional rituals and ceremonies, such as weddings and initiation rites, are preserved in modern times, often combined with contemporary elements to reflect current social contexts.
Japan: Traditional tea ceremonies and festivals, like the cherry blossom festival (Hanami), continue to be practiced, maintaining a link between past and present.
10. Technology Integration
South Korea: Traditional values of hard work and education influence the country's rapid technological advancements, with a focus on integrating technology into everyday life while preserving cultural heritage.
India: Modern technology is used to preserve and promote traditional arts and crafts, with online platforms providing new opportunities for artisans to reach global markets.
Examples of Tradition Influencing Modern Practices
Thanksgiving (USA): A blend of traditional harvest celebrations and modern customs, incorporating historical elements with contemporary practices like parades and football games.
Oktoberfest (Germany): A traditional Bavarian festival that has evolved into a global celebration, combining historical customs with modern entertainment and international participation.
Traditional customs serve as a foundation for cultural continuity, influencing and enriching modern practices across various aspects of life, from celebrations and cuisine to architecture and social behaviors.
This blend of tradition and modernity creates dynamic and evolving cultural landscapes.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Be part of Health Data 101.... Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan. With servers in Asia, Europe and America. Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365 For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
By Hugo Keji
Traditional customs significantly influence modern practices in various cultures, often blending the old with the new to create unique contemporary expressions.
Here are some ways traditional customs shape modern practices in different cultural contexts:
1. Festivals and Celebrations
India: Traditional festivals like Diwali and Holi continue to be widely celebrated, but with modern twists such as eco-friendly fireworks and digital greetings.
China: The Chinese New Year remains a major celebration with traditional elements like dragon dances and red envelopes, now often featuring digital transfers and virtual red envelopes.
2. Cuisine
Italy: Traditional recipes and cooking methods are preserved in modern Italian cuisine, with classic dishes like pasta and pizza being served in contemporary settings and often reinterpreted with new ingredients.
Japan: Traditional food items like sushi and ramen have been adapted for modern tastes, with fusion variations and innovative presentation techniques becoming popular worldwide.
3. Fashion
Africa: Traditional fabrics and patterns, such as kente cloth and Ankara prints, are incorporated into modern fashion, blending heritage with contemporary styles.
India: Traditional garments like sarees and kurta pajamas are often worn during festivals and formal occasions, sometimes updated with modern cuts and fabrics.
4. Architecture
China: Modern Chinese architecture often incorporates elements from traditional designs, such as curved roofs and Feng Shui principles, into contemporary buildings.
Middle East: Traditional Islamic architecture, with its geometric patterns and courtyards, influences modern designs in both residential and commercial buildings.
5. Medicine
India: Traditional Ayurvedic practices influence modern wellness and health practices, with yoga and meditation becoming mainstream worldwide.
China: Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) practices, including acupuncture and herbal treatments, are integrated into modern health and wellness routines.
6. Education
Finland: The Finnish education system incorporates traditional values of equality and cooperation, which are reflected in modern educational practices such as collaborative learning and emphasis on student well-being.
Japan: Traditional values of discipline and respect are maintained in modern educational settings, influencing classroom behavior and student-teacher relationships.
7. Art and Literature
Mexico: Traditional folk art and motifs influence modern Mexican art, with contemporary artists drawing inspiration from indigenous symbols and techniques.
Russia: Russian literature often reflects traditional themes and folklore, influencing contemporary writers who blend these elements with modern narratives.
8. Social Practices
Spain: The tradition of the siesta continues to influence modern work-life balance, with some businesses adopting flexible hours to allow for afternoon breaks.
Sweden: The concept of "fika," a traditional coffee break, remains a cherished social practice in modern Swedish culture, emphasizing the importance of taking time to relax and socialize.
9. Rituals and Ceremonies
Africa: Traditional rituals and ceremonies, such as weddings and initiation rites, are preserved in modern times, often combined with contemporary elements to reflect current social contexts.
Japan: Traditional tea ceremonies and festivals, like the cherry blossom festival (Hanami), continue to be practiced, maintaining a link between past and present.
10. Technology Integration
South Korea: Traditional values of hard work and education influence the country's rapid technological advancements, with a focus on integrating technology into everyday life while preserving cultural heritage.
India: Modern technology is used to preserve and promote traditional arts and crafts, with online platforms providing new opportunities for artisans to reach global markets.
Examples of Tradition Influencing Modern Practices
Thanksgiving (USA): A blend of traditional harvest celebrations and modern customs, incorporating historical elements with contemporary practices like parades and football games.
Oktoberfest (Germany): A traditional Bavarian festival that has evolved into a global celebration, combining historical customs with modern entertainment and international participation.
Traditional customs serve as a foundation for cultural continuity, influencing and enriching modern practices across various aspects of life, from celebrations and cuisine to architecture and social behaviors.
This blend of tradition and modernity creates dynamic and evolving cultural landscapes.
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Be part of Health Data 101.... Health Data 101 by SapperTek INC registered in Taiwan. With servers in Asia, Europe and America. Hospitals, Private Clinics, Federal, State and Local Government health departs gets an online storage of all it's data secured 24/7/365 For ONLY USD$3 ... Your patients will appreciate it. Hospitals don't need paper work/cards again.
BE A PARTNER IN YOUR COUNTRY.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com Absolutely risk free and FREE for download...
App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
1 yr. ago
Introduction to Hospital and Patient Management-
Hospital and patient management is a crucial aspect of healthcare that involves the systematic organization and coordination of healthcare services to ensure efficient delivery of care. This field encompasses a wide range of activities, including administration, clinical services, patient care, and the integration of technology to improve outcomes. Effective hospital and patient management is essential for providing high-quality care, optimizing resources, and enhancing patient satisfaction.
Be part of Health Data 101.... Hospital and patient management is a crucial aspect of healthcare that involves the systematic organization and coordination of healthcare services to ensure efficient delivery of care.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download... App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com/
https://healthdata101.com
Key Components of Hospital and Patient Management-
Hospital Administration: This involves the overall governance and strategic planning of the hospital. Administrators are responsible for policy development, financial management, human resources, and compliance with healthcare regulations. Effective administration ensures that the hospital operates smoothly and can adapt to changes in the healthcare environment.
Clinical Services Management: This includes the coordination of medical and surgical services, nursing care, and other clinical support services such as radiology, laboratory, and pharmacy. Effective clinical services management ensures that patients receive timely and appropriate care.
Patient Care Management: This focuses on the direct care of patients, ensuring that their medical, emotional, and psychological needs are met. It involves the management of patient admission, diagnosis, treatment, discharge, and follow-up care. Patient care management aims to provide a seamless experience for patients, enhancing their overall satisfaction and outcomes.
Technology Integration: The use of healthcare information technology (HIT) systems, such as electronic health records (EHR), telemedicine, and other digital tools, is essential in modern hospital and patient management. These technologies improve the accuracy of patient information, streamline processes, and facilitate better communication among healthcare providers.
Quality and Safety Management: Ensuring the quality and safety of healthcare services is a fundamental aspect of hospital management. This involves implementing best practices, adhering to clinical guidelines, and continuously monitoring and improving the quality of care. Safety protocols are established to prevent medical errors and enhance patient safety.
Resource Management: Efficient management of resources, including staff, equipment, and supplies, is critical to the functioning of a hospital. Resource management ensures that the hospital can provide continuous and high-quality care while maintaining financial stability.
Patient Experience and Engagement: Engaging patients in their care and ensuring a positive patient experience is increasingly recognized as a key component of hospital management. This includes effective communication, patient education, and involving patients in decision-making processes about their treatment plans.
Importance of Hospital and Patient Management-
Effective hospital and patient management leads to several significant benefits:
Improved Patient Outcomes: Proper management ensures that patients receive timely and appropriate care, leading to better health outcomes.
Increased Efficiency: Streamlined processes and efficient resource use reduce waste and lower healthcare costs.
Enhanced Patient Satisfaction: Focusing on patient needs and improving the care experience leads to higher levels of patient satisfaction.
Compliance and Risk Management: Adherence to healthcare regulations and implementation of risk management strategies protect the hospital from legal issues and enhance patient safety.
Sustainable Operations: Effective financial and resource management ensures the long-term sustainability of the hospital.
In conclusion, hospital and patient management is a multifaceted field that plays a crucial role in the delivery of high-quality healthcare. By integrating administration, clinical services, patient care, technology, and quality management, hospitals can improve patient outcomes, enhance satisfaction, and operate efficiently.
Data Security and Safe Data Holding in Healthcare;-
Data security and the safe holding of information are critical in the healthcare industry due to the sensitive nature of patient information and the legal requirements for protecting this data. Ensuring data security involves implementing robust measures to protect against data breaches, unauthorized access, and other cyber threats. Here’s an overview of key aspects related to data security and safe data holding in healthcare:
Key Components of Data Security in Healthcare
Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA Triad):
Confidentiality: Ensuring that patient information is accessible only to authorized individuals.
Integrity: Maintaining the accuracy and completeness of patient data.
Availability: Ensuring that data is accessible to authorized users when needed.
Regulatory Compliance:
Compliance with laws such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, and other regional regulations is essential. These regulations set standards for the protection of health information and mandate specific security measures.
Access Control:
Implementing strict access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information. This includes using user authentication methods such as passwords, biometrics, and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Data Encryption:
Encrypting data both at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted or accessed illegally, it remains unreadable without the appropriate decryption key.
Network Security:
Using firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and secure network architectures to protect data from cyber threats. Regularly updating and patching systems to address vulnerabilities is also crucial.
Regular Audits and Monitoring:
Conducting regular security audits and continuous monitoring of systems to detect and respond to security incidents promptly. Audits help identify potential vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security policies.
Data Backup and Recovery:
Implementing robust data backup solutions and disaster recovery plans to ensure data can be restored in case of loss or corruption. Regular backups should be stored securely and tested to ensure they are functional.
Physical Security:
Protecting physical access to servers, data centers, and other critical infrastructure. This includes using security measures such as access badges, surveillance cameras, and secure facilities.
Training and Awareness:
Providing regular training and awareness programs for healthcare staff to ensure they understand data security policies and best practices. Educating employees about phishing attacks, social engineering, and other common threats can help prevent security breaches.
Challenges in Healthcare Data Security;-
Evolving Cyber Threats: The healthcare industry is a prime target for cybercriminals due to the high value of medical data. Threats such as ransomware, phishing, and advanced persistent threats (APTs) are continually evolving.
Interoperability and Data Sharing: The need for interoperability and data sharing between different healthcare providers and systems can create security vulnerabilities if not managed properly.
Legacy Systems: Many healthcare institutions still use outdated systems and software that may not have the latest security features, making them more susceptible to attacks.
Resource Constraints: Some healthcare organizations, especially smaller ones, may have limited resources for implementing comprehensive security measures.
Best Practices for Safe Data Holding;-
Implement a Robust Security Framework: Adopting security frameworks such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework or ISO/IEC 27001 can provide a structured approach to managing and protecting sensitive data.
Regularly Update and Patch Systems: Keeping all software and systems up to date with the latest security patches is crucial to protect against known vulnerabilities.
Use Strong Authentication Mechanisms: Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an additional layer of security beyond traditional passwords.
Encrypt Sensitive Data: Use strong encryption methods for both data at rest and in transit to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Develop and Test Incident Response Plans: Having a well-defined incident response plan and conducting regular drills can help healthcare organizations respond effectively to data breaches and other security incidents.
Engage in Continuous Monitoring: Utilizing advanced monitoring tools to detect and respond to suspicious activities in real-time helps mitigate potential security threats.
In conclusion, ensuring data security and safe data holding in healthcare requires a comprehensive and proactive approach.
By implementing robust security measures, staying compliant with regulations, and fostering a culture of security awareness, healthcare organizations can protect sensitive patient information and maintain the trust of their patients.
Hospital and patient management is a crucial aspect of healthcare that involves the systematic organization and coordination of healthcare services to ensure efficient delivery of care. This field encompasses a wide range of activities, including administration, clinical services, patient care, and the integration of technology to improve outcomes. Effective hospital and patient management is essential for providing high-quality care, optimizing resources, and enhancing patient satisfaction.
Be part of Health Data 101.... Hospital and patient management is a crucial aspect of healthcare that involves the systematic organization and coordination of healthcare services to ensure efficient delivery of care.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download... App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com/
https://healthdata101.com
Key Components of Hospital and Patient Management-
Hospital Administration: This involves the overall governance and strategic planning of the hospital. Administrators are responsible for policy development, financial management, human resources, and compliance with healthcare regulations. Effective administration ensures that the hospital operates smoothly and can adapt to changes in the healthcare environment.
Clinical Services Management: This includes the coordination of medical and surgical services, nursing care, and other clinical support services such as radiology, laboratory, and pharmacy. Effective clinical services management ensures that patients receive timely and appropriate care.
Patient Care Management: This focuses on the direct care of patients, ensuring that their medical, emotional, and psychological needs are met. It involves the management of patient admission, diagnosis, treatment, discharge, and follow-up care. Patient care management aims to provide a seamless experience for patients, enhancing their overall satisfaction and outcomes.
Technology Integration: The use of healthcare information technology (HIT) systems, such as electronic health records (EHR), telemedicine, and other digital tools, is essential in modern hospital and patient management. These technologies improve the accuracy of patient information, streamline processes, and facilitate better communication among healthcare providers.
Quality and Safety Management: Ensuring the quality and safety of healthcare services is a fundamental aspect of hospital management. This involves implementing best practices, adhering to clinical guidelines, and continuously monitoring and improving the quality of care. Safety protocols are established to prevent medical errors and enhance patient safety.
Resource Management: Efficient management of resources, including staff, equipment, and supplies, is critical to the functioning of a hospital. Resource management ensures that the hospital can provide continuous and high-quality care while maintaining financial stability.
Patient Experience and Engagement: Engaging patients in their care and ensuring a positive patient experience is increasingly recognized as a key component of hospital management. This includes effective communication, patient education, and involving patients in decision-making processes about their treatment plans.
Importance of Hospital and Patient Management-
Effective hospital and patient management leads to several significant benefits:
Improved Patient Outcomes: Proper management ensures that patients receive timely and appropriate care, leading to better health outcomes.
Increased Efficiency: Streamlined processes and efficient resource use reduce waste and lower healthcare costs.
Enhanced Patient Satisfaction: Focusing on patient needs and improving the care experience leads to higher levels of patient satisfaction.
Compliance and Risk Management: Adherence to healthcare regulations and implementation of risk management strategies protect the hospital from legal issues and enhance patient safety.
Sustainable Operations: Effective financial and resource management ensures the long-term sustainability of the hospital.
In conclusion, hospital and patient management is a multifaceted field that plays a crucial role in the delivery of high-quality healthcare. By integrating administration, clinical services, patient care, technology, and quality management, hospitals can improve patient outcomes, enhance satisfaction, and operate efficiently.
Data Security and Safe Data Holding in Healthcare;-
Data security and the safe holding of information are critical in the healthcare industry due to the sensitive nature of patient information and the legal requirements for protecting this data. Ensuring data security involves implementing robust measures to protect against data breaches, unauthorized access, and other cyber threats. Here’s an overview of key aspects related to data security and safe data holding in healthcare:
Key Components of Data Security in Healthcare
Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA Triad):
Confidentiality: Ensuring that patient information is accessible only to authorized individuals.
Integrity: Maintaining the accuracy and completeness of patient data.
Availability: Ensuring that data is accessible to authorized users when needed.
Regulatory Compliance:
Compliance with laws such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, and other regional regulations is essential. These regulations set standards for the protection of health information and mandate specific security measures.
Access Control:
Implementing strict access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information. This includes using user authentication methods such as passwords, biometrics, and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Data Encryption:
Encrypting data both at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted or accessed illegally, it remains unreadable without the appropriate decryption key.
Network Security:
Using firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and secure network architectures to protect data from cyber threats. Regularly updating and patching systems to address vulnerabilities is also crucial.
Regular Audits and Monitoring:
Conducting regular security audits and continuous monitoring of systems to detect and respond to security incidents promptly. Audits help identify potential vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security policies.
Data Backup and Recovery:
Implementing robust data backup solutions and disaster recovery plans to ensure data can be restored in case of loss or corruption. Regular backups should be stored securely and tested to ensure they are functional.
Physical Security:
Protecting physical access to servers, data centers, and other critical infrastructure. This includes using security measures such as access badges, surveillance cameras, and secure facilities.
Training and Awareness:
Providing regular training and awareness programs for healthcare staff to ensure they understand data security policies and best practices. Educating employees about phishing attacks, social engineering, and other common threats can help prevent security breaches.
Challenges in Healthcare Data Security;-
Evolving Cyber Threats: The healthcare industry is a prime target for cybercriminals due to the high value of medical data. Threats such as ransomware, phishing, and advanced persistent threats (APTs) are continually evolving.
Interoperability and Data Sharing: The need for interoperability and data sharing between different healthcare providers and systems can create security vulnerabilities if not managed properly.
Legacy Systems: Many healthcare institutions still use outdated systems and software that may not have the latest security features, making them more susceptible to attacks.
Resource Constraints: Some healthcare organizations, especially smaller ones, may have limited resources for implementing comprehensive security measures.
Best Practices for Safe Data Holding;-
Implement a Robust Security Framework: Adopting security frameworks such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework or ISO/IEC 27001 can provide a structured approach to managing and protecting sensitive data.
Regularly Update and Patch Systems: Keeping all software and systems up to date with the latest security patches is crucial to protect against known vulnerabilities.
Use Strong Authentication Mechanisms: Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an additional layer of security beyond traditional passwords.
Encrypt Sensitive Data: Use strong encryption methods for both data at rest and in transit to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Develop and Test Incident Response Plans: Having a well-defined incident response plan and conducting regular drills can help healthcare organizations respond effectively to data breaches and other security incidents.
Engage in Continuous Monitoring: Utilizing advanced monitoring tools to detect and respond to suspicious activities in real-time helps mitigate potential security threats.
In conclusion, ensuring data security and safe data holding in healthcare requires a comprehensive and proactive approach.
By implementing robust security measures, staying compliant with regulations, and fostering a culture of security awareness, healthcare organizations can protect sensitive patient information and maintain the trust of their patients.
1 yr. ago
The UN-United Nations and ASEAN are useless. As they can't call China to order in respect to taken Philippines rights of ownership.
The frustration with the United Nations (UN) and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is understandable, especially concerning complex territorial disputes like the one between China and the Philippines. These organizations often face significant challenges in addressing such issues due to various political, economic, and strategic interests among their member states.
United Nations (UN)
Role and Challenges: The UN, particularly through its agencies like the International Court of Justice (ICJ) and the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), provides a framework for resolving disputes. However, enforcing rulings is difficult, especially when major powers like China are involved. The 2016 ruling by the Permanent Court of Arbitration in favor of the Philippines regarding the South China Sea is a notable example. China rejected the ruling, and the UN has limited means to enforce it without broad international support.
Political Dynamics: The UN's effectiveness is often hindered by the veto power of permanent members of the Security Council, including China. This structure can prevent the UN from taking decisive actions against major powers.
ASEAN
Role and Challenges: ASEAN aims to promote regional stability and economic cooperation. However, its consensus-based approach often leads to inaction on contentious issues. Member states have diverse interests, and some may avoid antagonizing China due to economic dependencies.
Diplomacy over Confrontation: ASEAN tends to prioritize diplomacy and engagement over confrontation. While this can facilitate dialogue, it can also lead to frustration when immediate or forceful action is desired.
The China-Philippines Dispute
Historical Context: The South China Sea dispute involves overlapping territorial claims by several countries, including China and the Philippines. China’s expansive claims, demarcated by the "nine-dash line," conflict with the territorial waters claimed by the Philippines under international law.
Philippines’ Position: The Philippines has sought to assert its rights through legal and diplomatic channels, including the 2016 arbitration ruling. However, enforcing these rights remains challenging without broad international support.
Possible Actions
International Pressure: Increasing international pressure on China through diplomatic means, economic sanctions, or coalition-building could be effective. This requires coordinated efforts from multiple countries and international bodies.
Regional Cooperation: Strengthening regional alliances and partnerships could help ASEAN member states present a unified front. Engaging other global powers that have interests in maintaining freedom of navigation and international law could also be beneficial.
Bilateral Negotiations: Continued negotiations between the Philippines and China, possibly facilitated by a neutral third party, could lead to a more sustainable resolution.
While it may seem that the UN and ASEAN are ineffective in this specific context, their roles in promoting dialogue, legal frameworks, and peaceful resolutions should not be entirely discounted.
Addressing such disputes often requires a combination of international pressure, regional cooperation, and bilateral negotiations.
China's territorial disputes and border confrontations with various countries in Asia indeed present a complex challenge for both regional and global bodies like ASEAN and the UN.
The reasons for the perceived ineffectiveness of these organizations in confronting China can be multifaceted:
Complexities in Confronting China:-
Economic Influence: China’s significant economic power and its role as a major trade partner make countries and organizations hesitant to take strong actions that could jeopardize economic relations.
Political Influence: China’s political influence, including its permanent seat and veto power on the UN Security Council, allows it to block or dilute measures that are against its interests.
Military Power: China’s growing military capabilities and strategic initiatives, such as the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), bolster its position, making other countries cautious in their approach.
Regional and International Bodies:-
United Nations (UN)
Veto Power: The veto power of the five permanent members of the Security Council, including China, often hampers the UN’s ability to take decisive action against any of these members.
Diplomacy and Consensus: The UN often emphasizes diplomacy and consensus-building over confrontation. This approach, while useful for many issues, can be less effective when dealing with assertive actions by major powers.
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
Consensus-Based Decision Making: ASEAN’s principle of consensus means that strong actions are often difficult to achieve, especially when member states have differing levels of dependence on China.
Internal Divisions: ASEAN countries have varying interests and relationships with China, leading to a lack of unified stance on territorial disputes.
Specific Regional Conflicts:-
South China Sea: Multiple countries, including Vietnam, the Philippines, Malaysia, and Brunei, have overlapping claims with China in the South China Sea. Despite the 2016 Permanent Court of Arbitration ruling in favor of the Philippines, China has continued its activities, asserting its claims.
India-China Border: The Line of Actual Control (LAC) between India and China has seen several standoffs and clashes, with both sides building up military infrastructure.
Taiwan: China’s claims over Taiwan and its increasing military maneuvers around the island are a significant point of tension with not just regional actors but also the United States.
Why Action is Limited:-
Avoidance of Escalation: Countries and organizations often seek to avoid actions that might lead to military escalation or economic retaliation.
Diplomatic Channels: There is a preference for resolving issues through diplomatic channels, even if progress is slow.
Global and Regional Interests: Balancing the interests of various stakeholders, including those who might benefit from stable relations with China, complicates taking a unified and strong stance.
Potential Approaches:-
Coalitions of the Willing: Countries with shared interests in countering China’s assertiveness could form coalitions to collectively apply diplomatic, economic, and military pressure.
Strengthening International Law: Continued efforts to uphold and strengthen international legal frameworks, like UNCLOS, can provide a basis for challenging unlawful territorial claims.
Engaging China: Constructive engagement with China through diplomatic and economic channels, while simultaneously building up regional security architectures, could help manage disputes more effectively.
Conclusion
The challenges posed by China’s territorial confrontations are indeed significant, and the actions of regional and international bodies are often constrained by a range of factors, including economic dependencies, political influence, and the risk of escalation.
While these bodies may not always appear effective in confronting China directly, their roles in facilitating dialogue, supporting international law, and promoting regional cooperation remain crucial.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
The frustration with the United Nations (UN) and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is understandable, especially concerning complex territorial disputes like the one between China and the Philippines. These organizations often face significant challenges in addressing such issues due to various political, economic, and strategic interests among their member states.
United Nations (UN)
Role and Challenges: The UN, particularly through its agencies like the International Court of Justice (ICJ) and the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), provides a framework for resolving disputes. However, enforcing rulings is difficult, especially when major powers like China are involved. The 2016 ruling by the Permanent Court of Arbitration in favor of the Philippines regarding the South China Sea is a notable example. China rejected the ruling, and the UN has limited means to enforce it without broad international support.
Political Dynamics: The UN's effectiveness is often hindered by the veto power of permanent members of the Security Council, including China. This structure can prevent the UN from taking decisive actions against major powers.
ASEAN
Role and Challenges: ASEAN aims to promote regional stability and economic cooperation. However, its consensus-based approach often leads to inaction on contentious issues. Member states have diverse interests, and some may avoid antagonizing China due to economic dependencies.
Diplomacy over Confrontation: ASEAN tends to prioritize diplomacy and engagement over confrontation. While this can facilitate dialogue, it can also lead to frustration when immediate or forceful action is desired.
The China-Philippines Dispute
Historical Context: The South China Sea dispute involves overlapping territorial claims by several countries, including China and the Philippines. China’s expansive claims, demarcated by the "nine-dash line," conflict with the territorial waters claimed by the Philippines under international law.
Philippines’ Position: The Philippines has sought to assert its rights through legal and diplomatic channels, including the 2016 arbitration ruling. However, enforcing these rights remains challenging without broad international support.
Possible Actions
International Pressure: Increasing international pressure on China through diplomatic means, economic sanctions, or coalition-building could be effective. This requires coordinated efforts from multiple countries and international bodies.
Regional Cooperation: Strengthening regional alliances and partnerships could help ASEAN member states present a unified front. Engaging other global powers that have interests in maintaining freedom of navigation and international law could also be beneficial.
Bilateral Negotiations: Continued negotiations between the Philippines and China, possibly facilitated by a neutral third party, could lead to a more sustainable resolution.
While it may seem that the UN and ASEAN are ineffective in this specific context, their roles in promoting dialogue, legal frameworks, and peaceful resolutions should not be entirely discounted.
Addressing such disputes often requires a combination of international pressure, regional cooperation, and bilateral negotiations.
China's territorial disputes and border confrontations with various countries in Asia indeed present a complex challenge for both regional and global bodies like ASEAN and the UN.
The reasons for the perceived ineffectiveness of these organizations in confronting China can be multifaceted:
Complexities in Confronting China:-
Economic Influence: China’s significant economic power and its role as a major trade partner make countries and organizations hesitant to take strong actions that could jeopardize economic relations.
Political Influence: China’s political influence, including its permanent seat and veto power on the UN Security Council, allows it to block or dilute measures that are against its interests.
Military Power: China’s growing military capabilities and strategic initiatives, such as the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), bolster its position, making other countries cautious in their approach.
Regional and International Bodies:-
United Nations (UN)
Veto Power: The veto power of the five permanent members of the Security Council, including China, often hampers the UN’s ability to take decisive action against any of these members.
Diplomacy and Consensus: The UN often emphasizes diplomacy and consensus-building over confrontation. This approach, while useful for many issues, can be less effective when dealing with assertive actions by major powers.
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
Consensus-Based Decision Making: ASEAN’s principle of consensus means that strong actions are often difficult to achieve, especially when member states have differing levels of dependence on China.
Internal Divisions: ASEAN countries have varying interests and relationships with China, leading to a lack of unified stance on territorial disputes.
Specific Regional Conflicts:-
South China Sea: Multiple countries, including Vietnam, the Philippines, Malaysia, and Brunei, have overlapping claims with China in the South China Sea. Despite the 2016 Permanent Court of Arbitration ruling in favor of the Philippines, China has continued its activities, asserting its claims.
India-China Border: The Line of Actual Control (LAC) between India and China has seen several standoffs and clashes, with both sides building up military infrastructure.
Taiwan: China’s claims over Taiwan and its increasing military maneuvers around the island are a significant point of tension with not just regional actors but also the United States.
Why Action is Limited:-
Avoidance of Escalation: Countries and organizations often seek to avoid actions that might lead to military escalation or economic retaliation.
Diplomatic Channels: There is a preference for resolving issues through diplomatic channels, even if progress is slow.
Global and Regional Interests: Balancing the interests of various stakeholders, including those who might benefit from stable relations with China, complicates taking a unified and strong stance.
Potential Approaches:-
Coalitions of the Willing: Countries with shared interests in countering China’s assertiveness could form coalitions to collectively apply diplomatic, economic, and military pressure.
Strengthening International Law: Continued efforts to uphold and strengthen international legal frameworks, like UNCLOS, can provide a basis for challenging unlawful territorial claims.
Engaging China: Constructive engagement with China through diplomatic and economic channels, while simultaneously building up regional security architectures, could help manage disputes more effectively.
Conclusion
The challenges posed by China’s territorial confrontations are indeed significant, and the actions of regional and international bodies are often constrained by a range of factors, including economic dependencies, political influence, and the risk of escalation.
While these bodies may not always appear effective in confronting China directly, their roles in facilitating dialogue, supporting international law, and promoting regional cooperation remain crucial.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
1 yr. ago
Why is United Nations quiet about this conflicts ravaging the region?
The perceived quietness or limited response of the United Nations (UN) regarding the conflicts in Sudan and South Sudan can be attributed to a range of factors involving institutional challenges, geopolitical considerations, and the complexities of the conflicts themselves. Here’s a detailed analysis of the reasons behind the UN's limited visibility or impact in addressing these crises:
1. Institutional Challenges
Bureaucratic Processes:
The UN's decision-making processes can be slow and cumbersome, involving multiple layers of bureaucracy. This can delay timely responses to rapidly evolving conflicts.
Resource Constraints:
The UN often faces financial and logistical constraints. Peacekeeping missions and humanitarian operations require substantial resources, which can be limited or diverted to other global crises.
2. Geopolitical Considerations
Veto Power Dynamics:
In the UN Security Council, the veto power held by permanent members (China, Russia, the United States, France, and the United Kingdom) can block resolutions or actions. Differing interests among these powers can lead to stalemates or watered-down responses.
International Politics:
Major global powers may have strategic interests in the region, leading to cautious or conflicting stances on intervention. For example, some countries might have economic or political ties with the governments or factions involved in the conflicts.
3. Complexity of the Conflicts
Intricate Conflicts:
The conflicts in Sudan and South Sudan are deeply rooted in ethnic, political, and historical complexities. This makes it challenging to design and implement effective intervention strategies.
Multiplicity of Actors:
The involvement of numerous armed groups, militias, and regional actors complicates the situation. Coordinating a response that addresses the interests and actions of all these parties is a daunting task.
4. Previous Engagements and Lessons Learned
Mixed Outcomes of Past Interventions:
Previous UN interventions in the region, such as the missions in Darfur (UNAMID) and South Sudan (UNMISS), have had mixed results. Limited success and high costs of these missions can lead to reluctance in committing to new extensive engagements.
Mandate Limitations:
Peacekeeping missions often operate under mandates that restrict their ability to engage in active combat or enforce peace. These limitations can hamper their effectiveness in volatile conflict zones.
5. Dependence on Member States
Funding and Support:
The UN relies on member states for funding and support of its missions. A lack of commitment or delays in contributions from member states can severely impact the UN’s capacity to respond effectively.
Military Contributions:
Peacekeeping forces are composed of troops contributed by member states. Variability in the quality, readiness, and willingness of these troops to engage in high-risk areas affects the UN’s operational capabilities.
6. Efforts at Quiet Diplomacy
Back-Channel Negotiations:
The UN often engages in behind-the-scenes diplomacy to resolve conflicts. This can include mediation efforts, shuttle diplomacy, and quiet negotiations, which may not be visible to the public but are crucial in conflict resolution.
Special Envoys and Mediators:
The UN appoints special envoys and mediators who work discreetly to broker peace deals. Their efforts might not always garner media attention but are essential in laying the groundwork for long-term solutions.
7. Focus on Humanitarian Assistance
Humanitarian Priorities:
In many conflict zones, the UN focuses on providing humanitarian aid and support to displaced populations. This work, while less visible than military interventions, is vital in addressing the immediate needs of affected civilians.
Coordination with NGOs:
The UN often works in coordination with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and other international bodies to deliver aid. This collaborative approach can diffuse visibility but enhances effectiveness on the ground.
Conclusion
The UN's limited visibility or impact in the conflicts in Sudan and South Sudan is shaped by a combination of institutional challenges, geopolitical dynamics, the complexity of the conflicts, lessons from past interventions, dependence on member states, efforts at quiet diplomacy, and a focus on humanitarian assistance. These factors collectively contribute to the perception of the UN being quiet or less active in addressing these ongoing crises.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Does it mean African Union is completely useless as it can't manage conflicts in Africa?
Labeling the African Union (AU) as completely useless is an oversimplification and does not fully account for the organization's complexities, achievements, and challenges. While the AU faces significant difficulties in managing conflicts, it has also made important contributions to peace and stability in Africa. Here’s a more balanced view of the AU’s role and effectiveness:
Achievements of the African Union
Peacekeeping and Conflict Resolution:
AMISOM in Somalia: The AU Mission in Somalia (AMISOM) has been crucial in combating Al-Shabaab and supporting the Somali government. Despite challenges, it has played a key role in improving security in Somalia.
Sudan and South Sudan: The AU has facilitated peace negotiations and agreements, such as the Comprehensive Peace Agreement (CPA) in 2005, which led to South Sudan’s independence in 2011.
Mediation Efforts:
Diplomatic Interventions: The AU has been involved in mediation efforts in numerous conflicts, including in the Central African Republic, Mali, and Burundi. These efforts have often been carried out by appointed special envoys and mediators.
Institutional Frameworks:
Peace and Security Architecture: The AU has established mechanisms such as the Peace and Security Council (PSC), the African Standby Force (ASF), and the Panel of the Wise, which provide a framework for conflict prevention, management, and resolution.
Promotion of Democratic Governance:
Election Monitoring: The AU regularly sends observer missions to monitor elections across the continent, promoting transparency and democratic practices.
Support for Constitutional Order: The AU has taken a stance against unconstitutional changes of government, as seen in its suspension of member states following coups, like in Mali and Guinea.
Challenges Facing the African Union
Resource Constraints:
Financial and Logistical Limitations: The AU often lacks sufficient funding and logistical resources to effectively implement its mandates. This limitation affects the scope and scale of its interventions.
Political Fragmentation:
Diverse Interests: Member states have diverse political interests and agendas, making it difficult to achieve consensus on collective actions. This fragmentation can lead to inaction or delayed responses.
Capacity Issues:
Operational Capabilities: The AU's peacekeeping missions often struggle with issues related to troop quality, equipment, and training. This affects their ability to maintain peace and security in conflict zones.
External Influence:
Dependency on International Partners: The AU relies on financial and logistical support from international partners such as the United Nations, European Union, and individual countries. This dependency can limit its autonomy and effectiveness.
Complexity of Conflicts:
Multifaceted Conflicts: Many conflicts in Africa are deeply rooted in ethnic, political, and economic issues, making them complex and difficult to resolve. The AU faces significant challenges in addressing these multifaceted problems.
Efforts to Improve Effectiveness
Institutional Reforms:
Revitalization Plans: The AU has undertaken various institutional reforms aimed at improving its efficiency and effectiveness, such as the Agenda 2063, which outlines a strategic framework for the socio-economic transformation of the continent.
Strengthening Partnerships:
Collaboration with International Bodies: The AU continues to strengthen its collaboration with the UN, EU, and other international organizations to enhance its capacity for peacekeeping and conflict resolution.
Capacity Building:
Training and Development: Efforts are being made to improve the training and development of AU peacekeeping forces and staff, enhancing their ability to respond to crises.
Conclusion
While the African Union faces significant challenges in managing conflicts in Africa, it is not entirely useless. The AU has made notable contributions to peace, security, and governance on the continent, despite its limitations. Recognizing both its achievements and its areas for improvement provides a more nuanced understanding of the AU’s role and potential in addressing African conflicts.
The perceived quietness or limited response of the United Nations (UN) regarding the conflicts in Sudan and South Sudan can be attributed to a range of factors involving institutional challenges, geopolitical considerations, and the complexities of the conflicts themselves. Here’s a detailed analysis of the reasons behind the UN's limited visibility or impact in addressing these crises:
1. Institutional Challenges
Bureaucratic Processes:
The UN's decision-making processes can be slow and cumbersome, involving multiple layers of bureaucracy. This can delay timely responses to rapidly evolving conflicts.
Resource Constraints:
The UN often faces financial and logistical constraints. Peacekeeping missions and humanitarian operations require substantial resources, which can be limited or diverted to other global crises.
2. Geopolitical Considerations
Veto Power Dynamics:
In the UN Security Council, the veto power held by permanent members (China, Russia, the United States, France, and the United Kingdom) can block resolutions or actions. Differing interests among these powers can lead to stalemates or watered-down responses.
International Politics:
Major global powers may have strategic interests in the region, leading to cautious or conflicting stances on intervention. For example, some countries might have economic or political ties with the governments or factions involved in the conflicts.
3. Complexity of the Conflicts
Intricate Conflicts:
The conflicts in Sudan and South Sudan are deeply rooted in ethnic, political, and historical complexities. This makes it challenging to design and implement effective intervention strategies.
Multiplicity of Actors:
The involvement of numerous armed groups, militias, and regional actors complicates the situation. Coordinating a response that addresses the interests and actions of all these parties is a daunting task.
4. Previous Engagements and Lessons Learned
Mixed Outcomes of Past Interventions:
Previous UN interventions in the region, such as the missions in Darfur (UNAMID) and South Sudan (UNMISS), have had mixed results. Limited success and high costs of these missions can lead to reluctance in committing to new extensive engagements.
Mandate Limitations:
Peacekeeping missions often operate under mandates that restrict their ability to engage in active combat or enforce peace. These limitations can hamper their effectiveness in volatile conflict zones.
5. Dependence on Member States
Funding and Support:
The UN relies on member states for funding and support of its missions. A lack of commitment or delays in contributions from member states can severely impact the UN’s capacity to respond effectively.
Military Contributions:
Peacekeeping forces are composed of troops contributed by member states. Variability in the quality, readiness, and willingness of these troops to engage in high-risk areas affects the UN’s operational capabilities.
6. Efforts at Quiet Diplomacy
Back-Channel Negotiations:
The UN often engages in behind-the-scenes diplomacy to resolve conflicts. This can include mediation efforts, shuttle diplomacy, and quiet negotiations, which may not be visible to the public but are crucial in conflict resolution.
Special Envoys and Mediators:
The UN appoints special envoys and mediators who work discreetly to broker peace deals. Their efforts might not always garner media attention but are essential in laying the groundwork for long-term solutions.
7. Focus on Humanitarian Assistance
Humanitarian Priorities:
In many conflict zones, the UN focuses on providing humanitarian aid and support to displaced populations. This work, while less visible than military interventions, is vital in addressing the immediate needs of affected civilians.
Coordination with NGOs:
The UN often works in coordination with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and other international bodies to deliver aid. This collaborative approach can diffuse visibility but enhances effectiveness on the ground.
Conclusion
The UN's limited visibility or impact in the conflicts in Sudan and South Sudan is shaped by a combination of institutional challenges, geopolitical dynamics, the complexity of the conflicts, lessons from past interventions, dependence on member states, efforts at quiet diplomacy, and a focus on humanitarian assistance. These factors collectively contribute to the perception of the UN being quiet or less active in addressing these ongoing crises.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Does it mean African Union is completely useless as it can't manage conflicts in Africa?
Labeling the African Union (AU) as completely useless is an oversimplification and does not fully account for the organization's complexities, achievements, and challenges. While the AU faces significant difficulties in managing conflicts, it has also made important contributions to peace and stability in Africa. Here’s a more balanced view of the AU’s role and effectiveness:
Achievements of the African Union
Peacekeeping and Conflict Resolution:
AMISOM in Somalia: The AU Mission in Somalia (AMISOM) has been crucial in combating Al-Shabaab and supporting the Somali government. Despite challenges, it has played a key role in improving security in Somalia.
Sudan and South Sudan: The AU has facilitated peace negotiations and agreements, such as the Comprehensive Peace Agreement (CPA) in 2005, which led to South Sudan’s independence in 2011.
Mediation Efforts:
Diplomatic Interventions: The AU has been involved in mediation efforts in numerous conflicts, including in the Central African Republic, Mali, and Burundi. These efforts have often been carried out by appointed special envoys and mediators.
Institutional Frameworks:
Peace and Security Architecture: The AU has established mechanisms such as the Peace and Security Council (PSC), the African Standby Force (ASF), and the Panel of the Wise, which provide a framework for conflict prevention, management, and resolution.
Promotion of Democratic Governance:
Election Monitoring: The AU regularly sends observer missions to monitor elections across the continent, promoting transparency and democratic practices.
Support for Constitutional Order: The AU has taken a stance against unconstitutional changes of government, as seen in its suspension of member states following coups, like in Mali and Guinea.
Challenges Facing the African Union
Resource Constraints:
Financial and Logistical Limitations: The AU often lacks sufficient funding and logistical resources to effectively implement its mandates. This limitation affects the scope and scale of its interventions.
Political Fragmentation:
Diverse Interests: Member states have diverse political interests and agendas, making it difficult to achieve consensus on collective actions. This fragmentation can lead to inaction or delayed responses.
Capacity Issues:
Operational Capabilities: The AU's peacekeeping missions often struggle with issues related to troop quality, equipment, and training. This affects their ability to maintain peace and security in conflict zones.
External Influence:
Dependency on International Partners: The AU relies on financial and logistical support from international partners such as the United Nations, European Union, and individual countries. This dependency can limit its autonomy and effectiveness.
Complexity of Conflicts:
Multifaceted Conflicts: Many conflicts in Africa are deeply rooted in ethnic, political, and economic issues, making them complex and difficult to resolve. The AU faces significant challenges in addressing these multifaceted problems.
Efforts to Improve Effectiveness
Institutional Reforms:
Revitalization Plans: The AU has undertaken various institutional reforms aimed at improving its efficiency and effectiveness, such as the Agenda 2063, which outlines a strategic framework for the socio-economic transformation of the continent.
Strengthening Partnerships:
Collaboration with International Bodies: The AU continues to strengthen its collaboration with the UN, EU, and other international organizations to enhance its capacity for peacekeeping and conflict resolution.
Capacity Building:
Training and Development: Efforts are being made to improve the training and development of AU peacekeeping forces and staff, enhancing their ability to respond to crises.
Conclusion
While the African Union faces significant challenges in managing conflicts in Africa, it is not entirely useless. The AU has made notable contributions to peace, security, and governance on the continent, despite its limitations. Recognizing both its achievements and its areas for improvement provides a more nuanced understanding of the AU’s role and potential in addressing African conflicts.
1 yr. ago
US pushing Netherlands, Japan to restrict more chipmaking equipment to China....
A U.S. official was headed to Japan after meeting with the Dutch government in an effort to push allies to further crack down on China's ability to produce cutting-edge semiconductors, a person familiar with the matter told Reuters on Tuesday.
Alan Estevez, the U.S. export policy chief, was again trying to build on a 2023 agreement between the three countries to keep chipmaking equipment from China that could modernize its military.
The U.S. first imposed sweeping restrictions in 2022 on shipments of advanced chips and chipmaking equipment to China from the likes of California-based Nvidia and Lam Research.
Last July, to align with U.S. policy, Japan, home to chip equipment makers Nikon Corp and Tokyo Electron, curbed exports of 23 types of equipment, from machines that deposit films on silicon wafers to devices that etch out the microscopic circuits.
Then the Dutch government began to regulate Netherlands-based ASML's deep ultra violet (DUV) semiconductor equipment to China and the U.S. imposed restrictions on additional DUV machines to a handful of Chinese factories, claiming jurisdiction because ASML's systems contain U.S. parts and components. ASML is the world's top chip equipment maker.
Washington is now talking to allies about adding 11 more Chinese chipmaking factories to a restricted list, the person said. There are currently five factories on the list, the person said, including SMIC, China's largest chipmaker.
The U.S. also is saying it wants to control additional chipmaking equipment, the person said.
A spokesperson for the U.S. Commerce Department declined comment.
U.S. officials visited the Netherlands in April in a push to stop ASML from servicing certain equipment in China. Under U.S. rules, American firms are barred from servicing equipment at advanced Chinese factories.
But the ASML servicing contracts are still in place, the person said, explaining that the Dutch government does not have the extraterratorial scope to cut them off.
The Chinese Embassy in Washington did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
Sanctioned Chinese telecoms giant Huawei last year came out with a phone powered by a sophisticated chip. The Huawei Mate 60 Pro was seen as a symbol of the China's technological resurgence despite Washington's efforts.
Senator says US needs to 'up our game' on tracking Chinese tech efforts......
The chair of the Senate Intelligence Committee said on Tuesday that U.S. intelligence agencies need to do a better job in tracking Chinese advanced technology and other efforts across a variety of fields.
"Our intel community is so used to traditionally spying - you spy on the military, you spy on the government. You don't necessarily follow all of the tech companies," Senator Mark Warner told reporters at a breakfast sponsored by the Christian Science Monitor. "You don't follow where China is getting extraction of rare earth minerals. We just need to kind of continue to up our game in following what China is doing, not just in this chip space but frankly in a lot of these other domains."
Warner said the intel side had "missed a couple times," citing Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corp's ability to produce advanced 7- nanometer semiconductor chips and other issues involving chipmaking tool manufacturers. He also expressed concerns about China's advanced efforts on life sciences and biotechnology.
"We've seen no indication that China is not pedal-to-the metal in terms of investing and trying to not just be successful but dominate," Warner added.
Warner said the United States needs to do more on limiting chips and chipmaking tools to China.
"Unfortunately, there may be Western chip manufacturers who are knowingly or unknowingly still having their tools and products circumventing the ban," Warner said.
Warner said he wished the U.S. investors in China-based ByteDance, parent of TikTok, would try "to urge China to go ahead and at least break off the non-Chinese portion" of the popular short video app used by 170 million Americans. U.S. investors own roughly 40% of ByteDance. Warner said he is not sure that China will allow a sale of TikTok.
TikTok did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
The U.S. Congress passed legislation in April requiring ByteDance to divest TikTok's U.S. assets by Jan. 19 of next year or face a ban. TikTok and ByteDance have sued to block the legislation. Warner, who opposes a ban, added: "But at the end of the day, the law is the law."
US Seeks Allies’ Help in Curbing China’s AI Chip Progress......
US Under Secretary of Commerce for Industry and Security Alan Estevez will press his counterparts in Tokyo and The Hague to put more limits on the activities in China of Dutch supplier ASML Holding NV and Japan’s Tokyo Electron Ltd., according to people familiar with the matter. Estevez’s requests, part of an ongoing dialogue with allies, will highlight Chinese chip factories developing so-called high-bandwidth memory chips, said the people, asking not to be identified because the discussions are private.
ASML and Tokyo Electron machines are used to produce dynamic random access memory dies, which are stacked together to make HBM chips. Chinese companies working on HBM chips include Wuhan Xinxin Semiconductor Manufacturing Co., a subsidiary of China’s leading memory chipmaker Yangtze Memory Technologies Co., according to China’s corporate data provider Qichacha. Huawei Technologies Co. and ChangXin Memory Technologies Inc. are also reportedly developing HBM.
The Biden administration has tried for years to limit China’s ability to buy and produce advanced semiconductors, arguing such steps are necessary for national security. Yet results have been mixed, with Huawei and others making significant advances. The US is seeking support from allies, who have implemented their own less stringent controls, to create a more effective global blockade.
“The United States is the most critical player in the global semiconductor equipment industry, but it’s far from the only country that matters. Japan and the Netherlands are also key providers of semiconductor equipment,” said Gregory Allen, director of the Wadhwani Center for AI and Advanced Technologies at the Center for Strategic and International Studies. “The Netherlands and Japan have restrictions on exports but not on servicing, and that’s a critical limitation in the overall technology controls architecture.”
Estevez is expected to repeat a standing US request for the two countries to tighten restrictions on ASML and Tokyo Electron’s ability to maintain and repair their other advanced equipment in China as well, the people said. The US has already imposed such restrictions on American rivals, such as Applied Materials Inc. and Lam Research Corp.
The US delegation’s visit to the Netherlands is expected to take place after the new Dutch cabinet is sworn in the first week of July. Reinette Klever of far-right lawmaker Geert Wilders’ Freedom Party is set to become the minister for foreign trade and development aid, a role that typically oversees the country’s export control policies.
The Dutch and Japanese governments have been resisting the US pressure, people familiar with the matter said earlier. The two countries want more time to evaluate the impact of current export bans on high-end chip-making equipment and to see the outcome of the US presidential election in November.
It is uncertain how the new Dutch government led by Wilders will react to US demands for additional measures. Klever is co-founder of a far-right TV channel Ongehoord Nederland, which stirred controversy for its pro-Russian reporting and climate change skepticism. The outgoing Foreign Trade Minister Liesje Schreinemacher paid a farewell visit to the US last week to lobby for the interests of ASML. Dutch King Willem-Alexander joined Schreinemacher in a meeting with New York Governor Kathy Hochul.
A representative of the US Commerce Department’s Bureau of Industry and Security declined to comment. A spokesperson for the Dutch foreign trade ministry declined to comment. Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry did not respond to requests for comment.
HBM chips are an indispensable part of the AI hardware ecosystem because they speed up access to memory, helping AI development. AI accelerators, made by Nvidia Corp. and Advanced Micro Devices Inc., need to be bundled with HBM chips for them to work. US officials are having early-stage conversations about restricting the export of HBM chips, Bloomberg has reported.
SK Hynix Inc. is the leading producer of HBM chips, with Samsung Electronics Co., and US-based Micron Technology Inc. pressing to catch up. SK Hynix relies on equipment from ASML and Tokyo Electron, according to Bloomberg’s supply chain data.
Korean equipment makers including Hanmi Semiconductor Co. and Hanwha Precision Machinery Co. also play a critical role in the HBM supply chain. Earlier this year, Washington asked Seoul to restrict the flow of equipment and technologies for making high-end logic and memory chips to China, Bloomberg News has reported.
Chinese companies can no longer buy the most advanced AI chips from Nvidia, but Huawei is developing its own AI accelerators, called Ascend. It is unclear which company or companies are providing advanced memory chips to Huawei. SK Hynix, Samsung and Micron all stopped supplying Huawei with chips after the US tightened sanctions against the Chinese company in 2020.
Washington officials have also grown worried about China’s own progress in chipmaking equipment. Lawmakers on Tuesday introduced a bipartisan bill to ban companies that receive US funding for chip factories from purchasing Chinese tools for those facilities.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
A U.S. official was headed to Japan after meeting with the Dutch government in an effort to push allies to further crack down on China's ability to produce cutting-edge semiconductors, a person familiar with the matter told Reuters on Tuesday.
Alan Estevez, the U.S. export policy chief, was again trying to build on a 2023 agreement between the three countries to keep chipmaking equipment from China that could modernize its military.
The U.S. first imposed sweeping restrictions in 2022 on shipments of advanced chips and chipmaking equipment to China from the likes of California-based Nvidia and Lam Research.
Last July, to align with U.S. policy, Japan, home to chip equipment makers Nikon Corp and Tokyo Electron, curbed exports of 23 types of equipment, from machines that deposit films on silicon wafers to devices that etch out the microscopic circuits.
Then the Dutch government began to regulate Netherlands-based ASML's deep ultra violet (DUV) semiconductor equipment to China and the U.S. imposed restrictions on additional DUV machines to a handful of Chinese factories, claiming jurisdiction because ASML's systems contain U.S. parts and components. ASML is the world's top chip equipment maker.
Washington is now talking to allies about adding 11 more Chinese chipmaking factories to a restricted list, the person said. There are currently five factories on the list, the person said, including SMIC, China's largest chipmaker.
The U.S. also is saying it wants to control additional chipmaking equipment, the person said.
A spokesperson for the U.S. Commerce Department declined comment.
U.S. officials visited the Netherlands in April in a push to stop ASML from servicing certain equipment in China. Under U.S. rules, American firms are barred from servicing equipment at advanced Chinese factories.
But the ASML servicing contracts are still in place, the person said, explaining that the Dutch government does not have the extraterratorial scope to cut them off.
The Chinese Embassy in Washington did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
Sanctioned Chinese telecoms giant Huawei last year came out with a phone powered by a sophisticated chip. The Huawei Mate 60 Pro was seen as a symbol of the China's technological resurgence despite Washington's efforts.
Senator says US needs to 'up our game' on tracking Chinese tech efforts......
The chair of the Senate Intelligence Committee said on Tuesday that U.S. intelligence agencies need to do a better job in tracking Chinese advanced technology and other efforts across a variety of fields.
"Our intel community is so used to traditionally spying - you spy on the military, you spy on the government. You don't necessarily follow all of the tech companies," Senator Mark Warner told reporters at a breakfast sponsored by the Christian Science Monitor. "You don't follow where China is getting extraction of rare earth minerals. We just need to kind of continue to up our game in following what China is doing, not just in this chip space but frankly in a lot of these other domains."
Warner said the intel side had "missed a couple times," citing Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corp's ability to produce advanced 7- nanometer semiconductor chips and other issues involving chipmaking tool manufacturers. He also expressed concerns about China's advanced efforts on life sciences and biotechnology.
"We've seen no indication that China is not pedal-to-the metal in terms of investing and trying to not just be successful but dominate," Warner added.
Warner said the United States needs to do more on limiting chips and chipmaking tools to China.
"Unfortunately, there may be Western chip manufacturers who are knowingly or unknowingly still having their tools and products circumventing the ban," Warner said.
Warner said he wished the U.S. investors in China-based ByteDance, parent of TikTok, would try "to urge China to go ahead and at least break off the non-Chinese portion" of the popular short video app used by 170 million Americans. U.S. investors own roughly 40% of ByteDance. Warner said he is not sure that China will allow a sale of TikTok.
TikTok did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
The U.S. Congress passed legislation in April requiring ByteDance to divest TikTok's U.S. assets by Jan. 19 of next year or face a ban. TikTok and ByteDance have sued to block the legislation. Warner, who opposes a ban, added: "But at the end of the day, the law is the law."
US Seeks Allies’ Help in Curbing China’s AI Chip Progress......
US Under Secretary of Commerce for Industry and Security Alan Estevez will press his counterparts in Tokyo and The Hague to put more limits on the activities in China of Dutch supplier ASML Holding NV and Japan’s Tokyo Electron Ltd., according to people familiar with the matter. Estevez’s requests, part of an ongoing dialogue with allies, will highlight Chinese chip factories developing so-called high-bandwidth memory chips, said the people, asking not to be identified because the discussions are private.
ASML and Tokyo Electron machines are used to produce dynamic random access memory dies, which are stacked together to make HBM chips. Chinese companies working on HBM chips include Wuhan Xinxin Semiconductor Manufacturing Co., a subsidiary of China’s leading memory chipmaker Yangtze Memory Technologies Co., according to China’s corporate data provider Qichacha. Huawei Technologies Co. and ChangXin Memory Technologies Inc. are also reportedly developing HBM.
The Biden administration has tried for years to limit China’s ability to buy and produce advanced semiconductors, arguing such steps are necessary for national security. Yet results have been mixed, with Huawei and others making significant advances. The US is seeking support from allies, who have implemented their own less stringent controls, to create a more effective global blockade.
“The United States is the most critical player in the global semiconductor equipment industry, but it’s far from the only country that matters. Japan and the Netherlands are also key providers of semiconductor equipment,” said Gregory Allen, director of the Wadhwani Center for AI and Advanced Technologies at the Center for Strategic and International Studies. “The Netherlands and Japan have restrictions on exports but not on servicing, and that’s a critical limitation in the overall technology controls architecture.”
Estevez is expected to repeat a standing US request for the two countries to tighten restrictions on ASML and Tokyo Electron’s ability to maintain and repair their other advanced equipment in China as well, the people said. The US has already imposed such restrictions on American rivals, such as Applied Materials Inc. and Lam Research Corp.
The US delegation’s visit to the Netherlands is expected to take place after the new Dutch cabinet is sworn in the first week of July. Reinette Klever of far-right lawmaker Geert Wilders’ Freedom Party is set to become the minister for foreign trade and development aid, a role that typically oversees the country’s export control policies.
The Dutch and Japanese governments have been resisting the US pressure, people familiar with the matter said earlier. The two countries want more time to evaluate the impact of current export bans on high-end chip-making equipment and to see the outcome of the US presidential election in November.
It is uncertain how the new Dutch government led by Wilders will react to US demands for additional measures. Klever is co-founder of a far-right TV channel Ongehoord Nederland, which stirred controversy for its pro-Russian reporting and climate change skepticism. The outgoing Foreign Trade Minister Liesje Schreinemacher paid a farewell visit to the US last week to lobby for the interests of ASML. Dutch King Willem-Alexander joined Schreinemacher in a meeting with New York Governor Kathy Hochul.
A representative of the US Commerce Department’s Bureau of Industry and Security declined to comment. A spokesperson for the Dutch foreign trade ministry declined to comment. Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry did not respond to requests for comment.
HBM chips are an indispensable part of the AI hardware ecosystem because they speed up access to memory, helping AI development. AI accelerators, made by Nvidia Corp. and Advanced Micro Devices Inc., need to be bundled with HBM chips for them to work. US officials are having early-stage conversations about restricting the export of HBM chips, Bloomberg has reported.
SK Hynix Inc. is the leading producer of HBM chips, with Samsung Electronics Co., and US-based Micron Technology Inc. pressing to catch up. SK Hynix relies on equipment from ASML and Tokyo Electron, according to Bloomberg’s supply chain data.
Korean equipment makers including Hanmi Semiconductor Co. and Hanwha Precision Machinery Co. also play a critical role in the HBM supply chain. Earlier this year, Washington asked Seoul to restrict the flow of equipment and technologies for making high-end logic and memory chips to China, Bloomberg News has reported.
Chinese companies can no longer buy the most advanced AI chips from Nvidia, but Huawei is developing its own AI accelerators, called Ascend. It is unclear which company or companies are providing advanced memory chips to Huawei. SK Hynix, Samsung and Micron all stopped supplying Huawei with chips after the US tightened sanctions against the Chinese company in 2020.
Washington officials have also grown worried about China’s own progress in chipmaking equipment. Lawmakers on Tuesday introduced a bipartisan bill to ban companies that receive US funding for chip factories from purchasing Chinese tools for those facilities.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
1 yr. ago
Introduction to Hospital and Patient Management (Continued)
Hospital and patient management is a crucial aspect of healthcare that involves the systematic organization and coordination of healthcare services to ensure efficient delivery of care. This field encompasses a wide range of activities, including administration, clinical services, patient care, and the integration of technology to improve outcomes. Effective hospital and patient management is essential for providing high-quality care, optimizing resources, and enhancing patient satisfaction.
Key Components of Data Security in Healthcare
Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA Triad):
Confidentiality: Ensuring that patient information is accessible only to authorized individuals.
Integrity: Maintaining the accuracy and completeness of patient data.
Availability: Ensuring that data is accessible to authorized users when needed.
Regulatory Compliance:
Compliance with laws such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, and other regional regulations is essential. These regulations set standards for the protection of health information and mandate specific security measures.
Access Control:
Implementing strict access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information. This includes using user authentication methods such as passwords, biometrics, and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Data Encryption:
Encrypting data both at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted or accessed illegally, it remains unreadable without the appropriate decryption key.
Network Security:
Using firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and secure network architectures to protect data from cyber threats. Regularly updating and patching systems to address vulnerabilities is also crucial.
Regular Audits and Monitoring:
Conducting regular security audits and continuous monitoring of systems to detect and respond to security incidents promptly. Audits help identify potential vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security policies.
Data Backup and Recovery:
Implementing robust data backup solutions and disaster recovery plans to ensure data can be restored in case of loss or corruption. Regular backups should be stored securely and tested to ensure they are functional.
Physical Security:
Protecting physical access to servers, data centers, and other critical infrastructure. This includes using security measures such as access badges, surveillance cameras, and secure facilities.
Training and Awareness:
Providing regular training and awareness programs for healthcare staff to ensure they understand data security policies and best practices. Educating employees about phishing attacks, social engineering, and other common threats can help prevent security breaches.
Be part of Health Data 101.... Hospital and patient management is a crucial aspect of healthcare that involves the systematic organization and coordination of healthcare services to ensure efficient delivery of care.
Earn as One country One AGENT.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download... App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
Challenges in Healthcare Data Security
Evolving Cyber Threats: The healthcare industry is a prime target for cybercriminals due to the high value of medical data. Threats such as ransomware, phishing, and advanced persistent threats (APTs) are continually evolving.
Interoperability and Data Sharing: The need for interoperability and data sharing between different healthcare providers and systems can create security vulnerabilities if not managed properly.
Legacy Systems: Many healthcare institutions still use outdated systems and software that may not have the latest security features, making them more susceptible to attacks.
Resource Constraints: Some healthcare organizations, especially smaller ones, may have limited resources for implementing comprehensive security measures.
Be part of Health Data 101.... Hospital and patient management is a crucial aspect of healthcare that involves the systematic organization and coordination of healthcare services to ensure efficient delivery of care.
Earn as One country One AGENT.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download... App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
Best Practices for Safe Data Holding
Implement a Robust Security Framework: Adopting security frameworks such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework or ISO/IEC 27001 can provide a structured approach to managing and protecting sensitive data.
Regularly Update and Patch Systems: Keeping all software and systems up to date with the latest security patches is crucial to protect against known vulnerabilities.
Use Strong Authentication Mechanisms: Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an additional layer of security beyond traditional passwords.
Encrypt Sensitive Data: Use strong encryption methods for both data at rest and in transit to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Develop and Test Incident Response Plans: Having a well-defined incident response plan and conducting regular drills can help healthcare organizations respond effectively to data breaches and other security incidents.
Engage in Continuous Monitoring: Utilizing advanced monitoring tools to detect and respond to suspicious activities in real-time helps mitigate potential security threats.
In conclusion, ensuring data security and safe data holding in healthcare requires a comprehensive and proactive approach. By implementing robust security measures, staying compliant with regulations, and fostering a culture of security awareness, healthcare organizations can protect sensitive patient information and maintain the trust of their patients.
Be part of Health Data 101.... Hospital and patient management is a crucial aspect of healthcare that involves the systematic organization and coordination of healthcare services to ensure efficient delivery of care.
Earn as One country One AGENT.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download... App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
Hospital and patient management is a crucial aspect of healthcare that involves the systematic organization and coordination of healthcare services to ensure efficient delivery of care. This field encompasses a wide range of activities, including administration, clinical services, patient care, and the integration of technology to improve outcomes. Effective hospital and patient management is essential for providing high-quality care, optimizing resources, and enhancing patient satisfaction.
Key Components of Data Security in Healthcare
Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA Triad):
Confidentiality: Ensuring that patient information is accessible only to authorized individuals.
Integrity: Maintaining the accuracy and completeness of patient data.
Availability: Ensuring that data is accessible to authorized users when needed.
Regulatory Compliance:
Compliance with laws such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, and other regional regulations is essential. These regulations set standards for the protection of health information and mandate specific security measures.
Access Control:
Implementing strict access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information. This includes using user authentication methods such as passwords, biometrics, and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Data Encryption:
Encrypting data both at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted or accessed illegally, it remains unreadable without the appropriate decryption key.
Network Security:
Using firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and secure network architectures to protect data from cyber threats. Regularly updating and patching systems to address vulnerabilities is also crucial.
Regular Audits and Monitoring:
Conducting regular security audits and continuous monitoring of systems to detect and respond to security incidents promptly. Audits help identify potential vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security policies.
Data Backup and Recovery:
Implementing robust data backup solutions and disaster recovery plans to ensure data can be restored in case of loss or corruption. Regular backups should be stored securely and tested to ensure they are functional.
Physical Security:
Protecting physical access to servers, data centers, and other critical infrastructure. This includes using security measures such as access badges, surveillance cameras, and secure facilities.
Training and Awareness:
Providing regular training and awareness programs for healthcare staff to ensure they understand data security policies and best practices. Educating employees about phishing attacks, social engineering, and other common threats can help prevent security breaches.
Be part of Health Data 101.... Hospital and patient management is a crucial aspect of healthcare that involves the systematic organization and coordination of healthcare services to ensure efficient delivery of care.
Earn as One country One AGENT.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download... App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
Challenges in Healthcare Data Security
Evolving Cyber Threats: The healthcare industry is a prime target for cybercriminals due to the high value of medical data. Threats such as ransomware, phishing, and advanced persistent threats (APTs) are continually evolving.
Interoperability and Data Sharing: The need for interoperability and data sharing between different healthcare providers and systems can create security vulnerabilities if not managed properly.
Legacy Systems: Many healthcare institutions still use outdated systems and software that may not have the latest security features, making them more susceptible to attacks.
Resource Constraints: Some healthcare organizations, especially smaller ones, may have limited resources for implementing comprehensive security measures.
Be part of Health Data 101.... Hospital and patient management is a crucial aspect of healthcare that involves the systematic organization and coordination of healthcare services to ensure efficient delivery of care.
Earn as One country One AGENT.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download... App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
Best Practices for Safe Data Holding
Implement a Robust Security Framework: Adopting security frameworks such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework or ISO/IEC 27001 can provide a structured approach to managing and protecting sensitive data.
Regularly Update and Patch Systems: Keeping all software and systems up to date with the latest security patches is crucial to protect against known vulnerabilities.
Use Strong Authentication Mechanisms: Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an additional layer of security beyond traditional passwords.
Encrypt Sensitive Data: Use strong encryption methods for both data at rest and in transit to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Develop and Test Incident Response Plans: Having a well-defined incident response plan and conducting regular drills can help healthcare organizations respond effectively to data breaches and other security incidents.
Engage in Continuous Monitoring: Utilizing advanced monitoring tools to detect and respond to suspicious activities in real-time helps mitigate potential security threats.
In conclusion, ensuring data security and safe data holding in healthcare requires a comprehensive and proactive approach. By implementing robust security measures, staying compliant with regulations, and fostering a culture of security awareness, healthcare organizations can protect sensitive patient information and maintain the trust of their patients.
Be part of Health Data 101.... Hospital and patient management is a crucial aspect of healthcare that involves the systematic organization and coordination of healthcare services to ensure efficient delivery of care.
Earn as One country One AGENT.
Contact for details: Email: sappertekincgmail.com
Absolutely risk free and FREE for download... App link: https://www.amazon.com/gp/...
https://healthdata101.com
1 yr. ago
(E)
India “Bets Big” On Russia Despite US Lure & Chinese Fear; Here Is Why Delhi & Moscow Remain ‘Trusted Pals’........(Part1)
The foundation of the China-Russia “no-limits” alliance is rooted in the evolving global power structure since the early 2010s. Both nations perceived a need to collaborate against the United States’ hegemonic, albeit declining, influence.
Under President Vladimir Putin, Russia has skillfully maneuvered the international landscape to enhance its global standing. Utilizing its substantial hard power — conventional military strength, extensive nuclear deterrence, private militias, energy resources, and strategic geopolitical moves — Russia seeks to maximize its bargaining power and extend its influence.
The Russo-China alliance is visibly strengthening through joint military exercises and defense agreements. This military cooperation serves multiple purposes, such as enhancing capabilities and deterring Western military intervention in their respective spheres of influence.
Economically, the alliance is bolstered by robust trade relations, particularly in energy and natural resources, where Russia is a critical supplier to China. China’s vast energy demands are met by Russian oil and gas exports, securing a stable supply while reducing dependency on potentially hostile Western sources.
Moscow’s strategy in the Russian war against Ukraine aims to disrupt the European security architecture. In Asia, China plans to focus on solidifying its dominance, including the strategic objectives of reunifying Taiwan, asserting control over the South China Sea and East China Sea, and ensuring unimpeded access to vital sea lanes in the Pacific and Indian Ocean.
A critical component of the China-Russia strategy is the concerted effort to undermine US-led global governance. This includes challenging American influence in international organizations like the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) and promoting alternative frameworks like BRICS+ and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO).
By doing so, Russia and China aim to create a multipolar world order that dilutes Western dominance. Economic collaboration between the two nations is equally significant. By increasing bilateral trade using national currencies — currently 92% in yuan and ruble — Russia and China are countering Western sanctions and reducing their reliance on the US dollar. This economic strategy extends to advanced technological collaboration, particularly in areas like artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and telecommunications.
The strategic partnership between China and Russia, even if transactional, poses a significant challenge to the US. This alliance creates a two-front scenario for Washington, compelling it to navigate a belligerent Russia in Europe and an increasingly aggressive China in the Indo-Pacific region.
The primary objective of the China-Russia alliance is to counterbalance US influence in international politics, compelling the US to divide its focus from a single theatre, be it in Europe or the Indo-Pacific.
Implications For India
As the 21st-century global dynamics evolve, India finds itself navigating an increasingly unstable international landscape. It is evident that neither a unipolar world dominated by the United States nor a bipolar order centered around US-China rivalry is in India’s strategic interest.
Instead, a multipolar world with a diminished yet strategically relevant Russian pole presents the most favorable scenario for India’s geopolitical aspirations.
However, Russia’s increasing closeness to China over recent years has been a cause for concern in New Delhi. India views this relationship with caution, mainly due to its extensive military and defense ties with Russia and the ongoing standoff with China. For New Delhi, managing the Russia-China axis presents a significant foreign policy challenge, altering its strategic outlook in fundamental ways.
Furthermore, a strengthened Sino-Russian economic collaboration might marginalize India in regional infrastructure projects and trade routes. Also, closer China-Russia cooperation on the global stage diminishes Indian influence in regional forums such as the SCO and BRICS.
This emerging configuration necessitates that India carefully recalibrate its foreign policy to maintain its space within these forums while safeguarding its national interests.
It is understood that Russia, China, and India seek a multipolar world order that diminishes the post-World War II hegemony of the United States. However, while India’s vision of a multipolar world is non-West, the one sought by Russia with China is anti-West.
This marks a significant divergence in their strategic interests. In forums like the SCO and BRICS, India aims to amplify the voice of the Global South, positioning itself as a bridge between the developed and developing worlds. This role was evident during the COVID-19 pandemic, where India partnered with the US, Australia, and Japan under the Quad framework to assist Indo-Pacific nations with vaccines.
Conversely, China and Russia seek to form an anti-Western bloc through their partnerships with the Global South, aiming to undermine the West. The differences between India and the China-Russia-Iran-North Korea bloc are fundamental.
India emphasizes multi-alignment, strategic autonomy, and constructive mini-lateralisms through groupings like the Quad and BIMSTEC. In contrast, the China-Russia axis approaches values, norms, and institutions from an anti-West perspective, aimed at militarily and economically countering the US and its allies, which does not precisely align with India’s approach.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
The foundation of the China-Russia “no-limits” alliance is rooted in the evolving global power structure since the early 2010s. Both nations perceived a need to collaborate against the United States’ hegemonic, albeit declining, influence.
Under President Vladimir Putin, Russia has skillfully maneuvered the international landscape to enhance its global standing. Utilizing its substantial hard power — conventional military strength, extensive nuclear deterrence, private militias, energy resources, and strategic geopolitical moves — Russia seeks to maximize its bargaining power and extend its influence.
The Russo-China alliance is visibly strengthening through joint military exercises and defense agreements. This military cooperation serves multiple purposes, such as enhancing capabilities and deterring Western military intervention in their respective spheres of influence.
Economically, the alliance is bolstered by robust trade relations, particularly in energy and natural resources, where Russia is a critical supplier to China. China’s vast energy demands are met by Russian oil and gas exports, securing a stable supply while reducing dependency on potentially hostile Western sources.
Moscow’s strategy in the Russian war against Ukraine aims to disrupt the European security architecture. In Asia, China plans to focus on solidifying its dominance, including the strategic objectives of reunifying Taiwan, asserting control over the South China Sea and East China Sea, and ensuring unimpeded access to vital sea lanes in the Pacific and Indian Ocean.
A critical component of the China-Russia strategy is the concerted effort to undermine US-led global governance. This includes challenging American influence in international organizations like the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) and promoting alternative frameworks like BRICS+ and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO).
By doing so, Russia and China aim to create a multipolar world order that dilutes Western dominance. Economic collaboration between the two nations is equally significant. By increasing bilateral trade using national currencies — currently 92% in yuan and ruble — Russia and China are countering Western sanctions and reducing their reliance on the US dollar. This economic strategy extends to advanced technological collaboration, particularly in areas like artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and telecommunications.
The strategic partnership between China and Russia, even if transactional, poses a significant challenge to the US. This alliance creates a two-front scenario for Washington, compelling it to navigate a belligerent Russia in Europe and an increasingly aggressive China in the Indo-Pacific region.
The primary objective of the China-Russia alliance is to counterbalance US influence in international politics, compelling the US to divide its focus from a single theatre, be it in Europe or the Indo-Pacific.
Implications For India
As the 21st-century global dynamics evolve, India finds itself navigating an increasingly unstable international landscape. It is evident that neither a unipolar world dominated by the United States nor a bipolar order centered around US-China rivalry is in India’s strategic interest.
Instead, a multipolar world with a diminished yet strategically relevant Russian pole presents the most favorable scenario for India’s geopolitical aspirations.
However, Russia’s increasing closeness to China over recent years has been a cause for concern in New Delhi. India views this relationship with caution, mainly due to its extensive military and defense ties with Russia and the ongoing standoff with China. For New Delhi, managing the Russia-China axis presents a significant foreign policy challenge, altering its strategic outlook in fundamental ways.
Furthermore, a strengthened Sino-Russian economic collaboration might marginalize India in regional infrastructure projects and trade routes. Also, closer China-Russia cooperation on the global stage diminishes Indian influence in regional forums such as the SCO and BRICS.
This emerging configuration necessitates that India carefully recalibrate its foreign policy to maintain its space within these forums while safeguarding its national interests.
It is understood that Russia, China, and India seek a multipolar world order that diminishes the post-World War II hegemony of the United States. However, while India’s vision of a multipolar world is non-West, the one sought by Russia with China is anti-West.
This marks a significant divergence in their strategic interests. In forums like the SCO and BRICS, India aims to amplify the voice of the Global South, positioning itself as a bridge between the developed and developing worlds. This role was evident during the COVID-19 pandemic, where India partnered with the US, Australia, and Japan under the Quad framework to assist Indo-Pacific nations with vaccines.
Conversely, China and Russia seek to form an anti-Western bloc through their partnerships with the Global South, aiming to undermine the West. The differences between India and the China-Russia-Iran-North Korea bloc are fundamental.
India emphasizes multi-alignment, strategic autonomy, and constructive mini-lateralisms through groupings like the Quad and BIMSTEC. In contrast, the China-Russia axis approaches values, norms, and institutions from an anti-West perspective, aimed at militarily and economically countering the US and its allies, which does not precisely align with India’s approach.
App link: FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
1 yr. ago
BEHAVIORAL ECONOMICS-
6 Types of Nudges Can Affect Your Choices.
Environmental cues can steer people’s decisions via six cognitive processes.
KEY POINTS-
Nudges refer to small cues from our choice environment that can affect people’s decisions.
New research suggests six different types of nudges, tapping into different cognitive processes.
Nudges can affect us by tapping into attention, perception, memory, effort, or intrinsic/extrinsic motivation.
Effort-based nudges, which work by making certain options easier, appear to be the most effective.
Many of our choices are swayed by subtle cues or so-called “nudges” from the environment. A well-known example of this phenomenon includes the layout of a cafeteria or supermarket. Placing an item at eye level makes it more likely to be chosen—even if it’s a salad. Another classic nudge is the strategic use of language to “frame” a choice. If advertisements evoke a fear of missing out, for instance, people will be more inclined to part with their hard-earned money.
Nudging is a phenomenon that has gained much attention since the publication of Nudge, Thaler and Sunstein’s popular book on the topic. Crucially, nudges never restrict people’s choices. Instead, subtle manipulations of the choice environment (also called “choice architecture”) merely tend to influence the way choices are processed. Nudges are most powerful in situations where people make quick, intuitive decisions without engaging analytical thinking skills.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Much research has been dedicated to understanding the principles of nudging, and national governments across many countries have allocated resources to leveraging the potential of nudges for improving the wellbeing of their citizens. A notable example includes the wide distribution of posters reminding citizens of good handwashing practices during the COVID-19 pandemic. Another is the traffic light labelling of food items, which uses intuitive colour codes to signal low-calorie options, thereby nudging people into healthier living.
A framework of nudges
While nudging is a well-known concept, the term is used indiscriminately to describe a large range of different influences on people’s decisions. Cafeteria layouts, language framing, handwash posters and food packaging—all fall under the same umbrella of phenomena. New research offers a helpful framework for categorising different types of nudges. Categories are based on six distinct cognitive mechanisms, through which a nudge might influence behaviour: (1) attention, (2) perception, (3) memory, (4) effort, (5) intrinsic motivation and (6) extrinsic motivation.
Attention. In a context of ever-increasing choice, it can be difficult to compare the available options. Many people intuitively go for the choice that stands out. The first type of nudges capitalises on this fact by tapping into attentional processes. Increasing the visibility of options or highlighting them through bright colours can increase salience, thereby making these options more likely to be chosen. The strategic item placement in cafeterias is a prime example of this process. Others might include the order of items on a restaurant’s food menu or webpages with colourful items, designed to catch your eye.
Perception. The second type of nudge refers to ways in which the choice architecture influences people’s subjective perception. Framing effects that highlight particular aspects of a choice fall into this category. The type of language used in advertisements can create a sense of urgency or a fear of missing out, influencing people through their innate sensitivity to losses. Similarly, colour-coded food items might help to frame choice, with red labels signalling a health risk and green labels giving customers the proverbial thumbs up.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Memory. Forgetting is a surprisingly common reason for not acting or for failing to make a choice. This is where the third type of nudge comes in. The choice environment can offer cues that prompt people’s memory, like the simple reminders of handwashing in public bathrooms mentioned above. Another example includes email messages by online companies to inform customers about items left (unpaid) in their shopping baskets.
Effort. Nobody likes to make an effort! The fourth nudge taps into this insight and influences choices by making some options easier than others. A common example of this is the use of defaults — that is, options that automatically come into place if a person fails to make a choice. Examples include newspaper subscriptions, which renew themselves unless customers choose otherwise, or automatic enrolment in pension schemes.
Intrinsic motivation. Some nudges tap into mechanisms of internal motivation — that is, increasing people’s desire for certain options. For example, relaying information about social norms can be surprisingly powerful. In the context of medical prescribing, for example, it might help to tell doctors if their prescribing rates are above average compared to colleagues. Nobody wants to stand out, so many adapt their medical decision making as a consequence. Similarly, if wanting to increase charitable donations, it could help to tell people how much their peers have already contributed.
Extrinsic motivation. The last type of nudge involves the process of extrinsic motivation. This includes offering external rewards for making certain choices. Receiving a sticker to inform people about a recent, voluntary blood donation could be an example. Another might involve the mentioning of professional achievements in staff meetings or organisational newsletters, thereby offering a reputational reward for a job well done.
Which nudges are best?
The framework outlined above highlights the surprising diversity of nudges and the different ways they might be used to influence people’s choices, for better or for worse. The researchers who proposed the framework provided additional insight by conducting a metanalysis of previous research on nudging. They reviewed 184 research studies that involved nudging to identify the most powerful type. Results suggest that effort-based nudges hold the biggest potential for changing people’s choices. In contrast, nudges tapping into intrinsic motivation appear to be the least powerful. While the authors warn about potential publication bias, which refers to the fact that significant or interesting research findings are more likely to get published than non-significant outcomes, these results offer some interesting insights: First, there’s a “toolbox” of nudges to choose from when trying to change people’s behaviours. Second, making a choice easy appears to be the most promising avenue. Human decision makers are busy creatures of habit, so any help with simplifying the ever-expanding maze of options is likely to go a long way.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
6 Types of Nudges Can Affect Your Choices.
Environmental cues can steer people’s decisions via six cognitive processes.
KEY POINTS-
Nudges refer to small cues from our choice environment that can affect people’s decisions.
New research suggests six different types of nudges, tapping into different cognitive processes.
Nudges can affect us by tapping into attention, perception, memory, effort, or intrinsic/extrinsic motivation.
Effort-based nudges, which work by making certain options easier, appear to be the most effective.
Many of our choices are swayed by subtle cues or so-called “nudges” from the environment. A well-known example of this phenomenon includes the layout of a cafeteria or supermarket. Placing an item at eye level makes it more likely to be chosen—even if it’s a salad. Another classic nudge is the strategic use of language to “frame” a choice. If advertisements evoke a fear of missing out, for instance, people will be more inclined to part with their hard-earned money.
Nudging is a phenomenon that has gained much attention since the publication of Nudge, Thaler and Sunstein’s popular book on the topic. Crucially, nudges never restrict people’s choices. Instead, subtle manipulations of the choice environment (also called “choice architecture”) merely tend to influence the way choices are processed. Nudges are most powerful in situations where people make quick, intuitive decisions without engaging analytical thinking skills.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Much research has been dedicated to understanding the principles of nudging, and national governments across many countries have allocated resources to leveraging the potential of nudges for improving the wellbeing of their citizens. A notable example includes the wide distribution of posters reminding citizens of good handwashing practices during the COVID-19 pandemic. Another is the traffic light labelling of food items, which uses intuitive colour codes to signal low-calorie options, thereby nudging people into healthier living.
A framework of nudges
While nudging is a well-known concept, the term is used indiscriminately to describe a large range of different influences on people’s decisions. Cafeteria layouts, language framing, handwash posters and food packaging—all fall under the same umbrella of phenomena. New research offers a helpful framework for categorising different types of nudges. Categories are based on six distinct cognitive mechanisms, through which a nudge might influence behaviour: (1) attention, (2) perception, (3) memory, (4) effort, (5) intrinsic motivation and (6) extrinsic motivation.
Attention. In a context of ever-increasing choice, it can be difficult to compare the available options. Many people intuitively go for the choice that stands out. The first type of nudges capitalises on this fact by tapping into attentional processes. Increasing the visibility of options or highlighting them through bright colours can increase salience, thereby making these options more likely to be chosen. The strategic item placement in cafeterias is a prime example of this process. Others might include the order of items on a restaurant’s food menu or webpages with colourful items, designed to catch your eye.
Perception. The second type of nudge refers to ways in which the choice architecture influences people’s subjective perception. Framing effects that highlight particular aspects of a choice fall into this category. The type of language used in advertisements can create a sense of urgency or a fear of missing out, influencing people through their innate sensitivity to losses. Similarly, colour-coded food items might help to frame choice, with red labels signalling a health risk and green labels giving customers the proverbial thumbs up.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...
Memory. Forgetting is a surprisingly common reason for not acting or for failing to make a choice. This is where the third type of nudge comes in. The choice environment can offer cues that prompt people’s memory, like the simple reminders of handwashing in public bathrooms mentioned above. Another example includes email messages by online companies to inform customers about items left (unpaid) in their shopping baskets.
Effort. Nobody likes to make an effort! The fourth nudge taps into this insight and influences choices by making some options easier than others. A common example of this is the use of defaults — that is, options that automatically come into place if a person fails to make a choice. Examples include newspaper subscriptions, which renew themselves unless customers choose otherwise, or automatic enrolment in pension schemes.
Intrinsic motivation. Some nudges tap into mechanisms of internal motivation — that is, increasing people’s desire for certain options. For example, relaying information about social norms can be surprisingly powerful. In the context of medical prescribing, for example, it might help to tell doctors if their prescribing rates are above average compared to colleagues. Nobody wants to stand out, so many adapt their medical decision making as a consequence. Similarly, if wanting to increase charitable donations, it could help to tell people how much their peers have already contributed.
Extrinsic motivation. The last type of nudge involves the process of extrinsic motivation. This includes offering external rewards for making certain choices. Receiving a sticker to inform people about a recent, voluntary blood donation could be an example. Another might involve the mentioning of professional achievements in staff meetings or organisational newsletters, thereby offering a reputational reward for a job well done.
Which nudges are best?
The framework outlined above highlights the surprising diversity of nudges and the different ways they might be used to influence people’s choices, for better or for worse. The researchers who proposed the framework provided additional insight by conducting a metanalysis of previous research on nudging. They reviewed 184 research studies that involved nudging to identify the most powerful type. Results suggest that effort-based nudges hold the biggest potential for changing people’s choices. In contrast, nudges tapping into intrinsic motivation appear to be the least powerful. While the authors warn about potential publication bias, which refers to the fact that significant or interesting research findings are more likely to get published than non-significant outcomes, these results offer some interesting insights: First, there’s a “toolbox” of nudges to choose from when trying to change people’s behaviours. Second, making a choice easy appears to be the most promising avenue. Human decision makers are busy creatures of habit, so any help with simplifying the ever-expanding maze of options is likely to go a long way.
App link: Absolutely FREE for download... https://www.amazon.com/dp/...